Influence of Hydrophilic Surfactants on the W1–W2 Coalescence in Double Emulsion Systems Investigated by Single Droplet Experiments
Abstract
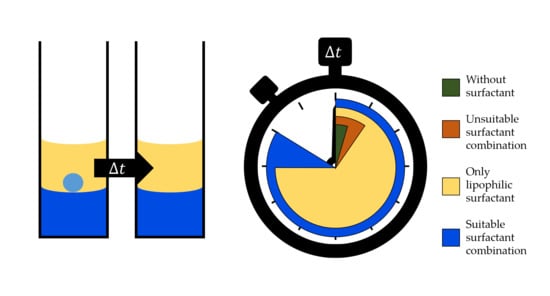
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Choice of Surfactant Concentrations
2.3. Interfacial Tension Measurements
2.4. Coalescence of Single Droplets
3. Results
3.1. General Discussion of Single-Droplet Experiments
3.1.1. Influence of the Purification Step
3.1.2. Statistical Considerations
3.2. Influence of the Lipophilic Surfactant Concentration
3.3. Interaction between Hydrophilic and Lipophilic Surfactants
3.3.1. Interactions between the Lipophilic Surfactant PGPH with Different Hydrophilic Surfactants
3.3.2. Interactions between PGPH and Hydrophilic Surfactants at Reduced Concentrations
3.3.3. Interactions between the Lipophilic Surfactant PEG-30 with Different Hydrophilic Surfactants
4. Discussion and Conclusions
- The concentration of the surfactant in the experiment must be determined empirically since the coalescence time must on the one hand be fast enough (shorter than 2 h) to prevent changes due to aging and diffusion. On the other hand, the coalescence time must be long enough to allow the optical detection of interface contact. A direct transfer of the surfactant concentration in single-droplet experiments to double-emulsion systems was not possible due to the significantly different volume-to-interface ratio.
- Experiments must be performed very carefully and with purified substances since small concentrations of interfacial active impurities can change the results significantly.
- Each experiment must be repeated several times since the coalescence time distributions measured are rather wide and must be approximated by a multiple determination.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muschiolik, G.; Dickinson, E. Double Emulsions Relevant to Food Systems: Preparation, Stability, and Applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 532–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garti, N.; Bisperink, C. Double emulsions: Progress and applications. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 3, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamba, H.; Sathish, K.; Sabikhi, L. Double Emulsions: Emerging Delivery System for Plant Bioactives. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2015, 8, 709–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchmann, H.P.; Schuch, A.; Köhler, K. Fettreduktion durch Doppelemulsionen: Grundlegende Untersuchungen zur Beeinflussung der Mikrostruktur von Doppelemulsionen und deren Auswirkung auf Konsumentenrelevante Produkteigenschaften (Mouth-Feel, Kremigkeit, Fettgeschmack, Sättigung). In Fettwahrnehmung und Sättigungsregulation: Ansatz zur Entwicklung Fettreduzierter Lebensmittel; Forschungskreis der Ernährungsindustrie e.V.: Bonn, Germany, 2012; pp. 25–39. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Colmenero, F. Potential applications of multiple emulsions in the development of healthy and functional foods. Food Res. Int. 2013, 52, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Knoth, A.; Muschiolik, G. Multiple Emulsionen für Lebensmittel. In Multiple Emulsionen: Herstellung und Eigenschaften; Muschiolik, G., Bunjes, H., Eds.; Behr: Hamburg, Germany, 2007; ISBN 3-89947-339-6. [Google Scholar]
- Garti, N.; Aserin, A. Double emulsions stabilized by macromolecular surfactants. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 65, 37–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Páez, M.; Quezada, C.M.; Ibarra-Bracamontes, L.; González-Ochoa, H.O.; Arauz-Lara, J.L. Coalescence in double emulsions. Langmuir 2012, 28, 5934–5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, W.C. Classification of surface-active agents by HLB. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 1949, 1, 311–326. [Google Scholar]
- Gülseren, İ.; Corredig, M. Interactions at the interface between hydrophobic and hydrophilic emulsifiers: Polyglycerol polyricinoleate (PGPR) and milk proteins, studied by drop shape tensiometry. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 29, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, S.M.; Wittstock, N.; van der Schaaf, U.S.; Karbstein, H.P. Interactions in water in oil in water double emulsions: Systematical investigations on the interfacial properties and emulsion structure of the outer oil in water emulsion. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 537, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosano, H.L.; Gandolfo, F.G.; Hidrot, J.-D.P. Stability of W1/O/W2 multiple emulsions: Influence of ripening and interfacial interactions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1998, 138, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Encapsulation, protection, and release of hydrophilic active components: Potential and limitations of colloidal delivery systems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 219, 27–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E. Double Emulsions Stabilized by Food Biopolymers. Food Biophys. 2011, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leister, N.; Karbstein, H.P. Evaluating the Stability of Double Emulsions—A Review of the Measurement Techniques for the Systematic Investigation of Instability Mechanisms. Colloids Interfaces 2020, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neumann, S.M.; van der Schaaf, U.S.; Karbstein, H.P. Structure stability and crystallization behavior of water in oil in water (WOW) double emulsions during their characterization by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 133, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, S.M.; van der Schaaf, U.S.; Karbstein, H.P. Investigations on the relationship between interfacial and single droplet experiments to describe instability mechanisms in double emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 553, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, S.M.; van der Schaaf, U.S.; Schuchmann, H.P. The Diffusion and Coalescence Time Analyzer (DCTA): A novel experimental setup for investigating instability phenomena in double emulsions. Food Struct. 2017, 12, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taboada, M.L.; Leister, N.; Karbstein, H.P.; Gaukel, V. Influence of the Emulsifier System on Breakup and Coalescence of Oil Droplets during Atomization of Oil-In-Water Emulsions. Chemengineering 2020, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitzsch, F.; Gäbler, A.; Kraume, M. Analysis of droplet expulsion in stagnant single water-in-oil-in-water double emulsion globules. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 4663–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitzsch, F. Koaleszenzphänomene in Wasser-in-Öl-in-Wasser-Doppelemulsionen. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Won, J.Y.; Krägel, J.; Makievski, A.V.; Javadi, A.; Gochev, G.; Loglio, G.; Pandolfini, P.; Leser, M.E.; Gehin-Delval, C.; Miller, R. Drop and bubble micro manipulator (DBMM)—A unique tool for mimicking processes in foams and emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 441, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politova, N.I.; Tcholakova, S.; Tsibranska, S.; Denkov, N.D.; Muelheims, K. Coalescence stability of water-in-oil drops: Effects of drop size and surfactant concentration. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 531, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanouni, M.; Rosano, H.; Naouli, N. Preparation of a stable double emulsion (W1/O/W2): Role of the interfacial films on the stability of the system. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 99, 229–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopierala, K.; Javadi, A.; Krägel, J.; Schano, K.-H.; Kalogianni, E.P.; Leser, M.E.; Miller, R. Dynamic interfacial tensions of dietary oils. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 382, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiljevic, D.; Parojcic, J.; Primorac, M.; Vuleta, G. An investigation into the characteristics and drug release properties of multiple W/O/W emulsion systems containing low concentration of lipophilic polymeric emulsifier. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 309, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuch, A.; Deiters, P.; Henne, J.; Köhler, K.; Schuchmann, H.P. Production of W/O/W (water-in-oil-in-water) multiple emulsions: Droplet breakup and release of water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 402, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaonkar, A.G. Interfacial tensions of vegetable oil/water systems: Effect of oil purification. J. Am. Oil. Chem. Soc. 1989, 66, 1090–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheva, E.S.; Gurkov, T.D.; Ivanov, I.B.; Bantchev, G.B.; Campbell, B.; Borwankar, R.P. Size Dependence of the Stability of Emulsion Drops Pressed against a Large Interface. Langmuir 1999, 15, 6764–6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Hodgson, T.D. Film flow and coalescence-I Basic relations, film shape and criteria for interface mobility. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1968, 23, 1375–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, T.; Kawaizumi, F.; Nii, S.; Takahashi, K. Study of drop coalescence behavior for liquid–liquid extraction operation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2000, 55, 5385–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.K.; Ghosh, P. Coalescence of Air Bubbles in Aqueous Solutions of Ionic Surfactants in Presence of Inorganic Salt. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2006, 84, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamp, J.; Villwock, J.; Kraume, M. Drop coalescence in technical liquid/liquid applications: A review on experimental techniques and modeling approaches. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2017, 33, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuster, S.; Bernewitz, R.; Guthausen, G.; Zapp, J.; Greiner, A.M.; Köhler, K.; Schuchmann, H.P. Analysis of W1/O/W2 double emulsions with CLSM: Statistical image processing for droplet size distribution. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 81, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernewitz, R.; Dalitz, F.; Köhler, K.; Schuchmann, H.P.; Guthausen, G. Characterisation of multiple emulsions by NMR spectroscopy and diffusometry. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 178, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuch, A.; Leal, L.G.; Schuchmann, H.P. Production of W/O/W double emulsions. Part I: Visual observation of deformation and breakup of double emulsion drops and coalescence of the inner droplets. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 461, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamnak, S.; Mirhosseini, H.; Tan, C.P.; Tabatabaee Amid, B.; Kazemi, M.; Hedayatnia, S. Encapsulation properties, release behavior and physicochemical characteristics of water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) emulsion stabilized with pectin–pea protein isolate conjugate and Tween 80. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficheux, M.-F.; Bonakdar, L.; Leal-Calderon, F.; Bibette, J. Some Stability Criteria for Double Emulsions. Langmuir 1998, 14, 2702–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, C.H.; Lawson, L.B.; Li, Y.; Papadopoulos, K.D. Internal Coalescence as a Mechanism of Instability in Water-in-Oil-in-Water Double-Emulsion Globules. Langmuir 2003, 19, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuch, A.; Helfenritter, C.; Funck, M.; Schuchmann, H.P. Observations on the influence of different biopolymers on coalescence of inner water droplets in W/O/W (water-in-oil-in-water) double emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 475, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pays, K. Double emulsions: How does release occur? J. Control. Release 2002, 79, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.J.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, J.-C. Preparations and temperature-dependent release properties of Pluronic F127-containing microcapsules prepared by a double emulsion technique. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2009, 15, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yafei, W.; Tao, Z.; Gang, H. Structural evolution of polymer-stabilized double emulsions. Langmuir 2006, 22, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.; Dickinson, E. Water-in-oil-in-water multiple emulsions stabilized by polymeric and natural emulsifiers. Food Colloids: Fundam. Formul. 2001, 258, 133. [Google Scholar]
- Debeli, D.K.; Lin, C.; Mekbib, D.B.; Hu, L.; Deng, J.; Gan, L.; Shan, G. Controlling the Stability and Rheology of Copolyol Dispersions in Fatty Alcohol Ethoxylate (AEO9)-Stabilized Multiple Emulsions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 18307–18317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilanova, N.; Solans, C.; Rodríguez-Abreu, C. Preparation of novel silicone multicompartment particles by multiple emulsion templating and their use as encapsulating systems. Langmuir 2013, 29, 15414–15422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Trade Name | Abbreviation | Chemical Description | Average Molecular Weight in g/mol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lutensol TO8 | Lutensol | C13 alcohol + 8 Ethoxylates | 600 |
| Eumulgin B2 | Eumulgin | C18 alcohol + 20 Ethoxylates | 1100 |
| Disponil SDS | SDS | Sodiumdodecylsulfate | 300 |
| Pluronic PE 6800 | Pluronic | Polyethylene–polypropylene glycol | 8400 |
| Dehymuls PGPH | PGPH | Polyglyceryl-2 Dipolyhydroxystearate | 2100 |
| Dehymuls LE | PEG-30 | PEG30–Dipolyhydroxylstearate | 5000 |
| Interfacial Tension in mN/m | Median Coalescence Time in s | |
|---|---|---|
| Unpurified oil | 23.6 ± 0.8 | 180 |
| Purified oil | 27.0 ± 0.5 | 5 |
| Surfactants | Hydrophilic Surfactant at 0.001 wt% | Hydrophilic Surfactant at 0.1 wt% |
|---|---|---|
| PGPH only | 12.8 ± 0.1 mN/m | |
| PGPH-Lutensol | 15.3 ± 0.7 mN/m | 4.0 ± 0.4 mN/m |
| PGPH–Eumulgin | 13.7 ± 0.2 mN/m | 6.3 ± 0.1 mN/m |
| PGPH–SDS | 13.5 ± 0.3 mN/m | 10.3 ± 0.8 mN/m |
| PGPH–Pluronic | 15.4 ± 0.4 mN/m | 11.9 ± 0.2 mN/m |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leister, N.; Karbstein, H.P. Influence of Hydrophilic Surfactants on the W1–W2 Coalescence in Double Emulsion Systems Investigated by Single Droplet Experiments. Colloids Interfaces 2021, 5, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids5020021
Leister N, Karbstein HP. Influence of Hydrophilic Surfactants on the W1–W2 Coalescence in Double Emulsion Systems Investigated by Single Droplet Experiments. Colloids and Interfaces. 2021; 5(2):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids5020021
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeister, Nico, and Heike P. Karbstein. 2021. "Influence of Hydrophilic Surfactants on the W1–W2 Coalescence in Double Emulsion Systems Investigated by Single Droplet Experiments" Colloids and Interfaces 5, no. 2: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids5020021
APA StyleLeister, N., & Karbstein, H. P. (2021). Influence of Hydrophilic Surfactants on the W1–W2 Coalescence in Double Emulsion Systems Investigated by Single Droplet Experiments. Colloids and Interfaces, 5(2), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids5020021