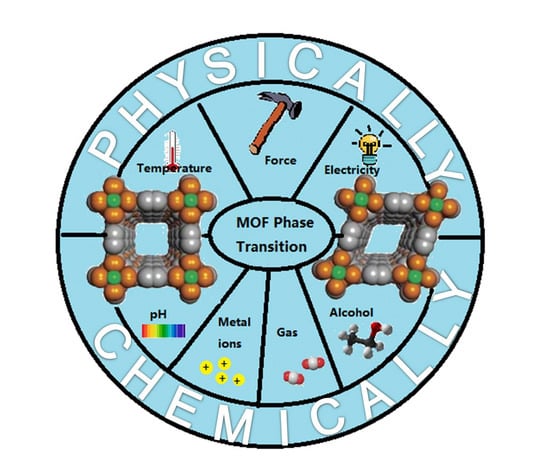
Metal-Organic Framework-Based Stimuli-Responsive Polymers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sensing Mechanism of MOF-Based SRPs
3. Physically Responsive MOF-Based SRPs
3.1. Temperature Responsive MOFs
3.2. Mechanical Force Responsive MOFs
3.3. Electrically Responsive MOFs
4. Chemically Responsive MOF-Based SRPs
4.1. PH Responsive MOFs
4.2. Metal Ion Responsive MOFs
4.3. Gas Responsive MOFs
4.4. Alcohol Responsive MOFs
5. Multi-Responsive MOFs
6. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.-K.; Chang, C.-J. Fabrications and applications of stimulus-responsive polymer films and patterns on surfaces: A review. Materials 2014, 7, 805–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, A.S. “Intelligent” polymers in medicine and biotechnology. Artif. Organs 1995, 19, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Serpe, M.J. Stimuli-responsive polymers and their applications. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stuart, M.A.C.; Huck, W.T.; Genzer, J.; Müller, M.; Ober, C.; Stamm, M.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Szleifer, I.; Tsukruk, V.V.; Urban, M. Emerging applications of stimuli-responsive polymer materials. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Yang, S.; Ozen, M.O.; Chen, P.; Liu, X.; Du, W.; Xiao, F.; Demirci, U. Multi-stimuli-responsive programmable biomimetic actuator. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, G.L.; Tai, C.A.; Neoh, K.; Kang, E.; Yang, X. Hybrid nanorattles of metal core and stimuli-responsive polymer shell for confined catalytic reactions. Polym. Chem. 2011, 2, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, D.A.; Riegel-Vidotti, I.C.; Ferreira, M.G.S.; Marino, C.E.B. Smart coating based on double stimuli-responsive microcapsules containing linseed oil and benzotriazole for active corrosion protection. Corros. Sci. 2018, 130, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Wan, J.; Zhou, L.; Ma, W.; Yang, Y.; Luo, W.; Yu, Z.; Wang, H. Stimuli-responsive nanotherapeutics for precision drug delivery and cancer therapy. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. 2019, 11, e1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sood, N.; Bhardwaj, A.; Mehta, S.; Mehta, A. Stimuli-responsive hydrogels in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 748–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conesa-Egea, J.; Zamora, F.; Amo-Ochoa, P. Perspectives of the smart Cu-Iodine coordination polymers: A portage to the world of new nanomaterials and composites. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 381, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Ma, L.; de Krafft, K.E.; Jin, A.; Lin, W. Porous phosphorescent coordination polymers for oxygen sensing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 132, 922–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, B.; Rachuri, Y.; Bisht, K.K.; Laiya, R.; Suresh, E. Mechanochemical and conventional synthesis of Zn(II)/Cd(II) luminescent coordination polymers: Dual sensing probe for selective detection of chromate anions and TNP in aqueous phase. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 2627–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Hu, Z.; Wang, G.; Uvdal, K. Coordination polymers for energy transfer: Preparations, properties, sensing applications, and perspectives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 284, 206–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.-Y.; Fan, W.-W.; Cheng, Y.; Cao, Q.-E. Reversible Phase Transition of Porous Coordination Polymers. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 2766. [Google Scholar]
- McConnell, A.J.; Wood, C.S.; Neelakandan, P.P.; Nitschke, J.R. Stimuli-responsive metal–ligand assemblies. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 7729–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, J.; Wu, F.; Yu, P.; Mao, L. On-site sensors based on infinite coordination polymer nanoparticles: Recent progress and future challenge. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 11, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, M. Stimuli-responsive metallo-supramolecular polymer films: Design, synthesis and device fabrication. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 9331–9341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.Y.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, W. Stimuli–responsive metallopolymers. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 319, 180–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, S. Engineering responsive polymer building blocks with host—Guest molecular recognition for functional applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2084–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Su, P.; Tang, Y. Stimuli-Responsive Lanthanide-Based Smart Luminescent Materials for Optical Encoding and Bio-applications. Chemnanomat 2018, 4, 1097–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pei, Z.; Feng, W.; Pei, Y. Stimuli-responsive supramolecular nano-systems based on pillar [n] arenes and their related applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 7656–7675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Sun, D. Stimuli-responsive structural changes in metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Comm. 2020, 56, 9416–9432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knebel, A.; Zhou, C.; Huang, A.; Zhang, J.; Kustov, L.; Caro, J. Smart Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs): Switching Gas Permeation through MOF Membranes by External Stimuli. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2018, 41, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarkar, S.S.; Desai, A.V.; Ghosh, S.K. Stimulus-responsive metal–Organic frameworks. Chem. Asian J. 2014, 9, 2358–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Che, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Zang, L. Fluorescent nanoscale zinc (II)-carboxylate coordination polymers for explosive sensing. Chem. Comm. 2011, 47, 2336–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.-H.; Qiu, W.-B.; Zhang, L.; Liang, R.-P.; Qiu, J.-D. Lanthanide coordination polymer nanoparticles as an excellent artificial peroxidase for hydrogen peroxide detection. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6342–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Brooks, W.L.; Sumerlin, B.S. New directions in thermoresponsive polymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7214–7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Pan, F.; Liu, Y.; Huang, S.; Li, Y.; Yong, J.; Li, Y.; Kirillov, A.M.; Wu, D. An efficient blue-emissive metal–organic framework (MOF) for lanthanide-encapsulated multicolor and stimuli-responsive luminescence. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 6362–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tom, L.; Kurup, M. A reversible thermo-responsive 2D Zn (II) coordination polymer as a potential self-referenced luminescent thermometer. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 2525–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Bomba, H.N.; Zhu, Y.; Gu, Z. Mechanical force-triggered drug delivery. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 12536–12563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, J.; Yao, S.; Ye, Y.; Cui, Z.; Yu, J.; Ghosh, T.K.; Zhu, Y.; Gu, Z. Stretch-triggered drug delivery from wearable elastomer films containing therapeutic depots. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 9407–9415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslahi, N.; Abdorahim, M.; Simchi, A. Smart polymeric hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering: A review on the chemistry and biological functions. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 3441–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tee, B.C.; Wang, C.; Allen, R.; Bao, Z. An electrically and mechanically self-healing composite with pressure-and flexion-sensitive properties for electronic skin applications. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Niu, W.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Wen, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Quan, Z. Pressure-induced phase engineering of gold nanostructures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 15783–15790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Luan, Y.; Jang, J.I.; Baikie, T.; Huang, X.; Li, R.; Saouma, F.O.; Wang, Z.; White, T.J.; Fang, J. Phase transitions of formamidinium lead iodide perovskite under pressure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 13952–13957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajamanickam, R.; Kwon, K.; Tae, G. Soft and elastic hollow microcapsules embedded silicone elastomer films with enhanced water uptake and permeability for mechanical stimuli responsive drug delivery applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 111, 110789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Tang, J.-H.; Chen, W.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Sepehrpour, H.; Cheng, G.-J.; Li, X.; Wang, P. Temperature-and mechanical-force-responsive self-assembled rhomboidal metallacycle. Organometallics 2019, 38, 4244–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, T.; Ozawa, M.; Akutagawa, T. Jumping Crystal of a Hydrogen-Bonded Organic Framework Induced by the Collective Molecular Motion of a Twisted π System. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 10345–10352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coudert, F.-X. Responsive metal–organic frameworks and framework materials: Under pressure, taking the heat, in the spotlight, with friends. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 1905–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, N.-N.; Wang, M.-S.; Sun, C.; Xing, X.-S.; Li, R.; Xu, J.-G.; Zheng, F.-K.; Guo, G.-C. Grinding size-dependent mechanoresponsive luminescent Cd (II) coordination polymer. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 18074–18078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Đaković, M.; Borovina, M.; Pisačić, M.; Aakeröy, C.B.; Soldin, Ž.; Kukovec, B.M.; Kodrin, I. Mechanically Responsive Crystalline Coordination Polymers with Controllable Elasticity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 14801–14805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, P.; Wieme, J.; Alvarez, E.; Vanduyfhuys, L.; Itié, J.-P.; Fabry, P.; Van Speybroeck, V.; Serre, C.; Yot, P.G.; Maurin, G. Mechanical properties of a gallium fumarate metal–organic framework: A joint experimental-modelling exploration. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 11047–11054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yot, P.G.; Yang, K.; Ragon, F.; Dmitriev, V.; Devic, T.; Horcajada, P.; Serre, C.; Maurin, G. Exploration of the mechanical behavior of metal organic frameworks UiO-66 (Zr) and MIL-125 (Ti) and their NH 2 functionalized versions. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 4283–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yot, P.G.; Vanduyfhuys, L.; Alvarez, E.; Rodriguez, J.; Itié, J.-P.; Fabry, P.; Guillou, N.; Devic, T.; Beurroies, I.; Llewellyn, P.L. Mechanical energy storage performance of an aluminum fumarate metal–organic framework. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.; Li, Y.; Shen, J.; Tong, Z.; Hu, Q.; Li, L.; Yu, G. Supramolecular chemotherapeutic drug constructed from pillararene-based supramolecular amphiphile. Chem. Comm. 2018, 54, 8198–8201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahlfuss, C.; Gibaud, T.; Denis-Quanquin, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Royal, G.; Chevallier, F.; Saint-Aman, E.; Bucher, C. Redox-Induced Molecular Metamorphism Promoting a Sol/Gel Phase Transition in a Viologen-Based Coordination Polymer. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 13009–13019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, M.; Zhang, N.; Xia, W.; Wu, X.; Yao, C.; Liu, X.; Hu, X.-Y.; Lin, C.; Wang, L. Dramatically promoted swelling of a hydrogel by pillar [6] arene–ferrocene complexation with multistimuli responsiveness. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6643–6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Li, F.; Zang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, Y.; Yu, X.; Luo, Q.; Guan, S.; Xu, J.; Liu, J. Diselenium-containing ultrathin polymer nanocapsules for highly efficient targeted drug delivery and combined anticancer effect. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 4927–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahata, M.; Takashima, Y.; Yamaguchi, H.; Harada, A. Redox-responsive self-healing materials formed from host–guest polymers. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, W.; Hu, X.-Y.; Chen, Y.; Lin, C.; Wang, L. A novel redox-responsive pillar [6] arene-based inclusion complex with a ferrocenium guest. Chem. Comm. 2013, 49, 5085–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoufi, A.; Benhamed, K.; Boukli-Hacene, L.; Maurin, G. Electrically induced breathing of the MIL-53 (Cr) metal–organic framework. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, C.A.; Martin, P.C.; Schaef, T.; Bowden, M.E.; Thallapally, P.K.; Dang, L.; Xu, W.; Chen, X.; McGrail, B.P. An electrically switchable metal-organic framework. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mortimer, R.J. Electrochromic materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1997, 26, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, G.; Tuncer, C.; Bütün, V. pH-Responsive polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 144–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.F.; Zheng, L.L.; Liang, L.J.; Yang, X.X.; Li, Y.F.; Huang, C.Z. A new type of pH-responsive coordination polymer sphere as a vehicle for targeted anticancer drug delivery and sustained release. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3202–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Zhao, Y.; Han, X.; Ding, J.; Meng, X.; Hou, H. Interesting pH-responsive behavior in benzothiadiazole-derived coordination polymer constructed via an in situ Click synthesis. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 7419–7425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.-Q.; Li, B.; Jiang, W.-P.; Xu, Y.-B.; Xu, Z.-Q.; Yong, G.-P. Reversible stimulus-responsive coordination polymers mainly involving conversion between the lone-pair–π and cation–π interactions. J. Coord. Chem. 2020, 73, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Fan, T.; Xia, T.; Cui, Y.; Yang, Y.; Qian, G. A luminescent terbium metal-organic framework for highly sensitive and selective detection of uric acid in aqueous media. J. Solid State Chem. 2019, 272, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, S.; Pope, S.J. Lanthanide-sensitized lanthanide luminescence: Terbium-sensitized ytterbium luminescence in a trinuclear complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 10526–10527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbatini, N.; Guardigli, M.; Lehn, J.-M. Luminescent lanthanide complexes as photochemical supramolecular devices. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1993, 123, 201–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Qu, X.; Chai, J.; Tong, C.; Fan, Y.; Wang, L. Stable coordination polymers with linear dependence color tuning and luminescent properties for detection of metal ions and explosives. Dye. Pigm. 2019, 170, 107583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.-W.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Wei, T.-B.; Wang, J.; Fan, Y.-Q.; Yao, H. Pillar [5] arene-based spongy supramolecular polymer gel and its properties in multi-responsiveness, dye sorption, ultrasensitive detection and separation of Fe3+. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 3241–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumpfer, J.R.; Jin, J.; Rowan, S.J. Stimuli-responsive europium-containing metallo-supramolecular polymers. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapton, D.; Burnworth, M.; Rowan, S.J.; Weder, C. Fluorescent Organometallic Sensors for the Detection of Chemical-Warfare-Agent Mimics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 5825–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-R.; Kuppler, R.J.; Zhou, H.-C. Selective gas adsorption and separation in metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1477–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Rao, H.; Lin, S.; Zhang, J. A vapochromic strategy for ammonia sensing based on a bipyridinium constructed porous framework. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 8204–8208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, N.; Kitayama, K.; Hijikata, Y.; Sato, H.; Matsuda, R.; Kubota, Y.; Takata, M.; Mizuno, M.; Uemura, T.; Kitagawa, S. Gas detection by structural variations of fluorescent guest molecules in a flexible porous coordination polymer. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Ma, J.; Wang, P. A hydrogen sulfide-sensitive supramolecular polymer constructed by crown ether-based host—Guest interaction and Ag-coordination. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 279, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, E.; Giménez-Marqués, M.; Espallargas, G.M.; Brammer, L. Tuning the magneto-structural properties of non-porous coordination polymers by HCl chemisorption. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, J.; Shi, G.; Zhou, T. Colorimetric assay for on-the-spot alcoholic strength sensing in spirit samples based on dual-responsive lanthanide coordination polymer particles with ratiometric fluorescence. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 942, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Ma, W.; Yu, P.; Mao, L. Colorimetric and fluorescent dual mode sensing of alcoholic strength in spirit samples with stimuli-responsive infinite coordination polymers. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6958–6965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. A Dual-Functional Lead (II) Metal–Organic Framework Based on 5-Aminonicotinic Acid as a Luminescent Sensor for Selective Sensing of Nitroaromatic Compounds and Detecting the Temperature. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.Q.; Xu, J.; Zou, B.; Hu, Z.; Wang, K.; Yuan, Y.J.; Chen, Y.P.; Feng, R.; Xiong, J.B.; Hao, J. A Dual-Stimuli-Responsive Coordination Network Featuring Reversible Wide-Range Luminescence-Tuning Behavior. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 5614–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, N.; Li, J.; Li, G.; Hu, B.; Li, J.; Liu, T.; Gong, L.; Huang, F.; Wang, Z.; Huang, X. Designing Polymorphic Bi3+-Containing Ionic Liquids for Stimuli-Responsive Luminescent Materials. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 8079–8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, S.; Bardhan, D.; Chand, D.K. Multistimuli-responsive hydrolytically stable “smart” mercury (II) coordination polymer. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 11369–11381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, M.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, X. Metal-Organic Framework-Based Stimuli-Responsive Polymers. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5040101
Wei M, Wan Y, Zhang X. Metal-Organic Framework-Based Stimuli-Responsive Polymers. Journal of Composites Science. 2021; 5(4):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5040101
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Menglian, Yu Wan, and Xueji Zhang. 2021. "Metal-Organic Framework-Based Stimuli-Responsive Polymers" Journal of Composites Science 5, no. 4: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5040101
APA StyleWei, M., Wan, Y., & Zhang, X. (2021). Metal-Organic Framework-Based Stimuli-Responsive Polymers. Journal of Composites Science, 5(4), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5040101