Development of Droplet Microfluidics Enabling High-Throughput Single-Cell Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
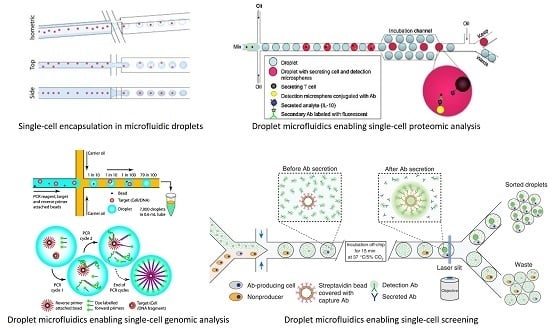
2. Prototype Demonstration of Single-Cell Encapsulation in Microfluidic Droplets
3. Technical Improvements in Single-Cell Encapsulation in Microfluidic Droplets
4. Microfluidic Droplets Enabling Single-Cell Proteomic Analysis
5. Microfluidic Droplets Enabling Single-Cell Genomic Analysis
6. Integrated Microfluidic Droplet Systems Enabling Single-Cell Screening
7. Conclusions and Future Work
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, D.; Bodovitz, S. Single cell analysis: The new frontier in ‘omics’. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritzsch, F.S.; Dusny, C.; Frick, O.; Schmid, A. Single-cell analysis in biotechnology, systems biology, and biocatalysis. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2012, 3, 129–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsioris, K.; Torres, A.J.; Douce, T.B.; Love, J.C. A new toolbox for assessing single cells. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2014, 5, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasdekis, A.E.; Stephanopoulos, G. Review of methods to probe single cell metabolism and bioenergetics. Metab. Eng. 2015, 27, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klepárník, K.; Foret, F. Recent advances in the development of single cell analysis—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 800, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haselgrübler, T.; Haider, M.; Ji, B.; Juhasz, K.; Sonnleitner, A.; Balogi, Z.; Hesse, J. High-throughput, multiparameter analysis of single cells. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 3279–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Marshall, D. Microfluidics for single cell analysis. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2012, 23, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, W.M.; Tseng, P.; Kunze, A.; Masaeli, M.; Chung, A.J.; Dudani, J.S.; Kittur, H.; Kulkarni, R.P.; di Carlo, D. Advances in high-throughput single-cell microtechnologies. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 25, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reece, A.; Xia, B.; Jiang, Z.; Noren, B.; McBride, R.; Oakey, J. Microfluidic techniques for high throughput single cell analysis. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 40, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squires, T.M.; Quake, S.R. Microfluidics: Fluid physics at the nanoliter scale. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2005, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitesides, G.M. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 2006, 442, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wootton, R.C.; de Mello, A.J. Microfluidics: Exploiting elephants in the room. Nature 2010, 464, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; van Noort, D. Cells in microfluidics. Top. Curr. Chem. 2011, 304, 295–321. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiong, B.; Ren, K.; Shu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shen, B.; Wu, H. Recent developments in microfluidics for cell studies. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5525–5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.M.; Paguirigan, A.L.; Kreutz, J.E.; Radich, J.P.; Chiu, D.T. Microfluidics for single-cell genetic analysis. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 3135–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Shin, Y.S.; Ma, C.; Wang, J.; Elitas, M.; Fan, R.; Heath, J.R. Microchip platforms for multiplex single-cell functional proteomics with applications to immunology and cancer research. Genome Med. 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, J.; Sutherland, A.; Wei, W.; Shin, Y.S.; Xue, M.; Heath, J.R. Microfluidics-based single-cell functional proteomics for fundamental and applied biomedical applications. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2014, 7, 275–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, B.; Li, X.; Chen, D.; Peng, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, J. Development of microfluidic systems enabling high-throughput single-cell protein characterization. Sensors 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Nguyen, J.; Wei, Y.; Sun, Y. Recent advances in microfluidic techniques for single-cell biophysical characterization. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2464–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, E.M.; Carlo, D.D. High-throughput assessment of cellular mechanical properties. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 17, 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, D.; Yue, W.; Chen, J. Constriction channel based single-cell mechanical property characterization. Micromachines 2015, 6, 1794–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xue, C.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, D.; Wu, M.H.; Wang, J. Microfluidic impedance flow cytometry enabling high-throughput single-cell electrical property characterization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 9804–9830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Xie, X.; Duan, Y.; Wang, L.; Cheng, Z.; Cheng, J. A review of impedance measurements of whole cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teh, S.Y.; Lin, R.; Hung, L.H.; Lee, A.P. Droplet microfluidics. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 198–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theberge, A.B.; Courtois, F.; Schaerli, Y.; Fischlechner, M.; Abell, C.; Hollfelder, F.; Huck, W.T.S. Microdroplets in microfluidics: An evolving platform for discoveries in chemistry and biology. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 5846–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralf, S.; Martin, B.; Thomas, P.; Stephan, H. Droplet based microfluidics. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 207–230. [Google Scholar]
- Basova, E.Y.; Foret, F. Droplet microfluidics in (bio)chemical analysis. Analyst 2015, 140, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leman, M.; Abouakil, F.; Griffiths, A.D.; Tabeling, P. Droplet-based microfluidics at the femtolitre scale. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shembekar, N.; Chaipan, C.; Utharala, R.; Merten, C.A. Droplet-based microfluidics in drug discovery, transcriptomics and high-throughput molecular genetics. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1314–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouzes, E. Droplet microfluidics for single-cell analysis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 853, 105–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joensson, H.; Andersson Svahn, H. Droplet microfluidics-a tool for single-cell analysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12176–12192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagus, T.P.; Edd, J.F. A review of the theory, methods and recent applications of high-throughput single-cell droplet microfluidics. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.J.; Neild, A.; de Mello, A.; Liu, A.Q.; Ai, Y. The poisson distribution and beyond: Methods for microfluidic droplet production and single cell encapsulation. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 3439–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Edgar, J.S.; Jeffries, G.D.; Lorenz, R.M.; Shelby, J.P.; Chiu, D.T. Selective encapsulation of single cells and subcellular organelles into picoliter- and femtoliter-volume droplets. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 1539–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.C.; Hettiarachchi, K.; Siu, M.; Pan, Y.R.; Lee, A.P. Controlled microfluidic encapsulation of cells, proteins, and microbeads in lipid vesicles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 5656–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Pullela, S.R.; Marquez, M.; Cheng, Z. Cell encapsules with tunable transport and mechanical properties. Biomicrofluidics 2007, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabert, M.; Viovy, J.L. Microfluidic high-throughput encapsulation and hydrodynamic self-sorting of single cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3191–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Um, E.; Lee, S.G.; Park, J.K. Random breakup of microdroplets for single-cell encapsulation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joensson, H.N.; Uhlen, M.; Svahn, H.A. Droplet size based separation by deterministic lateral displacement-separating droplets by cell-induced shrinking. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, T.; Ramji, R.; Warkiani, M.E.; Han, J.; Lim, C.T.; Chen, C.-H. Jetting microfluidics with size-sorting capability for single-cell protease detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 66, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edd, J.F.; di Carlo, D.; Humphry, K.J.; Koster, S.; Irimia, D.; Weitz, D.A.; Toner, M. Controlled encapsulation of single-cells into monodisperse picolitre drops. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 1262–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemna, E.W.M.; Schoeman, R.M.; Wolbers, F.; Vermes, I.; Weitz, D.A.; van den Berg, A. High-yield cell ordering and deterministic cell-in-droplet encapsulation using dean flow in a curved microchannel. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2881–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramji, R.; Wang, M.; Bhagat, A.A.S.; Tan Shao Weng, D.; Thakor, N.V.; Teck Lim, C.; Chen, C.-H. Single cell kinase signaling assay using pinched flow coupled droplet microfluidics. Biomicrofluidics 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagus, T.P.; Edd, J.F. High-throughput co-encapsulation of self-ordered cell trains: Cell pair interactions in microdroplets. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 20512–20522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagus, T.P.; Edd, J.F. High throughput single-cell and multiple-cell micro-encapsulation. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 64, e4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huebner, A.; Srisa-Art, M.; Holt, D.; Abell, C.; Hollfelder, F.; de Mello, A.J.; Edel, J.B. Quantitative detection of protein expression in single cells using droplet microfluidics. Chem. Commun. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huebner, A.; Olguin, L.F.; Bratton, D.; Whyte, G.; Huck, W.T.; de Mello, A.J.; Edel, J.B.; Abell, C.; Hollfelder, F. Development of quantitative cell-based enzyme assays in microdroplets. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3890–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huebner, A.; Bratton, D.; Whyte, G.; Yang, M.; de Mello, A.J.; Abell, C.; Hollfelder, F. Static microdroplet arrays: A microfluidic device for droplet trapping, incubation and release for enzymatic and cell-based assays. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, C.H.; Rowat, A.C.; Koster, S.; Weitz, D.A. Dropspots: A picoliter array in a microfluidic device. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, J.-U.; Olguin, L.F.; Whyte, G.; Scott, D.; Babtie, A.; Abell, C.; Huck, W.T.S.; Hollfelder, F. Simultaneous determination of gene expression and enzymatic activity in individual bacterial cells in microdroplet compartments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 15251–15256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srisa-Art, M.; Bonzani, I.C.; Williams, A.; Stevens, M.M.; de Mello, A.J.; Edel, J.B. Identification of rare progenitor cells from human periosteal tissue using droplet microfluidics. Analyst 2009, 134, 2239–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Zhu, Y.; Brown, S.; Oakeshott, J.; Peat, T.S.; Surjadi, R.; Easton, C.; Leech, P.W.; Sexton, B.A. A pmma microfluidic droplet platform for in vitroprotein expression using crude e. Coli s30 extract. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 3391–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baret, J.C.; Beck, Y.; Billas-Massobrio, I.; Moras, D.; Griffiths, A.D. Quantitative cell-based reporter gene assays using droplet-based microfluidics. Chem. Biol. 2010, 17, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rane, T.D.; Puleo, C.M.; Liu, K.J.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, A.P.; Wang, T.H. Counting single molecules in sub-nanolitre droplets. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadevall i Solvas, X.; Niu, X.; Leeper, K.; Cho, S.; Chang, S.I.; Edel, J.B.; de Mello, A.J. Fluorescence detection methods for microfluidic droplet platforms. J. Vis. Exp. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Sarkar, A.; Song, Y.A.; Miller, M.A.; Kim, S.J.; Griffith, L.G.; Lauffenburger, D.A.; Han, J. Enhancing protease activity assay in droplet-based microfluidics using a biomolecule concentrator. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 10368–10371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, S.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Zhu, Y.; Du, W.-B.; Yao, B.; Fang, Q. Multifunctional picoliter droplet manipulation platform and its application in single cell analysis. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 7570–7576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konry, T.; Dominguez-Villar, M.; Baecher-Allan, C.; Hafler, D.A.; Yarmush, M.L. Droplet-based microfluidic platforms for single T cell secretion analysis of IL-10 cytokine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2707–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcoux, P.R.; Dupoy, M.; Mathey, R.; Novelli-Rousseau, A.; Heran, V.; Morales, S.; Rivera, F.; Joly, P.L.; Moy, J.-P.; Mallard, F. Micro-confinement of bacteria into w/o emulsion droplets for rapid detection and enumeration. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 377, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martino, C.; Zagnoni, M.; Sandison, M.E.; Chanasakulniyom, M.; Pitt, A.R.; Cooper, J.M. Intracellular protein determination using droplet-based immunoassays. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 5361–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewan, A.; Kim, J.; McLean, R.H.; Vanapalli, S.A.; Karim, M.N. Growth kinetics of microalgae in microfluidic static droplet arrays. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 2987–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joensson, H.N.; Zhang, C.; Uhlen, M.; Andersson-Svahn, H. A homogeneous assay for protein analysis in droplets by fluorescence polarization. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Patil, S.N.; Bowden, S.D.; Poulter, S.; Pan, J.; Salmond, G.P.; Welch, M.; Huck, W.T.; Abell, C. Intra-species bacterial quorum sensing studied at single cell level in a double droplet trapping system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 10570–10581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chokkalingam, V.; Tel, J.; Wimmers, F.; Liu, X.; Semenov, S.; Thiele, J.; Figdor, C.G.; Huck, W.T. Probing cellular heterogeneity in cytokine-secreting immune cells using droplet-based microfluidics. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 4740–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konry, T.; Golberg, A.; Yarmush, M. Live single cell functional phenotyping in droplet nano-liter reactors. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbaspourrad, A.; Zhang, H.; Tao, Y.; Cui, N.; Asahara, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yue, D.; Koehler, S.A.; Ung, L.W.; Heyman, J.; et al. Label-free single-cell protein quantification using a drop-based mix-and-read system. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, T.K.; Lei, K.F.; Hsieh, C.H.; Hsiao, H.B.; Wang, H.M.; Wu, M.H. Development of a microfluidic-based optical sensing device for label-free detection of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) through their lactic acid metabolism. Sensors 2015, 15, 6789–6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, A.C.; Dunn, M.R.; Hatch, A.; Sau, S.P.; Youngbull, C.; Chaput, J.C. A general strategy for expanding polymerase function by droplet microfluidics. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Iizuka, R.; Nishi, S.; Yoshida, T.; Hatada, Y.; Takaki, Y.; Iguchi, A.; Yoon, D.H.; Sekiguchi, T.; Shoji, S.; et al. Culture-independent method for identification of microbial enzyme-encoding genes by activity-based single-cell sequencing using a water-in-oil microdroplet platform. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, E.X.; Miller, M.A.; Jing, T.; Chen, C.-H. Single cell multiplexed assay for proteolytic activity using droplet microfluidics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumaresan, P.; Yang, C.J.; Cronier, S.A.; Blazej, R.G.; Mathies, R.A. High-throughput single copy DNA amplification and cell analysis in engineered nanoliter droplets. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3522–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazutis, L.; Araghi, A.F.; Miller, O.J.; Baret, J.C.; Frenz, L.; Janoshazi, A.; Taly, V.; Miller, B.J.; Hutchison, J.B.; Link, D.; et al. Droplet-based microfluidic systems for high-throughput single DNA molecule isothermal amplification and analysis. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 4813–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaerli, Y.; Wootton, R.C.; Robinson, T.; Stein, V.; Dunsby, C.; Neil, M.A.A.; French, P.M.W.; de Mello, A.J.; Abell, C.; Hollfelder, F. Continuous-flow polymerase chain reaction of single-copy DNA in microfluidic microdroplets. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Cui, L.; Yang, C.J. Agarose droplet microfluidics for highly parallel and efficient single molecule emulsion pcr. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 2841–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Novak, R.; Shuga, J.; Smith, M.T.; Mathies, R.A. High-performance single cell genetic analysis using microfluidic emulsion generator arrays. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 3183–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatch, A.C.; Fisher, J.S.; Tovar, A.R.; Hsieh, A.T.; Lin, R.; Pentoney, S.L.; Yang, D.L.; Lee, A.P. 1-million droplet array with wide-field fluorescence imaging for digital pcr. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 3838–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindson, B.J.; Ness, K.D.; Masquelier, D.A.; Belgrader, P.; Heredia, N.J.; Makarewicz, A.J.; Bright, I.J.; Lucero, M.Y.; Hiddessen, A.L.; Legler, T.C.; et al. High-throughput droplet digital pcr system for absolute quantitation of DNA copy number. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8604–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mary, P.; Dauphinot, L.; Bois, N.; Potier, M.-C.; Studer, V.; Tabeling, P. Analysis of gene expression at the single-cell level using microdroplet-based microfluidic technology. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, R.; Zeng, Y.; Shuga, J.; Venugopalan, G.; Fletcher, D.A.; Smith, M.T.; Mathies, R.A. Single cell multiplex gene detection and sequencing using microfluidically-generated agarose emulsions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rane, T.D.; Zec, H.C.; Puleo, C.; Lee, A.P.; Wang, T.-H. Droplet microfluidics for amplification-free genetic detection of single cells. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 3341–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Jenkins, G.; Zou, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, C.J. Massively parallel single-molecule and single-cell emulsion reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction using agarose droplet microfluidics. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3599–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Leng, X.; Zhang, M.; Guan, Z.; Lu, J.; Yang, C.J. Highly sensitive and quantitative detection of rare pathogens through agarose droplet microfluidic emulsion pcr at the single-cell level. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 3907–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Li, C.; Lu, S.; Zhou, W.; Tang, F.; Xie, X.S.; Huang, Y. Uniform and accurate single-cell sequencing based on emulsion whole-genome amplification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11923–11928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, A.M.; Mazutis, L.; Akartuna, I.; Tallapragada, N.; Veres, A.; Li, V.; Peshkin, L.; Weitz, D.A.; Kirschner, M.W. Droplet barcoding for single-cell transcriptomics applied to embryonic stem cells. Cell 2015, 161, 1187–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, Y.; Hosokawa, M.; Maruyama, T.; Yamagishi, K.; Mori, T.; Takeyama, H. Monodisperse picoliter droplets for low-bias and contamination-free reactions in single-cell whole genome amplification. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baret, J.C.; Miller, O.J.; Taly, V.; Ryckelynck, M.; El-Harrak, A.; Frenz, L.; Rick, C.; Samuels, M.L.; Hutchison, J.B.; Agresti, J.J.; et al. Fluorescence-activated droplet sorting (fads): Efficient microfluidic cell sorting based on enzymatic activity. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1850–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouzes, E.; Medkova, M.; Savenelli, N.; Marran, D.; Twardowski, M.; Hutchison, J.B.; Rothberg, J.M.; Link, D.R.; Perrimon, N.; Samuels, M.L. Droplet microfluidic technology for single-cell high-throughput screening. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14195–14200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agresti, J.J.; Antipov, E.; Abate, A.R.; Ahn, K.; Rowat, A.C.; Baret, J.C.; Marquez, M.; Klibanov, A.M.; Griffiths, A.D.; Weitz, D.A. Ultrahigh-throughput screening in drop-based microfluidics for directed evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4004–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eun, Y.-J.; Utada, A.; Copeland, M.F.; Takeuchi, S.; Weibel, D.B. Encapsulating bacteria in agarose microparticles using microfluidics for high-throughput cell analysis and isolation. ACS Chem. Biol. 2011, 6, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kintses, B.; Hein, C.; Mohamed, M.F.; Fischlechner, M.; Courtois, F.; Lainé, C.; Hollfelder, F. Picoliter cell lysate assays in microfluidic droplet compartments for directed enzyme evolution. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazutis, L.; Gilbert, J.; Ung, W.L.; Weitz, D.A.; Griffiths, A.D.; Heyman, J.A. Single-cell analysis and sorting using droplet-based microfluidics. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 870–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.L.; Ghaderi, A.; Zhou, H.; Agresti, J.; Weitz, D.A.; Fink, G.R.; Stephanopoulos, G. Microfluidic high-throughput culturing of single cells for selection based on extracellular metabolite production or consumption. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammar, P.; Angermayr, S.A.; Sjostrom, S.L.; van der Meer, J.; Hellingwerf, K.J.; Hudson, E.P.; Joensson, H.N. Single-cell screening of photosynthetic growth and lactate production by cyanobacteria. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2015, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Interested Proteins | Detection Mechanisms | References |
|---|---|---|
| β-galactosidase of mast cells | Following cellular lysis, intracellular β-galactosidase catalyzed the substrate (fluorescein di-β-d-galactopyranoside) for fluorescence detection | [34] |
| Yellow fluorescent protein mutant of E. coli | The expression of yellow fluorescent proteins was correlated with the growth status of encapsulated E. coli | [46] |
| Alkaline phosphatase of E. coli | Expresssed alkaline phosphatase in the cellular periplasm catalyzed the substrate (3-O-methylfluorescein-phosphates) for fluorescence detection | [47] |
| Both red fluorescent protein and alkaline phosphatase of E. coli | Gene expression and enzymatic activity of E. coli were simultaneously and continuously monitored | [50] |
| IL-10 of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells | The secreted substance captured on the microsphere surface coated with capturing antibodies and detected via the further binding of fluorescence labled detection antibodies on microsphere surfaces | [58] |
| Intracellular HRas-mCitrine of HEK-293 cells and actin-EGFP of MCF-7 cells | Following cell encapsulation and lysis, proteins under interest were captured on the microsphere surface coated with capturing antibodies and detected via the further binding of fluorescence labled detection antibodies on microsphere surfaces | [60] |
| IL-2, IFN-γ, and TNF-α of activated T-cells | Cells were encapsulated in agarose droplets together with functionalized cytokine-capture beads for subsequent binding and detection of secreted cytokines from single cells | [64] |
| Receptor tyrosine kinases of PC-9 cells | Binding surface ligands of 8-hydroxy-5-(N,N-dimethylsulfonamido)-2-methylquinoline) with the receptor tyrosine kinases generates fluorescent signals | [43] |
| Multiple proteases of MDA-MB-231, PC-9, and K-562 cells | Protease-catalyzed multi-color Förster resonance energy transfer based enzymatic substrates, enabling the simultaneous measurement of six proteases | [70] |
| Interested Gene Sections | Working Mechanisms | References |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH gene of lymphocyte cells and gyr B gene of E. coli | A single cell and a primer functionalized microbead were encapsulated in droplets, followed by bulk PCR, droplet lysis, and bead analysis in flow cytometry | [71] |
| KI#128 island on the E. coli K12 and OI#43 island on the E. coli O157 cells | 96 channels were used to generate up to 3.4 × 106 nanoliter-volume droplets per hour, identifying rare pathogenic E. coli O157 cells (1:105 cells) | [75] |
| Chromosomal translocation t(14;18) of follicular lymphoma cells | Agarose droplets were formed to encapsulate cells and primer-functionalized microbeads, maintaining genome fidelity during cell lysis and DNA purification, leading to efficient PCR and subsequent gene sequencing | [79] |
| KI#128 island on the E. coli K12 and OI#43 island on the E. coli O157 cells | An agarose droplet was formed to encapsulate single cells and PCR mix with reverse primers covalently conjugated to agarose | [82] |
| Gene expression of EpCAM from | An agarose droplet was formed to encapsulate single cells and RT-PCR mix with primers covalently conjugated to agarose | [82] |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, N.; Zhao, Z.; Fan, B.; Chen, D.; Men, D.; Wang, J.; Chen, J. Development of Droplet Microfluidics Enabling High-Throughput Single-Cell Analysis. Molecules 2016, 21, 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070881
Wen N, Zhao Z, Fan B, Chen D, Men D, Wang J, Chen J. Development of Droplet Microfluidics Enabling High-Throughput Single-Cell Analysis. Molecules. 2016; 21(7):881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070881
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Na, Zhan Zhao, Beiyuan Fan, Deyong Chen, Dong Men, Junbo Wang, and Jian Chen. 2016. "Development of Droplet Microfluidics Enabling High-Throughput Single-Cell Analysis" Molecules 21, no. 7: 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070881
APA StyleWen, N., Zhao, Z., Fan, B., Chen, D., Men, D., Wang, J., & Chen, J. (2016). Development of Droplet Microfluidics Enabling High-Throughput Single-Cell Analysis. Molecules, 21(7), 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070881