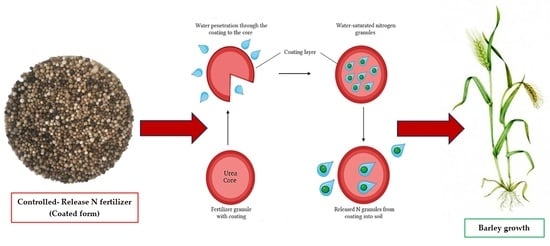
Mineral Nitrogen Release Patterns in Various Soil and Texture Types and the Impact of Urea and Coated Urea Potassium Humate on Barley Biomass
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nitrogen Sources
2.2. Study Areas and Soil Characteristics
2.3. Experimental Design and Treatments
2.4. Soil Sampling and Laboratory Analysis
2.5. Statistics Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Mineral Nitrogen Patterns in Different Soil and Texture Types
3.2. Impact of Soil and Texture Types on Mineral Nitrogen Accumulation
3.3. Availability Assessment of Mineral Nitrogen in the Soil
3.4. Effect of Urea Compounds on Germination and Barley Biomass
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, R.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, Z.; Gao, F.; Meng, Q.; Li, T.; Liu, A.; Wang, Q.; Wu, L.; et al. Blended Controlled-Release Nitrogen Fertilizer with Straw Returning Improved Soil Nitrogen Availability, Soil Microbial Community, and Root Morphology of Wheat. Soil. Tillage Res. 2021, 212, 105045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, W.; Yang, X.; Wu, L.; Ma, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Evaluation of Nitrogen Fertilizer and Cultivation Methods for Agronomic Performance of Rice. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, A.F.; Boumans, L.J.M.; Batjes, N.H. Estimation of Global NH3 Volatilization Loss from Synthetic Fertilizers and Animal Manure Applied to Arable Lands and Grasslands. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2002, 16, 8-1-8-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasisi, A.A.; Akinremi, O.O.; Zhang, Q.; Kumaragamage, D. Efficiency of Fall versus Spring Applied Urea-Based Fertilizers Treated with Urease and Nitrification Inhibitors I. Ammonia Volatilization and Mitigation by NBPT. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 949–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardinier, A.; Ketterings, Q.; Verbeten, B.; Hunter, M. Urea Fertilizer. In Agronomy Fact Sheet Series; Fact Sheet No. 80; Cornell University: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2013; Available online: http://nmsp.cals.cornell.edu/guidelines/factsheets.html (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- Gioacchini, P.; Ramieri, N.A.; Montecchio, D.; Marzadori, C.; Ciavatta, C. Dynamics of Mineral Nitrogen in Soils Treated with Slow-Release Fertilizers. Commun. Soil. Sci. Plant Anal. 2006, 37, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdock, L.W. Comparative Effectiveness of Urea, Ammonium Nitrate, and Urea Comparative Effectiveness of Urea, Ammonium Nitrate, and Urea Ammonium Polyphosphate on Fescue Production Ammonium Polyphosphate on Fescue Production. Agronomy Notes. 86. 1982. Available online: https://uknowledge.uky.edu/pss_notes/86 (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- Gao, J.; Luo, J.; Lindsey, S.; Shi, Y.; Wei, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L. Effects of Soil Properties on Urea-N Transformation and Efficacy of Nitrification Inhibitor 3, 4-Dimethypyrazole Phosphate (DMPP). Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 68, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianson, C.B. Factors Affecting N Release of Urea from Reactive Layer Coated Urea. Fert. Res. 1988, 16, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, P.; MacDonald, J.D.; Angers, D.A.; Chantigny, M.H. Banding of Urea Increased Ammonia Volatilization in a Dry Acidic Soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrencia, D.; Wong, S.K.; Low, D.Y.S.; Goh, B.H.; Goh, J.K.; Ruktanonchai, U.R.; Soottitantawat, A.; Lee, L.H.; Tang, S.Y. Controlled Release Fertilizers: A Review on Coating Materials and Mechanism of Release. Plants 2021, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Song, X.; Liu, K.; Li, T.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Q.; Li, Z.; et al. Mixture of Controlled-Release and Conventional Urea Fertilizer Application Changed Soil Aggregate Stability, Humic Acid Molecular Composition, and Maize Nitrogen Uptake. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.K.; Rose, M.T.; Wong, V.N.L.; Cavagnaro, T.R.; Patti, A.F. Nitrogen Dynamics in Soil Fertilized with Slow Release Brown Coal-Urea Fertilizers. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Salm, C.; Dolfing, J.; Heinen, M.; Velthof, G.L. Estimation of Nitrogen Losses via Denitrification from a Heavy Clay Soil under Grass. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 119, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, F.; Prasuhn, V.; Spiess, E.; Richner, W. Environmental Cross-Compliance Mitigates Nitrogen and Phosphorus Pollution from Swiss Agriculture. Environ. Sci. Policy 2008, 11, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalco Vera, J.; Portocarrero, R.; Piñeiro, G.; Acreche, M.M. Increases in Nitrogen Use Efficiency Decrease Nitrous Oxide Emissions but Can Penalize Yield in Sugarcane. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2022, 122, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.K.; Rose, M.T.; Van Zwieten, L.; Wong, V.N.L.; Patti, A.F. Slow Release Brown Coal-Urea Fertilizer Potentially Influences Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Nitrogen Use Efficiency, and Sweet Corn Yield in Oxisol. ACS Agric. Sci. Technol. 2021, 5, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, S.S.; Soon, Y.K.; Grant, C.A.; Lemke, R.; Lupwayi, N.; Lemke, C.A. Influence of Controlled-Release Urea on Seed Yield and N Concentration, and N Use Efficiency of Small Grain Crops Grown on Dark Gray Luvisols 1. Can. J. Soil. Sci. 2010, 90, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.K.A.; Yusop, M.K.; Oad, F.C.; Hussin, A.; Rahim, A.A. Nitrogen Mineralization and Volatilization from Controlled Release Urea Fertilizers in Selected Malaysian Soils. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2017, 39, 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Geng, J. Improving Crop Yields, Nitrogen Use Efficiencies, and Profits by Using Mixtures of Coated Controlled-Released and Uncoated Urea in a Wheat-Maize System. Field Crops Res. 2017, 205, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Dong, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, P. Effects of Controlled-Release Fertiliser on Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Summer Maize. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, B.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhu, T.; Ming, Y.; Li, C.; Li, C.; Wang, F.; Jiao, S.; Shi, L.; et al. The Application of Humic Acid Urea Improves Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Crop Yield by Reducing the Nitrogen Loss Compared with Urea. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Ortiz, R.; Naranjo, M.Á.; Ruiz-Navarro, A.; Atares, S.; García, C.; Zotarelli, L.; Bautista, A.S.; Vicente, O. Enhanced Agronomic Efficiency Using a New Controlled-Released, Polymeric-Coated Nitrogen Fertilizer in Rice. Plants 2020, 9, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaviv, A.; Mikkelsen, R.L. Controlled-Release Fertilizers to Increase Efficiency of Nutrient Use and Minimize Environmental Degradation—A Review. Fertil. Res. 1993, 35, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broschat, T.K.; Moore, K.K. Release Rates of Ammonium-Nitrogen, Nitrate-Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, Magnesium, Iron, and Manganese from Seven Controlled-Release Fertilizers. Commun. Soil. Sci. Plant Anal. 2007, 38, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paiva, D.M.; Cantarutti, R.B.; Guimarães, G.G.F.; da Silva, I.R. Urea Coated with Oxidized Charcoal Reduces Ammonia Volatilization. R. Bras. Ci. Solo 2012, 36, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wei, X. Controlled-Release Fertilizers as a Means to Reduce Nitrogen Leaching and Runoff in Container-Grown Plant Production. In Nitrogen in Agriculture—Updates; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jariwala, H.; Santos, R.M.; Lauzon, J.D.; Dutta, A.; Wai Chiang, Y. Controlled Release Fertilizers (CRFs) for Climate-Smart Agriculture Practices: A Comprehensive Review on Release Mechanism, Materials, Methods of Preparation, and Effect on Environmental Parameters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 53967–53995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.H.; Haque, K.M.S.; Khan, M.Z.H. A Review on Application of Controlled Released Fertilizers Influencing the Sustainable Agricultural Production: A Cleaner Production Process. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haderlein, L.; Jensen, T.L.; Dowbenko, R.E.; Blaylock, A.D. Controlled Release Urea as a Nitrogen Source for Spring Wheat in Western Canada: Yield, Grain N Content, and N Use Efficiency. Sci. World J. 2001, 1 (Suppl. S2), 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, W.M.; Dibb, D.W.; Johnston, A.E.; Smyth, T.J. The Contribution of Commercial Fertilizer Nutrients to Food Production. Agron. J. 2005, 97, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, M.T.; Perkins, E.L.; Saha, B.K.; Tang, E.C.W.; Cavagnaro, T.R.; Jackson, W.R.; Hapgood, K.P.; Hoadley, A.F.A.; Patti, A.F. A Slow Release Nitrogen Fertiliser Produced by Simultaneous Granulation and Superheated Steam Drying of Urea with Brown Coal. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2016, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.K.; Rose, M.T.; Wong, V.; Cavagnaro, T.R.; Patti, A.F. Hybrid Brown Coal-Urea Fertiliser Reduces Nitrogen Loss Compared to Urea Alone. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1496–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, N.S.; Saha, D. Influence of Organic Matter Vis-à-Vis Humic Acid on the Transformation of Inorganic and Organic Forms of Nitrogen in a Typic Haplustept Soil. Commun. Soil. Sci. Plant Anal. 2017, 48, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, M.; Anjum, M.A.; Mirza, J.I. Potassium Humate and NPK Application Rates Influence Yield and Economic Performance of Potato Crops Grown in Clayey Loam Soils. Soil. Environ. 2018, 37, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCarthy, P. The Principles of Humic Substances. Soil. Sci. 2001, 166, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Lin, H.; Gao, W.; Li, M. The Effects of Humic Acid Urea and Polyaspartic Acid Urea on Reducing Nitrogen Loss Compared with Urea. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 4425–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomida, M.; Nakato, T.; Matsunami, S.; Kakuchi, T. Convenient Synthesis of High Molecular Weight Poly(Succinimide) by Acid-Catalysed Polycondensation of l-Aspartic Acid. Polymer 1997, 38, 4733–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntari, R.; Retnowati, R.; Soemarno; Munir, M. Study on the Release of N-Available (NH4+ and NO3−) of Urea-Humate. Int. J. Agric. For. 2013, 3, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, W.Z. Preparation and Properties of Urea Slow Release Coated with Potassium Humate, Bentonite and Polyacrylamide as Compositely Fertilizer Which Reflected on the Productivity of Wheat Crop. J. Soil. Sci. Agric. Eng. 2018, 9, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsakov, K.; Stepanov, A.; Pozdnyakov, L.; Yakimenko, O. Humate-Coated Urea as a Tool to Decrease Nitrogen Losses in Soil. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhongjun, D.U.; Hao, Y.; Shuchang, W.; Li, X.; Bing, W.; Kanglin, W.; Songgang, L.; Haiyan, L. Advance of Homologous Polypeptides Polyaspartic Acids for Agriculture. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2011, 32, 2381. [Google Scholar]
- Swify, S.; Avizienyte, D.; Mazeika, R.; Braziene, Z. Influence of Modified Urea Compounds to Improve Nitrogen Use Efficiency under Corn Growth System. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntari, R.; Retnowati, R.; Soemarno; Munir, M. Determination of Urea-Humic Acid Dosage of Vertisols on the Growth and Production of Rice. Agrivita 2015, 37, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.H.; Yuan, Q.; Yuan, H.L. Changes of Chemical Properties of Humic Acids from Crude and Fungal Transformed Lignite. Fuel 2006, 85, 2402–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syukur, A.; Shiddieq, D.; Yuwono, T. Effect of Coated Urea with Humic-Calcium on Transformation of Nitrogen in Coastal Sandy Soil: A Soil Column Method. J. Trop. Soils 2010, 15, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- 47. Dong, L.; Córdova-Kreylos, A.L.; Yang, J.; Yuan, H.; Scow, K.M. Humic Acids Buffer the Effects of Urea on Soil Ammonia Oxidizers and Potential Nitrification. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2012, 41, 1612–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasim, S.; Ahmed, O.H.; Muhamad, N.; Majid, A. Reduction of Ammonia Loss by Mixing Urea with Liquid Humic and Fulvic Acids Isolated from Tropical Peat Soil. Am. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2009, 4, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taufik, M.; Yusuff, M.; Ahmed, O.H.; Muhamad, N.; Majid, A.; Campus, S. Effect of Mixing Urea with Humic Acid and Acid Sulphate Soil on Ammonia Loss, Exchangeable Ammonium and Available Nitrate. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 5, 588–591. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Nyborg, M.; Malhi, S.S.; Solberg, E.D. Localized Root Growth in Soil Induced by Controlled-Release Urea Granule and Barley Nitrogen Uptake. J. Plant Nutr. 2000, 23, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.E.; Burger, M.; Cavagnaro, T.R. Roots, Nitrogen Transformations, and Ecosystem Services. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 341–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, V.; Bacaicoa, E.; Zamarreño, A.M.; Aguirre, E.; Garnica, M.; Fuentes, M.; García-Mina, J.M. Action of Humic Acid on Promotion of Cucumber Shoot Growth Involves Nitrate-Related Changes Associated with the Root-to-Shoot Distribution of Cytokinins, Polyamines and Mineral Nutrients. J. Plant Physiol. 2010, 167, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, H.; Fawy, H. Effect of Different Levels of Humic Acids on the Nutrient Content, Plant Growth, and Soil Properties under Conditions of Salinity. Soil. Water Res. 2011, 6, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pukalchik, M.; Kydralieva, K.; Yakimenko, O.; Fedoseeva, E.; Terekhova, V. Outlining the Potential Role of Humic Products in Modifying Biological Properties of the Soil—A Review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, S.; Osmond, D.; Israel, D. Nitrogen Release from Coated Urea Fertilizers in Different Soils. Commun. Soil. Sci. Plant Anal. 2010, 41, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukantis, A. Klimatinis Rajonavimas. In Lietuvos Nacionalinis Atlasa; I Tomas; GIS-Centras Nacionaline Zemes Tarnyba Prie Zemes Ukio Ministerijos Vilniaus Universitetas: Vilnius, Lithuania, 2014; p. 74. [Google Scholar]
- Kažys, J. Vidutinė Metinė Oro Temperatūra. In Lietuvos Nacionalinis Atlasas; I Tomas; GIS-Centras Nacionaline Zemes Tarnyba Prie Zemes Ukio Ministerijos Vilniaus Universitetas: Vilnius, Lithuania, 2014; p. 69. [Google Scholar]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources. In International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps, 4th ed.; International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS): Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 10390:2005; Soil Quality—Determination of pH. International Organization for Standardization Case: Geneve, Switzerland, 2005.
- Buneviciene, K.; Drapanauskaite, D.; Mazeika, R.; Tilvikiene, V.; Baltrusaitis, J. Granulated Biofuel Ash as a Sustainable Source of Plant Nutrients. Waste Manag. Res. 2021, 39, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 11265:1994; Soil Quality—Determination of the Specific Electrical Conductivity. International Organization for Standardization Case: Geneve, Switzerland, 1994.
- ISO 11261:1995; Soil Quality —Determination of Total Nitrogen. International Organization for Standardization Case: Geneve, Switzerland, 1995.
- Black, C.A.; Evans, D.D.; White, J.L.; Ensminger, L.E.; Clark, F.E. Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2: Chemical and Microbiological Properties; American Society of Agronomy, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1983; 1572p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10694:1995; Soil Quality—Determination of Organic and Total Carbon after Dry Combustion (Elementary Analysis). International Organization for Standardization Case: Geneve, Switzerland, 1995.
- Soil Quality Indicators: PH. 1998. Available online: https://www.fs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/stelprdb5293776.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Zhian, L. Ammonia Volatilization Characteristics and Related Affecting Factors of Humic Acid Urea. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2010, 16, 208–213. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Köbke, S.; Dittert, K. Use of Urease and Nitrification Inhibitors to Reduce Gaseous Nitrogen Emissions from Fertilizers Containing Ammonium Nitrate and Urea. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Xue, Z.; Li, B.; An, S. Soil Organic Carbon Distribution in Relation to Land Use and Its Storage in a Small Watershed of the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2012, 88, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swify, S.S.F.; El-Aziz, A.; Selmy, S.A.H.; Elgharably, A.; Ragheb, H.M.A. Assessment and Spatial Variability Mapping of Soil Available Phosphorus and Potassium of Coarse-Textured Soils in New Valley, Egypt Using Geostatistical Technique. Assiut J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 48, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarella, H.; Otto, R.; Soares, J.R.; Silva, A.G. de B. Agronomic Efficiency of NBPT as a Urease Inhibitor: A Review. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 13, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anas, M.; Liao, F.; Verma, K.K.; Sarwar, M.A.; Mahmood, A.; Chen, Z.L.; Li, Q.; Zeng, X.P.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.R. Fate of Nitrogen in Agriculture and Environment: Agronomic, Eco-Physiological and Molecular Approaches to Improve Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coskun, D.; Britto, D.T.; Shi, W.; Kronzucker, H.J. Nitrogen Transformations in Modern Agriculture and the Role of Biological Nitrification Inhibition. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, R.; Castelli, F. Mineral Nitrogen Dynamics in Soil during Sugar Beet and Winter Wheat Crop Growth. Eur. J. Agron. 2011, 35, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.S.; Yuan, L.; Li, W.; An, L.Z.; Ting, L.Y.; Wen, H.S.; Qiang, Z.B. Effects of Urea Enhanced with Different Weathered Coal-Derived Humic Acid Components on Maize Yield and Fate of Fertilizer Nitrogen. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Brown, B.D.; Engel, R.; Horneck, D.; Olson-Rutz, K. Factors Affecting Nitrogen Fertilizer; Montana State University: Bozeman, MT, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, C.A.; Koenig, R.T.; Ellsworth, J.W.; Jackson, G.D. Management of Urea Fertilizer to Minimize Volatilization; Montana State University: Bozeman, MT, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gaihre, Y.K.; Singh, U.; Bible, W.D.; Fugice, J.; Sanabria, J. Mitigating N2O and NO Emissions from Direct-Seeded Rice with Nitrification Inhibitor and Urea Deep Placement. Rice Sci. 2020, 27, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolkowski, R.P.; Kelling, K.A.; Bundy, L.G. Nitrogen Management on Sandy Soils. In The Learning Store—Division of Extension; University of Wisconsin: Madison, WI, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Mthandi, J.; Kahimba, F.C.; Tarimo, A.; Salim, B.A.; Lowole, M. Nitrogen Movement in Coarse-Textured Soils and Its to Maize (Zea Mays L.) Plant. Agric. Sci. 2013, 4, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, J.D.; Bawden, A.D.; Coleman, D.C. Rates and pathways of mineral nitrogen transformation in a soil from pasture. Soil. Bid. Biochem. 1984, 16, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbačiauskas, J.; Staugaitis, G.; Vaišvila, Z.; Mažvila, J.; Adomaitis, T.; Šumskis, D.; Žičkienė, L.; Lubytė, J.; Mažeika, R. The Interdependence of Mineral Nitrogen Content in Different Soil Layers of Lithuanian Agricultural Lands. Zemdirb. Agric. 2014, 101, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staugaitis, G.; Mažvila, J.; Vaišvila, Z.; Arbačiauskas, J.; Dalangauskienė, A.; Adomaitis, T. Mineral Nitrogen in Lithuanian Soils. Žemės Ūkio Mokslai 2008, 15, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Rutkowska, A.; Fotyma, M. Calibration of Soil Test for Mineral Nitrogen in Poland. Commun. Soil. Sci. Plant Anal. 2009, 40, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, R.L.; Williams, H.M.; Behel, A.D. Nitrogen Leaching and Plant Uptake from Controlled-Release Fertilizers. Fertil. Res. 1994, 37, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.K.; Rose, M.T.; Wong, V.; Cavagnaro, T.R.; Patti, A.F. Brown Coal-Urea Blend for Increasing Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Biomass Yield. In Proceedings of theInternational Nitrogen Initiative Conference, “Solutions to Improve Nitrogen use Efficiency for the World”, Melbourne, Australia, 4–8 December 2016; pp. 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kochiieru, M.; Lamorski, K.; Feizienė, D.; Feiza, V.; Šlepetienė, A.; Volungevičius, J. Land Use and Soil Types Affect Macropore Network, Organic Carbon and Nutrient Retention, Lithuania. Geoderma Reg. 2022, 28, e00473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Jiao, S.; Ma, Z.; Lin, H.; Gao, W.; Chen, J. Humic Acid-Modified Bentonite Composite Material Enhances Urea-Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolling, P.; Porter, W. Barley Production and Soil Acidity. J. Dep. Agric. 1984, 25, 136–137. [Google Scholar]
- Dolling, P.J.; Porter, W.M.; Robson, A.D. Effect of Soil Acidity on Barley Production in the South-West of Western Australia. 2. Cereal Genotypes and Their Response to Lime. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 1991, 31, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Soil Characteristics | Rumokai | Dotnuva | Kazlu Ruda | Vezaiciai |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Type | Endogleyic Haplic Luvisol (Loamic, Aric) | Endogleyic Epistagnic Endocalcaric Cambisol (Loamic, Aric, Drainic) | Dystric Arenosol (Aric) | Glossic Epigleyic Dystric Retisol (Clayic, Aric, Cutanic, Drainic) |
| Texture | Loam (L) | Sandy Loam (SL) | Sand (S) | Sandy Clay (SC) |
| pHKcl mol/L | 7.4 | 6.9 | 5.3 | 4.5 |
| P2O5 mg·kg−1 | 244 | 266 | 102 | 139 |
| K2O mg·kg−1 | 201 | 308 | 40 | 240 |
| SOM * (%) | 1.04 | 1.26 | 0.79 | 1.25 |
| SOC ** (%) | 0.60 | 0.73 | 0.46 | 0.72 |
| Ece mS/m | 14.4 | 12.7 | 2.31 | 6.10 |
| Total N (%) | 0.148 | 0.151 | 0.013 | 0.120 |
| Nmin mg·kg−1 | 23.99 | 37.32 | 1.74 | 41.60 |
| NH4+–N mg·kg−1 | 2.06 | 1.33 | 0.98 | 3.68 |
| NO3−–N mg·kg−1 | 21.93 | 35.99 | 0.76 | 37.92 |
| Treatments | Mean | Correlation Coefficient | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dystric Arenosol (Aric)/Sandy Texture | ||||||
| NO3−–N | Nmin | NO3−–N | Nmin | NO3−–N | Nmin | |
| Control (C) | 2.22 | 10.36 | 0.612 | −0.249 | 0.107 | 0.552 |
| U100 | 16.70 | 30.52 | 0.827 * | 0.519 | 0.011 | 0.188 |
| U200 | 27.98 | 51.68 | 0.953 ** | 0.918 ** | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| UPH100 | 22.29 | 40.32 | 0.770 * | 0.593 | 0.025 | 0.121 |
| UPH200 | 40.24 | 58.23 | 0.961 ** | 0.920 ** | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| Endogleyic Epistagnic Endocalcaric Cambisol (Loamic, Aric, Drainic)/Sandy loam texture | ||||||
| NO3−–N | Nmin | NO3−–N | Nmin | NO3−–N | Nmin | |
| Control (C) | 36.88 | 43.57 | −0.432 | −0.422 | 0.285 | 0.298 |
| U100 | 130.46 | 155.84 | 0.948 ** | 0.826 * | 0.000 | 0.012 |
| U200 | 194.21 | 271.25 | 0.942 ** | 0.785 * | 0.000 | 0.021 |
| UPH100 | 144.50 | 158.10 | 0.898 ** | 0.844 ** | 0.002 | 0.008 |
| UPH200 | 161.42 | 212.78 | 0.964 ** | 0.819 * | 0.000 | 0.013 |
| Endogleyic Haplic Luvisol (Loamic, Aric)/Loamy texture | ||||||
| NO3−–N | Nmin | NO3−–N | Nmin | NO3−–N | Nmin | |
| Control (C) | 37.80 | 45.95 | 0.740 * | 0.455 | 0.036 | 0.258 |
| U100 | 104.26 | 131.79 | 0.742 * | 0.478 | 0.035 | 0.231 |
| U200 | 165.83 | 219.56 | 0.989 ** | 0.846 ** | 0.000 | 0.008 |
| UPH100 | 152.56 | 175.51 | 0.957 ** | 0.924 ** | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| UPH200 | 178.23 | 255.47 | 0.956 ** | 0.737 * | 0.000 | 0.037 |
| Glossic Epigleyic Dystric Retisol (Clayic, Aric, Cutanic, Drainic)/Sandy clay texture | ||||||
| NO3−–N | Nmin | NO3−–N | Nmin | NO3−–N | Nmin | |
| Control (C) | 42.99 | 53.15 | 0.879 ** | 0.753 * | 0.004 | 0.031 |
| U100 | 105.72 | 260.86 | 0.946 ** | 0.793 * | 0.000 | 0.019 |
| U200 | 139.95 | 425.08 | 0.958 ** | 0.750 * | 0.000 | 0.032 |
| UPH100 | 92.28 | 216.81 | 0.922 ** | 0.754 * | 0.001 | 0.031 |
| UPH200 | 144.67 | 331.69 | 0.969 ** | 0.621 | 0.000 | 0.100 |
| Soil Texture Type | NH4+–N | NO3−–N | Nmin |
|---|---|---|---|
| mg·kg−1 | |||
| Sand | 16.33 a | 21.89 a | 38.22 a |
| Sandy loam | 43.03 a | 133.49 c | 168.31 b |
| Loam | 37.92 a | 127.74 bc | 165.66 b |
| Sandy clay | 137.55 b | 105.12 bc | 257.52 c |
| p-value | p < 0.003 | p < 0.002 | p < 0.001 |
| Treatments | |||
| Control (C) | 9.87 a | 29.97 a | 38.26 a |
| U100 | 56.60 abc | 89.29 b | 144.75 b |
| U200 | 94.84 c | 132.00 d | 241.89 d |
| UPH100 | 45.71 abc | 102.91 bcd | 147.69 b |
| UPH200 | 86.51 bc | 131.14 cd | 214.54 bcd |
| p-value | p < 0.021 | p < 0.003 | p < 0.001 |
| The Application | Arenosol (S) | Cambisol (SL) | Luvisol (L) | Retisol (SC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | 5.3 | 6.9 | 7.4 | 4.5 |
| Control | 6.00 a | 6.90 a | 7.03 b | 4.27 abc |
| U100 | 6.20 abc | 6.93 a | 7.03 b | 4.03 a |
| U200 | 6.63 c | 6.83 a | 6.93 ab | 4.67 c |
| UPH100 | 6.37 abc | 6.83 a | 7.00 ab | 4.10 a |
| UPH200 | 6.47 abc | 6.87 a | 6.93 ab | 4.33 abc |
| p-value | 0.16 | 0.29 | 0.68 | 0.11 |
| Soil Texture Type | Min. | Max. | Mean | SD | CV (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nmin (mg·kg−1) | Sand | 10.36 | 58.23 | 38.22 | 18.85 | 23.41 |
| Sandy loam | 43.57 | 271.25 | 168.31 | 84.25 | 104.61 | |
| Loam | 45.95 | 255.47 | 165.66 | 81.46 | 101.15 | |
| Sandy clay | 53.15 | 425.08 | 257.52 | 138.76 | 172.29 | |
| NH4+–N (mg·kg−1) | Sand | 8.14 | 23.70 | 16.33 | 5.77 | 7.17 |
| Sandy loam | 6.69 | 80.96 | 43.03 | 35.26 | 43.78 | |
| Loam | 8.15 | 77.24 | 37.92 | 27.45 | 34.08 | |
| Sandy clay | 16.53 | 221.70 | 137.55 | 76.24 | 94.66 | |
| NO3−–N (mg·kg−1) | Sand | 2.22 | 40.24 | 21.89 | 14.03 | 17.43 |
| Sandy loam | 36.88 | 194.21 | 133.49 | 59.01 | 73.28 | |
| Loam | 37.80 | 178.23 | 127.74 | 57.57 | 71.48 | |
| Sandy clay | 42.99 | 144.67 | 105.12 | 41.24 | 51.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Swify, S.; Mažeika, R.; Volungevičius, J. Mineral Nitrogen Release Patterns in Various Soil and Texture Types and the Impact of Urea and Coated Urea Potassium Humate on Barley Biomass. Soil Syst. 2023, 7, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7040102
Swify S, Mažeika R, Volungevičius J. Mineral Nitrogen Release Patterns in Various Soil and Texture Types and the Impact of Urea and Coated Urea Potassium Humate on Barley Biomass. Soil Systems. 2023; 7(4):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7040102
Chicago/Turabian StyleSwify, Samar, Romas Mažeika, and Jonas Volungevičius. 2023. "Mineral Nitrogen Release Patterns in Various Soil and Texture Types and the Impact of Urea and Coated Urea Potassium Humate on Barley Biomass" Soil Systems 7, no. 4: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7040102
APA StyleSwify, S., Mažeika, R., & Volungevičius, J. (2023). Mineral Nitrogen Release Patterns in Various Soil and Texture Types and the Impact of Urea and Coated Urea Potassium Humate on Barley Biomass. Soil Systems, 7(4), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems7040102