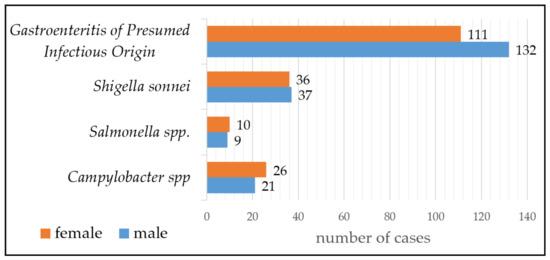
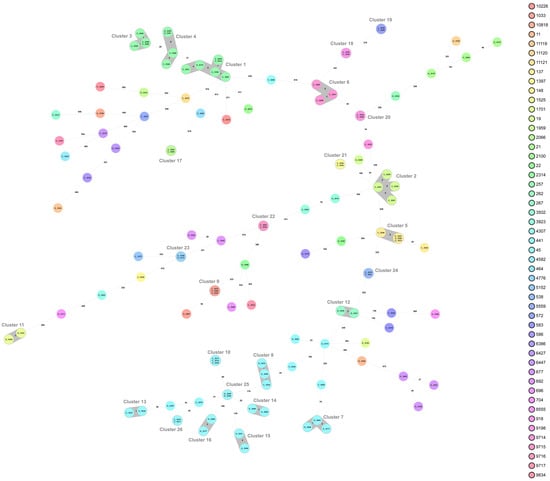
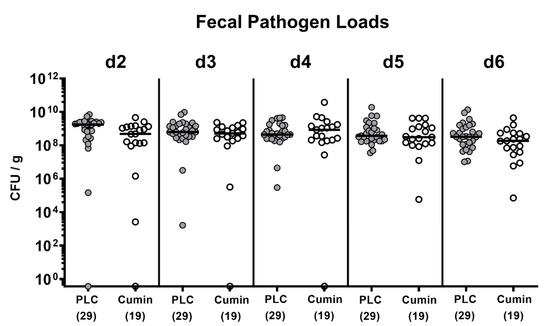
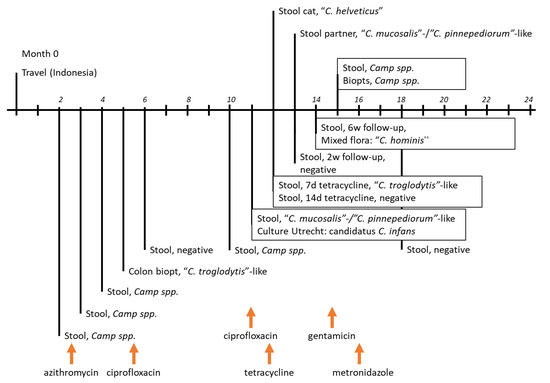
Campylobacter Infections Collection
A topical collection in Pathogens (ISSN 2076-0817). This collection belongs to the section "Bacterial Pathogens".
Viewed by 29295Editors
Interests: Campylobacter; epidemiology; prevention and control; reservoirs; diagnostics; pathogenicity
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: Campylobacter; campylobacteriosis; epidemiology; molecular typing; virulence factors; control strategies
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Campylobacter spp. are Gram-negative microaerobic bacteria that are sensitive to desiccation, high/low temperatures, and have specific growth requirements. Transport, handling, and analysis of samples for Campylobacter are cumbersome, and conventional methods used for many other bacteria are usually not applicable. Campylobacter infection in humans, campylobacteriosis, is a zoonosis and the most frequent cause of foodborne bacterial enteritis in humans worldwide. The incidence varies among countries, and the true incidence of campylobacteriosis is largely unknown. Poultry and poultry products are considered the most important sources of human infections, but other sources exist. The mechanisms behind the pathogenicity of Campylobacter still have to be clarified. The reservoirs, sources, and transmission routes need to be further investigated in order to understand the ecology and epidemiology of Campylobacter. Despite the vast amount of research and surveillance done in the last few decades, further development of various tools for the detection and control of Campylobacter is required in order to prevent campylobacteriosis in humans. For this Topical Collection of Pathogens, we invite you to submit a review or research article related to Campylobacter infections. We look forward to your contribution.
Potential topics include but are not limited to:
- Pathogenicity and virulence factors;
- Antimicrobial resistance in Campylobacter;
- Vaccine development;
- Other control strategies for reducing Campylobacter in the food chain;
- Role of non-jejuni/coli Campylobacter infections in humans;
- Survival in the environment, for example, in biofilms.
Dr. Ingrid Hansson
Dr. Eva Olsson Engvall
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Pathogens is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2200 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Campylobacter
- campylobacteriosis
- control
- ecology
- epidemiology
- diagnostics
- pathogenesis
- prevention
- reservoirs
- vaccine
Related Special Issue
- Campylobacter Infections in Pathogens (14 articles)