System Dynamics
A topical collection in Systems (ISSN 2079-8954).
Viewed by 45684
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
This collection aims at advances in various perspectives and methods of system dynamics. Dealing with societal, economic, managerial, biological, environmental or technical issues, prospective authors are invited to present their latest research outcomes. Not only does this collection pay attention to application of SD in interesting or unusual domains, but solutions to methodological issues or testing and verification of existing methods, tools or techniques applied in SD are also welcomed. Thus, we welcome studies focused, for instance, on:
- mathematical modelling and computer simulation of dynamic feedback systems;
- generic structures such as system archetypes or identification and analysis of widely applicable behavioural insights;
- SD support to development or verification of theories in various scientific fields;
- innovative techniques of work with casual-loop and stock-and-flow diagrams;
- issues related to differences in modelling and simulation of hard or soft systems;
- comparative evaluation of tools and techniques for SD modelling;
- novel techniques or procedures of capturing of mental models;
- complex comparative analysis of SD with other modelling approaches.
Dr. Vladimír Bureš
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Systems is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Published Papers (7 papers)
Open AccessSystematic Review
Knowledge Management as a Domain, System Dynamics as a Methodology
by
Marek Zanker and Vladimír Bureš
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3787
Abstract
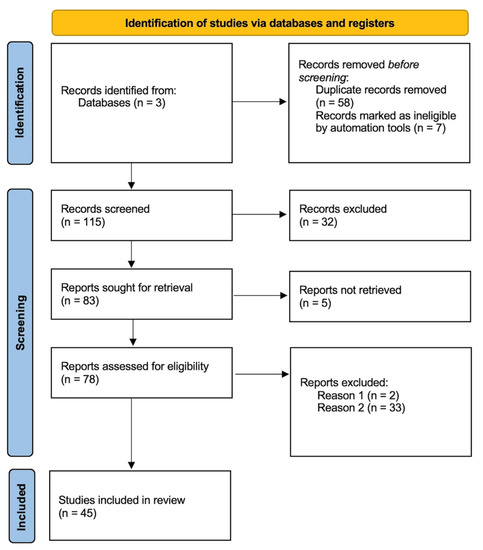
For decades, system dynamics has been utilised as a framework for evaluating and interpreting various types of systems with varying degrees of complexity and knowledge demands. Knowledge management is strongly related to system dynamics on a thematic level. We did a thorough review
[...] Read more.
For decades, system dynamics has been utilised as a framework for evaluating and interpreting various types of systems with varying degrees of complexity and knowledge demands. Knowledge management is strongly related to system dynamics on a thematic level. We did a thorough review to identify potential applications and analysed system dynamics and knowledge management domains. The systematic review followed the PRISMA method. We identified two major groups and one subgroup of the combination of system dynamics and knowledge management after examining and categorising 45 papers. Articles were searched for on Web of Science, Scopus, and LENS. We then concentrated on the categorisation of articles by theme. We discovered that system dynamics models were used as a component of a decision support tool or a knowledge management system in some instances, or the integration of knowledge management processes into specific systems. This study contributes to the growth of system dynamics as a methodology capable of generating novel ideas, highlighting limitations, and providing analogies for future research in a variety of academic areas.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Three Generic Policies for Sustained Market Growth Based on Two Interdependent Organizational Resources—A Simulation Study and Implications
by
Martin F. G. Schaffernicht
Viewed by 3593
Abstract
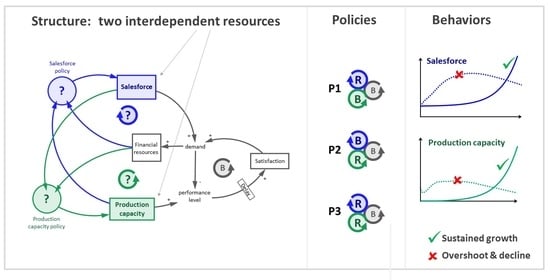
This article addresses the generic dynamic decision problem of how to achieve sustained market growth by increasing two interdependent organizational resources needed (1) to increase and (2) to sustain demand. The speed and costs of increasing each resource are different. Failure to account
[...] Read more.
This article addresses the generic dynamic decision problem of how to achieve sustained market growth by increasing two interdependent organizational resources needed (1) to increase and (2) to sustain demand. The speed and costs of increasing each resource are different. Failure to account for this difference leads to policies that drive a quick increase of demand followed by decline. Three generic policies derived from the literature have been implemented in a system dynamics model. Simulation shows that they all can generate sustained exponential growth but differ in performance: even policies criticized in the literature for provoking overshoot and collapse can drive sustained growth. This leads to questions for further research regarding (1) the set of generic policies and its structure and (2) concerning the reasoning of human decision-makers when choosing between such policies and the salience of important but easily overlooked features of the decision situation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessSystematic Review
Environment, Business, and Health Care Prevail: A Comprehensive, Systematic Review of System Dynamics Application Domains
by
Marek Zanker, Vladimír Bureš and Petr Tučník
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 6875
Abstract
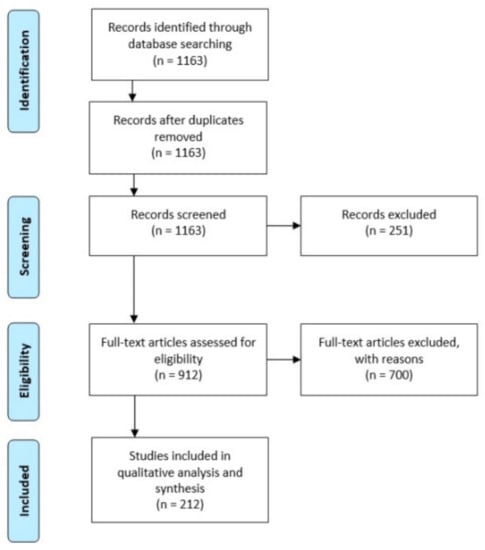
System dynamics, as a methodology for analyzing and understanding various types of systems, has been applied in research for several decades. We undertook a review to identify the latest application domains and map the realm of system dynamics. The systematic review was conducted
[...] Read more.
System dynamics, as a methodology for analyzing and understanding various types of systems, has been applied in research for several decades. We undertook a review to identify the latest application domains and map the realm of system dynamics. The systematic review was conducted according to the PRISMA methodology. We analyzed and categorized 212 articles and found that the vast majority of studies belong to the fields of business administration, health, and environmental research. Altogether, 20 groups of modeling and simulation topics can be recognized. System dynamics is occasionally supported by other modeling methodologies such as the agent-based modeling approach. There are issues related to published studies mostly associated with testing of validity and reasonability of models, leading to the development of predictions that are not grounded in verified models. This study contributes to the development of system dynamics as a methodology that can offer new ideas, highlight limitations, or provide analogies for further research in various research disciplines.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Operationalizing Accounting Reporting in System Dynamics Models
by
Kawika Pierson
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 6175
Abstract
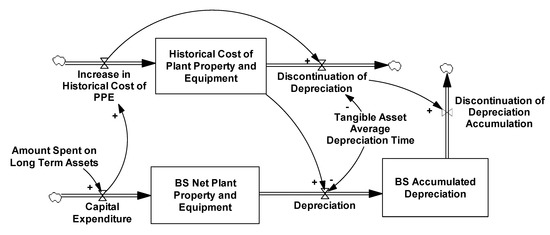
System dynamics implementations of financial statements are currently limited by the lack of a simple to use, yet sufficiently detailed model that operationally replicates the accounting reporting process for the income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, and statement of changes in owners’
[...] Read more.
System dynamics implementations of financial statements are currently limited by the lack of a simple to use, yet sufficiently detailed model that operationally replicates the accounting reporting process for the income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, and statement of changes in owners’ equity. While system dynamics accounting structures exist, they are inconsistently applied in the literature. In this paper, we offer a comprehensive accounting model in the hope that academics and practitioners will use its structures to better represent accounting reports in their projects.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A System Dynamics Modeling Support System Based on Computational Intelligence
by
Hassan Abdelbari and Kamran Shafi
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 6465
Abstract
System dynamics (SD) is a complex systems modeling and simulation approach with wide ranging applications in various science and engineering disciplines. While subject matter experts lead most of the model building, recent advances have attempted to bring system dynamics closer to fast growing
[...] Read more.
System dynamics (SD) is a complex systems modeling and simulation approach with wide ranging applications in various science and engineering disciplines. While subject matter experts lead most of the model building, recent advances have attempted to bring system dynamics closer to fast growing fields such as data sciences. This may prove promising for the development of novel support methods that augment human cognition and improve efficiencies in the model building process. A few different directions have been explored recently to support individual modeling stages, such as the generation of model structure, model calibration and policy optimization. However, an integrated approach that supports across the board modeling process is still missing. In this paper, a prototype integrated modeling support system is presented for the purpose of supporting the modelers at each stage of the process. The proposed support system facilitates data-driven inferring of causal loop diagrams (CLDs), stock-flow diagrams (SFDs), model equations and the estimation of model parameters using computational intelligence (CI) techniques. The ultimate goal of the proposed system is to support the construction of complex models, where the human power is not enough. With this goal in mind, we demonstrate the working and utility of the proposed support system. We have used two well-known synthetic reality case studies with small models from the system dynamics literature, in order to verify the support system performance. The experimental results showed the effectiveness of the proposed support system to infer close model structures to target models directly from system time-series observations. Future work will focus on improving the support system so that it can generate complex models on a large scale.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Energy Security within Malaysia’s Water-Energy-Food Nexus—A Systems Approach
by
Andrew Huey Ping Tan and Eng Hwa Yap
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 8822
Abstract
While knowledge of energy security has been thorough and elaborate, understanding energy security within the context of the water-energy-food nexus, where substantial inter-sectoral causes and effects exist, is less established, more so for Malaysia. This paper investigates the impact of two energy scenarios
[...] Read more.
While knowledge of energy security has been thorough and elaborate, understanding energy security within the context of the water-energy-food nexus, where substantial inter-sectoral causes and effects exist, is less established, more so for Malaysia. This paper investigates the impact of two energy scenarios on identified key indicators within the context of the water-energy-food nexus. By utilizing a mixed method of qualitative interview and quantitative system dynamics modelling, representative causal loop diagrams and stock-flow diagrams were constructed to predict and allow for the analysis of behaviors of selected key indicators. Key findings include the importance of allowing a reasonable penetration of 20% renewable energy for the long term, and having a proper consideration for nuclear energy to assist in keeping energy costs low for the mid-term.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Regulatory Limits to Corporate Sustainability: How Climate Change Law and Energy Reforms in Mexico May Impair Sustainability Practices in Mexican Firms
by
Antonio Lloret, Rogerio Domenge and Mildred Castro-Hernández
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 7793
Abstract
This paper aims to show that sustainable behavior by firms may be impaired by regulatory restrictions. We challenge the assumption that regulation aimed at curbing greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) in the form of a target to meet the Country’s GHG emissions commitments will
[...] Read more.
This paper aims to show that sustainable behavior by firms may be impaired by regulatory restrictions. We challenge the assumption that regulation aimed at curbing greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) in the form of a target to meet the Country’s GHG emissions commitments will promote sustainable corporations. We argue that, in fact, such regulation may impair sustainability practices because it creates unintended consequences. This paper tackles the efficiency of the institutional framework chosen through the lenses of the analytical themes of fit, scale, and interplay, then we use a systems dynamic approach to represent how regulation in the arenas of energy efficiency and GHG emissions reduction may withhold competitive business outcomes and corporate sustainability schemes. We exemplify and simulate a single regulation scheme: a clean energy target for firms; and found that as a result of such scheme, the system is dominated by negative feedback processes resulting in lesser outcomes that would be better tackled by firms not being subject to the restrictions imposed by the regulation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures