Transportation Planning and Public Transport
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Dr. Hamid R. Sayarshad
Dr. Hamid R. Sayarshad
 Dr. Hamid R. Sayarshad
Dr. Hamid R. Sayarshad
E-Mail
Website
Guest Editor
School of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA
Interests: demand analysis; freight transportation and logistics; transportation network optimization and modeling; dynamic optimization models; dynamic vehicle routing and pricing problems; machine learning
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
This Special Issue aims to bring together emerging research on different transport models to address current and future issues in transportation, transport economics, traffic demand, and transportation resilience. This Special Issue also aims to expand research on public transport systems, such as shared mobility systems and transit services. Submissions should improve our understanding of the sustainability of public transport services in terms of public welfare and social needs. This Special Issue encourages submissions of original research articles that report significant research findings on the following topics:
- transport demand and travel behavior;
- route choice models and traffic assignment;
- shared mobility systems (dial-a-ride, dial-a-bus, and dial-a-flight problems and flying taxis, bikes, buses, subways, car-sharing platforms, and parking mechanisms);
- interaction between public transport and other modes;
- social welfare through public transportation;
- game theory and social choice models in transportation systems;
- clean transport systems (electric taxis, energy consumption, infrastructure charging facilities);
- transport information (travel behavior, weather prediction, demand prediction);
- resilience and recovery of transportation networks;
- freight transport models.
Dr. Hamid R. Sayarshad
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Published Papers (13 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Research on Optimization Strategies of Regional Cross-Border Transportation Networks—Implications for the Construction of Cross-Border Transport Corridors in Xinjiang
by
Xiaomin Dai, Menghan Liu and Qiang Lin
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1054
Abstract
Facility connectivity plays a pioneering role in the Belt and Road Initiative proposed by General Secretary Xi Jinping in 2013. Xinjiang, as the core area of the Silk Road Economic Belt bordering eight Eurasian countries, plays a crucial role in cross-border transportation and
[...] Read more.
Facility connectivity plays a pioneering role in the Belt and Road Initiative proposed by General Secretary Xi Jinping in 2013. Xinjiang, as the core area of the Silk Road Economic Belt bordering eight Eurasian countries, plays a crucial role in cross-border transportation and humanistic exchanges and is the focus of the national connectivity initiative. While the current analysis on regional accessibility has become more diversified, analyses on long-distance cross-border corridors are still relatively rare. Therefore, this paper takes the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR) of China as the main study area extending westward to the five Central Asian countries. Modified accessibility accounting methods and gravity models are used to analyze the current status of accessibility and the strength of economic ties between Xinjiang and the five Central Asian countries. The results showed that the distance decay effect of transportation accessibility between Xinjiang and the five Central Asian countries is obvious; the constraints of “natural geography + transportation economy” affect the accessibility level from each state in Xinjiang to the five Central Asian countries and shows a trend of strength in the north and weakness in the south. From the optimization of the regional planning road network in a reverse projection, G3033 and other highways and the construction of the Yi-A railroad will improve the status quo of “east-west access but not north-south access” in Xinjiang. The “corridor effect” and spatial polarization characteristics of economic connection intensity from Xinjiang to the five Central Asian countries are significant. This study has important theoretical and practical significance for the construction of cross-border corridors.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Determining Usage Intention for the Sustainability of Public Transport in Northern Cyprus Using the Theory of Planned Behaviour
by
Mehmet Angın, Shaban Ismael Albrka Ali and Hussin A. M. Yahia
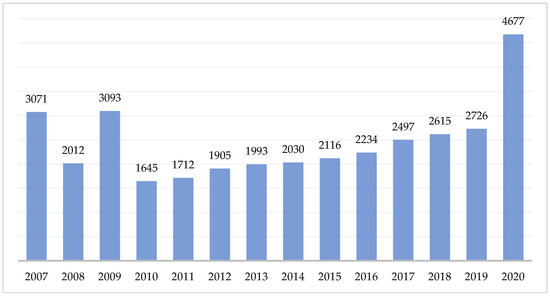
Viewed by 1645
Abstract
Transportation plays an important role in serving economic, social, political, and population mobility. Public transport is gaining importance for providing sustainability, such as by reducing traffic congestion, noise levels, providing better air quality, and contributing to public health. Public transportation facilities are undeveloped
[...] Read more.
