Millimeter and Terahertz Wireless Communications
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Yosef Pinhasi
Prof. Dr. Yosef Pinhasi
 Prof. Dr. Yosef Pinhasi
Prof. Dr. Yosef Pinhasi
E-Mail
Website
Guest Editor
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Ariel University, Ariel 40700, Israel
Interests: generation and utilization of electromagnetic waves; millimeter-wave communications; THz radiation; MIMO systems; radar technology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The demand for broadband communication links and the deficiency of wide, free bands in the electromagnetic spectrum being used for wireless communications calls for the allocation of new frequency regions above 30GHz. While these extremely high frequencies (EHF) in the millimeter wavelengths (MMW) and even above (terahertz frequencies), have been studied for stand-off detection and remote sensing and radars, they are still not massively used for wireless communication applications. At present, some bands in the EHF are being considered for the fifth generation of the cellular communications (5G). This will enable extension of the capacity and availability of the cellular network and expected to increase their quality of service.
Although the millimeter and terahertz waves cover a wide range of frequencies, which are relatively free of users, these regimes present principal challenges in the realization of wireless communication links and radars in all aspects. This Special Issue is aimed at addressing issues that are involved in the analysis, design, and implementation of the different communication layers featuring in a wireless link operating in the millimeter and submillimeter (Terahertz) regimes. This includes:
- Communication techniques
- Millimeter and terahertz wave technology
- Transmitter and receiver architectures
- The physical and the medium access control (MAC) layers
- Modulation waveforms and coding
- Passive and active components
- Antennas
- Terrestrial links
- Satellite communications
- Personal, local, and wide area wireless networks
- The 5th generation of cellular communication
- Propagation in the atmospheric medium and through the ionosphere
- Weather conditions effects (humidity, fog, haze, dust, rain, etc.)
- Frequency allocation and standardization
- Utilization of unlicensed bands
- The 6th generation in the future
Prof. Dr. Yosef Pinhasi
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Electronics is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- millimeter waves
- terahertz
- MMW communications
- 5th generation of cellular communications (5G)
- satellite communications
- the electromagnetic spectrum
- antennas and propagation
Published Papers (17 papers)
Open AccessCommunication
Developing PCM-Based Microwave and Millimetre-Wave Switching Networks by Optimised Building Blocks
by
Rodica Ramer and King Yuk Chan
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2083
Abstract
The implementation of microwave and millimetre-wave switching networks using phase change material (PCM) is presented in this paper. We propose integrating a combination of ultra-wide bandwidth-optimised building cells into a unique semi-T type switch. The construction of arrays with different dimensions is enabled.
[...] Read more.
The implementation of microwave and millimetre-wave switching networks using phase change material (PCM) is presented in this paper. We propose integrating a combination of ultra-wide bandwidth-optimised building cells into a unique semi-T type switch. The construction of arrays with different dimensions is enabled. The present paper selected GeTe for the PCM-based switches, which are 150 nm GeTe thin-film offering on- and off-state
σon = 37,203,703 S/m and
σoff = 94.97 S/m conductivities by a customised eight-step fabrication process. The integrated semi-T switch cell with two, thru, and turn operational states allows easy expansion into the form of a staircase switch matrix. The simulated results for the semi-T type switch show excellent insertion loss of better than 0.8 dB, return loss of better than 20 dB, and isolation of 40 dB for both the thru and turn paths from DC to 120 GHz. The proposed 4 × 4 staircase switch matrix with a dimension of only 510 × 510 μm
2 is also the smallest in its class. The switch matrix exhibits better than 17 dB return loss and 40 dB isolations across all possible combinations and paths.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Full Investigation of Terahertz Wave Power Transmission in Plasma from Theoretical, Numerical, and Experimental Perspectives
by
Ke Yang, Di Peng, Jinhong Wang, Ping Ma and Bin Li
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1688
Abstract
Radio communication is a vital challenge during vehicle reentry into the Earth’s atmosphere in practice, because the plasma covering the aerospace vehicle can block the communication as the spacecraft reenters the atmosphere. To investigate the potential of the terahertz wave, the transfer function
[...] Read more.
