Effect of Food Emulsifiers on Aroma Release
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
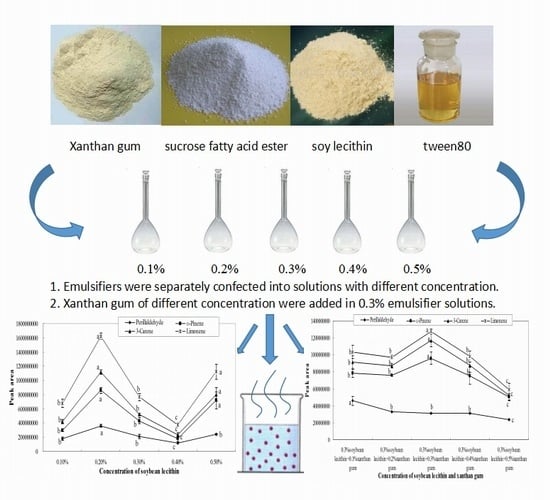
2.1. Influence of Single Emulsifier System on Aroma Release
2.2. Influence of Xanthan Gum on Aroma Release
2.3. Influence of Different Emulsifier Systems with Added Thickener on Aroma Release
- (1)
- When 0.3% Tween 80 was mixed with different concentrations of xanthan gum (0.1%, 0.2%, 0.3%, 0.4%, and 0.5%), the quantity released with 0.2% xanthan gum was lower than that of other concentrations as shown in Figure 5. After 0.3%, the amount released showed a downward trend.
- (2)
- The quantity of carvone released presented a significant downward trend, seen in Figure 6a. With 0.3% soybean lecithin, the quantities of carvone, perillaldehyde, and (E)-2-hexenal released were restrained with the increase of xanthan gum concentration. All these compounds had the lowest peak area when the concentration of xanthan gum was 0.5%. However, the amount of ethyl acetate released was not significantly changed. As shown in Figure 6b, the amount released presented a significant (p < 0.05) downward trend after 0.3%.
- (3)
- When 0.3% sucrose fatty acid ester was mixed with xanthan gum at different concentrations (0.1%, 0.2%, 0.3%, 0.4%, and 0.5%), aroma release showed a sharp decline after 0.4% (Figure 7). The lowest peak areas were observed when the concentration of xanthan gum was 0.5%. After 0.4%, the interactions between emulsifiers and xanthan gum influence the aroma release by entrapping aroma molecules or generating hydrogen bonds with aroma molecules [24].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Reference Samples
3.2. Preparation of the Mother Liquor of the Aroma Substance
3.3. Preparation of Single Emulsifier System
3.4. Preparation of Different Emulsifier Systems Supplemented with Thickener
3.5. Extraction and Analysis of Aroma Substances
3.6. GC-MS Analysis
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsumiya, K.; Sasaki, M.; Murakami, H.; Matsumura, Y. Oil droplet coalescence does not necessarily affect the flavor release from oil-in-water emulsions. Colloid Surf. A 2015, 475, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landy, P.; Druaux, C.; Voilley, A. Retention of aroma compounds by proteins in aqueous solution. Food Chem. 1995, 54, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seuvre, A.M.; Philippe, E.; Rochard, S.; Voilley, A. Retention of aroma compounds in food matrices of similar rheological behaviour and different compositions. Food Chem. 2006, 96, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Seedi, H.R.; El-Said, A.M.A.; Khalifa, S.A.M.; Göransson, U.; Bohlin, L.; Borg-Karlson, A.-K.; Verpoorte, R. Biosynthesis, Natural sources, dietary intake, pharmacokinetic properties, and biological activities of hydroxycinnamic acids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10877–10895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Kennedy, B.T.O.; Roos, Y.H.; Hannon, J.A.; Miao, S. Effect of monoglyceride self-assembled structure on emulsion properties and Subsequent flavor release. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaiskou, S.; Blekas, G.; Paraskevopoulou, A. Aroma release from gum Arabic or egg yolk/xanthan-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saskia, M.; Ruth, V.; King, C.; Giannouli, P. Influence of lipid fraction, emulsifier fraction, and mean particle diameter of oil-in-water emulsions on the release of 20 aroma compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2365–2371. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, D.D.; Pollien, P.; Watzke, B. Experimental and modeling studies showing the effect of lipid type and level on flavor release from milk-based liquid emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guichard, E. Interactions between flavor compounds and food ingredients and their influence on flavor perception. Food Rev. Int. 2002, 18, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toms, L.G.; Carbonell, I.; Costel, E. Influence of type, concentration and flow behaviour of hydrocolloid solutions on aroma perception. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2004, 218, 248–252. [Google Scholar]
- McClements, D.J. Food Emulsions: Principles, Practices and Techniques, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ruth, S.M.V.; Vries, G.D.; Geary, M.; Giannouli, P. Influence of composition and structure of oil-in-water emulsions on retention of aroma compounds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2002, 82, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Gunasekaran, S.; Richards, M.P. Effect of xanthan gum on physicochemical properties of whey protein isolate stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocolloids 2007, 21, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.S.; Xue, Y.; Xie, L.Y. Natural Food Emulsifier and Emulsion; Science press: Beijing, China, 1999; pp. 180–812. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.J.; Qin, X.J.; Jia, C.X. Research progress of the soybean lecithin. Acad. Period. Farm Prod. Process. 2009, 10, 55–57. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.Z.; Pang, C.X. Synthesis and applications of sucrose fatty acid ester. J. Chin. Beet Sugar 2005, 9, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Tan, L. The component analysis of tween 80. Chin. Pharmacol. J 2012, 47, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Bylaite, E.; Nissen, J.A.; Meyer, A.S. Effect of Xanthan on flavor release from thickened viscous food model systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 3577–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouquand, C.; Aguni, Y.; Malhiac, C.; Grisel, M. Influence of chemical composition of polysaccharides on aroma retention. Food Hydrocolloids 2008, 22, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secouard, S.; Grisel, M.; Malhiac, C. Flavour release study as a way to explain xanthan-galactomannan interactions. Food Hydrocolloids 2007, 21, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terta, M.; Blekas, G.; Paraskevopoulou, A. Retention of selected aroma compounds by polysaccharide solutions: A thermodynamic and kinetic approach. Food Hydrocolloids 2006, 20, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milas, M.; Rinaudo, M.; Knipper, M.; Schuppiser, J.L. Flow and viscosity properties of xanthan gum solution. Macromolecules 1990, 23, 2506–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhosseini, H.; Tan, C.P.; Hamid, N.S.A.; Yusof, S. Effect of Arabic gum, xanthan gum and orange oil on flavor release from diluted orange beverage emulsion. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miettinen, S.M.; Tuorila, H.; Piironen, V. Effect of emulsion characteristics on the release of aroma as detected by sensory evaluation, static headspace gas chromatography, and electronic nose. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4232–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, O.; Silcock, P.; Leus, M.; Everett, D.W. Multilayer emulsions as delivery systems for controlled release of volatile compounds using pH and salt triggers. Food Hydrocolloids 2012, 27, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landy, P.; Courthaudon, J.L.; Dubois, C. Effect of interface in model food emulsions on the volatility of aroma compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guichard, E.; Langourieux, S. Interactions between β-lactoglobulin and favour compounds. Food Chem. 2000, 71, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, M.; Hills, B.P.; Bakker, J.; Clothier, T. Mathematical models of flavor release from liquid emulsions. J. Food Sci. 1997, 62, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.N.; Tai, Y.N.; Dong, M.; Shao, J.H.; Yang, S.Z.; Pan, S.Y.; Fan, G. Characterisation of free and bound volatile compounds from six different varieties of citrus fruits. Food Chem. 2015, 185, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Not available.










© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.-J.; Dong, M.; Liu, Y.-L.; Zhang, L.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Ren, J.-N.; Pan, S.-Y.; Fan, G. Effect of Food Emulsifiers on Aroma Release. Molecules 2016, 21, 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040511
Li J-J, Dong M, Liu Y-L, Zhang L-L, Zhang Y, Yang Z-Y, Ren J-N, Pan S-Y, Fan G. Effect of Food Emulsifiers on Aroma Release. Molecules. 2016; 21(4):511. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040511
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jia-Jia, Man Dong, Yan-Long Liu, Lu-Lu Zhang, Yan Zhang, Zi-Yu Yang, Jing-Nan Ren, Si-Yi Pan, and Gang Fan. 2016. "Effect of Food Emulsifiers on Aroma Release" Molecules 21, no. 4: 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040511
APA StyleLi, J. -J., Dong, M., Liu, Y. -L., Zhang, L. -L., Zhang, Y., Yang, Z. -Y., Ren, J. -N., Pan, S. -Y., & Fan, G. (2016). Effect of Food Emulsifiers on Aroma Release. Molecules, 21(4), 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040511