Transportation plays an important role in serving economic, social, political, and population mobility. Public transport is gaining importance for providing sustainability, such as by reducing traffic congestion, noise levels, providing better air quality, and contributing to public health. Public transportation facilities are undeveloped in Northern Cyprus, and only buses and minibuses are available. Many people are ready to shift to public transportation if safe, reliable, and affordable transportation options are available. The theory of planned behaviour was used, and an online survey including 33 questions was conducted with the contributions of 385 participants. All variables of the theory of planned behaviour have a greater than 0.70 Cronbach’s alpha value; therefore, multiple linear regression analysis with the SPSS V27 program was conducted to detect the impact of attitude, subjective norms, and perceived behavioural control on behavioural intention. Note that 32.2% of intention is indicated by attitude, subjective norms, and perceived behavioural control. The study concluded that subjective norms and perceived behavioural control have a positive influence on behavioural intention. Attitude is not a predictor of behavioural intention. Subjective norms are the strongest (β = 0.438,
p < 0.001), and perceived behavioural control is the weakest (β = 0.438,
p < 0.001) predictor of public transport usage intention.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Predicting Model for Air Transport Demand under Uncertainties Based on Particle Filter
by
Bin Chen and Jin Wu
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 1344
Abstract
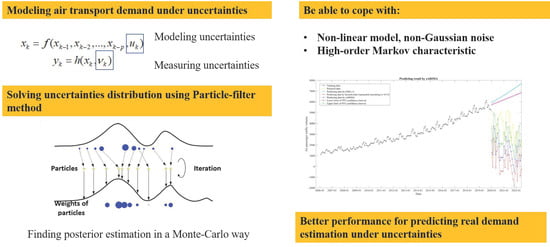
The outbreak of the COVID-19 has brought about huge economic loss and civil aviation industries all over the world have suffered severe damage. An effective method is urgently needed to accurately predict air-transport demand under the influences of such accidental factors. This paper
[...] Read more.
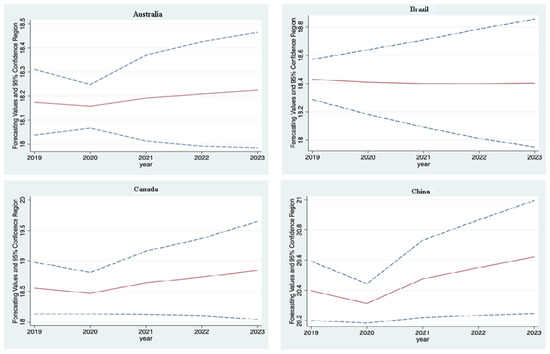
The outbreak of the COVID-19 has brought about huge economic loss and civil aviation industries all over the world have suffered severe damage. An effective method is urgently needed to accurately predict air-transport demand under the influences of such accidental factors. This paper proposes a novel predicting framework for the air-transport demand considering the uncertainties caused by accidental factors including regional wars, climatic anomalies, and virus outbreaks. By employing a seasonal autoregressive integrated moving average (sARIMA) model as the basic model, a particle filter (PF)-based sARIMA-pf model is proposed. The applicability of adapting the high-order sARIMA model as the state transition model in a PF framework is shown and proven to be effective. The proposed method has the advantage of coping with short-term prediction with known uncertainties. By conducting case studies on the prediction of air passenger traffic volume in China, the sARIMA-pf model showed better performance than the sARIMA model and improved the accuracy by 49.29% and 44.96% under the conventional and pandemic scenarios, respectively, when using the root mean square error (RMSE) as the indicator.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Are There Transit Deserts in Europe? A Study Focusing on Four European Cases through Publicly Available Data
by
Yefu Chen and Junfeng Jiao
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 1900
Abstract
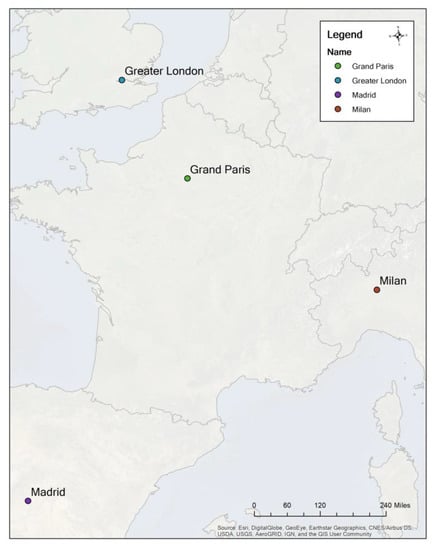
Public transit has been proven as an affordable travel method, while the inequitable distribution is a rising concern among practitioners and researchers. A transit desert, based on the demand and supply concept in measuring the mismatch in allocating the level of public transit
[...] Read more.