Radio communication is a vital challenge during vehicle reentry into the Earth’s atmosphere in practice, because the plasma covering the aerospace vehicle can block the communication as the spacecraft reenters the atmosphere. To investigate the potential of the terahertz wave, the transfer function method is first applied to study the wave propagation behavior in plasma, validated by the numerical and the experimental results. The comparison of all three results shows a decent agreement, with the average absolute difference around 1.1 dB for the power loss between the theoretical and numerical results for 100 GHz and 220 GHz and around 0.8 dB for the power loss between the simulation and measurement for 100 GHz and 220 GHz, which shows the validity of the transfer function method and the great potential of the numerical model for future study. Moreover, the results shows the possibility of the application of the THz wave to deal with the blackout problem.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A 560 GHz Sub-Harmonic Mixer Using Half-Global Design Method
by
Bo Zhang, Yong Zhang, Liucheng Pan, Yu Li, Jianhang Cui, Ruimin Xu and Bo Yan
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2593
Abstract
In this paper, a 560 GHz terahertz sub-harmonic mixer using a new half-global design method is reported. This method combines the advantages of the subdivision design method and the global design method, and greatly enhances the abilities of the optimization of matching variables
[...] Read more.
In this paper, a 560 GHz terahertz sub-harmonic mixer using a new half-global design method is reported. This method combines the advantages of the subdivision design method and the global design method, and greatly enhances the abilities of the optimization of matching variables while retaining the portability of the unit circuit. When the local oscillator (LO) frequency was fixed with 3 mW power at 280 GHz, average up-conversion double sideband (DSB) conversion loss of 8 dB with intermediate frequency (IF) power of −5 dBm was achieved.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Design of 300 GHz Combined Doubler/Subharmonic Mixer Based on Schottky Diodes with Integrated MMIC Based Local Oscillator
by
José M. Pérez-Escudero, Carlos Quemada, Ramón Gonzalo and Iñigo Ederra
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 3093
Abstract
In this paper the design and experimental characterization of a combined doubler-subharmonic mixer based on Schottky diodes which uses a 75 GHz MMIC based local oscillator is presented. This solution integrates in the same substrate the doubler and the mixer, which share the
[...] Read more.
In this paper the design and experimental characterization of a combined doubler-subharmonic mixer based on Schottky diodes which uses a 75 GHz MMIC based local oscillator is presented. This solution integrates in the same substrate the doubler and the mixer, which share the same metallic packaging with the local oscillator. The prototype has been fabricated and measured. For characterization, the Y-Factor technique has been used and the prototype yields a best conversion loss and equivalent noise temperature of 11 dB and 1976 K, respectively, at 305 GHz. This performance is close to the state of the art, and shows the potential of this approach, which allows a significant reduction in terms of size and volume.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Ka-Band Diplexer for 5G mmWave Applications in Inverted Microstrip Gap Waveguide Technology
by
Carlos Sanchez-Cabello, Luis Fernando Herran and Eva Rajo-Iglesias
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 4910
Abstract
A new cost-efficient, low-loss Ka-band diplexer designed in inverted microstrip gap waveguide technology is presented in this paper. Gap waveguide allows to propagate quasi-TEM modes in the air between two metal plates without the need for contact between them by using periodic metasurfaces.
[...] Read more.
A new cost-efficient, low-loss Ka-band diplexer designed in inverted microstrip gap waveguide technology is presented in this paper. Gap waveguide allows to propagate quasi-TEM modes in the air between two metal plates without the need for contact between them by using periodic metasurfaces. The diplexer is realized by using a bed of nails as AMC (Artificial Magnetic Conductor), first modeled with a PMC (Perfect Magnetic Conductor) surface for design simplification, and two fifth order end-coupled passband filters (BPFs) along with a power divider. The experimental verification confirms that the two channels centered at 24 GHz and 28 GHz with 1 GHz of bandwidth show measured insertion losses of 1.5 dB and 2 dB and 60 dB of isolation between them. A slight shift in frequency is observed in the measurements that can be easily explained by the variation in the permittivity of the substrate.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Atmospheric Effects on OFDM Wireless Links Operating in the Millimeter Wave Regime
by
Yosef Golovachev, Gad A. Pinhasi and Yosef Pinhasi
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2730
Abstract
The development of millimeter wave communication links and the allocation of bands within the Extremely High Frequency (EHF) range for the next generation cellular network present significant challenges due to the unique propagation effects emerging in this regime of frequencies. This includes susceptibility
[...] Read more.
The development of millimeter wave communication links and the allocation of bands within the Extremely High Frequency (EHF) range for the next generation cellular network present significant challenges due to the unique propagation effects emerging in this regime of frequencies. This includes susceptibility to amplitude and phase distortions caused by weather conditions. In the current paper, the widely used Orthogonal Division Frequency Multiplexing (OFDM) transmission scheme is tested for resilience against weather-induced attenuation and phase shifts, focusing on the effect of rainfall rates. Operating frequency bands, channel bandwidth, and other modulation parameters were selected according to the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Technical Specification. The performance and the quality of the wireless link is analyzed via constellation diagram and BER (Bit Error Rate) performance chart. Simulation results indicate that OFDM channel performance can be significantly improved by consideration of the local atmospheric conditions while decoding the information by the receiver demodulator. It is also demonstrated that monitoring the weather conditions and employing a corresponding phase compensation assist in the correction of signal distortions caused by the atmospheric dispersion, and consequently leads to a lower bit error rate.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Innovative Reconfigurable Metasurface 2-D Beam-Steerable Reflector for 5G Wireless Communication
by
David Rotshild, Efraim Rahamim and Amir Abramovich
Cited by 22 | Viewed by 4966
Abstract
A tunable reflector component based on metasurface (MS) with a low profile and reduced mass is offered for indoor and outdoor 5G communication methods to overcome obstacles such as buildings, walls, and turns, and to allow wireless quasi-line of sight path communication at
[...] Read more.
A tunable reflector component based on metasurface (MS) with a low profile and reduced mass is offered for indoor and outdoor 5G communication methods to overcome obstacles such as buildings, walls, and turns, and to allow wireless quasi-line of sight path communication at 37 GHz. Integrating varactors with MS unit cells allows tunability and reconfigurability. This approach was presented in many studies, with frequencies of up to K–band. However, today, higher frequencies are used, especially in communication. This work presents the design of a reconfigurable MS reflector, at Ka-band frequencies, based on a new type of resonant unit cell, with uniformed reflection for wide-incident-angular-range, and a simple stimulating DC bias for each MS unit cell, which allows a two–dimensional (2-D) continuous reflection phase manipulation. The unit cell provides a dynamic reflection phase range of over 300° at a wide bandwidth. Simulations of one-dimensional (1-D) and (2-D) at 37 GHz are presented. A steering range of up to ±48° was obtained for azimuth or elevation. A simultaneous independent 2-D beam steering range of up to ±10° in azimuth and up to ± 5° in elevation, allowing obstacles to overcome covering at a practical angular spatial cone of 20° and 10°, is presented.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
QPSK MMW Wireless Communication System Based On p-i-n InGaAs Photomixer
by
Asemahegn Wudu, Daniel Rozban and Amir Abramovich
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3416
Abstract
Millimeter-wave (MMW) frequencies (30–300 GHz), located between the microwave and infrared (IR), are promising solutions for the increasing demand of high data rate applications, UHD multimedia, HD gaming, security, surveillance, and the emergence of 5G Internet of Things (IoT). In this article, we
[...] Read more.
Millimeter-wave (MMW) frequencies (30–300 GHz), located between the microwave and infrared (IR), are promising solutions for the increasing demand of high data rate applications, UHD multimedia, HD gaming, security, surveillance, and the emergence of 5G Internet of Things (IoT). In this article, we experimentally demonstrated MMW wireless communication link using InGaAs p-i-n photomixer and commercially available telecom components at W-band (75–110 GHz). The photomixer was excited by two 1.5 µm lasers via standard telecom fiber optics, to generate frequency difference at W-band. QPSK modulated signal transmitted by the photomixer and received horn antenna integrated MMW mixer and analyzed using a spectrum analyzer and Vector Signal Analyzer (VSA) software.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
THz CMOS On-Chip Antenna Array Using Defected Ground Structure
by
Changmin Lee and Jinho Jeong
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 4114
Abstract
In this paper, we design a THz CMOS on-chip patch antenna with defected ground structure (DGS) and utilize it to implement a broadband and high gain on-chip antenna array. It is verified from the simulation that the DGS not only can increase the
[...] Read more.
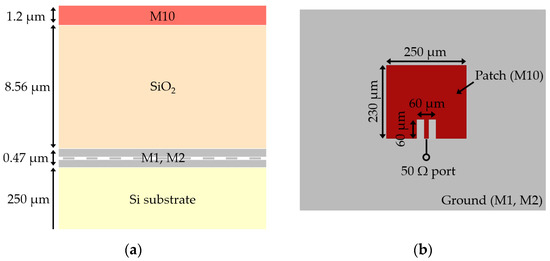
In this paper, we design a THz CMOS on-chip patch antenna with defected ground structure (DGS) and utilize it to implement a broadband and high gain on-chip antenna array. It is verified from the simulation that the DGS not only can increase the gain and bandwidth of the antenna element, but also can increase the isolation between the antenna elements in the on-chip array. Therefore, it allows the design of the compact 1 × 2 and 2 × 2 on-chip antenna array with high gain and broad bandwidth. The element spacing and feedline structures of the antenna array are designed and optimized by the simulations. The designed antenna element, and 1 × 2 and 2 × 2 antenna arrays are fabricated in a commercial 65 nm CMOS process. In the on-wafer measurement, they exhibit an antenna gain of 3.1 dBi, 7.2 dBi, and 8.2 dBi with a bandwidth of 14.0%, 21.3%, and 28.0% for the reflection coefficient less than −10 dB, respectively, at 300 GHz. This result corresponds to very good performance compared to the reported THz CMOS on-chip antenna array. Therefore, the designed CMOS on-chip antenna element and array using DGS in this work can be effectively applied to build low-cost and high performance THz systems, because they can be fully implemented in a conventional CMOS process without requiring any additional processes or manufacturing techniques.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Meteorological Attenuation on Channel Characterization at 300 GHz
by
Zhengrong Lai, Haofan Yi, Ke Guan, Bo Ai, Wuning Zhong, Jianwu Dou, Yi Zeng and Zhangdui Zhong
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 3390
Abstract
Terahertz (THz) communication is a key candidate for the upcoming age of beyond-fifth-generation mobile networks (B5G) or sixth-generation mobile networks (6G) in the next decade and can achieve ultra-high data rates of dozens of gigabits or even terabits per second. As the carrier
[...] Read more.
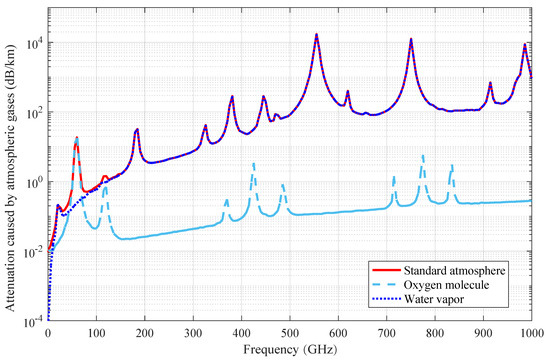
Terahertz (THz) communication is a key candidate for the upcoming age of beyond-fifth-generation mobile networks (B5G) or sixth-generation mobile networks (6G) in the next decade and can achieve ultra-high data rates of dozens of gigabits or even terabits per second. As the carrier frequency increases from radio frequency (RF) to the THz band, the impact of meteorological factors on the wireless link is expected to become more pronounced. In this work, we first provide an overview of the attenuation caused by atmospheric gases, fog, and rain on terrestrial THz wireless communications using the recommendations of the International Telecommunication Union-Radiocommunication (ITU-R). Measured data from the literature are used to predict the attenuation caused by snow. Because unfavorable weather conditions may harm sensitive measurement equipment, ray-tracing (RT) simulations are sometimes used as an alternative to extend sparse empirical data. In this study, the terrestrial channel in an urban scenario at 300 GHz, with a bandwidth of 8 GHz, is characterized using RT simulations under different meteorological factors. The key performance parameters are explored, including path loss (PL), Rician K-factor (KF), root-mean-square (RMS) delay spread (DS), and four angular spreads. The channel characteristics under different meteorological conditions studied in this work are expected to aid the design of future outdoor terrestrial THz communications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Experimental Study of Fog and Suspended Water Effects on the 5G Millimeter Wave Communication Channel
by
Ariel Etinger, Yosef Golovachev, Ofir Shoshanim, Gad A. Pinhasi and Yosef Pinhasi
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 4956
Abstract
Controlled experiments were conducted to examine the effect of fog on signal propagation in wireless communication and radar links operating in millimeter wavelengths. The experiments were carried out in a fog laboratory to verify theoretical results obtained from Liebe’s model. Attenuation and phase
[...] Read more.
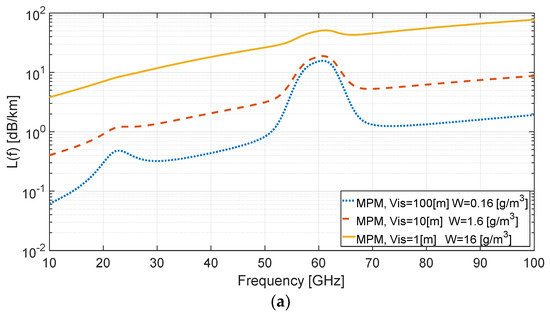
Controlled experiments were conducted to examine the effect of fog on signal propagation in wireless communication and radar links operating in millimeter wavelengths. The experiments were carried out in a fog laboratory to verify theoretical results obtained from Liebe’s model. Attenuation and phase shifts of millimeter wave (mmW) radiation were measured, at different fog density characterized by the visibility distance and its water vapor content. Utilizing a vector network analyzer (VNA) enabled us to examine the actual atmospheric attenuation and the phase shift caused by the fog retardation. The experimental results demonstrate good agreement with the simulations even for very low visibility in highly dense fog. The study can be used to estimate link budget of mmW wireless links, including those allocated for the fifth generation (5G) of cellular networks.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Millimeter Wave Propagation in Long Corridors and Tunnels—Theoretical Model and Experimental Verification
by
Liat Rapaport, Gad A. Pinhasi and Yosef Pinhasi
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 3013
Abstract
The development of the Fifth-Generation (5G) of cellular communications considers bands in millimeter waves (MMW) for indoor, short-range links. The propagation of MMW is affected by atmospheric and weather conditions, specular reflections from surfaces, and the directivity of the antennas. The short wavelength
[...] Read more.
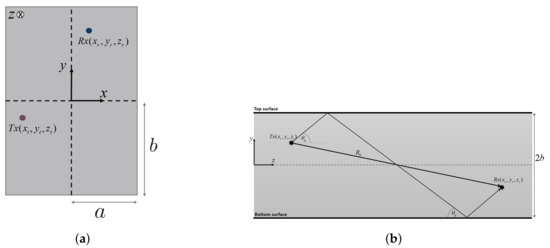
The development of the Fifth-Generation (5G) of cellular communications considers bands in millimeter waves (MMW) for indoor, short-range links. The propagation of MMW is affected by atmospheric and weather conditions, specular reflections from surfaces, and the directivity of the antennas. The short wavelength enables utilization of a quasi-optical propagation model for the description of indoor multi-path scenarios. A study of MMW propagation in tunnels, long corridors, or canyons is carried out using ray-tracing to evaluate the link budget and group delay. The analysis considers radiation patterns of both transmitting and receiving antennas, deriving a criterion for the number of dominating rays. Error analysis demonstrates the convergence of the method, while using a finite number of reflected rays. Experiments in a small-scale tunnel model demonstrate the accuracy of the analysis.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
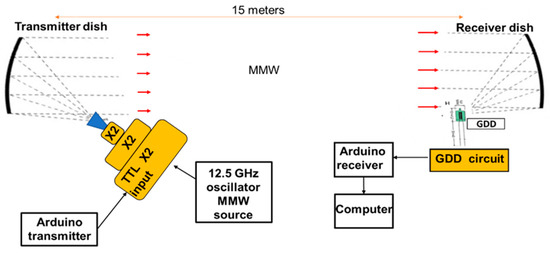
Inexpensive Millimeter-Wave Communication Channel Using Glow Discharge Detector and Satellite Dish Antenna
by
Lidor Kahana, Daniel Rozban, Moshe Gihasi, Amir Abramovich, Yitzhak Yitzhaky and Natan Kopeika
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 3526
Abstract
A full proof of concept for low-cost millimeter wave (MMW) communication link is demonstrated in this study. The suggested MMW channel is based on a very inexpensive commercially available off-axis dish antenna usually used for TV satellites, two Arduino Uno micro controller boards,
[...] Read more.
A full proof of concept for low-cost millimeter wave (MMW) communication link is demonstrated in this study. The suggested MMW channel is based on a very inexpensive commercially available off-axis dish antenna usually used for TV satellites, two Arduino Uno micro controller boards, and glow discharge detectors (GDD). The GDD is a robust and inexpensive room-temperature plasma device which was found to be a sensitive MMW radiation detector. The Arduino micro controllers are used to encode a text message into serial bits and also decode it. Those serial bits were used to modulate the MMW radiation in On-Off keying. The detection of MMW radiation was performed using a simple and inexpensive GDD. The suggested MMW channel can be used as point to point backhaul wireless communication for the 5th generation of cellular communication.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Highly Integrated Resonant Tunneling Diode with Rectangular Waveguide Output for W-Band Communication System
by
Caixia Wang, Yuan Yao, Hang Jiang, Tao Xiu, Mohsin A. Shah Syedd, Junsheng Yu and Xiaodong Chen
Viewed by 2818
Abstract
A packaged resonant tunneling diode (RTD) with rectangular waveguide output for highly integrated wireless communication is proposed. The output signal of the RTD chip is radiated to the rectangular waveguide through an E plane probe transformer. Next, the RTD chip is electrically connected
[...] Read more.
A packaged resonant tunneling diode (RTD) with rectangular waveguide output for highly integrated wireless communication is proposed. The output signal of the RTD chip is radiated to the rectangular waveguide through an E plane probe transformer. Next, the RTD chip is electrically connected to the transformer by using gold wire bonding. The packaged RTD exhibits an oscillation frequency of 92 GHz, while the maximum radio frequency (RF) output power is −7 dBm. A miniaturized and high data rate wireless communication system with a 7 Gbps on–off keying (OOK) module by using the RTD is demonstrated, and the bit error rate (BER) of the 7 Gbps is below 3.8 × 10
−3.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Constant Envelope Modulation Techniques for Limited Power Millimeter Wave Links
by
Yael Balal, Monika Pinchas and Yosef Pinhasi
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 3895
Abstract
The demand for increased capacity and link availability for mobile communications requires the utilization of higher frequencies, such as millimeter waves at extremely high frequencies (EHFs) above 30 GHz. In this regime of frequencies, the waves are subjected to high atmospheric attenuation and
[...] Read more.
The demand for increased capacity and link availability for mobile communications requires the utilization of higher frequencies, such as millimeter waves at extremely high frequencies (EHFs) above 30 GHz. In this regime of frequencies, the waves are subjected to high atmospheric attenuation and dispersion effects that lead to a degradation in communication reliability. The fact that solid-state millimeter and sub-millimeter wave sources are producing low power calls for effective signaling utilizing waveforms with a low peak to average power ratio (PAPR), such as constant envelope (CE) modulation. The CE techniques present a PAPR of 0 dB resulting in peak power transmission with high energy efficiency. The study of the performances of constant envelope orthogonal modulation techniques in the presence of co-channel interference is presented. The performance is evaluated in terms of the average symbol error rate (SER) using analytical results and simulations. The theory is carried out for the CE-M-ary time orthogonal (CE-MTO) and CE-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (CE-OFDM), demonstrating comparable performances while leading to a simpler implementation than that of the CE-OFDM.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Combination of High-Order Modulation and Non-Binary LDPC Codes over GF(7) for Non-Linear Satellite Channels
by
Yanyan Liu, Weigang Chen, Anguo Wang and Changcai Han
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 5522
Abstract
High-order modulations are necessary to improve the bandwidth efficiency of the satellite communication system. However, the non-linear characteristic of satellite channels limits the application of high-order modulations. In this paper, we propose a new 7-point constellation which is expected to be effectively applied
[...] Read more.
High-order modulations are necessary to improve the bandwidth efficiency of the satellite communication system. However, the non-linear characteristic of satellite channels limits the application of high-order modulations. In this paper, we propose a new 7-point constellation which is expected to be effectively applied to the satellite communication system, and combine it with non-binary low-density parity-check (NB-LDPC) codes over Galois field GF(7) to guarantee the reliability of the data transmission. The exact expression for the average symbol error probability (SEP) of 7-order quadrature amplitude modulation (7-QAM) over the Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) channel is derived, and the non-linear distortion over satellite channels is also analyzed. Simulation results reveal that, compared with the traditional 8-order phase-shift keying (8-PSK), the 7-QAM method can achieve about 3 dB gain over the AWGN channel without channel coding at symbol error rate (SER) of
. Moreover, the proposed combined coded modulation scheme also has better SER performance than the NB-LDPC coded 8-PSK modulation scheme over the non-linear satellite channel.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Wideband Terahertz Transmissive Polarization Manipulator Based on Metasurfaces
by
Ayesha Kosar Fahad, CunJun Ruan and Kanglong Chen
Cited by 20 | Viewed by 4064
Abstract
Wideband and multifunction operation for THz polarization manipulating devices has been desired for a wide range of applications. In this paper, a novel wideband transmissive type polarization manipulator based on metasurfaces is proposed in the THz region. The designed metasurface acts as a
[...] Read more.
Wideband and multifunction operation for THz polarization manipulating devices has been desired for a wide range of applications. In this paper, a novel wideband transmissive type polarization manipulator based on metasurfaces is proposed in the THz region. The designed metasurface acts as a multifunctional polarization manipulator, performing linear to circular polarization conversion (LCPC) for relative bandwidth 43.9% (0.94 THz to 1.47 THz) for incident x/y polarizations and a wideband bandpass filter with relative bandwidth 67% (0.713 THz to 1.4346 THz) for incident slant (xy) polarizations. Wideband LCPC operation is achieved using a unique diagonal symmetric structure based on a bilayered metasurface. In order to confirm the validation of proposed results, electromagnetic simulation was carried out in two industry-standard software packages, HFSS and CST, using frequency domain and time domain solvers, respectively. Close agreement between numerical results depicts the validity and reliability of the proposed design. Polarized wave trajectory, equivalent microscopic circuit, physical mechanisms, and impact of different geometrical parameters on the performance is investigated. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first polarization manipulator based on bilayered metasurfaces. The same structure can be used as for LCPC and the transmit reject filter for THz wireless communication, including THz satellite communications, the future of communication. Moreover, they can be used in THz imaging and biomolecular control devices.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures