Microfiber Contamination in Potable Water: Detection and Mitigation Using a Filtering Device
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
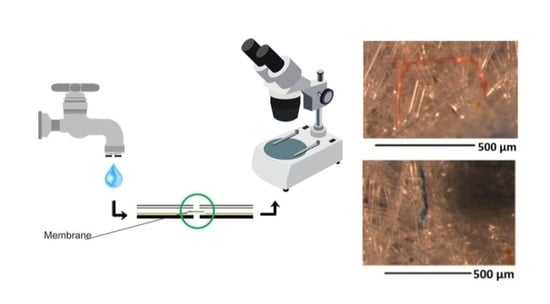
2.1. Filtration Device
2.2. Sampling Method
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Browne, M.A.; Crump, P.; Niven, S.J.; Teuten, E.; Tonkin, A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Accumulation of Microplastic on Shorelines Woldwide: Sources and Sinks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9175–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Vidal, A.; Thompson, R.C.; Canals, M.; de Haan, W.P. The imprint of microfibres in southern European deep seas. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Villiers, S. Microfibre pollution hotspots in river sediments adjacent to South Africa’s coastline. Water SA 2019, 45, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Rocher, V.; Tassin, B. Synthetic and non-synthetic anthropogenic fibers in a river under the impact of Paris Megacity: Sampling methodological aspects and flux estimations. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palazzo, L.; Coppa, S.; Camedda, A.; Cocca, M.; De Falco, F.; Vianello, A.; Massaro, G.; de Lucia, G.A. A novel approach based on multiple fish species and water column compartments in assessing vertical microlitter distribution and composition. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 116419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosuth, M.; Mason, S.A.; Wattenberg, E.V. Anthropogenic contamination of tap water, beer, and sea salt. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniggendorf, A.K.; Wetzel, C.; Roth, B. Microplastics detection in streaming tap water with raman spectroscopy. Sensors 2019, 19, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mason, S.A.; Welch, V.G.; Neratko, J. Synthetic Polymer Contamination in Bottled Water. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liebezeit, G.; Liebezeit, E. Synthetic particles as contaminants in German beers. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2014, 31, 1574–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iñiguez, M.E.; Conesa, J.A.; Fullana, A. Microplastics in Spanish Table Salt. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Shi, H.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Jabeen, K.; Kolandhasamy, P. Microplastic Pollution in Table Salts from China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 13622–13627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, A.; Golieskardi, A.; Keong Choo, C.; Larat, V.; Galloway, T.S.; Salamatinia, B. The presence of microplastics in commercial salts from different countries. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eerkes-Medrano, D.; Leslie, H.A.; Quinn, B. Microplastics in drinking water: A review and assessment. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Heal. 2019, 7, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santonicola, S.; Volgare, M.; Di Pace, E.; Cocca, M.; Mercogliano, R.; Colavita, G. Occurrence of potential plastic microfibers in mussels and anchovies sold for human consumption: Preliminary results. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2021, 10, 9962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebezeit, G.; Liebezeit, E. Non-pollen particulates in honey and sugar. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 2136–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.; Friot, D. Primary Microplastics in the Oceans: A Global Evaluation of Sources; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2017; p. 43. [Google Scholar]
- Volgare, M.; De Falco, F.; Avolio, R.; Castaldo, R.; Errico, M.E.; Gentile, G.; Ambrogi, V.; Cocca, M. Washing load influences the microplastic release from polyester fabrics by affecting wettability and mechanical stress. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, F.; Pace, E.; Cocca, M.; Avella, M. The contribution of washing processes of synthetic clothes to microplastic pollution. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, F.; Gullo, M.P.; Gentile, G.; Di Pace, E.; Cocca, M.; Gelabert, L.; Brouta-Agnésa, M.; Rovira, A.; Escudero, R.; Villalba, R.; et al. Evaluation of microplastic release caused by textile washing processes of synthetic fabrics. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarfl, C. Promising techniques and open challenges for microplastic identification and quantification in environmental matrices. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 3743–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, S.; Tacconi, S.; Fidaleo, M.; Rossi, M.; Dini, L. Micro and Nanoplastics Identification: Classic Methods and Innovative Detection Techniques. Front. Toxicol. 2021, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the Marine Environment: A Review of the Methods Used for Identification and Quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J. Handbook of Textile Design; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allievo, T. Le Fibre Tessili Di Applicazione Industriale; Degli, A.T., Ed.; Tipografia degli Artigianelli: Torino, Italy, 1908. [Google Scholar]
- Quaglierini, C. Chimica Delle Fibre Tessili; Zanichelli: Bologna, Italy, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Preferred Fiber & Materials Market Report 2020 Welcome to the 2020 Preferred Fiber & Materials Market Report. Available online: https://textileexchange.org/2020-preferred-fiber-and-materials-market-report-pfmr-released-2/ (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Rocher, V.; Mohamed, S.; Tassin, B. Microplastic contamination in an urban area: A case study in Greater Paris. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Mirande, C.; Mandin, C.; Guerrouache, M.; Langlois, V.; Tassin, B. A first overview of textile fibers, including microplastics, in indoor and outdoor environments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mintenig, S.M.; Löder, M.G.J.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Low numbers of microplastics detected in drinking water from ground water sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIlwraith, H.; Lin, J.; Erdle, L.; Mallos, N.; Diamond, M.; Rochman, C. Capturing microfibers—marketed technologies reduce microfiber emissions from washing machines. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 139, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Ros, M.; Johnston, E.L. Pore-size and polymer affect the ability of filters for washing-machines to reduce domestic emissions of fibres to sewage. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napper, I.E.; Barrett, A.C.; Thompson, R.C. The efficiency of devices intended to reduce microfibre release during clothes washing. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 140412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, F.; Di Pace, E.; Avella, M.; Gentile, G.; Errico, M.E.; Krzan, A.; ElKhiar, H.; Zupan, M.; Cocca, M. Development and Performance Evaluation of a Filtration System for Washing Machines to Reduce Microfiber Release in Wastewater. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivokonsky, M.; Cermakova, L.; Novotna, K.; Peer, P.; Cajthaml, T.; Janda, V. Occurrence of microplastics in raw and treated drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesa, F.S.; Turra, A.; Checon, H.H.; Leonardi, B.; Baruque-Ramos, J. Laundering and textile parameters influence fibers release in household washings. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, M.C.; Pawlak, J.J.; Daystar, J.; Ankeny, M.; Cheng, J.J.; Venditti, R.A. Microfibers generated from the laundering of cotton, rayon and polyester based fabrics and their aquatic biodegradation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.; Webb, H.; Lindeque, P.K.; Fileman, E.S.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Isolation of microplastics in biota-rich seawater samples and marine organisms. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cózar, A.; Echevarría, F.; González-Gordillo, J.I.; Irigoien, X.; Úbeda, B.; Hernández-León, S.; Palma, Á.T.; Navarro, S.; García-de-Lomas, J.; Ruiz, A.; et al. Plastic debris in the open ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10239–10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Faure, F.; Saini, C.; Potter, G.; Galgani, F.; de Alencastro, L.F.; Hagmann, P. An evaluation of surface micro- and mesoplastic pollution in pelagic ecosystems of the Western Mediterranean Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 12190–12197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, R.; Mason, S.A.; Stanek, S.K.; Willis-Norton, E.; Wren, I.F.; Box, C. Microplastic contamination in the San Francisco Bay, California, USA. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmau-Soler, J.; Ballesteros-Cano, R.; Boleda, M.R.; Paraira, M.; Ferrer, N.; Lacorte, S. Microplastics from headwaters to tap water: Occurrence and removal in a drinking water treatment plant in Barcelona Metropolitan area (Catalonia, NE Spain). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 59462–59472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adib, D.; Mafigholami, R.; Tabeshkia, H.; Walker, T.R. Optimization of polypropylene microplastics removal using conventional coagulants in drinking water treatment plants via response surface methodology. J Environ Heal Sci Eng. 2022, 20, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sol, D.; Laca, A.; Laca, A.; Díaz, M. Microplastics in wastewater and drinking water treatment plants: Occurrence and removal of microfibres. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Paul Chen, J. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review on occurrence, environmental effects, and methods for microplastics detection. Water Res. 2018, 137, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. The plastic in microplastics: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J. Additives for Plastics Handbook, 2nd ed.; Elsevier B.V.: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA; Tokyo, Japan, 2001; pp. 30–60. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, S.; Sinclair, C.; Boxall, A. Occurrence, degradation, and effect of polymer-based materials in the environment. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Whitacre, D.M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 227, pp. 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talsness, C.E.; Andrade, A.J.M.; Kuriyama, S.N.; Taylor, J.A.; Saal, F.S.V. Components of plastic: Experimental studies in animals and relevance for human health. Philos. Trans. R Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2079–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Triebskorn, R.; Braunbeck, T.; Grummt, T.; Hanslik, L.; Huppertsberg, S.; Jekel, M.; Knepper, T.P.; Krais, S.; Müller, Y.K.; Pittroff, M.; et al. Relevance of nano- and microplastics for freshwater ecosystems: A critical review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 375–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrigno, S.; Guadagnini, R.; Tyrell, K. Is Cotton Conquering Its Chemical Addiction; Pesticide Action Network: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Directive (EU) 2020/2184 of the European Parlliament and of the Council of 16 December 2020 on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption; Official Journal of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2020; pp. 1–62. [Google Scholar]








| Sample | Location | Microfibers (N) | Microfibers (N/L) | Min. Length (μm) | Max. Length (μm) | Mean Length (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pot na Brido, Ankaran, Slovenia | 16 | 0.8 | 242 | 1576 | 638 |
| 2 | Bosamarin 21, Koper | 3 | 0.15 | 356 | 4908 | 2033 |
| 3 | Bosamarin 12, Koper | 28 | 1.4 | 120 | 4021 | 1208 |
| 4 | Prisoje, Koper | 10 | 0.5 | 124 | 1311 | 646 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Volgare, M.; Avolio, R.; Castaldo, R.; Errico, M.E.; El Khiar, H.; Gentile, G.; Sinjur, A.; Susnik, D.; Znidarsic, A.; Cocca, M. Microfiber Contamination in Potable Water: Detection and Mitigation Using a Filtering Device. Microplastics 2022, 1, 322-333. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1030024
Volgare M, Avolio R, Castaldo R, Errico ME, El Khiar H, Gentile G, Sinjur A, Susnik D, Znidarsic A, Cocca M. Microfiber Contamination in Potable Water: Detection and Mitigation Using a Filtering Device. Microplastics. 2022; 1(3):322-333. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1030024
Chicago/Turabian StyleVolgare, Michela, Roberto Avolio, Rachele Castaldo, Maria Emanuela Errico, Hakim El Khiar, Gennaro Gentile, Andreja Sinjur, Danilo Susnik, Andrej Znidarsic, and Mariacristina Cocca. 2022. "Microfiber Contamination in Potable Water: Detection and Mitigation Using a Filtering Device" Microplastics 1, no. 3: 322-333. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1030024
APA StyleVolgare, M., Avolio, R., Castaldo, R., Errico, M. E., El Khiar, H., Gentile, G., Sinjur, A., Susnik, D., Znidarsic, A., & Cocca, M. (2022). Microfiber Contamination in Potable Water: Detection and Mitigation Using a Filtering Device. Microplastics, 1(3), 322-333. https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics1030024