Feature Papers in Advanced Energy Materials
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Vassilis Stathopoulos
Prof. Dr. Vassilis Stathopoulos
 Prof. Dr. Vassilis Stathopoulos
Prof. Dr. Vassilis Stathopoulos
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Laboratory of Chemistry and Materials Technology, Department of Agricultural Development, Agrofood and Management of Natural Resources, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Psachna Campus, 34400 Evia, Greece
Interests: environmental ceramics; functional coatings; surface phenomena; energy-related applications of ceramics and coatings; catalysts
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Advanced energy materials are crucial for the required technology breakthroughs in the transformation of the global energy sector from fossil-based to zero-carbon. There is a continuous effort on research and development for novel and improved materials applied in energy generation, low energy processing, energy conservation and conversion that supports the energy transition.
In this Topical Collection, papers selected by invitation (publication fees waived) will be featured, covering interesting advances in materials for energy storage and conversion applications including:
- Energy to chemicals;
- Energy related catalysis;
- Thermoelectrics, photovoltaics, and photo-electrosynthesis cell;
- Waste heat recovery and thermal energy management;
- Batteries, electrolytes and electrodes;
- Fuel cells;
- New inorganic, hybrid, bioinspired and bioderived materials.
Prof. Dr. Vassilis Stathopoulos
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Energies is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- power to chemicals
- catalysis
- thermoelectrics
- photovoltaics
- photo-electrosynthesis
- thermal energy management
- batteries
- fuel cells
- bioinspired
- bioderived
- hybrid
- perovskites
Published Papers (3 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Heating Rate on the Pyrolysis Behavior and Kinetics of Coconut Residue and Activated Carbon: A Comparative Study
by
Inamullah Mian, Noor Rehman, Xian Li, Hidayat Ullah, Abbas Khan, Chaejin Choi and Changseok Han
Viewed by 678
Abstract
The pyrolysis process of coconut residue and the activated carbon was investigated using thermogravimetric analysis in the range of 25 to 900 °C, with three altered heating rates: 3, 5, and 10 °C/min. The results of the thermal decomposition showed that it occurred
[...] Read more.
The pyrolysis process of coconut residue and the activated carbon was investigated using thermogravimetric analysis in the range of 25 to 900 °C, with three altered heating rates: 3, 5, and 10 °C/min. The results of the thermal decomposition showed that it occurred in three distinct phases: dehydration, active pyrolysis, and passive pyrolysis. The derivative thermogravimetric analysis indicated that increasing the heating rate led to a shift in the maximum weight loss rate towards higher temperatures. To better understand the kinetics constraints, the Coats–Redfern method was applied to determine the activation energy (
Ea) and the frequency factor (
A). The activation energies for the pyrolysis process varied between 159.57 and 177.45 kJ/mol for RCR and from 132.62 to 147.1 kJ/mol for ACCR at different heating rates. Additionally, the physical properties of the samples were investigated using techniques like scanning electron microscopy and the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller surface analysis. The findings of the study demonstrated that the activation energies of the activated carbon were lower than those of the original biomass. Furthermore, the activation energy values achieved from the D1–D4 models were considered reliable, indicating that the D model was more suitable compared to other models for describing the pyrolysis process and predicting its kinetics.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
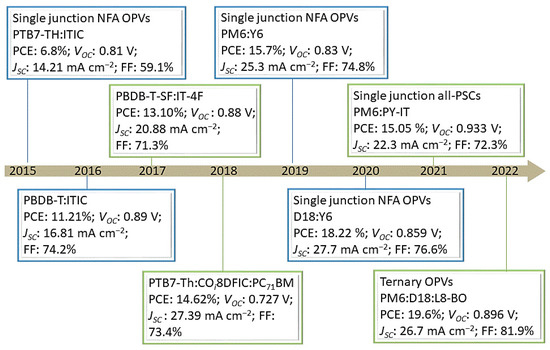
Critical Progress of Polymer Solar Cells with a Power Conversion Efficiency over 18%
by
Hongyue Tian, Mingxin Zhao, Xiaoling Ma, Chunyu Xu, Wenjing Xu, Zhongyuan Liu, Miao Zhang and Fujun Zhang
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 3001
Abstract
The power conversion efficiencies (PCEs) of organic photovoltaics (OPVs) have reached more than 19%, along with the prosperous development of materials and device engineering. It is meaningful to make a comprehensive review of the research of OPVs for further performance improvement. In this
[...] Read more.
The power conversion efficiencies (PCEs) of organic photovoltaics (OPVs) have reached more than 19%, along with the prosperous development of materials and device engineering. It is meaningful to make a comprehensive review of the research of OPVs for further performance improvement. In this review, some typical materials of high-performance OPVs are summarized, including representative polymer donor materials, non-fullerene acceptor materials, and interfacial modification materials, as well as their design rules for molecular engineering. From the point of view of device engineering, active layer treatment and deposition technology are introduced, which can play a critical role in adjusting the degree of molecular aggregation and vertical distribution. Meanwhile, a ternary strategy has been confirmed as an efficient method for improving the performance of OPVs, and the multiple roles of the appropriate third component in the photo-electronic conversion process are emphasized and analyzed. The challenges and perspectives concerning this region are also put forward for further developing high-performance OPVs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
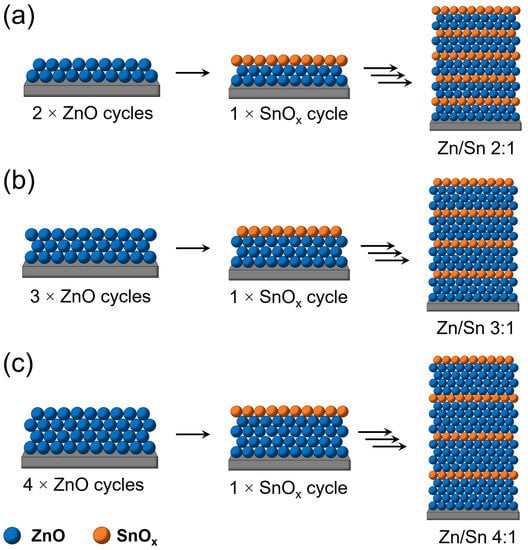
Effect of the ZnSnO/AZO Interface on the Charge Extraction in Cd-Free Kesterite Solar Cells
by
Carla Gobbo, Valerio Di Palma, Vanira Trifiletti, Claudia Malerba, Matteo Valentini, Ilaria Matacena, Santolo Daliento, Simona Binetti, Maurizio Acciarri and Giorgio Tseberlidis
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 2010
Abstract
Cu
2ZnSnS
4 (CZTS) is a promising absorber material to produce thin film solar cells thanks to its high absorption coefficient, low cost and low toxicity. CdS is commonly used as a buffer layer for CZTS solar cells but, beyond its toxicity,
[...] Read more.
Cu
2ZnSnS
4 (CZTS) is a promising absorber material to produce thin film solar cells thanks to its high absorption coefficient, low cost and low toxicity. CdS is commonly used as a buffer layer for CZTS solar cells but, beyond its toxicity, it has a nonoptimal band alignment with CZTS. Zn
xSn
1−xO (ZTO), based on earth-abundant and nontoxic elements and with a large and tunable band gap, is a suitable alternative buffer layer. In this paper, the atomic layer deposition (ALD) of ZTO was employed by testing different compositions and thicknesses. ALD not only leads to very compact and homogenous ZTO layers (enabling tuning the stoichiometry of the ZTO so prepared) but also makes the i-ZnO layer (usually sandwiched between the buffer layer and the transparent contact) redundant and detrimental. Through SCAPS simulation and impedance measurements, the ZnSnO/AZO interface impact on the Cd-free kesterite solar cells’ performances has been investigated, highlighting its leading role in achieving an effective charge extraction and the detrimental effect of the i-ZnO layer. With this approach, a solar cell based on an architecture simpler and more eco-friendly than the conventional one has been produced with comparable efficiencies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures