A Study of the Interaction of Human Smart Characteristics with Demographic Dynamics and Built Environment: The Case of Limassol, Cyprus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- RQ1
- How do human smart dimensions change at different urban neighborhoods? In other words, are the dimensions global, stationary across the city’s neighborhoods, or local, varying from one location to another?
- RQ2
- What are the local determinants that contribute to these human smart dimension changes?
2. Defining the Human Smart Dimensions through European Context
3. Study Methodology
3.1. Procedure Steps
3.2. Data Source
3.3. Geographical Analysis
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Case Study Area
4.1. Main Variables Descrpition
4.2. Supportive Variables Description
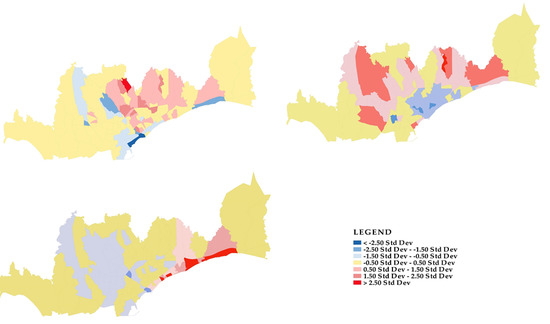
5. Results
5.1. Correlations
5.2. Results of PCA Evaluation Factors
- -
- OSA PC1 (KIS employed, university and IT educated),
- -
- OSA PC2 (high H/H size, single housing) and
- -
- OSA PC3 (high % of foreigners, rented housing and high recycling rates)
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albino, V.; Berardi, U.; Dangelico, R.M. Smart cities: Definitions, dimensions, performance, and initiatives. J. Urban Technol. 2015, 22, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourabi, H.; Nam, T.; Walker, S.; Gil-Garcia, J.R.; Mellouli, S.; Nahon, K.; Scholl, H.J. Understanding smart cities: An integrative framework. In Proceedings of the 45th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (IEEE), Maui, HI, USA, 4–7 January 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Meijer, A.; Bolivar, M.P.R. Governing the Smart City: A review of the literature on smart urban governance. Int. Rev. Adm. Sci. 2015, 82, 392–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, T.; Pardo, T.A. Conceptualizing Smart City with dimensions of technology, people, and institutions. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual International Conference on Digital Government Research, College Park, MD, USA, 12–15 June 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEC. Cities of Tomorrow; Council of European Community: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bibri, S.E.; Krogstie, J. Smart sustainable cities of the future: An extensive interdisciplinary literature review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 31, 183–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caragliu, A.; Del Bo, C.; Nijkamp, P. Smart cities in Europe. J. Urban Technol. 2011, 18, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, E.M. Smart City: Adding to the Complexity of Cities. In Complexity & Simplicity—Proceedings of the 34th eCAADe Conference; University of Oulu: Oulu, Finland, 2016; Volume 1, pp. 651–660. [Google Scholar]
- BSI. Smart Cities—Vocabulary (PAS 180:2014, 3.1.62); British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gil-Garcia, J.R.; Pardo, T.A.; Nam, T.A. A Comprehensive View of the 21st Century City: Smartness as Technology and Innovation in Urban Contexts. In Smarter as the New Urban Agenda; Gil-Garcia, J.R., Pardo, T.A., Nam, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Giffinger, R.; Fertner, C.; Kramar, H.; Kalasek, R.; Pichler-Milanovi, N.; Meijers, E. Smart Cities: Ranking of European Medium-Sized Cities; Centre of Regional Science, Vienna University of Technology: Vienna, Austria, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Giffinger, R.; Fertner, C.; Kramar, H.; Meijers, E. City-Ranking of European Medium-Sized Cities; Centre of Regional Science, Vienna University of Technology: Vienna, Austria, 2007; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Angelidou, M. Smart cities: A conjuncture of four forces. Cities 2015, 47, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huovila, A.; Bosch, P.; Airaksinen, M. Comparative analysis of standardized indicators for Smart sustainable cities: What indicators and standards to use and when? Cities 2019, 89, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manville, C.; Cochrane, G.; Cave, J.; Millard, J.; Pederson, J.K.; Thaarup, R.K.; Liebe, A.; Wissner, M.; Massink, R.; Kotterink, B. Mapping Smart Cities in the EU; DG for Internal Policies, European Parliament, Strasbourg: Brussels, Belgium, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Neirotti, P.; De Marco, A.; Cagliano, A.C.; Mangano, G.; Scorrano, F. Current trends in Smart City initiatives: Some stylised facts. Cities 2014, 38, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monzon, A. Smart Cities Concept and Challenges. Bases for the Assessment of Smart City Projects. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems (SMARTGREENS), Lisbon, Portugal, 20–22 May 2015; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Batty, M. The New Science of Cities; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zaman, A.U.; Lehmann, S. Challenges and opportunities in transforming a city into a “zero waste city”. Challenges 2011, 2, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGrath, B.; Pickett, S. The metacity: A conceptual framework for integrating ecology and urban design. Challenges 2011, 2, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, E.S.; Nunes, E.O.; Santos, L.B. The use of ISO 37122 as standard for assessing the maturity level of a smart city. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Sci. 2018, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, A.; Parmaxi, A.; Papadima-Sophocleous, S.; Boglou, D. Language education in a multilingual city: The case of Limassol. Lond. Rev. Educ. 2016, 14, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, F.; Rindone, C.; Panuccio, P. European plans for the smart city: From theories and rules to logistics test case. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2016, 24, 1709–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidou, M. Smart city policies: A spatial approach. Cities 2014, 41, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dameri, R.P.; Rosenthal-Sabroux, C. Smart City: How to Create Public and Economic Value with High Technology in Urban Space; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2014; ISBN 978-3-319-06159-7. [Google Scholar]
- Andreani, S.; Kalchschmidt, M.; Pinto, R.; Sayegh, A. Reframing technologically enhanced urban scenarios: A design research model towards human centered smart cities. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 142, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zygiaris, S. Smart city reference model: Assisting planners to conceptualize the building of smart city innovation ecosystems. J. Knowl. Econ. 2013, 4, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, G.H. The economic value of smart city technology. Econ. Manag. Financ. Mark. 2015, 10, 76–82. Available online: https://www.ceeol.com/search/article-detail?id=306532 (accessed on 30 November 2019).
- Anttiroiko, A.V. Smart cities: Building platforms for innovative local economic restructuring. In Transforming City Governments for Successful Smart Cities; Rodríguez-Bolívar, M.P., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 23–42. ISBN 978-3-319-03166-8. [Google Scholar]
- Kourtit, K.; Nijkamp, P. In praise of megacities in a global world. Reg. Sci. Policy Pract. 2013, 5, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, C.R.; Glaeser, E.L. The divergence of human capital levels across cities. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2005, 84, 407–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glaeser, E.L.; Berry, C.R. Why are smart places getting smarter. In Rappaport Institute for Greater Boston; Policy Briefs, PB-2006-2; Taubman Centre for State and Local Government: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006; Available online: https://www.hks.harvard.edu/sites/default/files/centers/taubman/files/brief_divergence.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2018).
- Shapiro, J.M. Smart cities: Quality of life, productivity, and the growth effects of human capital. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2006, 88, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollands, R.G. Will the real Smart City please stand up? Intelligent, progressive or entrepreneurial? City 2008, 12, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winters, J.V. Why are smart cities growing? Who moves and who stays. J. Reg. Sci. 2011, 51, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, R.; Dotoli, M.; Pellegrino, R.; Ranieri, L. Measuring and Managing the Smartness of Cities: A Framework for Classifying Performance Indicators. In Proceedings of the IEEE Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Manchester, UK, 13–16 October 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaroiu, G.C.; Roscia, M. Definition methodology for the smart cities model. Energy 2012, 47, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtit, K.; Macharis, C.; Nijkamp, P. A multi-actor multi-criteria analysis of the performance of global cities. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 49, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilpoorarabi, N.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Guaralda, M. Place quality and urban competitiveness symbiosis? A position paper. Int. J. Knowl.-Based Dev. 2016, 7, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komninos, N. Intelligent cities: Towards interactive and global innovation environments. Int. J. Innov. Reg. Dev. 2009, 1, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T. Smart cities: An effective urban development and management model? Aust. Plan. 2015, 52, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, P.; Giordano, S.; Farouh, H.; Wael, Y. An analytic network model for Smart cities. In Proceedings of the 11th International Symposium on the Analytic Hierarchy Process, Sorrento, Italy, 15–18 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Letaifa, S. How to strategize smart cities: Revealing the SMART model. J. Bus. Res. 2015, 68, 1414–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrionuevo, J.M.; Berrone, P.; Ricart, J.E. Smart cities, sustainable progress. IESE Insight 2012, 14, 50–57. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Pascual_Berrone/publication/276088190_Smart_Cities_Sustainable_Progress_Opportunities_for_Urban_Development/links/563f9a3908ae8d65c0150f53.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2019).
- Yigitcanlar, T. Innovating urban policymaking and planning mechanisms to deliver knowledge-based agendas: A methodological approach. Int. J. Knowl.-Based Dev. 2014, 5, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dirks, S.; Keeling, M. A Vision of Smarter Cities: How Cities Can Lead the Way into a Prosperous and Sustainable Future; IBM Global Business Services: Somers, NY, USA, 2009; Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/e46b/641d546a348df63762b8ce79b23911568f36.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Hughes, S.; Pincetl, S.; Boone, C. Triple exposure: Regulatory, climatic, and political drivers of water management in Los Angeles. Cities 2013, 32, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toppeta, D. The Smart City Vision: How Innovation and ICT Can Build Smart, “Livable”, Sustainable Cities. Innov. Knowl. Found. 2010, 5, 1–9. Available online: http://www.thinkinnovation.org/file/research/23/en/Toppeta_Report_005_2010.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2018).
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G. The internet of things: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 2787–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahizhnan, A. Smart cities. The Singapore case. Cities 1999, 16, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakıcı, T.; Almirall, E.; Wareham, J. A Smart City initiative: The case of Barcelona. J. Knowl. Econ. 2013, 4, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Anez, V.; Fernández-Güell, J.M.; Giffinger, R. Smart City implementation and discourses: An integrated conceptual model. The case of Vienna. Cities 2018, 78, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeijer, D.; de Groot, R.S. A conceptual framework for selecting environ-mental indicator sets. Ecol. Indic. 2008, 8, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spangenberg, J. Environmental space and the prism of sustainability: Frameworks for indicators measuring sustainable development. Ecol. Indic. 2002, 2, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossel, H. Indicators for Sustainable Development: Theory, Method, Applications; International Institute for Sustainable Development: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Duinker, P. Criteria and indicators of sustainable forest management in Canada: Progress and problems in integrating science and politics at the local level. In Criteria and Indicators for Sustainable Forest Management at the Forest Management Unit Level; Franc, A., La roussinie, O., Karjalainen, T., Eds.; European Forest Institute Proceedings: Joensuu, Finland; Gummerus Printing: Saarijarvi, Finland, 2001; Volume 38, pp. 7–27. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, G. The development of indicators for sustainable tourism: Results of a Delphi survey of tourism researchers. Tour. Manag. 2001, 22, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liverman, D.M.; Hanson, M.E.; Brown, B.J.; Meredith, R.W. Global sustainability: Toward Measurement. Environ. Manag. 1988, 20, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, G.B.; Kibert, C.J. Developing Indicators of Sustainability: US experience. Build. Res. Inf. 1998, 26, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoyer-Tomic, K.; Hewko, J.; Hodgson, J. Spatial accessibility and equity of playgrounds in Edmonton, Canada. Can. Geogr. 2004, 48, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyk, L. The ecological footprint housing component: A geographic information system analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 16, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolossov, V.; Vendina, O.; O’Loughlin, J. Moscow as an Emergent World City: International Links, Business Developments, and the Entrepreneurial City. Eurasian Geogr. Econ. 2002, 43, 170–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, H.; Shea Rose, L.; Taha, H. Analyzing the land cover of an urban environment using high-resolution orthophotos. Landsc. Urban Plan 2003, 63, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, M.A. Accuracy assessment of digitized and classified land cover data for wildlife habitat. Landsc. Urban Plan 2006, 78, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.N.; Lu, Z.Z.; Xu, L.Y. Multivariate sensitivity analysis based on the direction of Eigen space through principal component analysis. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2017, 165, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, R.; Ma, Y.; Sastry, S.S. Generalized Principal Component Analysis. In Interdisciplinary Applied Mathematics 40; Springer: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-0-387-87810-2. [Google Scholar]
- Tabachnick, B.G.; Fidell, L.S. Using Multivariate Statistics, 5th ed.; Pearson Education: Boston, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Alverti, M.; Themistocleous, K.; Kyriakidis, P.; Hadjimitsis, D. A Human Centric Approach on the Analysis of the Smart City Concept: The case of Limassol city in Cyprus. Adv. Geosci. 2018, 45, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ministry of Interior, Department of Planning and Housing (2011). Limassol Structure Plan. Provisions and Policy Measures. Available online: http://www.moi.gov.cy/moi/tph/tph.nsf/page72_gr/page72_gr?OpenForm (accessed on 1 September 2019). (In Greek)
- Pashardes, P.; Savva, C.S. Factors Affecting House Prices in Cyprus: 1988–2008. Cyprus Econ. Policy Rev. 2009, 3, 3–25. Available online: http://www.ucy.ac.cy/erc/documents/FullTextPashardesSavva.pdf (accessed on 29 March 2018).
- Leontidou, L. Beyond the Borders of Mediterranean Cities: The Mediterranean City Transition. J. Interdiscip. Hist. 2007, 22, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Aesaert, K.; Voogt, J.; Kuiper, E.; van Braak, J. Accuracy and bias of ICT self-efficacy: An empirical study into students’ over- and under estimation of their ICT competences. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 75, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeneveld, R.A.; Meeden, G. Measuring skewness and kurtosis. Statistician 1984, 33, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E.; Tatham, R.L. Multivariate Data Analysis, 6th ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, A.W.; Rainer, R.K., Jr. The Influence of Individual Differences on Skill in End-User Computing. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 1992, 9, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, Y. Technophobia or technophilia? A preliminary look at why second language teachers do or do not use technology in their classrooms. Can. Mod. Lang. Rev. 2000, 56, 389–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, E.M. Exploring the Relationship between Teaching Staff’ Age and Their Attitude towards Information and Communications Technologies. Int. J. Instr. 2013, 6, 215–226. [Google Scholar]
- Scheerder, A.; Deursen, A.; van Dijk, J. Determinants of Internet skills, uses and outcomes. A systematic review of the second- and third-level digital divide. Telemat. Inform. 2017, 30, 1607–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briguglio, M.; Formosa, G. When households go solar: Determinants of uptake of a Photovoltaic Scheme and policy insights. Energy Policy 2017, 108, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostakis, I.; Theodoropoulou, E.; Mitoula, R. Which are the determinants of recycling? A case study in Greece. Cyprus J. Sci. 2015, 13, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Briguglio, M.; Delaney, L.; Wood, A. Voluntary recycling despite disincentives. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2015, 59, 1751–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| EU Policy Objectives | Urban Challenges | Human Smart City Dimensions | Variable Description | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (i), (iv) | Improving labor force market competitiveness/social innovation economy | Level of Educational Attainment | Share of population with University degree | [7,11,12,16,35,36,37] |
| (i), (v) | Managing adaptation to innovation and knowledge-based economies | Creativity - Innovation | Share of employed in Knowledge Intensive Services (KIS) | [16,37,38,39,40,41] |
| (ii) | Increasing waste management disposal (separation/recycling/reuse) and promoting circular economy | Environmental Awareness | Proportion of waste recycled | [16,38,42,43,44,45] |
| (ii), (v) | Reducing ecological footprint and pressure on ecosystems. Promoting renewable energy such as solar, wind etc. | Energy Transition (Renewable/green energy) | Proportion of renewable energy consumed | [2,4,16,46,47,48] |
| (iii) | Improving ICT networks and access to citizens. Promoting ICT connectivity | Use of ICT | Proportion of households with broadband internet connection | [2,7,12,49] |
| (iii) | Improving citizens digital skills | Digital Inclusion | Share of population using digital divices | [16,48,50,51] |
| (iv) | Enhancing social inclusion of migrants and refugees | Social Plurality and Ethnic Diversity | Share of population whose country of birth is not Cyprus | [11,37,38,52] |
| Variable | Variable Description | Coverage | Obs. | Min | Max | Mean | Mode | S.D. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human smartcharacteristics | COMPUT_USE | Share of households with personal computer | High | 50 | 35.4 | 72.68 | 57.31 | 35.44 | 8.77 |
| Medium | 46 | 18.62 | 89.45 | 64.77 | 18.62 | 14.29 | |||
| Low | 40 | 43.18 | 100 | 73.49 | 81.82 | 13.13 | |||
| LMA | 136 | 18.62 | 100 | 64.59 | 81.82 | 13.74 | |||
| INTERN_USE | Share of households with internet connection | High | 50 | 76.22 | 96.43 | 87.33 | 76.22 | 4.56 | |
| Medium | 46 | 77.5 | 100 | 89.56 | 77.5 | 5.37 | |||
| Low | 40 | 75.62 | 100 | 90.54 | 100 | 6.02 | |||
| LMA | 136 | 75.62 | 100 | 89.03 | 100 | 5.43 | |||
| KIS | Share employed in Knowledge Intensive Services (J,K,M,O,P,Q,R by NACE rev.2) | High | 50 | 21.51 | 46.67 | 32.16 | 21.51 | 5.69 | |
| Medium | 46 | 17.8 | 47.08 | 32.8 | 17.8 | 7.73 | |||
| Low | 40 | 12 | 54.5 | 34.98 | 12 | 9.8 | |||
| LMA | 136 | 12 | 54.5 | 33.2 | 34.83 | 7.8 | |||
| NO_NATIVES | Share of population whose country of birth is not Cyprus | High | 50 | 10.48 | 61.5 | 27.39 | 10.48 | 11.49 | |
| Medium | 46 | 8.11 | 76.62 | 27.15 | 8.11 | 20.47 | |||
| Low | 40 | 4.65 | 69.81 | 18.9 | 4.65 | 14.01 | |||
| LMA | 136 | 4.65 | 76.62 | 24.81 | 4.65 | 16.09 | |||
| RECYCLED/100 INH | Average recycling (PMD, paper, glass) per 100 inhabitants in tons for years 2010/2011/2012 | High | 49 | 2.23 | 7.62 | 3.68 | 3.65 | 0.89 | |
| Medium | 45 | 2.23 | 7.62 | 3.69 | 3.65 | 1.51 | |||
| Low | 32 | 2.23 | 10.58 | 3.95 | 2.23 | 2.28 | |||
| LMA | 126 | 2.23 | 10.58 | 3.75 | 3.65 | 1.55 | |||
| SOLAR_PV_USE | Share of living quarters using solar energy and photovoltaics | High | 50 | 62.27 | 99.87 | 93.39 | 62.27 | 8.01 | |
| Medium | 46 | 53.77 | 100 | 94.76 | 53.77 | 7.66 | |||
| Low | 40 | 59.67 | 100 | 95.95 | 100 | 6.7 | |||
| LMA | 136 | 53.77 | 100 | 94.61 | 100 | 7.54 | |||
| UNIV | Share of population (>15 ages) with university degree (level 6 by ISCED 2011) | High | 50 | 6.76 | 26.67 | 16.01 | 11.61 | 5.09 | |
| Medium | 46 | 2.72 | 31.4 | 17.61 | 2.72 | 6.71 | |||
| Low | 40 | 2.85 | 35.77 | 17.02 | 13.9 | 7.35 | |||
| LMA | 136 | 2.72 | 35.77 | 16.85 | 9.83 | 6.36 | |||
| Demographicdynamics | HH_SIZE | Average household size | High | 50 | 2.12 | 3.32 | 2.56 | 2.12 | 0.25 |
| Medium | 46 | 1.8 | 3.45 | 2.79 | 1.8 | 0.43 | |||
| Low | 40 | 2.01 | 5.14 | 3.24 | 2.01 | 0.55 | |||
| LMA | 136 | 1.8 | 5.14 | 2.84 | 1.8 | 0.5 | |||
| R_AGE_DEPEND | Age dependency ratio | High | 50 | 30.13 | 59.26 | 43.22 | 30.13 | 6.76 | |
| Medium | 46 | 27.36 | 62.59 | 38.27 | 27.36 | 8.27 | |||
| Low | 40 | 24.05 | 63.64 | 42.8 | 24.05 | 9.42 | |||
| LMA | 136 | 24.05 | 63.64 | 41.42 | 24.05 | 8.38 | |||
| LONE_FAMILIES | Share of lone families to total family nuclei | High | 50 | 8.21 | 19.13 | 12.72 | 12.73 | 2.43 | |
| Medium | 46 | 5.67 | 21.46 | 11.16 | 5.67 | 3.33 | |||
| Low | 40 | 0 | 38.46 | 9.57 | 14.29 | 5.82 | |||
| LMA | 136 | 0 | 38.46 | 11.27 | 12.73 | 4.15 | |||
| Built Infrastucture | AV_RENT | Average dwelling monthly rent in Euros | High | 50 | 297.85 | 545.13 | 443.32 | 297.85 | 51.73 |
| Medium | 46 | 253 | 835.75 | 513.73 | 253 | 122.45 | |||
| Low | 33 | 350.38 | 880 | 592.51 | 350.38 | 135.8 | |||
| LMA | 129 | 253 | 880 | 506.59 | 253 | 119.96 | |||
| RENTED | Share of living quarters with rented tenure status | High | 50 | 4.6 | 46.35 | 25.75 | 4.6 | 9.56 | |
| Medium | 46 | 1.72 | 68.52 | 22.18 | 1.72 | 17.25 | |||
| Low | 35 | 0 | 52.14 | 11.01 | 0 | 9.79 | |||
| LMA | 131 | 0 | 68.52 | 20.56 | 0 | 14.08 | |||
| TB>200 | Share of living quarters with size over 200 m2 | High | 50 | 1.15 | 22.33 | 8.95 | 1.15 | 5.13 | |
| Medium | 46 | 0.35 | 49.77 | 17.48 | 0.35 | 14.18 | |||
| Low | 39 | 0 | 89.66 | 29.81 | 0 | 19.19 | |||
| LMA | 135 | 0 | 89.66 | 17.88 | 0 | 15.9 | |||
| TB_SH | Share of dwellings located in single-house buildings | High | 50 | 3.48 | 93.71 | 22.58 | 3.48 | 12.43 | |
| Medium | 46 | 2.56 | 84.58 | 32.51 | 2.56 | 19.39 | |||
| Low | 40 | 9.69 | 100 | 61.67 | 9.69 | 22.77 | |||
| LMA | 136 | 2.56 | 100 | 37.44 | 2.56 | 24.39 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | COMPUT_USE | High | 1 | 0.347 * | 0.544 ** | −0.024 | 0.27 | 0.116 | 0.661 ** | 0.295 * | −0.487 ** | −0.356 * | 0.806 ** | −0.019 | 0.556 ** | −0.338 * |
| Medium | 1 | 0.338 * | 0.709 ** | −0.123 | 0.018 | 0.15 | 0.662 ** | 0.531 ** | −0.562 ** | −0.614 ** | 0.680 ** | −0.125 | 0.748 ** | 0.253 | ||
| Low | 1 | 0.663 ** | 0.663 ** | −0.026 | −0.079 | 0.069 | 0.650 ** | 0.544 ** | −0.231 | −0.205 | 0.632 ** | −0.175 | 0.699 ** | 0.075 | ||
| LMA | 1 | 0.502 ** | 0.635 ** | −0.166 | 0.047 | 0.164 | 0.603 ** | 0.622 ** | −0.367 ** | −0.445 ** | 0.742 ** | −0.287 ** | 0.751 ** | 0.358 ** | ||
| 2 | INTERN_USE | High | 1 | 0.358 * | −0.166 | 0.26 | 0.429 ** | 0.272 | 0.261 | −0.211 | −0.105 | 0.526 ** | −0.232 | 0.441 ** | −0.024 | |
| Medium | 1 | 0.403 ** | 0.058 | 0.025 | 0.209 | 0.396 ** | 0.152 | −0.327 * | −0.253 | 0.408 ** | 0.06 | 0.376 * | 0.094 | |||
| Low | 1 | 0.640 ** | −0.164 | −0.022 | 0.340 * | 0.524 ** | 0.607 ** | 0.088 | −0.534 ** | 0.668 ** | −0.454 ** | 0.563 ** | 0.286 | |||
| LMA | 1 | 0.502 ** | −0.102 | 0.06 | 0.340 ** | 0.419 ** | 0.426 ** | −0.15 | −0.400 ** | 0.541 ** | −0.214 * | 0.486 ** | 0.252 ** | |||
| 3 | KIS | High | 1 | −0.304 * | 0.006 | 0.274 | 0.610 ** | 0.09 | 0.155 | −0.185 | 0.509 ** | −0.24 | 0.531 ** | −0.038 | ||
| Medium | 1 | −0.483 ** | −0.18 | 0.324 * | 0.507 ** | 0.624 ** | −0.155 | −0.656 ** | 0.491 ** | −0.444 ** | 0.813 ** | 0.354 * | ||||
| Low | 1 | −0.273 | −0.168 | 0.253 | 0.508 ** | 0.453 ** | 0.038 | −0.133 | 0.458 ** | −0.27 | 0.682 ** | 0.102 | ||||
| LMA | 1 | −0.382 ** | −0.124 | 0.287 ** | 0.525 ** | 0.453 ** | 0.005 | −0.314 ** | 0.475 ** | −0.356 ** | 0.651 ** | 0.223 ** | ||||
| 4 | NO_NATIVES | High | 1 | 0.319 * | −0.728 ** | 0.419 ** | −0.725 ** | −0.228 | 0.342 * | 0.134 | 0.931 ** | −0.188 | −0.438 ** | |||
| Medium | 1 | 0.623 ** | −0.644 ** | 0.433 ** | −0.784 ** | −0.390 ** | 0.417 ** | 0.209 | 0.918 ** | −0.364 * | −0.625 ** | |||||
| Low | 1 | 0.836 ** | −0.528 ** | 0.397 * | −0.485 ** | −0.341 * | −0.025 | 0.144 | 0.871 ** | −0.105 | −0.324 * | |||||
| LMA | 1 | 0.541 ** | −0.624 ** | 0.391 ** | −0.640 ** | −0.331 ** | 0.249 ** | 0.057 | 0.893 ** | −0.300 ** | −0.499 ** | |||||
| 5 | RECYCLED/100 INH | High | 1 | 0.079 | 0.421 ** | −0.145 | −0.208 | −0.036 | 0.358 * | 0.303 * | 0.227 | −0.166 | ||||
| Medium | 1 | −0.287 | 0.453 ** | −0.435 ** | −0.28 | 0.264 | 0.294 * | 0.540 ** | −0.079 | −0.401 ** | ||||||
| Low | 1 | −0.510 ** | 0.212 | −0.342 | −0.241 | −0.036 | 0.256 | 0.739 ** | −0.158 | −0.245 | ||||||
| LMA | 1 | −0.249 ** | 0.333 ** | −0.237 ** | −0.228 * | 0.031 | 0.277 ** | 0.429 ** | −0.042 | −0.172 | ||||||
| 6 | SOLAR_PV_USE | High | 1 | −0.244 | 0.648 ** | 0.088 | −0.269 | 0.003 | −0.646 ** | 0.157 | 0.361 * | |||||
| Medium | 1 | −0.251 | 0.578 ** | 0.166 | −0.274 | 0.044 | −0.578 ** | 0.321 * | 0.496 ** | |||||||
| Low | 1 | 0.006 | 0.359 * | 0.397 * | −0.048 | −0.04 | −0.644 ** | 0.139 | 0.356 * | |||||||
| LMA | 1 | −0.153 | 0.472 ** | 0.191 * | −0.195* | 0.062 | −0.573 ** | 0.229 ** | 0.377 ** | |||||||
| 7 | UNIV | High | 1 | −0.358 * | −0.138 | −0.049 | 0.714 ** | 0.416 ** | 0.535 ** | −0.376 ** | ||||||
| Medium | 1 | −0.106 | −0.549 ** | −0.271 | 0.759 ** | 0.345 * | 0.464 ** | −0.211 | ||||||||
| Low | 1 | 0.114 | −0.194 | −0.256 | 0.576 ** | 0.235 | 0.616 ** | 0.065 | ||||||||
| LMA | 1 | −0.013 | −0.320 ** | −0.226 ** | 0.637 ** | 0.245 ** | 0.465 ** | −0.105 | ||||||||
| 8 | HH_SIZE | High | 1 | −0.346 * | −0.525 ** | 0.032 | −0.717 ** | 0.203 | 0.331 * | |||||||
| Medium | 1 | −0.039 | −0.712 ** | 0.143 | −0.741 ** | 0.726 ** | 0.742 ** | |||||||||
| Low | 1 | 0.429 ** | −0.352 * | 0.335 | −0.719 ** | 0.518 ** | 0.571 ** | |||||||||
| LMA | 1 | 0.097 | −0.546 ** | 0.408 ** | −0.753 ** | 0.690 ** | 0.739 ** | |||||||||
| 9 | R_AGE_DEP | High | 1 | 0.248 | −0.402 ** | −0.155 | −0.103 | 0.256 | ||||||||
| Medium | 1 | 0.272 | −0.473 ** | −0.414 ** | −0.236 | 0.086 | ||||||||||
| Low | 1 | −0.057 | −0.193 | −0.556 ** | −0.158 | 0.382 * | ||||||||||
| LMA | 1 | 0.099 | −0.346 ** | −0.318 ** | −0.16 | 0.203 * | ||||||||||
| 10 | LONE_FAMILIES | High | 1 | −0.137 | 0.314 * | −0.206 | −0.18 | |||||||||
| Medium | 1 | −0.299 * | 0.411 ** | −0.681 ** | −0.568 ** | |||||||||||
| Low | 1 | −0.295 | 0.193 | −0.325 * | −0.289 | |||||||||||
| LMA | 1 | −0.436 ** | 0.468 ** | −0.502 ** | −0.446 ** | |||||||||||
| 11 | AV_RENT | High | 1 | 0.05 | 0.628 ** | −0.279 * | ||||||||||
| Medium | 1 | 0.013 | 0.648 ** | 0.058 | ||||||||||||
| Low | 1 | −0.093 | 0.697 ** | 0.15 | ||||||||||||
| LMA | 1 | −0.199 * | 0.757 ** | 0.342 ** | ||||||||||||
| 12 | RENTED | High | 1 | −0.227 | −0.470 ** | |||||||||||
| Medium | 1 | −0.429 ** | −0.675 ** | |||||||||||||
| Low | 1 | −0.282 | −0.570 ** | |||||||||||||
| LMA | 1 | −0.487 ** | −0.675 ** | |||||||||||||
| 13 | TB>200 | High | 1 | 0.248 | ||||||||||||
| Medium | 1 | 0.546 ** | ||||||||||||||
| Low | 1 | 0.372 * | ||||||||||||||
| LMA | 1 | 0.611 ** | ||||||||||||||
| 14 | TB_SH | High | 1 | |||||||||||||
| Medium | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Low | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| LMA | 1 |
| ALL STUDY AREA | GROUP_A | GROUP_B | GROUP_C | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Coverage | Medium Coverage | Low Coverage | |||||||||||
| Correlation Determinant | 0.000000226 | 0.000000118 | 0.0000000643 | 0.000000032 | |||||||||
| Rotation converged in iterations | 5 | 5 | 8 | 7 | |||||||||
| KMO | Meas. of samp. adeq. | 0.802 | 0.735 | 0.624 | 0.766 | ||||||||
| Bartlett’sTest of Sphericity | Approx. Chi-Square | 1721.817 | 454.735 | 521.641 | 681.619 | ||||||||
| df | 91 | 91 | 91 | 91 | |||||||||
| Sig. | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |||||||||
| Rotation Sums of Sq. Loadings | Total | 3.773 | 3.657 | 3.182 | 4.937 | 3.646 | 1.938 | 3.737 | 3.484 | 3.140 | 4.764 | 3.948 | 2.279 |
| % of Variance | 26.948 | 26.125 | 22.732 | 35.265 | 26.045 | 13.841 | 26.696 | 24.882 | 22.428 | 34.03 | 28.2 | 16.28 | |
| Cumulative % | 26.948 | 53.073 | 75.805 | 35.265 | 61.310 | 75.151 | 26.696 | 51.578 | 74.006 | 34.03 | 62.23 | 78.52 | |
| Cronbach’s Alpha coefficients | 0.874 | 0.878 | 0.882 | 0.888 | |||||||||
| Thematic Domain | Variable | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 |
| Human smart characteristics | COMPUT_USE | 0.712 | 0.568 | 0.848 | −0.325 | 0.690 | 0.583 | 0.914 | |||||
| INTERN_USE | 0.738 | 0.374 | 0.744 | 0.783 | 0.383 | ||||||||
| KIS | 0.840 | 0.373 | 0.707 | 0.471 | 0.348 | 0.393 | 0.656 | 0.838 | |||||
| NO_NATIVES | −0.461 | 0.839 | −0.967 | −0.957 | 0.763 | −0.578 | |||||||
| RECYCLED/100 | 0.671 | −0.530 | 0.504 | −0.439 | 0.464 | 0.479 | −0.680 | ||||||
| SOLAR_PV_USE | −0.702 | 0.890 | 0.763 | 0.319 | 0.850 | ||||||||
| UNIV | 0.841 | 0.415 | −0.408 | 0.834 | −0.373 | 0.371 | 0.740 | 0.828 | 0.386 | ||||
| Demographic dynamics | HH_SIZE | 0.842 | −0.374 | 0.874 | −0.385 | 0.650 | 0.649 | 0.461 | −0.760 | 0.306 | |||
| R_AGE_DEPEND | −0.359 | −0.651 | 0.910 | 0.360 | −0.663 | −0.352 | −0.522 | 0.347 | |||||
| LONE_FAMILIES | −0.327 | −0.761 | −0.455 | −0.845 | −0.455 | 0.668 | |||||||
| Built Infrastucture | AV_RENT | 0.745 | 0.447 | 0.900 | 0.528 | 0.756 | 0.818 | ||||||
| RENTED | −0.586 | 0.718 | −0.934 | −0.913 | 0.833 | −0.441 | |||||||
| TB > 200 | 0.660 | 0.653 | 0.350 | 0.757 | 0.707 | 0.423 | 0.855 | ||||||
| TB_SH | 0.793 | −0.304 | 0.656 | −0.402 | 0.385 | 0.556 | 0.580 | −0.828 | |||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alverti, M.N.; Themistocleous, K.; Kyriakidis, P.C.; Hadjimitsis, D.G. A Study of the Interaction of Human Smart Characteristics with Demographic Dynamics and Built Environment: The Case of Limassol, Cyprus. Smart Cities 2020, 3, 48-73. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities3010004
Alverti MN, Themistocleous K, Kyriakidis PC, Hadjimitsis DG. A Study of the Interaction of Human Smart Characteristics with Demographic Dynamics and Built Environment: The Case of Limassol, Cyprus. Smart Cities. 2020; 3(1):48-73. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities3010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlverti, Maroula N., Kyriakos Themistocleous, Phaedon C. Kyriakidis, and Diofantos G. Hadjimitsis. 2020. "A Study of the Interaction of Human Smart Characteristics with Demographic Dynamics and Built Environment: The Case of Limassol, Cyprus" Smart Cities 3, no. 1: 48-73. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities3010004
APA StyleAlverti, M. N., Themistocleous, K., Kyriakidis, P. C., & Hadjimitsis, D. G. (2020). A Study of the Interaction of Human Smart Characteristics with Demographic Dynamics and Built Environment: The Case of Limassol, Cyprus. Smart Cities, 3(1), 48-73. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities3010004