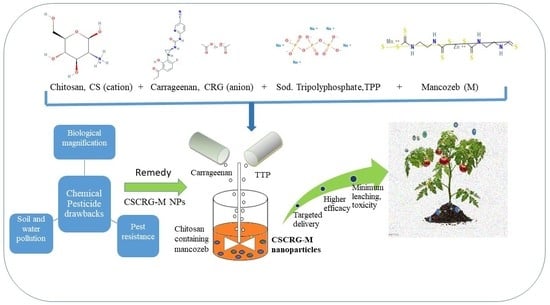
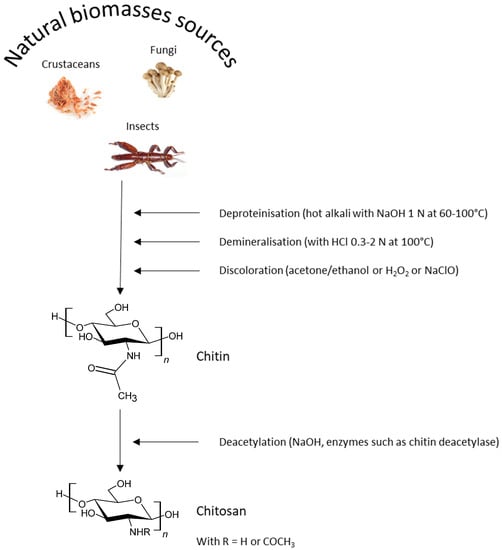
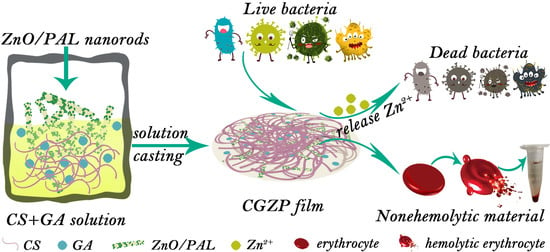
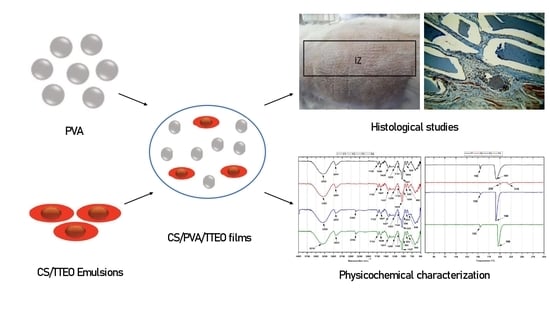
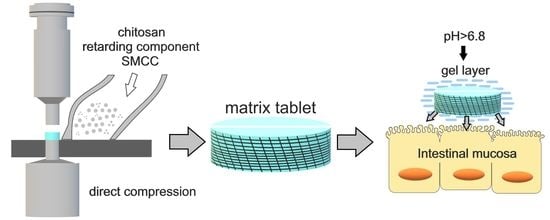
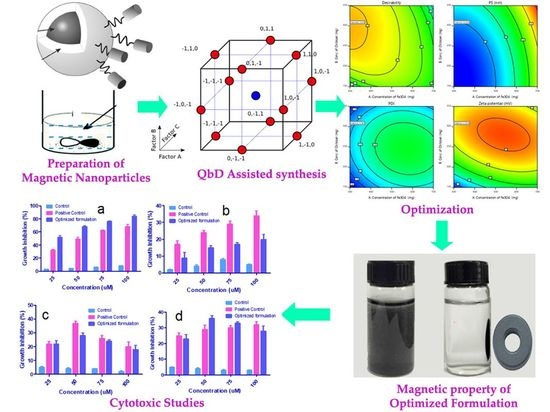
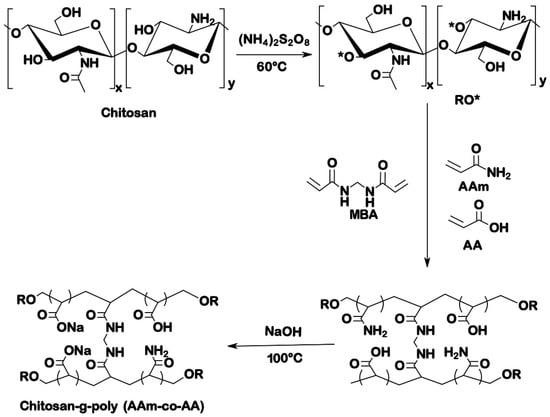
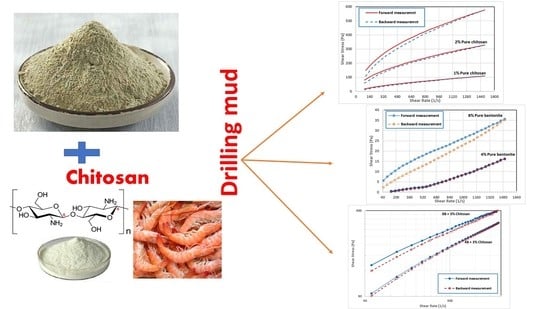
Chitosan and its Derivatives: Structure, Properties, and Applications (Closed)
A topical collection in Polymers (ISSN 2073-4360). This collection belongs to the section "Biobased and Biodegradable Polymers".
Viewed by 18668Editor
Interests: synthesis and characterization of polyesters; development of biobased polymers; biodegradable polymers; polymer composites and nanocomposites; synthesis and characterization of copolymers; polymer blends; recycling of polymers with various techniques; enzymatic hydrolysis studies; modification of natural polymers; polymer for wastewater treatment pollutant removal; polymers for tissue engineering and drug delivery applications; drug–polymer solid dispersions; drug targeting; drug nanoencapsulation and microencapsulation
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
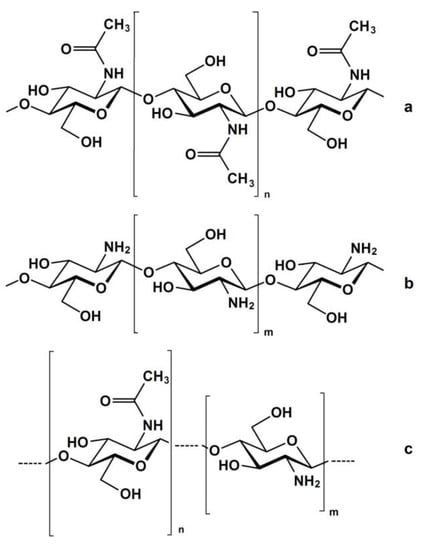
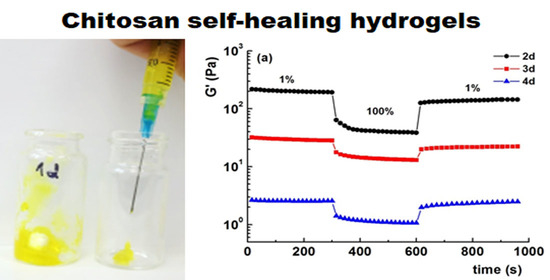
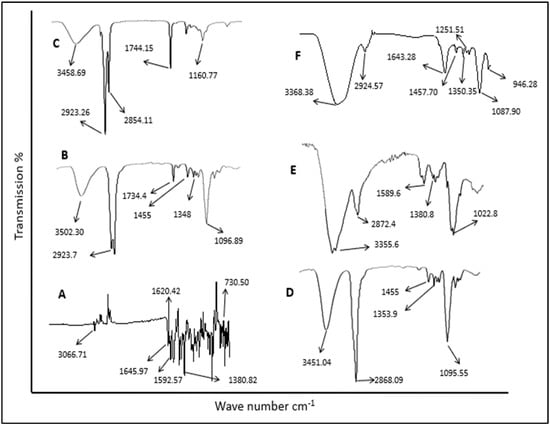
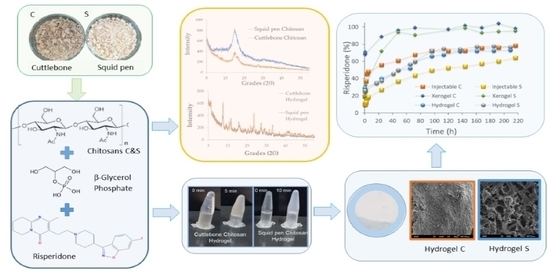
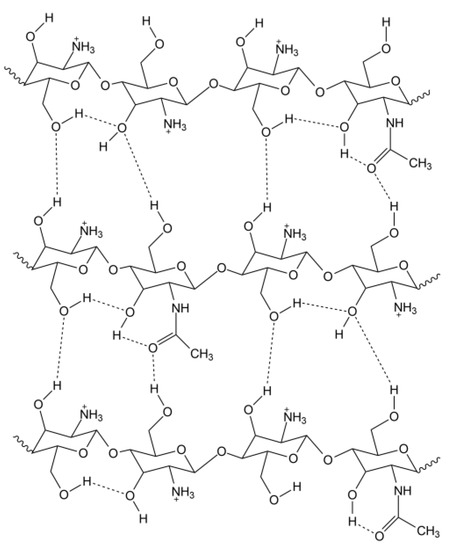
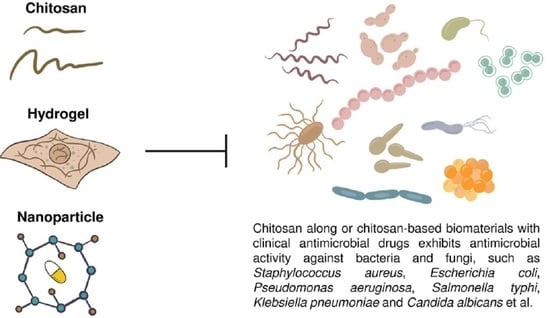
Chitosan (CS) is a hemi-synthetic cationic linear polysaccharide consisting of randomly distributed D-glucosamine and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine units, linked via β-(1→4) glycosidic bonds. It is synthesized by the deacetylation of chitin, which is a naturally occurring polysaccharide. CS is water-soluble only in weakly acidic pH (>4.5) due to the protonation of its free amino groups. It is an easily accessible polymer, but most importantly it is non-toxic, highly biocompatible and biodegradable, stable and sterilizable, and with low immunogenicity. CS has a unique hydrophilic character since, along with its polymeric chains, it also contains free water-loving hydroxyl and amino groups, which can be used for its chemical modification. This is an additional crucial advantage, allowing for easy tuning of its physicochemical properties, leading to functionalized derivatives with desired and appropriate features for several applications (biotechnology, medicine, membranes, cosmetics, food industry, etc.).
CS has inherent antibacterial and mucoadhesive properties, and a gel-forming ability, also acting as a permeation enhancer in some cases. Due to these characteristics, CS is an excellent candidate for pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and biomedical applications (micro and nanoparticles, films, membranes, sponges, gels, etc.,) and several CS-containing products have already been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. It has been extensively used as a single polymer matrix in several drug delivery systems, including oral administration routes, the micro-/nano-encapsulation of drugs for ocular and nasal delivery, and the topical and transdermal delivery systems in the form of patches or gels.
CS and its derivatives have been widely used in regenerative medicine for the development of versatile scaffolds for tissue engineering applications and the preparation of artificial tissues and organs (bones, teeth, cartilage, joints, blood vessels, nerves, skin, etc.).
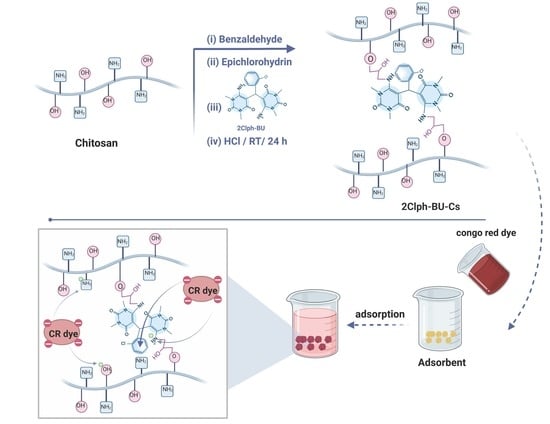
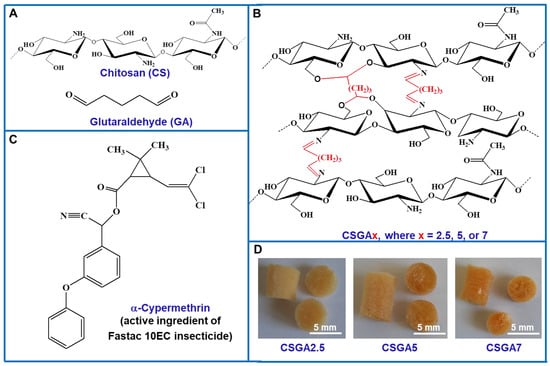
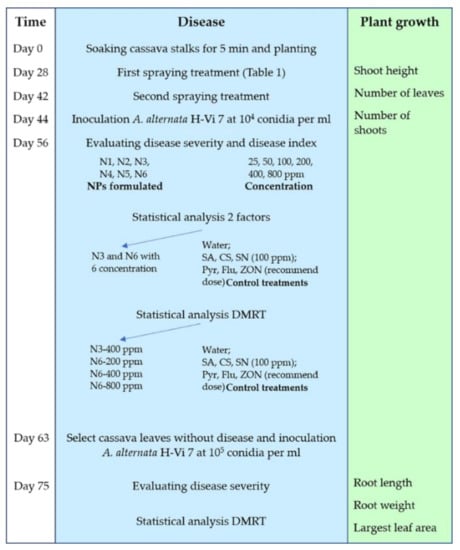
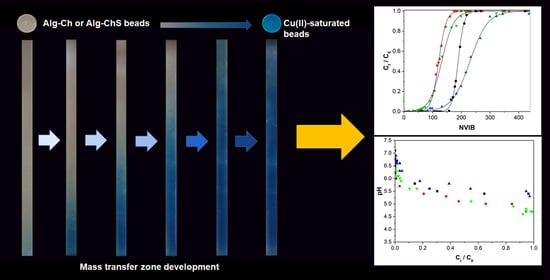
Due to its functional groups, chitosan and/or its appropriately modified derivatives can be used as a flocculant/coagulant or bioabsorbent in wastewater treatment removing several pollutants such as heavy metal ions, organochloride pesticides, textile wastewater dyes, drugs, fatty and oil impurities, etc., or in drinking water purification.
Composites and nanocomposites of chitosan, and various natural or synthetic polymer chitosan blends are also of high interest for several applications.
Papers exploring the processing of chitosan and its derivatives, their properties, physical and chemical characterization, and their applications are welcome in this Topical Collection.
Prof. Dr. Dimitrios Bikiaris
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Polymers is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- chitosan
- polysaccharide
- natural polymer
- biobased
- biodegradable polymer
- chitosan derivatives
- nanocomposites
- blends
- drug delivery applications
- biomedical applications
- tissue engineering applications
- wastewater treatment
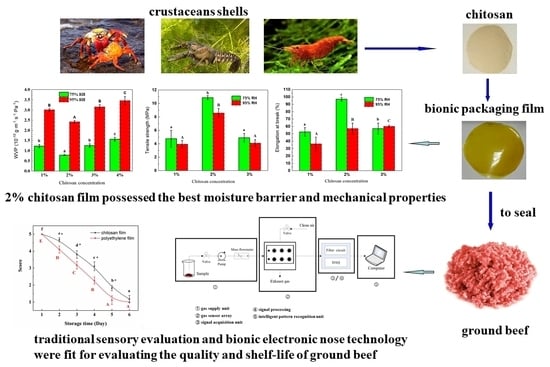
- food industry
Related Special Issues
- Functional Chitosan-Based Composites II in Polymers (12 articles - displayed below)
- Chitosan and Chitosan Derivatives in Biomedical Applications in Polymers (17 articles - displayed below)
- Functional Chitosan-Based Materials in Polymers (6 articles - displayed below)
- Chitosan, Chitin, and Cellulose Nanofiber Biomaterials in Polymers (11 articles - displayed below)