Public transit has been proven as an affordable travel method, while the inequitable distribution is a rising concern among practitioners and researchers. A transit desert, based on the demand and supply concept in measuring the mismatch in allocating the level of public transit service, has proved its ability to be applied in cases across countries. According to this concept, this study investigated transit deserts in four cases in Europe. Results indicate that the public transit system in Grand Paris and Madrid are superior due to a smaller population living in areas where public transit cannot meet the demand. Moreover, we noticed that the spatial distributions of transit deserts were significantly different, and the public transit accessibility of green spaces in Greater London and Madrid requires attention. These findings prove the potentials of the transit desert concept in generally evaluating and comparing the performance of different regional public transit systems which can guide the public transit investments by regional/cross-national agencies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Trip Generation Model for a Petrol Station with a Convenience Store and a Fast-Food Restaurant
by
Shafida Azwina Mohd Shafie, Lee Vien Leong and Ahmad Farhan Mohd Sadullah
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 4268
Abstract
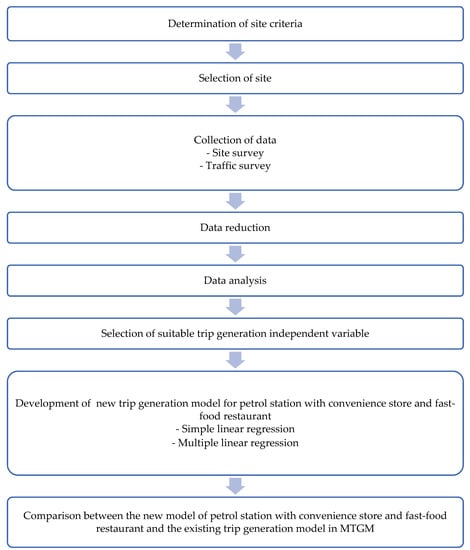
A trip generation manual and database are important for transportation planners and engineers to forecast new trip generation for any new development. Nowadays, many petrol stations have fast-food restaurant outlets. However, this land use category has yet to be included in the Malaysian
[...] Read more.
A trip generation manual and database are important for transportation planners and engineers to forecast new trip generation for any new development. Nowadays, many petrol stations have fast-food restaurant outlets. However, this land use category has yet to be included in the Malaysian Trip Generation Manual. Therefore, this study attempted to develop a new trip generation model for the new category of “petrol station with convenience store and fast-food restaurant”. Significant factors influencing the trip generation were also determined. Manual vehicle counts at the selected sites were conducted for 3 h during morning, afternoon and evening peak hours. Regression analysis was used in this study to develop the model. A simple trip generation model based on the independent variable number of restaurant seats showed a greater value for the coefficient of determination, R
2, compared with the independent variables gross floor area in thousand square feet and number of pumps. The multivariable trip generation model using three independent variables generated the highest R
2 among all of the models but was still below a satisfactory level. Further study is needed to improve the model for this new land use category. We must ensure more accuracy in trip generation estimation for future planning and development.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Will COVID-19 Threaten the Survival of the Airline Industry?
by
Xiao Xuan, Khalid Khan, Chi-Wei Su and Adnan Khurshid
Cited by 26 | Viewed by 7354
Abstract
The pandemic causes social distancing and lockdown, which impedes consumer confidence and contracts the economy. Hence, this study analyzes the corona (COVID-19) impact on the airline industry revenues (ALR) and forecast by the vector autoregression (VAR) method. The results indicate that gross domestic
[...] Read more.
The pandemic causes social distancing and lockdown, which impedes consumer confidence and contracts the economy. Hence, this study analyzes the corona (COVID-19) impact on the airline industry revenues (ALR) and forecast by the vector autoregression (VAR) method. The results indicate that gross domestic product (GDP) and air cargo are the best predictors of ALR. The forecasting outcomes explore if ALR will decline and expect to back to pre-COVID-19 in 2023. Our results resemble both the V-shaped and U-shaped, which suggests slow gradual recovery with longer lockdown and border disclosure. The government can restore confidence building by providing economic stimulus packages and can encourage the airline to return to travel. Furthermore, softening the passenger rules concerning the refund of unflown ticket, reducing taxes, and reducing overflight taxes, all reduce the costs. Similarly, the mutually recognized global standards are crucial for effective execution, and any temporary measures taken by the government should have a clear exit strategy. The study major limitation includes the lack of relevant research and data availability.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Car-Access Attractiveness of Urban Districts Regarding Shopping and Working Trips for Usage in E-Mobility Traffic Simulations
by
Florian Straub, Otto Maier and Dietmar Göhlich
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2076
Abstract
With the continuous proliferation of private battery electric vehicles, the demand for electrical energy and power is constantly increasing. As a result, the electrical grid may need to be expanded. To plan for such expansion, information about the spatial distribution of the energy
[...] Read more.
