Chlorine Isotope Effects from Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry Suggest Intramolecular C-Cl Bond Competition in Trichloroethene (TCE) Reductive Dehalogenation
Abstract
:1. Introduction


2. Experimental Section
Biodegradation Experiments and Carbon and Chlorine Isotope Analysis
3. Mathematical Equations for Fitting Substrate and Product Isotope Ratios (I): Compound-Average Isotope Effects


3.1. Compound-Average Isotope Effects from Reactant Values






3.2. Expressions for Product Isotope Values

3.3. Carbon Isotope Effects from Product Values


3.4. Chlorine Isotope Effects from Product Values
4. Mathematical Equations for Fitting Product Data (II): Insight into Primary and Secondary Chlorine Isotope Effects
4.1. Case 1—PCE: Indistinguishable Molecular Positions
4.1.1. General Equations








4.1.2. Interpretation of Product Isotope Enrichment Trends (εChlorine) and intercepts (εDifference) for PCE
4.2. Case 2—TCE: Distinguishable Molecular Positions





4.2.1. Interpretation of the Product Curve Enrichment Trends εTCE->chloride and εTCE->cis-DCE for TCE

4.2.2. Contributions from α-Positions to εTCE->chloride and εTCE->cis-DCE
4.2.3. Interpretation of Intercepts K for the TCE Case
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Compound-Specific Carbon Isotope Effects in Reductive Dehalogenation of PCE to TCE by Desulfitobacterium sp. Strain Viet1 and of TCE to cis-DCE by Geobacter Lovleyi Strain SZ

5.2. Compound-Specific and Position-Specific Chlorine Isotope Effects in Reductive Dehalogenation of PCE to TCE by Desulfitobacterium sp. Strain Viet1






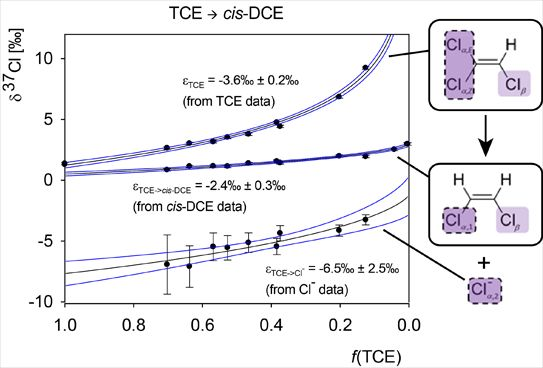
5.3. Compound-Specific and Position-Specific Chlorine Isotope Effects in Reductive Dehalogenation of TCE to cis-DCE by Geobacter lovleyi Strain SZ





6. Conclusions

Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gribble, G.W. Naturally occurring organohalogen compounds. Acc. Chem. Res. 1998, 31, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patai, S. The Chemistry of the Carbon-Halogen Bond: Part 1; John Wiley & Sons: London, UK; New York, NY, USA; Sidney, Austrilia; Toronto, ON, Canada, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.B.; Zhang, W.X. Synthesizing nanoscale iron particles for rapid and complete dechlorination of TCE and PCBs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2154–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillham, R.W.; O’Hannesin, S.F. Enhanced Degradation of Halogenated Aliphatics by Zero-Valent Iron. Ground Water 1994, 32, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holliger, C.; Wohlfarth, G.; Diekert, G. Reductive dechlorination in the energy metabolism of anaerobic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 22, 383–398. [Google Scholar]
- Adrian, L.; Szewzyk, U.; Wecke, J.; Gorisch, H. Bacterial dehalorespiration with chlorinated benzenes. Nature 2000, 408, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grostern, A.; Duhamel, M.; Dworatzek, S.; Edwards, E.A. Chloroform respiration to dichloromethane by a Dehalobacter population. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.Z.; Ritalahti, K.M.; Yang, K.L.; Koenigsberg, S.S.; Löffler, F.E. Detoxification of vinyl chloride to ethene coupled to growth of an anaerobic bacterium. Nature 2003, 424, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, B.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Löffler, F.E. Anaerobic microbial reductive dechlorination of tetrachloroethene to predominately trans-1,2-dichloroethene. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4300–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duhamel, M.; Wehr, S.D.; Yu, L.; Rizvi, H.; Seepersad, D.; Dworatzek, S.; Cox, E.E.; Edwards, E.A. Comparison of anaerobic dechlorinating enrichment cultures maintained on tetrachloroethene, trichloroethene, cis-dichloroethene and vinyl chloride. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4193–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidt, H.; de Vos, W.M. Anaerobic microbial dehalogenation. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 58, 43–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, F.; Buchanan, D. Preparation of 1-Methyl-2,2-diphenylcyclopropylcobaloxime and Theoretical Considerations for Its Mode of Formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1973, 153–154. [Google Scholar]
- Semadeni, M.; Chiu, P.C.; Reinhard, M. Reductive transformation of trichloroethene by cobalamin: Reactivities of the intermediates acetylene, chloroacetylene, and the DCE isomers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhl, M.; Golubnychiy, V. On the intermediacy of chlorinated alkylcobalt complexes in the reductive dehalogenation of chloroalkenes. A first-principles molecular dynamics study. Organometallics 2007, 26, 6213–6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glod, G.; Angst, W.; Holliger, C.; Schwarzenbach, R.P. Corrinoid-mediated reduction of tetrachloroethylene, trichloroethylene and trichlorofluoroethane in homogeneoues aqueous solution: Reaction kinetics and reaction mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliegman, S.; McNeill, K. Dechlorination of chloroethylenes by cob(i)alamin and cobalamin model complexes. Dalton Trans. 2008, 4191–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliegman, S.; McNeill, K. Reconciling Disparate Models of the Involvement of Vinyl Radicals in Cobalamin-Mediated Dechlorination Reactions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 8961–8967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, W.; Holliger, C.; Zehnder, A.J.B.; Hagen, W.R. Redox chemistry of cobalamin and iron-sulfur cofactors in the tetrachloroethene reductase of Dehalobacter restrictus. FEBS Lett. 1997, 409, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follett, A.D.; McNabb, K.A.; Peterson, A.A.; Scanlon, J.D.; Cramer, C.J.; McNeill, K. Characterization of Co-C bonding in dichlorovinylcobaloxime complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonnenberg, C.; van der Donk, W.A.; Zipse, H. Reductive Dechlorination of Trichloroethylene: A Computational Study. J. Phys. Chem. A 2002, 106, 8708–8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, D.A.; van der Donk, W.A. On the role of alkylcobalamins in the vitamin B12-catalyzed reductive dehalogenation of perchloroethylene and trichloroethylene. Chem. Commun. 2006, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, D.A.; Thomas, A.A. High-Precision Simultaneous Determination of Multiple Small Kinetic Isotope Effects at Natural-Abundance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 9357–9358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perras, F.A.; Bryce, D.L. Direct Investigation of Covalently Bound Chlorine in Organic Compounds by Solid-State 35Cl NMR Spectroscopy and Exact Spectral Line-Shape Simulations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 4227–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoreson, K.A. Probing Reduced Metal Center-Mediated Dechlorination Mechanisms through the Use of Model Complexes and Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, USA, June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Shouakar-Stash, O.; Drimmie, R.J.; Zhang, M.; Frape, S.K. Compound-specific chlorine isotope ratios of TCE, PCE and DCE isomers by direct injection using CF-IRMS. Appl. Geochem. 2006, 21, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsner, M.; Hunkeler, D. Evaluating Chlorine Isotope Effects from Isotope Ratios and Mass Spectra of Polychlorinated Molecules. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 4731–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Aravena, R.; Zopfi, J.; Shouakar-Stash, O.; Cox, E.; Roberts, J.D.; Hunkeler, D. Carbon and Chlorine Isotope Fractionation during Aerobic Oxidation and Reductive Dechlorination of Vinyl Chloride and cis-1,2-Dichloroethene. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegert, C.; Mandalakis, M.; Knowles, T.; Polymenakou, P.N.; Aeppli, C.; Macháčková, J.; Holmstrand, H.; Evershed, R.P.; Pancost, R.D.; Gustafsson, Ö. Carbon and Chlorine Isotope Fractionation During Microbial Degradation of Tetra- and Trichloroethene. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6449–6456. [Google Scholar]
- Cretnik, S.; Thoreson, K.A.; Bernstein, A.; Ebert, K.; Buchner, D.; Laskov, C.; Haderlein, S.; Shouakar-Stash, O.; Kliegman, S.; McNeill, K.; et al. Reductive Dechlorination of TCE by Chemical Model Systems in Comparison to Dehalogenating Bacteria: Insights from Dual Element Isotope Analysis (13C/12C, 37Cl/35Cl). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6855–6863. [Google Scholar]
- Kuder, T.; van Breukelen, B.M.; Vanderford, M.; Philp, P. 3D-CSIA: Carbon, Chlorine, and Hydrogen Isotope Fractionation in Transformation of TCE to Ethene by a Dehalococcoides Culture. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9668–9677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunkeler, D.; van Breukelen, B.M.; Elsner, M. Modeling Chlorine Isotope Trends during Sequential Transformation of Chlorinated Ethenes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6750–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, B.K.; Christ, J.A.; Abriola, L.M.; Pennell, K.D.; Löffler, F.E. Experimental Evaluation and Mathematical Modeling of Microbially Enhanced Tetrachloroethene (PCE) Dissolution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.; Fletcher, K.F.; Ritalaliti, K.M.; Apkarian, R.P.; Ramos-Hernandez, N.; Sanford, R.A.; Mesbah, N.M.; Löffler, F.E. Geobacter lovleyi sp nov strain SZ, a novel metal-reducing and tetrachloroethene-dechlorinating bacterium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2775–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melander, L.; Saunders, W.H. Reaction Rates of Isotopic Molecules; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Elsner, M.; Zwank, L.; Hunkeler, D.; Schwarzenbach, R.P. A new concept linking observable stable isotope fractionation to transformation pathways of organic pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6896–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsner, M. Stable isotope fractionation to investigate natural transformation mechanisms of organic contaminants: Principles, prospects and limitations. J. Environ. Monit. 2010, 12, 2005–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follett, A.D.; McNeill, K. Reduction of Trichloroethylene by Outer-Sphere Electron-Transfer Agents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 844–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, K.M.; Wilson, S.R.; van der Donk, W.A. Synthesis and characterization of chlorinated alkenylcobaloximes to probe the mechanism of vitamin B-12-catalyzed dechlorination of priority pollutants. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 41, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follett, A.D.; McNeill, K. Evidence for the Formation of a cis-Dichlorovinyl Anion upon Reduction of cis-1,2-Dichlorovinyl(pyridine)cobaloxime. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 2727–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paneth, P. Chlorine kinetic isotope effects on enzymatic dehalogenations. Acc. Chem. Res. 2003, 36, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2014 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Cretnik, S.; Bernstein, A.; Shouakar-Stash, O.; Löffler, F.; Elsner, M. Chlorine Isotope Effects from Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry Suggest Intramolecular C-Cl Bond Competition in Trichloroethene (TCE) Reductive Dehalogenation. Molecules 2014, 19, 6450-6473. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19056450
Cretnik S, Bernstein A, Shouakar-Stash O, Löffler F, Elsner M. Chlorine Isotope Effects from Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry Suggest Intramolecular C-Cl Bond Competition in Trichloroethene (TCE) Reductive Dehalogenation. Molecules. 2014; 19(5):6450-6473. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19056450
Chicago/Turabian StyleCretnik, Stefan, Anat Bernstein, Orfan Shouakar-Stash, Frank Löffler, and Martin Elsner. 2014. "Chlorine Isotope Effects from Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry Suggest Intramolecular C-Cl Bond Competition in Trichloroethene (TCE) Reductive Dehalogenation" Molecules 19, no. 5: 6450-6473. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19056450
APA StyleCretnik, S., Bernstein, A., Shouakar-Stash, O., Löffler, F., & Elsner, M. (2014). Chlorine Isotope Effects from Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry Suggest Intramolecular C-Cl Bond Competition in Trichloroethene (TCE) Reductive Dehalogenation. Molecules, 19(5), 6450-6473. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19056450