Stratum Corneum Structure and Function Studied by X-ray Diffraction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Structural Study on the Stratum Corneum by X-ray Diffraction
2.1. What Can We Get from the X-ray Diffraction Experiments on the Stratum Corneum?
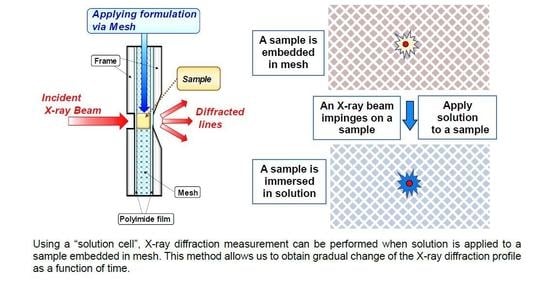
2.2. Principle of X-ray Diffraction Experiments: With Attention to the Structures That Appear in the Stratum Corneum
2.3. Structural Study by X-ray Diffraction to the Further Analysis of the Long-Period Lamellar Structure
2.4. X-ray Diffraction Studies on Short-Period Lamellar Structure, Soft Keratin, and Ordered Hydrocarbon-Chain Packing Structures
3. Disruption and Reconstruction of Long-Period Lamellar Structure in Stratum Corneum
3.1. Disruption of Human Stratum Corneum Lipid Structure by Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate
3.2. Reconstruction of Damaged Long-Period Lamellar Structure
4. Water Retention and Moisturizing in Stratum Corneum
4.1. Key Water Content 25 wt% in Stratum Corneum
4.2. Working Principle of Glycerol in Stratum Corneum as Moisturizer
5. Liquid State in Intercellular Lipid Matrix Underlying the 500 Da Rule
6. Summary
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elias, P.M. Epidermal lipids, barrier function and desquamation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1983, 80, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspers, P.J.; Lucassen, G.W.; Carter, E.A.; Bruining, H.A.; Puppels, G.J. In Vivo Confocal Raman Microspectroscopy of the Skin: Noninvasive Determination of Molecular Concentration Profiles. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 116, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowther, J.M.; Sieg, A.; Blenkiron, P.; Marcott, C.; Matts, P.J.; Kaczvinsky, J.R.; Rawlings, A.V. Measuring the effects of topical moisturizers on changes in stratum corneum thickness, water gradients and hydration in vivo. Brit. J. Dermatol. 2008, 159, 567–577. [Google Scholar]
- Egawa, M.; Kajikawa, T. Changes in the depth profile of water in the stratum corneum treated with water. Skin Res. Technol. 2009, 15, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; de Graaff, A.; Gert, S.; Gooris, G.S.; Nijsse, J.; Wiechers, J.W.; van Aelstz, A.C. Water Distribution and Related Morphology in Human Stratum Corneum at Different Hydration Levels. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, C.R. The stratum corneum: Structure and function in health and disease. Dermatol. Therapy 2014, 17, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalambopoulou, G.C.; Steriotis, T.A.; Hauss, T.; Stubos, A.K.; Kanellopoulos, N.K. Structural alterations of fully hydrated human stratum corneum. Physica 2004, 350, e603–e606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartzendruber, D.C.; Wertz, P.W.; Kitko, D.J.; Madison, K.C.; Downing, D.T. Molecular models of the intercellular lipid lamellae in mammalian stratum corneum. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1989, 92, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, I.; Han, H.; den Hollander, L.; Svensson, S.; Ofverstedt, L.G.; Anwar, J.; Brewer, J.; Bloksgaard, M.; Laloeuf, A.; Nosek, D.; et al. The human skin barrier Is organized as stacked bilayers of fully extended ceramides with cholesterol molecules associated with the ceramide sphingoid moiety. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 2215–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.H.; Mirejovsky, D.; King, G.I. Structure of lamellar lipid domains and corneocyte envelopes of murine stratum corneum. An X-ray diffraction study. Biochemistry 1988, 27, 3725–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Gooris, G.S.; van der Spek, J.A.; Bras, W. Structural Investigations of Human Stratum Corneum by Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 97, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohta, N.; Ban, S.; Tanaka, H.; Nakata, S.; Hatta, I. Swelling of intercellular lipid lamellar structure with short repeat distance in hairless mouse stratum corneum as studied by X-ray diffraction. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2003, 123, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, D.; Gooris, G.S.; Bouwstra, J.A. New Insights into the Stratum Corneum Lipid Organization by X-Ray Diffraction Analysis. Biophys. J. 2009, 97, 2242–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Gooris, G.S.; van der Spek, J.A.; Lavrijsen, S.; Bras, W. The lipid and protein structure of mouse stratum corneum: A wide and small angle diffraction study. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1212, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilgram, G.S.K.; van Pelt, A.M.; Spies, F.; Bouwstra, J.A.; Koerten, H.K. Cryo-electron diffraction as a tool to study local variations in the lipid organization of human stratum corneum. J. Microsc. 1988, 189, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucet, J.; Potter, A.; Baltenneck, C.; Domanov, Y.A. Micron-scale assessment of molecular lipid organization in human stratum corneum using microprobe X-ray diffraction. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatta, I.; Ohta, N.; Nakazawa, H. A Possible Percutaneous Penetration Pathway That Should Be Considered. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatta, I.; Nakazawa, H.; Ohta, N.; Uchino, T.; Yanase, K. Stratum Corneum Function: A Structural Study with Dynamic Synchrotron X-ray Diffraction Experiments. J. Oleo Sci. 2021, 70, 1181–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Gooris, G.S.; Salomons-de Vries, M.A.; van der Spek, J.A.; Bras, W. Structure of human stratum corneum as a function of temperature and hydration: A wide-angle X-ray diffraction study. Int. J. Pharm. 1992, 84, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatta, I.; Ohta, N.; Inoue, K.; Yagi, N. Coexistence of two domains in intercellular lipid matrix of stratum corneum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1758, 1830–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilgram, G.S.K.; Engelsma-van Pelt, A.M.; Bouwstra, J.A.; Koerten, H.K. Electron Diffraction Provides New Information on Human Stratum Corneum Lipid Organization Studied in Relation to Depth and Temperature. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 113, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakazawa, H.; Imai, T.; Hatta, I.; Sakai, S.; Inoue, S.; Kato, S. Low-flux electron diffraction study for the intercellular lipid organization on a human corneocyte. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1828, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damien, F.; Boncheva, M. The Extent of Orthorhombic Lipid Phases in the Stratum Corneum Determines the Barrier Efficiency of Human Skin In Vivo. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Smeden, J.; Boiten, W.A.; Hankemeier, T.; Rissmann, R.; Bouwstra, J.A.; Vreeken, R.J. Combined LC/MS-platform for analysis of all major stratum corneum lipids, and the profiling of skin substitutes. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masukawa, Y.; Narita, H.; Sato, H.; Naoe, A.; Kondo, N.; Sugai, Y.; Oba, T.; Homma, R.; Ishikawa, J.; Takagi, Y.; et al. Comprehensive quantification of ceramide species in human stratum corneum. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1708–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, B.M. Crystal structure of cholesterol monohydrate. Nature 1976, 260, 727–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojumdar, E.H.; Gooris, G.S.; Groen, D.; Barlow, D.J.; Lawrence, M.J.; Demé, B.; Bouwstra, J.A. Stratum corneum lipid matrix: Location of acyl ceramide and cholesterol in the unit cell of the long periodicity phase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1858, 1926–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokura, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Tokuda, H.; Imokawa, G. Molecular Analysis of Elastic Properties of the Stratum Corneum by Solid-State 13C-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1995, 104, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojumdar, E.H.; Pham, Q.D.; Topgaard, D.; Sparr, E. Skin hydration: Interplay between molecular dynamics, structure and water uptake in the stratum corneum. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garson, J.-C.; Doucet, J.; Lévêque, J.-L.; Tsoucaris, G. Oriented Structure in Human Stratum Corneum Revealed by X-Ray Diffraction. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 96, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, G.L.; Nguyen, A.-L.; Wildnauer, R. Structure-Property relations of human neonatal rat stratum corneum I. Thermal stability of the crystalline lipid structure, as studied by X-ray diffraction and differential thermal analysis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1973, 304, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Habuka, A.; Hatta, I. Moisturizing mechanism of glycerol and diglycerol on human stratum corneum studied by synchrotron X-ray diffraction. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2021, 43, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornwell, P.A.; Barry, B.W.; Stoddart, C.P.; Bouwstra, J.A. Wide-angle X-ray Diffraction of Human Stratum Corneum: Effects of Hydration and Terpene Enhancer Treatment. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1994, 46, 938–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreplak, L.; Doucet, J.; Briki, F. Unraveling Double Stranded α-Helical Coiled Coils: An X-ray Diffraction Study on Hard α-Keratin Fibers. Biopolymers 2001, 58, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, M.J.; Taylor, D.J.; Derbyshire, W. Water Sorption by Human Callus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1978, 540, 518–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, H.; Ohta, N.; Hatta, I. A possible regulation mechanism of water content in human stratum corneum via intercellular lipid matrix. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2012, 165, 2238–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalambopoulou, G.C.; Karamertzanis, P.; Kikkinides, E.S.; Stubos, A.K.; Kanellopoulos, N.K.; Papaioannou, A.T. A Study on Structural and Diffusion Properties of Porcine Stratum Corneum Based on Very Small Angle Neutron Scattering Data. Pharm. Res. 2000, 17, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, N.; Aoyama, K.; Ohta, N. Microbeam X-ray diffraction study of lipid structure in stratum corneum of human skin. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, G.W. X-ray diffraction in water: The nature of Molecular Association. Phys. Rev. 1931, 37, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribaud, C.; Garson, J.-C.; Doucet, J.; Lévêque, J.-L. Organization of Stratum Corneum Lipids in Relation to Permeability: Influence of Sodium Lauryl Sulfate and Preheating. Pharm. Res. 1994, 11, 1414–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paepe, K.; Roseeuw, D.; Rogiers, V. Repair of acetone- and sodium lauryl sulphate-damaged human skin barrier function using topically applied emulsions containing barrier lipids. J. Europ. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2002, 16, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, Y.K. X-ray Diffraction Studies of Membranes. Progr. Surf. Sci. 1973, 3, 279–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. Communication in the Presence of Noise. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 447–457, The same paper is reprinted from Proc. IRE 1949, 37, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayre, D. Some implications of a theorem due to Shannon. Acta Crystallogr. 1952, 5, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, T.J. Organization of Skin Stratum Corneum Extracellular Lamellae: Diffraction Evidence for Asymmetric Distribution of Cholesterol. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, T. A new method for determining the phase in the X-ray diffraction structure analysis of phosphatidylcholine/alcohol. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2000, 107, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Ohta, N.; Hatta, I. X-ray diffraction study on interdigitated structure of phosphatidylcholines in glycerol. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2001, 112, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.C.; Barry, B.W. Penetration enhancers. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatta, I.; Nakazawa, H.; Obata, Y.; Ohta, N.; Inoue, K.; Yagi, N. Novel method to observe subtle structural modulation of stratum corneum on applying chemical agents. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2010, 163, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Uchino, T.; Hatta, I.; Miyazaki, Y.; Kato, S.; Sasaki, K.; Kagawa, Y. Evaluation of the molecular lipid organization in millimeter-sized stratum corneum by synchrotron X-ray diffraction. Skin Res. Technol. 2018, 24, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, R.D.B.; MacRae, T.P.; Miller, A.; Suzuki, E. The Quantitative Analysis of Fibril Packing from Electron Micrographs. J. Mol. Biol. 1964, 9, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, R.D.B.; MacRae, T.P.; Miller, A. The Coiled-coil Model of α-Keratin Structure. J. Mol. Biol. 1964, 10, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yang, W.; McKittrick, J.; Meyers, M.A. Keratin: Structure, mechanical properties, occurrence in biological organisms, and efforts at bioinspiration. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 76, 229–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horita, D.; Hatta, I.; Yoshimoto, M.; Kitao, Y.; Todo, H.; Sugibayashi, K. Molecular mechanisms of action of different concentrations of ethanol in water on ordered structures of intercellular lipids and soft keratin in the stratum corneum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1848, 1196–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denda, M.; Koyama, J.; Namba, R.; Horii, I. Stratum corneum lipid morphology and transepidermal water loss in normal skin and surfactant-induced scaly skin. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1994, 286, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.M.; Singh, P.; Maibach, H.I. Cumulative irritancy in man to sodium lauryl sulfate: The overlap phenomenon. Int. J. Pharm. 1994, 110, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imokawa, G.; Akasaki, S.; Minematsu, Y.; Kawai, M. Importance of intercellular lipids in water retention properties of the stratum corneum: Induction and recovery study of surfactant dry skin. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1989, 281, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froebe, C.L.; Simion, F.A.; Rhein, L.D.; Cagan, R.H.; Kligman, A. Stratum corneum lipid removal by surfactants: Relation to in vivo irritation. Dermatologica 1990, 181, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Maza, A.; Coderch, L.; Lopez, O.; Baucells, J.; Parra, J.L. Permeability changes caused by surfactants in liposomes that model the stratum corneum lipid composition. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1997, 74, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, G.; Flach, C.R.; Mendelsohn, R.; Walters, R.M. Imaging the distribution of sodium dodecyl sulfate in skin by confocal Ra-man and infrared microspectroscopy. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 2189–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhein, L.D.; Robbins, C.R.; Kernee, K.; Cantore, R. Surfactant structure effects on swelling of isolated human stratum corneum. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 1986, 37, 125–139. [Google Scholar]
- Warner, R.R.; Boissy, Y.L.; Lilly, N.A.; Spears, M.J.; McKillop, K.; Marshall, J.L.; Stone, K.J. Water disrupts stratum corneum lipid lamellae: Damage is similar to surfactants. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 113, 960–966. [Google Scholar]
- Ananthapadmanabhan, K.P.; Lips, A.; Vincent, C.; Meyer, F.; Caso, S.; Johnson, A.; Subramanyan, K.; Vethamuthu, M.; Rattinger, G.; Moore, D.J. pH-induced alterations in stratum corneum properties. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2003, 25, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.J.; Zhou, X.J.; Sun, G.Q.; Zhang, Y. Morphological alterations of stratum corneum lipids induced by sodium lauryl sulfate treatment in hairless mice. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2003, 32, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanase, K.; Hatta, I. Disruption of human stratum corneum lipid structure by sodium dodecyl sulphate. Intern. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2018, 40, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanase, K.; Hatta, I. Disruption of human stratum corneum lipid structure by sodium dodecyl sulfate. SPring-8 Res. Front. 2017, 2018, 90–91. [Google Scholar]
- Moghadam, S.H.; Saliaj, E.; Wettig, S.D.; Dong, C.; Ivanova, M.V.; Huzil, J.T.; Foldvari, M. Effect of Chemical Permeation Enhancers on Stratum Corneum Barrier Lipid Organizational Structure and Interferon Alpha Permeability. Mol. Phram. 2013, 10, 2248–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, D.T.; Abraham, W.; Wegner, B.K.; Willman, K.W.; Marshall, J.L. Partition of sodium dodecyl sulfate into stratum corneum lipid liposomes. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1993, 285, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Dubbelaar, F.E.R.; Gooris, G.S.; Ponec, M. The lipid organization in the skin barrier. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2000, 208, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Gooris, G.S.; Dubbelaar, F.E.R.; Ponec, M. Phase behavior of stratum corneum lipid mixtures based on human ceramides: The role of natural and synthetic ceramide-1. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 118, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuemple, D.; Swartzendruber, D.C.; Squier, C.A.; Wertz, P.W. In vitro reconstitution of stratum corneum lipid lamellae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1988, 1372, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, S.; Monti, M.; Sesana, S.; Caputo, R.; Carelli, S.; Ghidoni, R. Ceramide composition of the psoriatic scale. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1993, 1182, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrijsen, A.P.; Bouwstra, J.A.; Gooris, G.S.; Weerheim, A.; Boddé, H.E.; Ponec, M. Reduced skin barrier function parallels abnormal stratum corneum lipid organization in patients with lamellar ichthyosis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1995, 105, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paige, D.G.; Morse-Fisher, N.; Harper, J.I. Quantification of stratum corneum ceramides and lipid envelope ceramides in the hereditary ichthyoses. Br. J. Dermatol. 1994, 131, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, S.; Monti, M.; Sesana, S.; Mellesi, L.; Ghidoni, R.; Caputo, R. Abnormality of water barrier function in psoriasis. Role of ceramide fractions. Arch. Dermatol. 1994, 130, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farwanah, H.; Raith, K.; Neubert, R.H.; Wohlrab, J. Ceramide profiles of the uninvolved skin in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis are comparable to those of healthy skin. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2005, 296, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Smeden, J.; Janssens, M.; Boiten, W.A.; van Drongelen, V.; Furio, L.; Vreeken, R.J.; Hovnanian, A.; Bouwstra, J.A. Intercellular skin barrier lipid composition and organization in Netherton syndrome patients. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imokawa, G.; Abe, A.; Jin, K.; Higaki, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Hidano, A. Decreased level of ceramides in stratum corneum of atopic dermatitis: An etiologic factor in atopic dry skin? J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 96, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.; Harding, C.; Mayo, A.; Banks, J.; Rawlings, A. Stratum corneum lipids: The effect of ageing and the seasons. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1996, 288, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, J.; Shimotoyodome, Y.; Ito, S.; Miyauchi, Y.; Fujimura, T.; Kitahara, T.; Hase, T. Variations in the ceramide profile in different seasons and regions of the body contribute to stratum corneum functions. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2013, 305, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, V.; Gooris, G.S.; Pfeiffer, S.; Lanzendörfer, G.; Wenck, H.; Diembeck, W.; Proksch, E.; Bouwstra, J.A. Barrier characteristics of different human skin types investigated with X-ray diffraction, lipid analysis, and electron microscopy imaging. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 114, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Ponec, M. The skin barrier in healthy and diseased state. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1758, 2080–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jager, M.; Gooris, G.; Ponec, M.; Bouwstra, J. Acylceramide Head Group Architecture Affects Lipid Organization in Synthetic Ceramide Mixtures. J. Investig. Deramtol. 2004, 123, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jager, M.W.; Gooris, G.S.; Ponec, M.; Bouwstra, J.A. Lipid mixtures prepared with well-defined synthetic ceramides closely mimic the unique stratum corneum lipid phase behavior. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 2649–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, D.; Gooris, G.S.; Bouwstra, J.A. Model Membranes Prepared with Ceramide EOS, Cholesterol and Free Fatty Acids Form a Unique Lamellar Phase. Langmuir 2010, 26, 4168–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaune-Iijima, A.; Sugishima, A.; Omura, G.; Kitaoka, H.; Tashiro, T.; Kageyama, S.; Hatta, I. Topical treatments with acylceramide dispersions restored stratum corneum lipid lamellar structures in a reconstructed human epidermis model. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2018, 215, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartzendruber, D.C.; Burnett, I.H.; Wertz, P.W.; Madison, K.C.; Squier, C.A. Osmium tetroxide and ruthenium tetroxide are complementary reagents for the preparation of epidermal samples for transmission electron microscopy. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1995, 104, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatta, I.; Ohta, N.; Ban, S.; Tanaka, H.; Nakata, S. X-ray diffraction study on ordered, disordered and reconstituted intercellular lipid lamellar structure in stratum corneum. Biophys. Chem. 2001, 89, 239–242. [Google Scholar]
- Walkley, K. Bound water in stratum corneum measured by differential scanning calorimetry. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1972, 59, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imokawa, G.; Kuno, H.; Kawai, M. Stratum corneum lipids serve as a bound-water modulator. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 96, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, C.S.; Schleusener, J.; Lademann, J.; Darvin, M.E. Keratin-water-NMF interaction as a three layer model in the human stratum corneum using in vivo confocal Raman microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, A.V.; Harding, C.R.; Watkinson, A.; Chandar, P.; Scott, I.R. Humectant. In Skin Moisturization; Leyden, J.J., Rawlings, A.V., Eds.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 245–266. [Google Scholar]
