SAR Interferometry Data Exploitation for Infrastructure Monitoring Using GIS Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area, Hydrogeological Context, and Infrastructure Network
2.1. Hydrogeological Context
2.2. Infrastructure Network
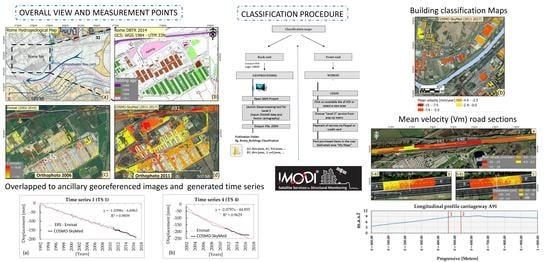
- Area 1: Located in the center of Rome in the Tiber River valley, it does not show important changes in urbanization; therefore, the SAR observation on the A1 infrastructures have been continuous since 1992.
- Area 2: Located in the Tiber River delta, there is an increase in urbanization and important changes, mainly new constructions in the logistics and commercial field, such as the Rome fair, and service infrastructure, such as parking lots, carried out between 2006 and 2011. Unlike the A91 Highway built in 1959.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Collection
3.2. SAR Image Processing
3.3. GIS Mapping
- Back--end: the operators access the I.MODI virtual machine through a VPN connection, launch the geoprocessing tool developed in GIS for the Level service, verify the quality of the product, and save the final map in the folder publication that is automatically displayed in I.MODI WebGIS.
- Front--end: users enter I.MODI WebGIS using their account, select, and pay for the available products displayed in their personal area. Otherwise, they may require a new analysis using a specific form. For the new area, a feasibility analysis (e.g., availability of DInSAR data) will be carried out before accepting the application.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Area 1
4.2. Area 2
4.3. Settlement Interpretation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gigli, G.; Fanti, R.; Canuti, P.; Casagli, N. Integration of advanced monitoring and numerical modeling techniques for the complete risk scenario analysis of rockslides: The case of Mt. Beni (Florence, Italy). Eng. Geol. 2011, 120, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bru, G.; González, P.J.; Mateos, R.M.; Roldán, F.J.; Herrera, G.; Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Fernández, J. A-dinsar monitoring of landslide and subsidence activity: A case of urban damage in Arcos de la Frontera, Spain. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, F.; Gagliardi, V.; Bianchini Ciampoli, L.; Tosti, F. Integration of InSAR and GPR techniques for monitoring transition areas in railway bridges. NDT E Int. 2020, 115, 102291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini Ciampoli, L.; Gagliardi, V.; Clementini, C.; Latini, D.; Del Frate, F.; Benedetto, A. Transport infrastructure monitoring by InSAR and GPR data fusion. Surv. Geophys. 2020, 41, 371–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshr, A.A.; Abo Elnaga, I.M. Investigating the accuracy of digital levels and reflectorless total stations for purposes of geodetic engineering. Alex. Eng. J. 2011, 50, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lienhart, W. Geotechnical monitoring using total stations and laser scanners: Critical aspects and solutions. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2017, 7, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miano, A.; Di Carlo, F.; Mele, A.; Giannetti, I.; Nappo, N.; Rompato, M.; Striano, P.; Bonano, M.; Bozzano, F.; Lanari, R.; et al. GIS Integration of DInSAR Measurements, Geological Investigation and Historical Surveys for the Structural Monitoring of Buildings and Infrastructures: An Application to the Valco San Paolo Urban Area of Rome. Infrastructures 2022, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, S.; Ciampalini, A.; Raspini, F.; Bardi, F.; Di Traglia, F.; Moretti, S.; Casagli, N. Multi-temporal evaluation of landslide movements and impacts on buildings in San Fratello (Italy) by means of C-band and X-band PSI data. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2015, 172, 3043–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scifoni, S.; Bonano, M.; Marsella, M.; Sonnessa, A.; Tagliafierro, V.; Manunta, M.; Lanari, R.; Ojha, C.; Sciotti, M. On the joint exploitation of long-term DInSAR time series and geological information for the investigation of ground settlements in the town of Roma (Italy). Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 182, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arangio, S.; Calò, F.; Di Mauro, M.; Bonano, M.; Marsella, M.; Manunta, M. An application of the SBAS-DInSAR technique for the assessment of structural damage in the city of Rome. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2014, 10, 1469–1483P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peduto, D.; Ferlisi, S.; Nicodemo, G.; Reale, D.; Pisciotta, G.; Gullà, G. Empirical fragility and vulnerability curves for buildings exposed to slow-moving landslides at medium and large scales. Landslides 2017, 14, 1993–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.J.; Bastos, L.F.S. Multi-temporal SAR interferometry reveals acceleration of bridge sinking before collapse. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazecky, M.; Hlaváčová, I.; Bakon, M.; Sousa, J.J.; Perissin, D.; Patricio, G. Bridge Displacements Monitoring Using Space-Borne X-Band SAR Interferometry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Dollevoet, R.P.B.J.; Hanssen, R.F. Nationwide Railway Monitoring Using Satellite SAR Interferometry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhou, G.; Perissin, D. Monitoring of Subsidence along Jingjin Inter-City Railway with High-Resolution TerraSAR-X MT-InSAR Analysis. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissin, D.; Wang, Z.; Lin, H. Shanghai subway tunnels and highways monitoring through Cosmo-SkyMed Persistent Scatterers. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 73, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí, J.G.; Nevard, S.; Sanchez, J. The Use of InSAR (Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar) to Complement Control of Construction and Protect Third Party Assets; Crossrail Learning Legacy Report; Crossrail Ltd.: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Milillo, P.; Giardina, G.; DeJong, M.J.; Perissin, D.; Milillo, G. Multi-Temporal InSAR Structural Damage Assessment: The London Crossrail Case Study. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccari, A.; Batabyal, T.; Tabassum, N.; Hoppe, E.; Bruckno, B.S.; Acton, S.T. Integrating Remote Sensing Data in Decision Support Systems for Transportation Asset Management. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2018, 2672, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, D.; Di Martire, D.; Confuorto, P.; Tessitore, S.; Ramondini, M.; Calcaterra, D. Differential Sar Interferometry Technique for Control of Linear Infrastructures Affected by Ground Instability Phenomena. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 3, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, F.; Delgado Blasco, J.M.; Foumelis, M.; D’Aranno, P.J.; Marsella, M.A.; Di Mascio, P. Dinsar for road infrastructure monitoring: Case study highway network of Rome metropolitan (Italy). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, F.; Mancini, F.; Bassoli, E.; Vincenzi, L. Contribution of anthropogenic consolidation processes to subsidence phenomena from multi-temporal DInSAR: A GIS-based approach. GIScience Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 1901–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditiya, A.; Aoki, Y.; Anugrah, R.D. Surface deformation monitoring of Sinabung volcano using multi temporal InSAR method and GIS analysis for affected area assessment. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Science, Technology, and Interdisciplinary Research (IC-STAR), Bandar Lampung City, Indonesia, 18–20 September 2017; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 344, No. 1; p. 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devara, M.; Tiwari, A.; Dwivedi, R. Landslide susceptibility mapping using MT-InSAR and AHP enabled GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2021, 12, 675–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Mei, G.; Sun, Y.; Xu, N. Investigating mining-induced surface subsidence and potential damages based on SBAS-InSAR monitoring and GIS techniques: A case study. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline 641 differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, C.; Wegmuller, U.; Strozzi, T.; Wiesmann, A. Interferometric point target analysis for deformation mapping. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2003, IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IEEE Cat. No. 03CH37477), Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 7, pp. 4362–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, R.; Mora, O.; Manunta, M.; Mallorquí, J.J.; Berardino, P.; Sansosti, E. A small-baseline approach for investigating deformations on full-resolution differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. A new algorithm for processing interferometric data-stacks: SqueeSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casu, F.; Manzo, M.; Lanari, R. A quantitative assessment of the SBAS algorithm performance for surface deformation retrieval from DInSAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, R.; Casu, F.; Manzo, M.; Lundgren, P. Application of the SBAS-DInSAR technique to fault creep: A case study of the Hayward fault, California. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonano, M.; Manunta, M.; Pepe, A.; Paglia, L.; Lanari, R. From previous C-band to new X-band SAR systems: Assessment of the DInSAR mapping improvement for deformation time-series retrieval in urban areas. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 1973–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, F.; Hormazábal, J.; Montalva, G.; Moreno, M. Measuring Coastal Subsidence after Recent Earthquakes in Chile Central Using SAR Interferometry and GNSS Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, F.; Moreno, M.; Yáñez, G. High-Resolution Deformation Monitoring from DInSAR: Implications for Geohazards and Ground Stability in the Metropolitan Area of Santiago, Chile. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Dollevoet, R.P.; Hanssen, R.F. Monitoring line-infrastructure with multisensor SAR interferometry: Products and performance assessment metrics. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 1593–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martire, D.; Paci, M.; Confuorto, P.; Costabile, S.; Guastaferro, F.; Verta, A.; Calcaterra, D. A nation-wide system for landslide mapping and risk management in Italy: The second Not-ordinary Plan of Environmental Remote Sensing. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 63, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Solari, L.; Mróz, M.; Balasis-Levinsen, J.; Casagli, N.; Frei, M.; Oyen, A.; Moldestad, D.A.; Bateson, L.; Guerrieri, L.; et al. The evolution of wide-area DInSAR: From regional and national services to the European Ground Motion Service. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milillo, P.; Giardina, G.; Perissin, D.; Milillo, G.; Coletta, A.; Terranova, C. Pre-Collapse Space Geodetic Observations of Critical Infrastructure: The Morandi Bridge, Genoa, Italy. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, C.; Bonano, M.; Casu, F.; Fusco, A.; Lanari, R.; Manunta, M.; Manzo, M.; Pepe, A.; Zinno, I. Automatic and systematic Sentinel-1 SBAS-DInSAR processing chain for deformation time-series generation. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 100, 1176–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milli, S.; D’Ambrogi, C.; Bellotti, P.; Calderoni, G.; Carboni, M.G.; Celant, A.; Di Bella, L.; Di Rita, F.; Frezza, V.; Magri, D.; et al. The transition from wave-dominated estuary to wave-dominated delta: The Late Quaternary stratigraphic architecture of Tiber River deltaic succession (Italy). Sediment. Geol. 2013, 284, 159–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.; Moscatelli, M.; Stigliano, F.; Cavinato, G.P.; Marini, M.; Milli, S.; Simionato, M.; Cosentino, G.; Polpetta, F. Middle Pleistocene fluvial incised valleys from the subsoil of the centre of Rome: Facies, stacking pattern and controls on sedimentation. In Proceedings of the Congresso Nazionale della Società Geologica Italiana–Geosciences on a Changing Planet: Learning from the Past, Exploring the Future, Napoli, Italy, 7–9 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- La Vigna, F.; Mazza, R.; Amanti, M.; Di Salvo, C.; Petitta, M.; Pizzino, L. The synthesis of decades of groundwater knowledge: The new Hydrogeological Map of Rome. Acque Sotter. Ital. J. Groundw. 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Vigna, F.; Mazza, R.; Amanti, M.; Di Salvo, C.; Petitta, M.; Pizzino, L.; Pietrosante, A.; Martarelli, L.; Bonfà, I.; Capelli, G.; et al. Groundwater of Rome. J. Maps 2016, 12 (Suppl. 1), 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, R.; La Vigna, F.; Capelli, G.; Dimasi, M.; Mancini, M.; Mastrorillo, L. Idrogeologia del territorio di Roma. Acque Sotter. It. J. Groundw 2016, 4, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Bozzano, F.; Esposito, C.; Mazzanti, P.; Patti, M.; Scancella, S. Imaging Multi-Age Construction Settlement Behavior by Advanced SAR Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, G.; Mazza, R.; Taviani, S. Acque sotterranee nella città di Roma. Mem. Descr. Carta Geol. D’it. 2008, 80, 221–245. [Google Scholar]
- Di Salvo, C.; Di Luzio, E.; Mancini, M.; Moscatelli, M.; Capelli, G.; Cavinato, G.P.; Mazza, R. GIS-based hydrostratigraphic modeling of the city of Rome (Italy): Analysis of the geometric relationships between a buried aquifer in the Tiber Valley and the confining hydrostratigraphic complexes. Hydrogeol. J. 2012, 20, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramondo, S.; Bozzano, F.; Marra, F.; Wegmuller, U.; Cinti, F.R.; Moro, M.; Saroli, M. Subsidence induced by urbanisation in the city of Rome detected by advanced InSAR technique and geotechnical investigations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3160–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manunta, M.; Marsella, M.; Zeni, G.; Sciotti, M.; Atzori, S.; Lanari, R. Two-scale surface deformation analysis using the SBAS-DInSAR technique: A case study of the city of Rome, Italy. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 1665–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaro, G.; Serafino, F.; Reale, D. 4-D SAR imaging: The case study of Rome. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comerci, V.; Cipolloni, C.; di Manna, P.; Guerrieri, L.; Vittori, E.; Bertoletti, E.; Ciuffreda, M.; Succhiarelli, C. PanGeo: Enabling Access to Geological Information in Support of GMES-D7.1.26 Geohazard Description for Rome. 2012. Available online: https://nora.nerc.ac.uk/id/eprint/19289 (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- Cigna, F.; Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N.; Milillo, P.; Tapete, D. Persistent scatterer interferometry processing of COSMO-skymed stripmap HIMAGE time series to depict deformation of the historic centre of Rome, Italy. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 12593–12618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado Blasco, J.M.D.; Foumelis, M.; Stewart, C.; Hooper, A. Measuring Urban Subsidence in the Rome Metropolitan Area (Italy) with Sentinel-1 SNAP-StaMPS Persistent Scatterer Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aranno, P.J.; Marsella, M.; Scifoni, S.; Scutti, M.; Sonnessa, A.; Bonano, M. Advanced DInSAR analysis for building damage assessment in large urban areas: An application to the city of Roma, Italy. In Proceedings of the SPIE 9642, SAR Image Analysis, Modeling, and Techniques XV, Toulouse, France, 23 October 2015; p. 96420L. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-González, M.; Devanthéry, N.; Crippa, B. Persistent scatterer interferometry: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, F.; Rivera, D.; Montalva, G.; Arumi, J.L. InSAR-Based Early Warning Monitoring Framework to Assess Aquifer Deterioration. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Adam, N.; Parizzi, A.; Bremmer, C.; Dortland, S.; van Leijen, F.J. Final report of the Validation of existing processing chains in Terrafirma stage 2. Terrafirma project, ESRIN. Contract 2008, 19366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Iglesias, R.; Crippa, B. Persistent scatterer interferometry: Potential, limits and initial C-and X-band comparison. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2010, 76, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretto, S.; Bozzano, F.; Esposito, C.; Mazzanti, P.; Rocca, A. bAssessment of landslide pre-failure monitoring and forecasting using satellite SAR interferometry. Geosciences 2017, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aranno, P.; Di Benedetto, A.; Fiani, M.; Marsella, M. Remote sensing technologies for linear infrastructure monitoring. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milillo, P.; Riel, B.; Minchew, B.; Yun, S.-H.; Simons, M.; Lundgren, P. On the Synergistic Use of SAR Constellations Data Exploitation for Earth Science and Natural Hazard Response. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Parcharidis, I.; Ma, P.; Xiao, R.; Xu, J.; Zhou, W.; Tang, P.; Foumelis, M. Surface Motion and Structural Instability Monitoring of Ming Dynasty City Walls by Two-Step Tomo-PSInSAR Approach in Nanjing City, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzaghi, K.; Peck, R.B.; Mesri, G. Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Lambe, T.W.; Whitman, R.V. Soil Mechanics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1979; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]


















| Data | Year |
|---|---|
| Orthophoto | 1988 |
| Orthophoto | 2000 |
| Orthophoto | 2006 |
| LiDAR and Digital Surface Model (DSM) | 2011 |
| Orthophoto | 2012 |
| Buildings Layers SHP format from DBTR | 2014 |
| Roads Layers SHP from DBTR | 2014 |
| Rome Hydrogeological map (scale: 1: 50,000) | 2015 |
| Data | Temporal Cover | SAR Band/Wavelength | Orbit | N° Images |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERS-Envisat | 1992–2010 | C/5.6 cm | Descending | 137 |
| Envisat | 2002–2010 | C/5.6 cm | Descending | 59 |
| COSMO-SkyMed | 2011–2017 | X/3.1 cm | Descending | 67 |
| Building | N° Measurement Points | Vm (mm/Year) | SD | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 15 | −12.3 | 0.83 | 0.73 |
| B | 18 | −14.5 | 0.41 | 0.69 |
| C | 22 | −18.2 | 0.23 | 0.89 |
| D | 26 | −10.5 | 0.37 | 0.81 |
| E | 29 | −16.2 | 0.56 | 0.75 |
| Building | N° Measurement Points | Vm (mm/Year) | SD | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 28 | −11.4 | 0.89 | 0.95 |
| B | 37 | −12.1 | 0.52 | 0.88 |
| C | 29 | −12.8 | 0.44 | 0.72 |
| D | 43 | −8.5 | 0.53 | 0.83 |
| E | 47 | −11.9 | 0.75 | 0.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orellana, F.; D’Aranno, P.J.V.; Scifoni, S.; Marsella, M. SAR Interferometry Data Exploitation for Infrastructure Monitoring Using GIS Application. Infrastructures 2023, 8, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures8050094
Orellana F, D’Aranno PJV, Scifoni S, Marsella M. SAR Interferometry Data Exploitation for Infrastructure Monitoring Using GIS Application. Infrastructures. 2023; 8(5):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures8050094
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrellana, Felipe, Peppe J. V. D’Aranno, Silvia Scifoni, and Maria Marsella. 2023. "SAR Interferometry Data Exploitation for Infrastructure Monitoring Using GIS Application" Infrastructures 8, no. 5: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures8050094
APA StyleOrellana, F., D’Aranno, P. J. V., Scifoni, S., & Marsella, M. (2023). SAR Interferometry Data Exploitation for Infrastructure Monitoring Using GIS Application. Infrastructures, 8(5), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures8050094