Anticancer Drug Discovery and Development
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Dr. Hidayat Hussain
Dr. Hidayat Hussain
 Dr. Hidayat Hussain
Dr. Hidayat Hussain
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Bioorganic Chemistry, Leibniz Institute of Plant Biochemistry, Weinberg 3, D-06120 Halle (Salle), Germany
Interests: synthetic chemistry; natural product chemistry; medicinal chemistry; bioorganic chemistry
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Cancer is a world health issue and affects all communities around the globe and this disease is the second leading cause of death globally. Moreover, there has been continued progress in anticancer drug development in the last few years. New anticancer agents have been approved for cancer treatment but majority of these approved molecules have serious adverse side effects. This illustrates that there is still an urgent need for the development of novel anti-cancer drugs with a unique mechanism of action.
The focus of this Topical Collection is on Natural products (NPs)-based anticancer molecules, and synthetic anticancer compounds. Notably, this Topical Collection will also emphasis on the relationship between the chemical structure and the biological activity of the molecules along with appplication of bioinformatics in cancers. Furthermore, this Topical Collection also wellcome articles anticancer effects as vascular targeting agents, tubulin inhibitors, and topoisomerase targeting agents. In addition, this Topical Collection will also focus on the development of new therapeutic agents for cancer treatment, employing the newest techniques of pharmacology, biotechnology, and genetic engineering. This Topical Collection welcomes original articles, communications and reviews dealing with the cancer treatment.
Dr. Hidayat Hussain
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. International Journal of Molecular Sciences is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
There is an Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this
open access journal. For details about the APC please see here.
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- anticancer natural products
- anticancer synthetic compounds
- chemotherapy
- mode of action
- drug resistance
- tubulin inhibitors
- topoisomerase inhibitors
- chemotherapy
- bioinformatics
- oncology
- tumor cells
Published Papers (17 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Targeting Oxidative Phosphorylation with a Novel Thiophene Carboxamide Increases the Efficacy of Imatinib against Leukemic Stem Cells in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
by
Kana Kusaba, Tatsuro Watanabe, Keisuke Kidoguchi, Yuta Yamamoto, Ayaka Tomoda, Toshimi Hoshiko, Naoto Kojima, Susumu Nakata and Shinya Kimura
Viewed by 861
Abstract
Patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) respond to tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs); however, CML leukemic stem cells (LSCs) exhibit BCR::ABL kinase-independent growth and are insensitive to TKIs, leading to disease relapse. To prevent this, new therapies targeting CML-LSCs are needed. Rates of mitochondria-mediated
[...] Read more.
Patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) respond to tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs); however, CML leukemic stem cells (LSCs) exhibit BCR::ABL kinase-independent growth and are insensitive to TKIs, leading to disease relapse. To prevent this, new therapies targeting CML-LSCs are needed. Rates of mitochondria-mediated oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) in CD34
+CML cells within the primitive CML cell population are higher than those in normal undifferentiated hematopoietic cells; therefore, the inhibition of OXPHOS in CML-LSCs may be a potential cure for CML. NK-128 (C
33H
61NO
5S) is a structurally simplified analog of JCI-20679, the design of which was based on annonaceous acetogenins. NK-128 exhibits antitumor activity against glioblastoma and human colon cancer cells by inhibiting OXPHOS and activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Here, we demonstrate that NK-128 effectively suppresses the growth of CML cell lines and that the combination of imatinib and NK-128 is more potent than either alone in a CML xenograft mouse model. We also found that NK-128 inhibits colony formation by CD34
+ CML cells isolated from the bone marrow of untreated CML patients. Taken together, these findings suggest that targeting OXPHOS is a beneficial approach to eliminating CML-LSCs, and may improve the treatment of CML.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Advances in Anti-Cancer Drug Development: Metformin as Anti-Angiogenic Supplemental Treatment for Glioblastoma
by
Siddharth Shah, Hadeel M. Mansour, Tania M. Aguilar and Brandon Lucke-Wold
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1882
Abstract
According to the WHO 2016 classification, glioblastoma is the most prevalent primary tumor in the adult central nervous system (CNS) and is categorized as grade IV. With an average lifespan of about 15 months from diagnosis, glioblastoma has a poor prognosis and presents
[...] Read more.
According to the WHO 2016 classification, glioblastoma is the most prevalent primary tumor in the adult central nervous system (CNS) and is categorized as grade IV. With an average lifespan of about 15 months from diagnosis, glioblastoma has a poor prognosis and presents a significant treatment challenge. Aberrant angiogenesis, which promotes tumor neovascularization and is a prospective target for molecular target treatment, is one of its unique and aggressive characteristics. Recently, the existence of glioma stem cells (GSCs) within the tumor, which are tolerant to chemotherapy and radiation, has been linked to the highly aggressive form of glioblastoma. Anti-angiogenic medications have not significantly improved overall survival (OS), despite various preclinical investigations and clinical trials demonstrating encouraging results. This suggests the need to discover new treatment options. Glioblastoma is one of the numerous cancers for which metformin, an anti-hyperglycemic medication belonging to the Biguanides family, is used as first-line therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and it has shown both in vitro and in vivo anti-tumoral activity. Based on these findings, the medication has been repurposed, which has shown the inhibition of many oncopromoter mechanisms and, as a result, identified the molecular pathways involved. Metformin inhibits cancer cell growth by blocking the LKB1/AMPK/mTOR/S6K1 pathway, leading to selective cell death in GSCs and inhibiting the proliferation of CD133+ cells. It has minimal impact on differentiated glioblastoma cells and normal human stem cells. The systematic retrieval of information was performed on PubMed. A total of 106 articles were found in a search on metformin for glioblastoma. Out of these six articles were Meta-analyses, Randomized Controlled Trials, clinical trials, and Systematic Reviews. The rest were Literature review articles. These articles were from the years 2011 to 2024. Appropriate studies were isolated, and important information from each of them was understood and entered into a database from which the information was used in this article. The clinical trials on metformin use in the treatment of glioblastoma were searched on clinicaltrials.gov. In this article, we examine and evaluate metformin’s possible anti-tumoral effects on glioblastoma, determining whether or not it may appropriately function as an anti-angiogenic substance and be safely added to the treatment and management of glioblastoma patients.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Biological Evaluation of 8-Methoxy-2,5-dimethyl-5H-indolo[2,3-b] Quinoline as a Potential Antitumor Agent via PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling
by
Yunhao Ma, Hongmei Zhu, Xinrong Jiang, Zhongkun Zhou, Yong Zhou, Yanan Tian, Hao Zhang, Mengze Sun, Lixue Tu, Juan Lu, Yuqing Niu, Huanxiang Liu, Yingqian Liu and Peng Chen
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1390
Abstract
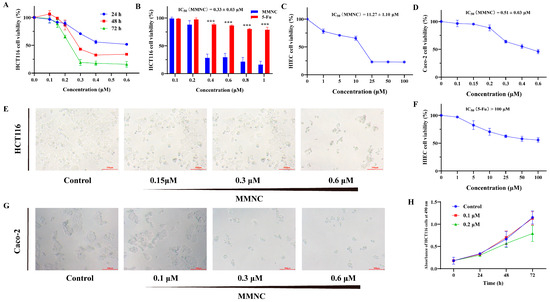
Chemotherapy is commonly used clinically to treat colorectal cancer, but it is usually prone to drug resistance, so novel drugs need to be developed continuously to treat colorectal cancer. Neocryptolepine derivatives have attracted a lot of attention because of their good cytotoxic activity;
[...] Read more.
Chemotherapy is commonly used clinically to treat colorectal cancer, but it is usually prone to drug resistance, so novel drugs need to be developed continuously to treat colorectal cancer. Neocryptolepine derivatives have attracted a lot of attention because of their good cytotoxic activity; however, cytotoxicity studies on colorectal cancer cells are scarce. In this study, the cytotoxicity of 8-methoxy-2,5-dimethyl-5H-indolo[2,3-b] quinoline (MMNC) in colorectal cells was evaluated. The results showed that MMNC inhibits the proliferation of HCT116 and Caco-2 cells, blocks the cell cycle in the G2/M phase, decreases the cell mitochondrial membrane potential and induces apoptosis. In addition, the results of western blot experiments suggest that MMNC exerts cytotoxicity by inhibiting the expression of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway-related proteins. Based on these results, MMNC is a promising lead compound for anticancer activity in the treatment of human colorectal cancer.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Synthesis and Characterisation of Fluorescent Novel Pt(II) Cyclometallated Complexes with Anticancer Activity
by
Brondwyn S. McGhie, Jennette Sakoff, Jayne Gilbert, Christopher P. Gordon and Janice R. Aldrich-Wright
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 1526
Abstract
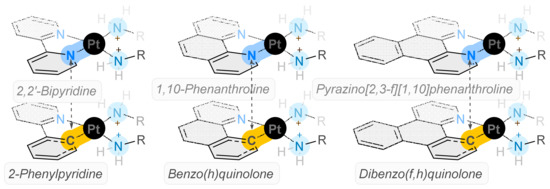
Cancer poses a significant threat to global health and new treatments are required to improve the prognosis for patients. Previously, unconventional platinum complexes designed to incorporate polypyridyl ligands paired with diaminocyclohexane have demonstrated anticancer activity in KRAS mutated cells, previously thought to be
[...] Read more.
Cancer poses a significant threat to global health and new treatments are required to improve the prognosis for patients. Previously, unconventional platinum complexes designed to incorporate polypyridyl ligands paired with diaminocyclohexane have demonstrated anticancer activity in KRAS mutated cells, previously thought to be undruggable and have cytotoxicity values up to 100 times better than cisplatin. In this work, these complexes were used as inspiration to design six novel cyclometallated examples, whose fluorescence could be exploited to better understand the mechanism of action of these kinds of platinum drugs. The cytotoxicity results revealed that these cyclometallated complexes (CMCs) have significantly different activity compared to the complexes that inspired them; they are as cytotoxic as cisplatin and have much higher selectivity indices in breast cancer cell lines (MCF10A/MCF-7). Complexes
1b,
2a, and
3b all had very high selectivity indexes compared to previous Pt(II) complexes. This prompted further investigation into their DNA binding properties, which revealed that they had good affinity to ctDNA, especially CMCs
1a and
3b. Their inherent fluorescence was successfully utilised in the calculation of their DNA binding affinity and could be useful in future work.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Addressing the Reciprocal Crosstalk between the AR and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathways for Prostate Cancer Treatment
by
Fabio Raith, Daniel H. O’Donovan, Clara Lemos, Oliver Politz and Bernard Haendler
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 5453
Abstract
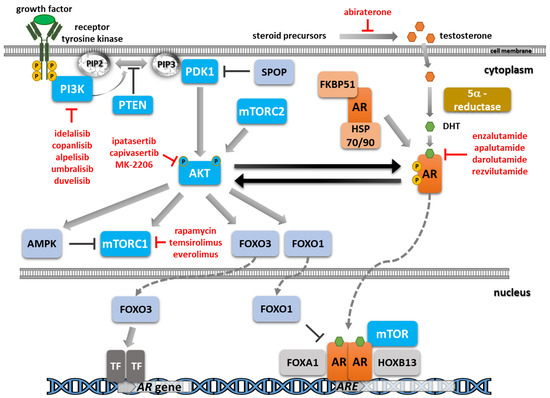
The reduction in androgen synthesis and the blockade of the androgen receptor (AR) function by chemical castration and AR signaling inhibitors represent the main treatment lines for the initial stages of prostate cancer. Unfortunately, resistance mechanisms ultimately develop due to alterations in the
[...] Read more.