- Fowler, J. Understanding the role of natural moisturizing factor in skin hydration. Pract. Dermatol. 2012, 9, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Vonk, C. Computerization of Ruland’s X-ray method for determination of the crystallinity in polymers. J. Appl. Cryst. 1973, 6, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björklund, S.; Nowacka, A.; Bouwstra, J.A.; Sparr, E.; Topgaard, D. Characterization of stratum corneum molecular dynamics by natural abundance 13C Solid-State NMR. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrams, K.; Harvell, J.D.; Shriner, D.; Wertz, P.; Maibach, H.; Maibach, H.I.; Rehfeld, S.J. Effect of organic solvents on in vitro human skin water barrier function. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1993, 101, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, L.B.; Friberg, S.E.; Wahlberg, J.E. The effect of solvent extraction on lipids of the stratum corneum in relation to observed immediate whitening of the skin. Contact Dermititis 1988, 19, 348–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bommannan, D.; Potts, R.O.; Guy, R.H. Examination of the effect of ethanol on human stratum corneum in vivo using infrared spectroscopy. J. Control. Res. 1991, 16, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Merwe, D.; Riviere, J.E. Comparative studies on the effects of water, ethanol and water/ethanol mixtures on chemical partitioning into porcine stratum corneum and silastic membrane. Tox. In Vitro 2005, 19, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, J.D.; Meldardi, M.M.H.M. The 500 Dalton rule for the skin penetration of chemical compounds and drugs. Exp. Dermatol. 2000, 9, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.W.; Mekenyan, O.G.; Dimitrov, S.D.; Dimitrova, G.D. What determined sensitization potencymyths, maybe and realities. Part 1. The 500 molecular weight cut-off. Contact Derm. 2012, 68, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, R.O.; Guy, R.H. Predicting skin permeability. Pharm. Res. 1992, 9, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertz, P.W. The nature of the epidermal barrier: Biochemical aspects. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1996, 18, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paepe, K.; Rogiers, V. Analytical techniques for skin lipids. In Cosmetic Lipids and the Skin Barrier; Förster, T., Ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 149–183. [Google Scholar]
- Wertz, P.W. Biochemistry of human stratum corneum lipids. In Skin Barrier; Elias, P., Feingolded, K., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wertz, P.; Norlén, L. “Confidence intervals” for the “true” lipid composition of the human skin barrier? In Skin, Hair and Nails, Structure and Function; Forslind, B., Lindberg, M., Eds.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 85–106. [Google Scholar]
















| Measurable Sample | Distribution or Localization of Water | What Is Observed | Spatial Resolution or Structure at the Molecular Level | Reference Number When the Methods Appear in Text | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X-ray Diffraction * | ex vivo | water storage and regulation | changes of lamellar, lateral hydrocarbon-chain packing and keratin structures | molecular arrangement | 10, 11, 12, 49, etc. |
| ATR-FTIR | in vivo | hard to obtain direct evidence | change of hydrocarbon-chain packing structure near skin surface | clear separation of hexagonal and orthorhombic spectra | 23, 101 |
| Confocal Raman Microscopy | in vivo | acquiring spectrum of water in skin depth direction | distribution of water, NMF, etc., in depth direction | ca. 3 μm | 2, 3, 4, 60, 91 |
| TEWL | in vivo | leakage of water through skin damage | relative variation in skin condition to external changes | ca. 1 cm intervals on skin surface | 23, 41 |
| Electrical Conductance or Capacitance Measurements | in vivo | water-holding capacity within skin | relative variation of water content in skin | ca. 1 cm intervals on skin surface | 41 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hatta, I. Stratum Corneum Structure and Function Studied by X-ray Diffraction. Dermato 2022, 2, 79-108. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato2030009
Hatta I. Stratum Corneum Structure and Function Studied by X-ray Diffraction. Dermato. 2022; 2(3):79-108. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato2030009
Chicago/Turabian StyleHatta, Ichiro. 2022. "Stratum Corneum Structure and Function Studied by X-ray Diffraction" Dermato 2, no. 3: 79-108. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato2030009
APA StyleHatta, I. (2022). Stratum Corneum Structure and Function Studied by X-ray Diffraction. Dermato, 2(3), 79-108. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermato2030009