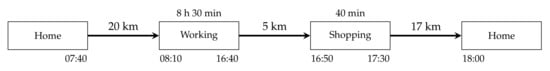
With the continuous proliferation of private battery electric vehicles, the demand for electrical energy and power is constantly increasing. As a result, the electrical grid may need to be expanded. To plan for such expansion, information about the spatial distribution of the energy demand is necessary. This can be determined from e-mobility traffic simulations, where travel schedules of individuals are combined with an attractiveness rating of locations to estimate traffic flows. Typically, attractiveness is determined from the “size” of locations (e.g., number of employees or sales area), which is applicable when all modes of transportation are considered. This approach leads to inaccuracies for the estimation of car traffic flows, since the parking situation is neglected. To overcome these inaccuracies and fill this research gap, we have developed a method to determine the car-access attractiveness of districts for shopping and working trips. Our method consists of two steps. First, we determine the car-access attractiveness of buildings within a district based on the parking situation of each individual building and then aggregate the results at the district level. The approach is demonstrated for the city of Berlin. The results confirm that conventional models cannot be used to determine the car-access attractiveness of districts. According to these models, attractive districts are predominantly located in the city centre due to the large amount of sales areas or the large number of employees. However, due to the high density of buildings, only limited space is available for parking. Attractive districts rated according to our new approach are mainly located in the outer areas of the city and thus match the parking situation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Multi-Objective Meta-Heuristic Approach to Improve the Bus Transit Network: A Case Study of Fargo-Moorhead Area
by
Mohsen Momenitabar and Jeremy Mattson
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 2487
Abstract
In this study, the Transit Network Design Problem (TNDP) is studied to determine the set of routes and frequency on each route for public transportation systems. To ensure the important concerns of planners like route length, route configuration, demand satisfaction, and attractiveness of
[...] Read more.
In this study, the Transit Network Design Problem (TNDP) is studied to determine the set of routes and frequency on each route for public transportation systems. To ensure the important concerns of planners like route length, route configuration, demand satisfaction, and attractiveness of the transit routes, the TNDP is solved to generate a set of routes by proposing an initial route set generation (IRSG) procedure embedded into the NSGA-II algorithm. The proposed IRSG algorithm aims to produce high-quality initial route set solutions to reach better optimization procedures. Moreover, the Multi-Objective Mixed-Integer Non-Linear Programming (MOMINLP) model is proposed to formulate the frequency setting problem on each route by minimizing the total travel time of passengers (user costs) and operator costs simultaneously, while maximizing the service coverage area near all the bus stops. The MOMINLP model is solved by applying the NSGA-II algorithm to produce a Pareto front between the first and the second objective functions. The model was applied to the Fargo-Moorhead Area (FMA), a small urban area. Results were compared with the existing transit network to measure the efficiency of the NSGA-II solution methodology. The proposed algorithm was found to considerably decrease the total travel time of passengers.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Regional Transport Plans: From Direction Role Denied to Common Rules Identified
by
Francesco Russo and Corrado Rindone
Cited by 33 | Viewed by 3055
Abstract
This paper concerns transportation planning with a specific focus on the regional level. In the context of spatial and transport integrated planning, the paper proposes a structured and systematic identification of the plans. At the European level, specific indications, prescriptive communications, and finalized
[...] Read more.
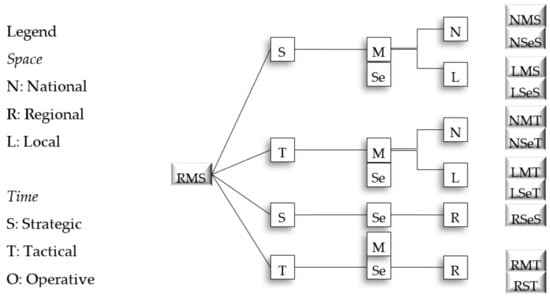
This paper concerns transportation planning with a specific focus on the regional level. In the context of spatial and transport integrated planning, the paper proposes a structured and systematic identification of the plans. At the European level, specific indications, prescriptive communications, and finalized funds are given to the national infrastructures by means of the TEN-T plan and program, while a Communication and specific guidelines for the Sustainable Urban Mobility Plan have been published as a useful tool to uniform and compare urban transport planning. However, there are no indications for the planning of transport at the regional scale. This paper focuses on regional transport plans, analyzing the general contents and deepening and comparing the contents related to public transport. A case study of Italy is presented. Reference is made to the national guidelines and therefore to the transport plans approved in Italy by the regions. The Italian experience, and the results evidenced, could be a valid reference for all European or extra-European regions or, in any case, for intermediate territorial planning between the national and local ones.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Low-Carbon Multimodal Transportation Path Optimization under Dual Uncertainty of Demand and Time
by
Xu Zhang, Fei-Yu Jin, Xu-Mei Yuan and Hai-Yan Zhang
Cited by 26 | Viewed by 4254
Abstract
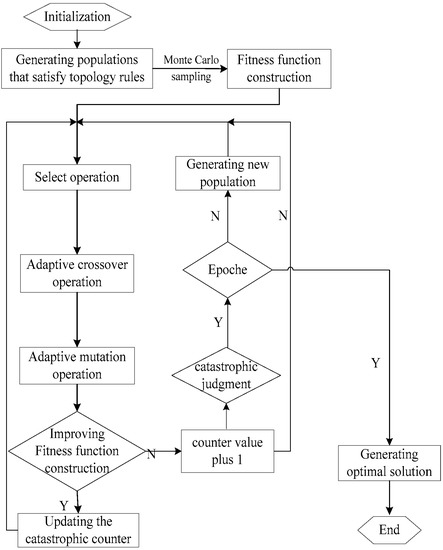
The research on the optimization of a low-carbon multimodal transportation path under uncertainty can have an important theoretical and practical significance in the high-quality development situation. This paper investigates the low-carbon path optimization problem under dual uncertainty. A hybrid robust stochastic optimization (HRSO)
[...] Read more.
The research on the optimization of a low-carbon multimodal transportation path under uncertainty can have an important theoretical and practical significance in the high-quality development situation. This paper investigates the low-carbon path optimization problem under dual uncertainty. A hybrid robust stochastic optimization (HRSO) model is established considering the transportation cost, time cost and carbon emission cost. In order to solve this problem, a catastrophic adaptive genetic algorithm (CA-GA) based on Monte Carlo sampling is designed and tested for validity. The multimodal transportation schemes and costs under different modes are compared, and the impacts of uncertain parameters are analyzed by a 15-node multimodal transportation network numerical example. The results show that: (1) the uncertain mode will affect the decision-making of multimodal transportation, including the route and mode; (2) robust optimization with uncertain demand will increase the total cost of low-carbon multimodal transportation due to the pursuit of stability; (3) the influence of time uncertainty on the total cost is significant and fuzzy, showing the trend of an irregular wave-shaped change, like the ups and downs of the mountains. The model and algorithm we proposed can provide a theoretical basis for the administrative department and logistic services providers to optimize the transportation scheme under uncertainty.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of the Evolutionary Game between the Government and Urban Rail Transit Enterprises under the Loss-Subsidy Mode: A Case Study of Beijing
by
Chen Yan and Qiong Tong
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1837
Abstract
Most of the urban rail transit enterprises in China have high construction and operation costs, while the government imposes price control on their fares, making their revenues unable to cover their costs and thus causing certain losses. In order to ensure the economic
[...] Read more.
Most of the urban rail transit enterprises in China have high construction and operation costs, while the government imposes price control on their fares, making their revenues unable to cover their costs and thus causing certain losses. In order to ensure the economic sustainability of urban rail transit enterprises, the government then subsidizes their losses. In the context of loss subsidies as the main subsidy mode for urban rail transit, the government regulates whether urban rail transit enterprises waste cost in order to protect social welfare and reduce the financial pressure of subsidies. This paper constructs an evolutionary game model between government regulators and urban rail transit enterprises, establishes replicated dynamic equations to obtain the evolutionary stabilization strategies of the government and urban rail transit enterprises under different situations, and analyzes the effects of various parameters on the cost control behaviors of urban rail transit enterprises under different loss-subsidy modes through numerical simulations. The theoretical study and simulation results show the following: When only the regulatory policy is adopted, the optimal strategy of urban rail transit enterprises may be cost saving or cost wasting under different subsidy models; if only the penalty policy is adopted, the enterprises will choose the cost wasting strategy when the penalty is small, and the enterprises will choose the cost saving strategy when the penalty is large; if only the fixed proportion subsidy model is adopted, no matter how large the proportion k of government subsidies is, the urban the optimal strategy for rail transit enterprises is cost wasting. If only the regressive loss subsidy model is adopted, the different sizes of its various parameter settings will also lead to the enterprises’ choice of cost wasting strategy or cost saving strategy. Therefore, the government should formulate corresponding policies according to different cost control objectives.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Dynamic Inventory Routing and Pricing Problem with a Mixed Fleet of Electric and Conventional Urban Freight Vehicles
by
Hamid R. Sayarshad, Vahid Mahmoodian and Nebojša Bojović
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3040
Abstract
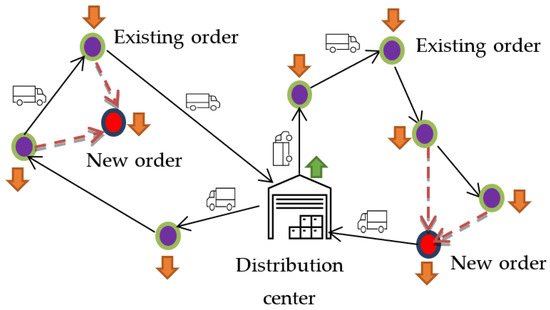
Urban freight transport is essential for supporting our society regarding providing the daily needs of consumers and local businesses. In addition, it allows for the movement of goods, is distributed within urban environments, provides thousands of jobs, and supports economic growth. However, a
[...] Read more.
Urban freight transport is essential for supporting our society regarding providing the daily needs of consumers and local businesses. In addition, it allows for the movement of goods, is distributed within urban environments, provides thousands of jobs, and supports economic growth. However, a number of issues are associated with urban freight transport, including environmental impacts, road congestion, and land use of freight facilities that conflicts with residential land use. Electric freight vehicles create zero emissions and provide a sustainable delivery system in comparison with conventional freight vehicles. In this study, a novel dynamic inventory routing and pricing problem under a mixed fleet of electric and conventional vehicles was formulated to minimize the total travel and charging costs. The proposed model is capable of deciding on replenishment times and amounts and vehicle routes. We aimed to determine the maximum social welfare (SW) capable of providing an optimal trade-off between the supplier cost and customer delay that uses a mixed fleet of vehicles. Our computational study was conducted on real data generated from a delivery dataset in Tehran. Under the proposed policy with a fleet of only electric vehicles, the SW increased by 3% while the average customer delay reduced by 15% compared with a fleet of conventional vehicles. The results show that the number of served customers and customer delay would be affected by transitioning conventional urban freight vehicles to electric vehicles. Therefore, the proposed delivery system has a significant impact on energy savings and emissions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
User Preferences in the Design of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems
by
Sara Paiva, Xabiel García Pañeda, Victor Corcoba, Roberto García, Próspero Morán, Laura Pozueco, Marina Valdés and Covadonga del Camino
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 4094
Abstract
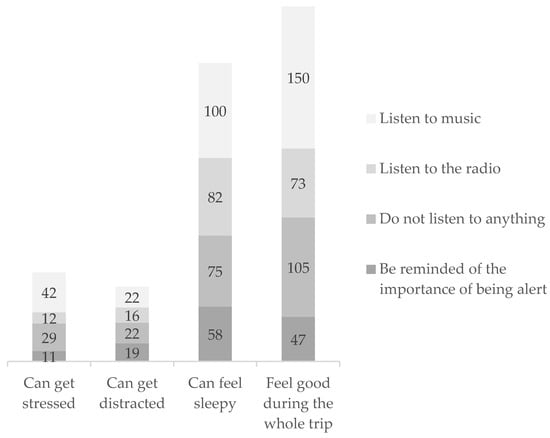
The transport network and mobility aspects are constantly changing, and major changes are expected in the coming years in terms of safety and sustainability purposes. In this paper, we present the main conclusions and analysis of data collected from a survey of drivers
[...] Read more.
The transport network and mobility aspects are constantly changing, and major changes are expected in the coming years in terms of safety and sustainability purposes. In this paper, we present the main conclusions and analysis of data collected from a survey of drivers in Spain and Portugal regarding user preferences, highlighting the main functionalities and behavior that an advanced driver assistance system must have in order to grant it special importance on the road to prevent accidents and also to enable drivers to have a pleasant journey. Based on the results obtained from the survey, we developed and present a working prototype for an advanced driver assistance system (ADAS), its architecture and rules systems that allowed us to create and test some scenarios in a real environment.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures