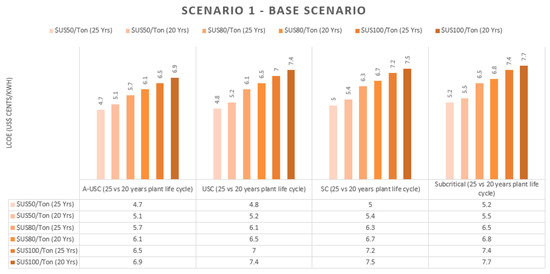
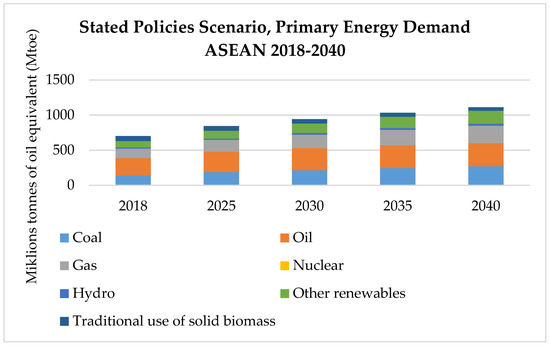
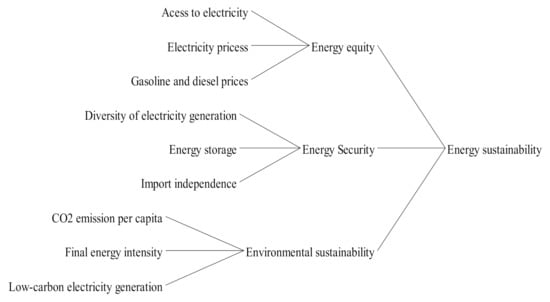
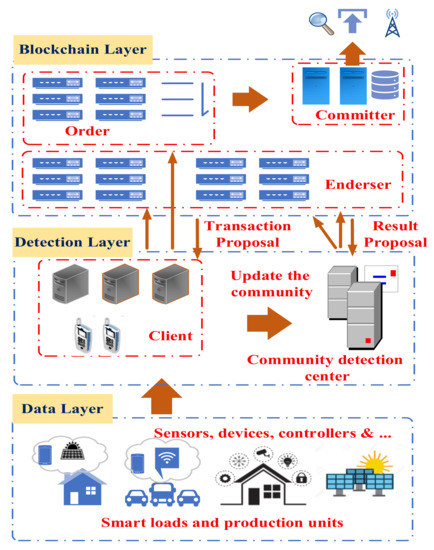
Secure and Sustainable Energy System
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Energy Sustainability".
Viewed by 92180Editors
Interests: energy policy; energy finance; green finance; sustainability; banking and finance
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: energy policy; energy finance; green finance; sustainability; banking and finance
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Alarming reports from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) have shown that climate change is a pressing matter that needs to be addressed, and in 2015, United Nations (UN) members agreed upon keeping global warming below 2°C through their Nationally Determined Contribution. The UN also acknowledged the matter by adding ‘Climate Action’ as one of their Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Yet, IPCC and the UN Environment Programme (UNEP) reports keep highlighting that further actions need to be taken to reach this goal and fulfill SDGs. Increasing the share of sustainable energy resources in the energy baskets would not only reduce Green House Gas (GHG) emissions — in line with the SDGs and the Paris Agreement — but would also increase energy security (Taghizadeh et al. 2019).
Several developed and developing economies are still following pro-fossil fuel energy policies, and the extra GHG generated by new coal-fired power plants could more than wipe out any reductions in emissions made by other nations. One of the biggest barriers in the development of sustainable energy system is the low level of investment (Sachs, Woo, Yoshino, and Taghizadeh-Hesary, 2019). The lack of long‐term financing, the low rate of return, the existence of various risks, and the lack of capacity of market players are major challenges for the development of sustainable energy systems. (Taghizadeh-Hesary and Yoshino, 2019; 2020).
With this background, this Special Issue aims to collect high-quality, unpublished, empirical case studies or thematic studies that assess the challenges for the development of secure and sustainable energy systems and provide practical policy recommendations. Empirical studies need to be developed based on well-established theoretical frameworks. Papers needs to be prepared based on the “Sustainability” guideline for the authors.
Guest Editors,
Reference:
Sachs J.D., Woo W.T., Yoshino N., Taghizadeh-Hesary F. (2019) Importance of Green Finance for Achieving Sustainable Development Goals and Energy Security. Handbook of Green Finance. Energy Security and Sustainable Development. Sachs J.D., Woo W.T., Yoshino N., Taghizadeh-Hesary F. (eds.), Tokyo: Springer
Taghizadeh-Hesary, F., Yoshino, N., Chang, Y., Rillo, A.D. (2019). Introduction. Achieving Energy Security in Asia: Diversification, Integration and Policy Implications. F. Taghizadeh-Hesary, N. Yoshino, Y. Chang, A.D. Rillo (eds.) Singapore: World Scientific
Taghizadeh-Hesary F., Yoshino N. (2019). The way to induce private participation in green finance and investment, Finance Research Letters, 31: 98-103
Taghizadeh-Hesary, F.; Yoshino, N. (2020). Sustainable Solutions for Green Financing and Investment in Renewable Energy Projects. Energies, 13, 788, https://doi.org/10.3390/en13040788
Prof. Dr. Farhad Taghizadeh–Hesary
Dr. Han Phoumin
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
• Energy security
• Sustainable energy
• Green energy
• Low-carbon energy
• Renewable energy
• Clean energy
• Green finance
• Green economy
• Green development
• Green fiscal policy
• Green bond
• Green bank
• Carbon taxation
• Pollution taxation
• Energy efficiency
• Energy systems
• Liberalization and the environment.