The reduction in androgen synthesis and the blockade of the androgen receptor (AR) function by chemical castration and AR signaling inhibitors represent the main treatment lines for the initial stages of prostate cancer. Unfortunately, resistance mechanisms ultimately develop due to alterations in the AR pathway, such as gene amplification or mutations, and also the emergence of alternative pathways that render the tumor less or, more rarely, completely independent of androgen activation. An essential oncogenic axis activated in prostate cancer is the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway, as evidenced by the frequent alterations of the negative regulator phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) and by the activating mutations in PI3K subunits. Additionally, crosstalk and reciprocal feedback loops between androgen signaling and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling cascade that activate pro-survival signals and play an essential role in disease recurrence and progression have been evidenced. Inhibitors addressing different players of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway have been evaluated in the clinic. Only a limited benefit has been reported in prostate cancer up to now due to the associated side effects, so novel combination approaches and biomarkers predictive of patient response are urgently needed. Here, we reviewed recent data on the crosstalk between AR signaling and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, the selective inhibitors identified, and the most advanced clinical studies, with a focus on combination treatments. A deeper understanding of the complex molecular mechanisms involved in disease progression and treatment resistance is essential to further guide therapeutic approaches with improved outcomes.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A New Manganese Superoxide Dismutase Mimetic Improves Oxaliplatin-Induced Neuropathy and Global Tolerance in Mice
by
Caroline Prieux-Klotz, Henri Chédotal, Martha Zoumpoulaki, Sandrine Chouzenoux, Charlotte Chêne, Alvaro Lopez-Sanchez, Marine Thomas, Priya Ranjan Sahoo, Clotilde Policar, Frédéric Batteux, Hélène C. Bertrand, Carole Nicco and Romain Coriat
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2913
Abstract
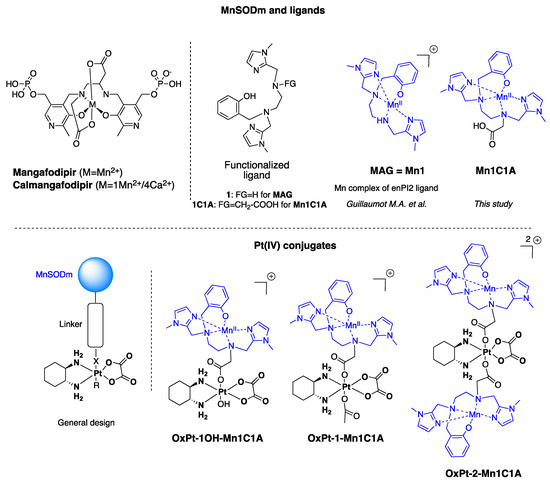
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are produced by every aerobic cell during mitochondrial oxidative metabolism as well as in cellular response to xenobiotics, cytokines, and bacterial invasion. Superoxide Dismutases (SOD) are antioxidant proteins that convert superoxide anions (O
2•−) to hydrogen peroxide
[...] Read more.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are produced by every aerobic cell during mitochondrial oxidative metabolism as well as in cellular response to xenobiotics, cytokines, and bacterial invasion. Superoxide Dismutases (SOD) are antioxidant proteins that convert superoxide anions (O
2•−) to hydrogen peroxide (H
2O
2) and dioxygen. Using the differential in the level of oxidative stress between normal and cancer cells, SOD mimetics can show an antitumoral effect and prevent oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy. New Pt(IV) conjugate prodrugs (OxPt-x-Mn1C1A (x = 1, 1-OH, 2)), combining oxaliplatin and a Mn SOD mimic (MnSODm Mn1C1A) with a covalent link, were designed. Their stability in buffer and in the presence of sodium ascorbate was studied. In vitro, their antitumoral activity was assessed by the viability and ROS production of tumor cell lines (CT16, HCT 116, KC) and fibroblasts (primary culture and NIH 3T3). In vivo, a murine model of colorectal cancer was created with subcutaneous injection of CT26 cells in Balb/c mice. Tumor size and volume were measured weekly in four groups: vehicle, oxaliplatin, and oxaliplatin associated with MnSODm Mn1C1A and the bis-conjugate OxPt-2-Mn1C1A. Oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy (OIPN) was assessed using a Von Frey test reflecting chronic hypoalgesia. Tolerance to treatment was assessed with a clinical score including four items: weight loss, weariness, alopecia, and diarrhea. In vitro, Mn1C1A associated with oxaliplatin and Pt(IV) conjugates treatment induced significantly higher production of H
2O
2 in all cell lines and showed a significant improvement of the antitumoral efficacy compared to oxaliplatin alone. In vivo, the association of Mn1C1A to oxaliplatin did not decrease its antitumoral activity, while OxPt-2-Mn1C1A had lower antitumoral activity than oxaliplatin alone. Mn1C1A associated with oxaliplatin significantly decreased OIPN and also improved global clinical tolerance of oxaliplatin. A neuroprotective effect was observed, associated with a significantly improved tolerance to oxaliplatin without impairing its antitumoral activity.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
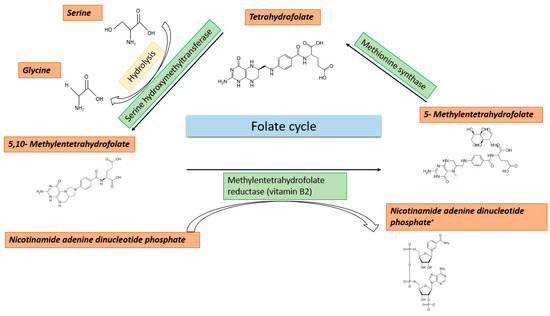
Methyl Group Metabolism in Differentiation, Aging, and Cancer
by
Lars Erichsen, Chantelle Thimm and Simeon Santourlidis
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 3358
Abstract
Methyl group metabolism belongs to a relatively understudied field of research. Its importance lies in the fact that methyl group metabolic pathways are crucial for the successful conversion of dietary nutrients into the basic building blocks to carry out any cellular methylation reaction.
[...] Read more.
Methyl group metabolism belongs to a relatively understudied field of research. Its importance lies in the fact that methyl group metabolic pathways are crucial for the successful conversion of dietary nutrients into the basic building blocks to carry out any cellular methylation reaction. Methyl groups play essential roles in numerous cellular functions such as DNA methylation, nucleotide- and protein biosynthesis. Especially, DNA methylation is responsible for organizing the genome into transcriptionally silent and active regions. Ultimately, it is this proper annotation that determines the quality of expression patterns required to ensure and shape the phenotypic integrity and function of a highly specialized cell type. Life is characterized by constantly changing environmental conditions, which are addressed by changes in DNA methylation. This relationship is increasingly coming into focus as it is of fundamental importance for differentiation, aging, and cancer. The stability and permanence of these metabolic processes, fueling the supplementation of methyl groups, seem to be important criteria to prevent deficiencies and erosion of the methylome. Alterations in the metabolic processes can lead to epigenetic and genetic perturbations, causative for diverse disorders, accelerated aging, and various age-related diseases. In recent decades, the intake of methyl group compounds has changed significantly due to, e.g., environmental pollution and food additives. Based on the current knowledge, this review provides a brief overview of the highly interconnected relationship between nutrition, metabolism, changes in epigenetic modifications, cancer, and aging. One goal is to provide an impetus to additionally investigate changes in DNA methylation as a possible consequence of an impaired methyl group metabolism.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
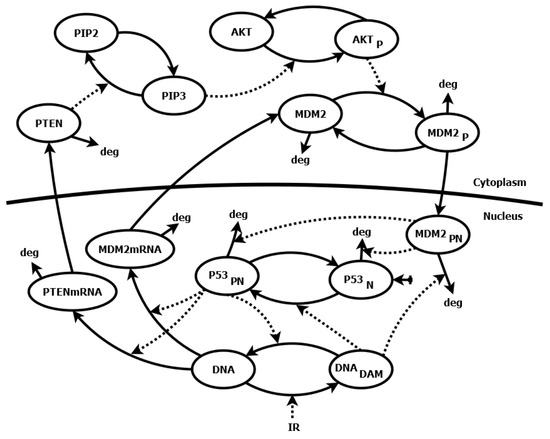
Application of Sensitivity Analysis to Discover Potential Molecular Drug Targets
by
Malgorzata Kardynska, Jaroslaw Smieja, Pawel Paszek and Krzysztof Puszynski
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 1992
Abstract
Mathematical modeling of signaling pathways and regulatory networks has been supporting experimental research for some time now. Sensitivity analysis, aimed at finding model parameters whose changes yield significantly altered cellular responses, is an important part of modeling work. However, sensitivity methods are often
[...] Read more.
Mathematical modeling of signaling pathways and regulatory networks has been supporting experimental research for some time now. Sensitivity analysis, aimed at finding model parameters whose changes yield significantly altered cellular responses, is an important part of modeling work. However, sensitivity methods are often directly transplanted from analysis of technical systems, and thus, they may not serve the purposes of analysis of biological systems. This paper presents a novel sensitivity analysis method that is particularly suited to the task of searching for potential molecular drug targets in signaling pathways. Using two sample models of pathways, p53/Mdm2 regulatory module and IFN-
-induced JAK/STAT signaling pathway, we show that the method leads to biologically relevant conclusions, identifying processes suitable for targeted pharmacological inhibition, represented by the reduction of kinetic parameter values. That, in turn, facilitates subsequent search for active drug components.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
New Potential Agents for Malignant Melanoma Treatment—Most Recent Studies 2020–2022
by
Paweł Kozyra, Danuta Krasowska and Monika Pitucha
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 3400
Abstract
Malignant melanoma (MM) is the most lethal skin cancer. Despite a 4% reduction in mortality over the past few years, an increasing number of new diagnosed cases appear each year. Long-term therapy and the development of resistance to the drugs used drive the
[...] Read more.
Malignant melanoma (MM) is the most lethal skin cancer. Despite a 4% reduction in mortality over the past few years, an increasing number of new diagnosed cases appear each year. Long-term therapy and the development of resistance to the drugs used drive the search for more and more new agents with anti-melanoma activity. This review focuses on the most recent synthesized anti-melanoma agents from 2020–2022. For selected agents, apart from the analysis of biological activity, the structure–activity relationship (SAR) is also discussed. To the best of our knowledge, the following literature review delivers the latest achievements in the field of new anti-melanoma agents.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
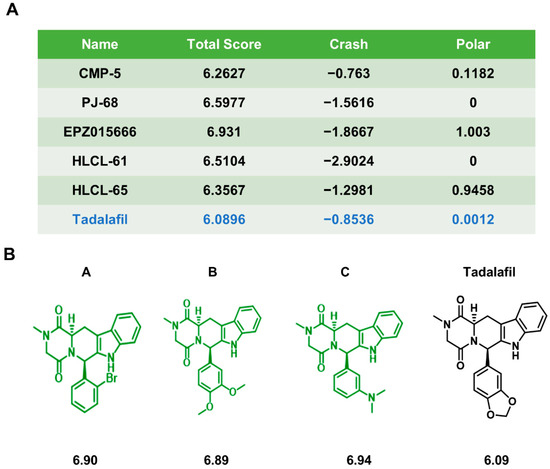
Open AccessArticle
Novel Chemicals Derived from Tadalafil Exhibit PRMT5 Inhibition and Promising Activities against Breast Cancer
by
Ziyan Yang, Tian Xiao, Zezhi Li, Jian Zhang and Suning Chen
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 2900
Abstract
Breast cancer seriously endangers women’s health worldwide. Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) is highly expressed in breast cancer and represents a potential druggable target for breast cancer treatment. However, because the currently available clinical PRMT5 inhibitors are relatively limited, there is an urgent
[...] Read more.
Breast cancer seriously endangers women’s health worldwide. Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) is highly expressed in breast cancer and represents a potential druggable target for breast cancer treatment. However, because the currently available clinical PRMT5 inhibitors are relatively limited, there is an urgent need to develop new PRMT5 inhibitors. Our team previously found that the FDA-approved drug tadalafil can act as a PRMT5 inhibitor and enhance the sensitivity of breast cancer patients to doxorubicin treatment. To further improve the binding specificity of tadalafil to PRMT5, we chemically modified tadalafil, and designed three compounds, A, B, and C, based on the PRMT5 protein structure. These three compounds could bind to PRMT5 through different binding modes and inhibit histone arginine methylation. They arrested the proliferation and triggered the apoptosis of breast cancer cells in vitro and also promoted the antitumor effects of the chemotherapy drugs cisplatin, doxorubicin, and olaparib in combination regimens. Among them, compound A possessed the highest potency. Finally, the anti-breast cancer effects of PRMT5 inhibitor A and its ability to enhance chemosensitivity were further verified in a xenograft mouse model. These results indicate that the new PRMT5 inhibitors A, B, and C may be potential candidates for breast cancer treatment.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
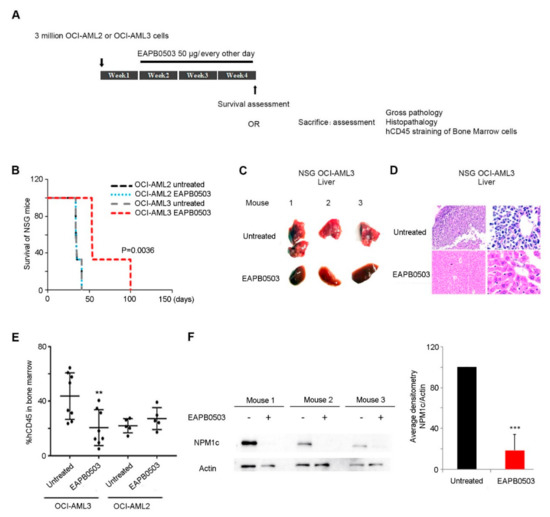
Open AccessArticle
EAPB0503, an Imidazoquinoxaline Derivative Modulates SENP3/ARF Mediated SUMOylation, and Induces NPM1c Degradation in NPM1 Mutant AML
by
Hala Skayneh, Batoul Jishi, Rita Hleihel, Maguy Hamie, Rana El Hajj, Carine Deleuze-Masquefa, Pierre-Antoine Bonnet, Marwan El Sabban and Hiba El Hajj
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 3135
Abstract
Nucleophosmin-1 (NPM1) is a pleiotropic protein involved in numerous cellular processes. NPM1 shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm, but exhibits a predominant nucleolar localization, where its fate and functions are exquisitely controlled by dynamic post-translational modifications (PTM). Sentrin/SUMO Specific Peptidase 3 (SENP3)
[...] Read more.
Nucleophosmin-1 (NPM1) is a pleiotropic protein involved in numerous cellular processes. NPM1 shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm, but exhibits a predominant nucleolar localization, where its fate and functions are exquisitely controlled by dynamic post-translational modifications (PTM). Sentrin/SUMO Specific Peptidase 3 (SENP3) and ARF are two nucleolar proteins involved in NPM1 PTMs. SENP3 antagonizes ARF-mediated NPM1 SUMOylation, to promote ribosomal biogenesis. In Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML), NPM1 is frequently mutated, and exhibits an aberrant cytoplasmic localization (NPM1c). NPM1c mutations define a separate AML entity with good prognosis in some AML patients, rendering NPM1c as a potential therapeutic target. SENP3-mediated NPM1 de-SUMOylation induces resistance to therapy in NPM1c AML. Here, we demonstrate that the imidazoquinoxaline EAPB0503 prolongs the survival and results in selective reduction in the leukemia burden of NPM1c AML xenograft mice. Indeed, EAPB0503 selectively downregulates HDM2 expression and activates the
p53 pathway in NPM1c expressing cells, resulting in apoptosis. Importantly, we unraveled that NPM1c expressing cells exhibit low basal levels of SUMOylation paralleled with high SENP3 and low ARF basal levels. EAPB0503 reverted these molecular players by inducing NPM1c SUMOylation and ubiquitylation, leading to its proteasomal degradation. EAPB0503-induced NPM1c SUMOylation is concurrent with SENP3 downregulation and ARF upregulation in NPM1c expressing cells. Collectively, these results provide a strong rationale for testing therapies modulating NPM1c post-translational modifications in the management of NPM1c AML.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
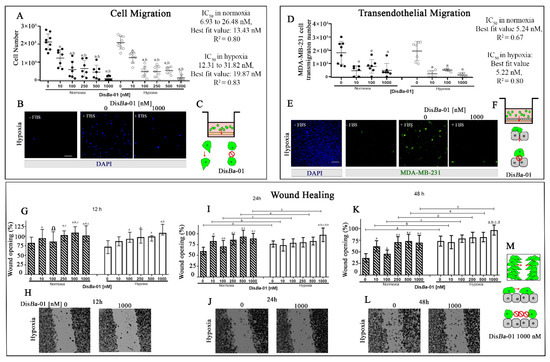
The Effects of αvβ3 Integrin Blockage in Breast Tumor and Endothelial Cells under Hypoxia In Vitro
by
Bruna C. Casali, Larissa T. Gozzer, Matheus P. Baptista, Wanessa F. Altei and Heloisa S. Selistre-de-Araújo
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 3656
Abstract
Breast cancer is characterized by a hypoxic microenvironment inside the tumor mass, contributing to cell metastatic behavior. Hypoxia induces the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1α), a transcription factor for genes involved in angiogenesis and metastatic behavior, including the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF),
[...] Read more.
Breast cancer is characterized by a hypoxic microenvironment inside the tumor mass, contributing to cell metastatic behavior. Hypoxia induces the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1α), a transcription factor for genes involved in angiogenesis and metastatic behavior, including the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), and integrins. Integrin receptors play a key role in cell adhesion and migration, being considered targets for metastasis prevention. We investigated the migratory behavior of hypoxia-cultured triple-negative breast cancer cells (TNBC) and endothelial cells (HUVEC) upon αvβ3 integrin blocking with Dis
Ba-01, an RGD disintegrin with high affinity to this integrin. Boyden chamber, HUVEC transmigration, and wound healing assays in the presence of Dis
Ba-01 were performed in hypoxic conditions. Dis
Ba-01 produced similar effects in the two oxygen conditions in the Boyden chamber and transmigration assays. In the wound healing assay, hypoxia abolished Dis
Ba-01′s inhibitory effect on cell motility and decreased the MMP-9 activity of conditioned media. These results indicate that αvβ3 integrin function in cell motility depends on the assay and oxygen levels, and higher inhibitor concentrations may be necessary to achieve the same inhibitory effect as in normoxia. These versatile responses add more complexity to the role of the αvβ3 integrin during tumor progression.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
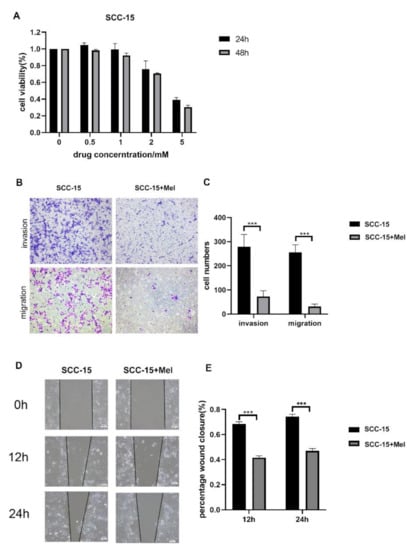
Melatonin Suppresses Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas Migration and Invasion through Blocking FGF19/FGFR 4 Signaling Pathway
by
Leilei Wang, Yuxiong Su and Wing Shan Choi
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 2669
Abstract
Oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCCs) are one of the most prevalent malignancies, with a low five-year survival rate, thus warranting more effective drugs or therapy to improve treatment outcomes. Melatonin has been demonstrated to exhibit oncostatic effects. In this study, we explored the
[...] Read more.
Oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCCs) are one of the most prevalent malignancies, with a low five-year survival rate, thus warranting more effective drugs or therapy to improve treatment outcomes. Melatonin has been demonstrated to exhibit oncostatic effects. In this study, we explored the anti-cancer effects of melatonin on OSCCs and the underlying mechanisms. A human tongue squamous cell carcinoma cell line (SCC-15) was treated with 2 mM melatonin, followed by transwell migration and invasion assays. Relative expression levels of Fibroblast Growth Factor 19 (FGF19) was identified by Cytokine Array and further verified by qPCR and Western blot. Overexpression and downregulation of FGF19 were obtained by adding exogenous hFGF19 and FGF19 shRNA lentivirus, respectively. Invasion and migration abilities of SCC-15 cells were suppressed by melatonin, in parallel with the decreased FGF19/FGFR4 expression level. Exogenous hFGF19 eliminated the inhibitory effects of melatonin on SCC-15 cells invasion and migration, while FGF19 knocking-down showed similar inhibitory activities with melatonin. This study proves that melatonin suppresses SCC-15 cells invasion and migration through blocking the FGF19/FGFR4 pathway, which enriches our knowledge on the anticancer effects of melatonin. Blocking the FGF19/FGFR4 pathway by melatonin could be a promising alternative for OSCCs prevention and management, which would facilitate further development of novel strategies to combat OSCCs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
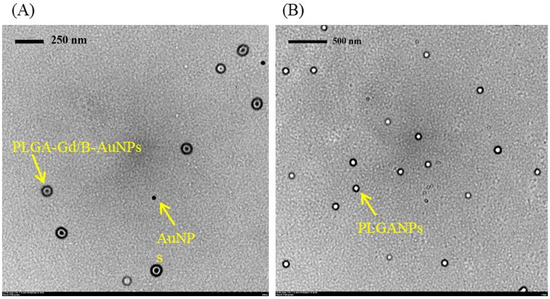
Development of MRI-Detectable Boron-Containing Gold Nanoparticle-Encapsulated Biodegradable Polymeric Matrix for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT)
by
Chun-Yi Wu, Hsin-Hua Hsieh, Ting-Yu Chang, Jia-Jia Lin, Chin-Ching Wu, Ming-Hua Hsu, Ming-Chia Lin and Shin-Lei Peng
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 3142
Abstract
This study aimed to develop a novel magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-detectable boron (B)-containing nanoassemblies and evaluate their potential for boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT). Starting from the citrate-coated gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) (23.9 ± 10.2 nm), the diameter of poly (D, L-lactide-co-glycolide) AuNPs (PLGA-AuNPs)
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to develop a novel magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-detectable boron (B)-containing nanoassemblies and evaluate their potential for boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT). Starting from the citrate-coated gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) (23.9 ± 10.2 nm), the diameter of poly (D, L-lactide-co-glycolide) AuNPs (PLGA-AuNPs) increased approximately 110 nm after the encapsulation of the PLGA polymer. Among various B drugs, the self-produced B cages had the highest loading efficiency. The average diameter of gadolinium (Gd)- and B-loaded NPs (PLGA-Gd/B-AuNPs) was 160.6 ± 50.6 nm with a B encapsulation efficiency of 28.7 ± 2.3%. In vitro MR images showed that the signal intensity of PLGA-Gd/B-AuNPs in T1-weighted images was proportional to its Gd concentration, and there exists a significantly positive relationship between Gd and B concentrations (
R2 = 0.74,
p < 0.005). The hyperintensity of either 250 ± 50 mm
3 (larger) or 100 ± 50 mm
3 (smaller) N87 xenograft was clearly visualized at 1 h after intravenous injection of PLGA-Gd/B-AuNPs. However, PLGA-Gd/B-AuNPs stayed at the periphery of the larger xenograft while located near the center of the smaller one. The tumor-to-muscle ratios of B content, determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, in smaller- and larger-sized tumors were 4.17 ± 1.42 and 1.99 ± 0.55, respectively. In summary, we successfully developed theranostic B- and Gd-containing AuNPs for BNCT in this study.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
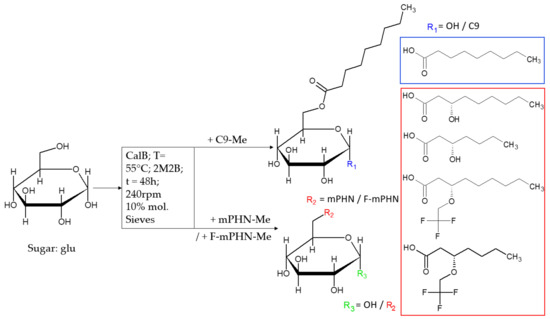
In Search of Effective Anticancer Agents—Novel Sugar Esters Based on Polyhydroxyalkanoate Monomers
by
Wojciech Snoch, Dawid Wnuk, Tomasz Witko, Jakub Staroń, Andrzej J. Bojarski, Ewelina Jarek, Francisco J. Plou and Maciej Guzik
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 3345
Abstract
Cancer is one of the deadliest illness globally. Searching for new solutions in cancer treatments is essential because commonly used mixed, targeted and personalized therapies are sometimes not sufficient or are too expensive for common patients. Sugar fatty acid esters (SFAEs) are already
[...] Read more.
Cancer is one of the deadliest illness globally. Searching for new solutions in cancer treatments is essential because commonly used mixed, targeted and personalized therapies are sometimes not sufficient or are too expensive for common patients. Sugar fatty acid esters (SFAEs) are already well-known as promising candidates for an alternative medical tool. The manuscript brings the reader closer to methods of obtaining various SFAEs using combined biological, chemical and enzymatic methods. It presents how modification of SFAE’s hydrophobic chains can influence their cytotoxicity against human skin melanoma and prostate cancer cell lines. The compound’s cytotoxicity was determined by an MTT assay, which followed an assessment of SFAEs’ potential metastatic properties in concentrations below IC
50 values. Despite relatively high IC
50 values (63.3–1737.6 μM) of the newly synthesized SFAE, they can compete with other sugar esters already described in the literature. The chosen bioactives caused low polymerization of microtubules and the depolymerization of actin filaments in nontoxic levels, which suggest an apoptotic rather than metastatic process. Altogether, cancer cells showed no propensity for metastasis after treating them with SFAE. They confirmed that lactose-based compounds seem the most promising surfactants among tested sugar esters. This manuscript creates a benchmark for creation of novel anticancer agents based on 3-hydroxylated fatty acids of bacterial origin.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
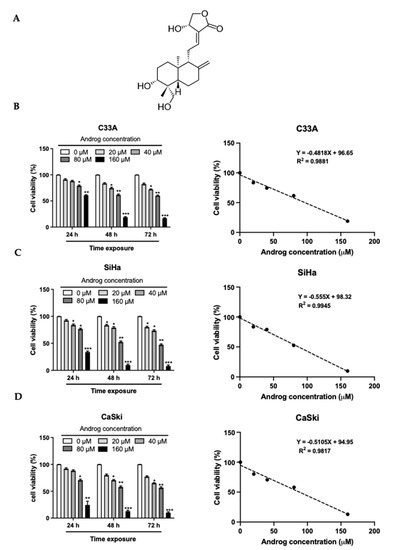
Proteomics Analysis of Andrographolide-Induced Apoptosis via the Regulation of Tumor Suppressor p53 Proteolysis in Cervical Cancer-Derived Human Papillomavirus 16-Positive Cell Lines
by
Pariyakorn Udomwan, Chamsai Pientong, Panwad Tongchai, Ati Burassakarn, Nuchsupha Sunthamala, Sittiruk Roytrakul, Supawadee Suebsasana and Tipaya Ekalaksananan
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 3161
Abstract
Regardless of the prophylactic vaccine accessibility, persistent infections of high-risk human papillomaviruses (hr-HPVs), recognized as an etiology of cervical cancers, continues to represent a major health problem for the world population. An overexpression of viral early protein 6 (E6) is linked to carcinogenesis.
[...] Read more.
Regardless of the prophylactic vaccine accessibility, persistent infections of high-risk human papillomaviruses (hr-HPVs), recognized as an etiology of cervical cancers, continues to represent a major health problem for the world population. An overexpression of viral early protein 6 (E6) is linked to carcinogenesis. E6 induces anti-apoptosis by degrading tumor suppressor proteins p53 (p53) via E6-E6-associated protein (E6AP)-mediated polyubiquitination. Thus, the restoration of apoptosis by interfering with the E6 function has been proposed as a selective medicinal strategy. This study aimed to determine the activities of andrographolide (Androg) on the disturbance of E6-mediated p53 degradation in cervical cancer cell lines using a proteomic approach. These results demonstrated that Androg could restore the intracellular p53 level, leading to apoptosis-induced cell death in HPV16-positive cervical cancer cell lines, SiHa and CaSki. Mechanistically, the anti-tumor activity of Androg essentially relied on the reduction in host cell proteins, which are associated with ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis pathways, particularly HERC4 and SMURF2. They are gradually suppressed in Androg-treated HPV16-positive cervical cancer cells. Collectively, the restoration of p53 in HPV16-positive cervical cancer cells might be achieved by disruption of E3 ubiquitin ligase activity by Androg, which could be an alternative treatment for HPV-associated epithelial lesions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
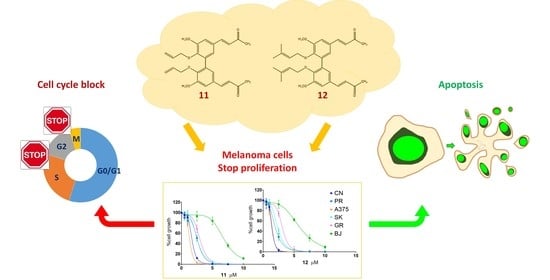
Anticancer Activity of Two Novel Hydroxylated Biphenyl Compounds toward Malignant Melanoma Cells
by
Marina Pisano, Maria Antonietta Dettori, Davide Fabbri, Giovanna Delogu, Giuseppe Palmieri and Carla Rozzo
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 2753
Abstract
Melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, is still one of the most difficult cancers to treat despite recent advances in targeted and immune therapies. About 50% of advanced melanoma do not benefit of such therapies, and novel treatments are requested. Curcumin and
[...] Read more.
Melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, is still one of the most difficult cancers to treat despite recent advances in targeted and immune therapies. About 50% of advanced melanoma do not benefit of such therapies, and novel treatments are requested. Curcumin and its analogs have shown good anticancer properties and are being considered for use in combination with or sequence to recent therapies to improve patient outcomes. Our group previously published the synthesis and anticancer activity characterization of a novel curcumin-related compound against melanoma and neuroblastoma cells (D6). Here, two hydroxylated biphenyl compounds—namely, compounds
11 and
12—were selected among a small collection of previously screened C2-symmetric hydroxylated biphenyls structurally related to D6 and curcumin, showing the best antitumor potentiality against melanoma cells (IC
50 values of 1.7 ± 0.5 μM for
11 and 2.0 ± 0.7 μM for
12) and no toxicity of normal fibroblasts up to 32 µM. Their antiproliferative activity was deeply characterized on five melanoma cell lines by performing dose-response and clonal growth inhibition assays, which revealed long-lasting and irreversible effects for both compounds. Apoptosis induction was ascertained by the annexin V and TUNEL assays, whereas Western blotting showed caspase activation and PARP cleavage. A cell cycle analysis, following cell treatments with either compound
11 or
12, highlighted an arrest in the G2/M transition. Taking all this evidence together,
11 and
12 were shown to be good candidates as lead compounds to develop new anticancer drugs against malignant melanoma.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures