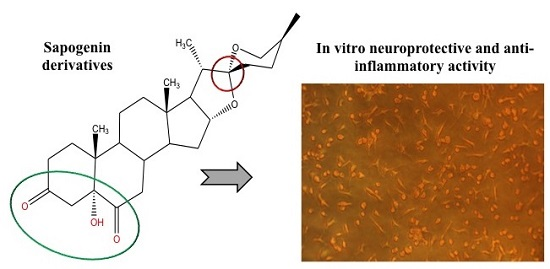
In Vitro Neuroprotective and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Natural and Semi-Synthetic Spirosteroid Analogues
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Activity
2.2.1. Treatments to PC12 Cell Cultures
2.2.2. Measurements of IL-1β and Nitric Oxide Levels
2.2.3. Rat Uterotrophic Assay
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. (25R)-5-Spirost-3β-ol-3-acetate (6)
3.1.2. (25R)-5,6-Epoxy-spirost-3β-ol-3-acetate (7)
3.1.3. (25R)-Spirost-3β,5α-dihydroxy-6-one-3-acetate (8)
3.1.4. (25R)-Spirost-3β,5α-dihydroxy-6-one (S9)
3.1.5. (25R)-Spirost-5α-hydroxy-3,6-dione (S15)
3.2. Biological Activity Assays
3.2.1. Treatments for PC12 Cell Cultures
3.2.2. MTT Assay
3.2.3. Microglia-Enriched Primary Cultures
3.2.4. IL-1β and Nitric Oxide Assay
3.2.5 Immature Rat Uterotrophic Assay
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mukherjee, D.; Patil, C.G. Epidemiology and the global burden of stroke. World Neurosurg. 2011, 76, S85–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirnagl, U. Pathobiology of injury after stroke: The neurovascular unit and beyond. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1268, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirnagl, U.; Iadecola, C.; Moskowitz, M.A. Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: An integrated view. Trends Neurosci. 1999, 22, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouns, R.; de Deyn, P.P. The complexity of neurobiological processes in acute ischemic stroke. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2009, 111, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iadecola, C.; Anrather, J. The immunology of stroke: From mechanisms to translation. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.R.; Hsu, J.T.; Chang, I.T.; Young, Y.C.; Lin, C.M.; Ying, C. The effects of glutamate can be attenuated by estradiol via estrogen receptor dependent pathway in rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells. Endocrine 2007, 31, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.W.; Maulucci-Gedde, M.; Kriegstein, A.R. Glutamate neurotoxicity in cortical cell culture. J. Neurosci. 1987, 7, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.F.; Oliveira, C.R. Oxidative glutamate toxicity involves mitochondrial dysfunction and perturbation of intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis. Neurosci. Res. 2000, 37, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.M.; Oliveira, C.R. Glutamate toxicity on a PC12 cell line involves glutathione (GSH) depletion and oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 23, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olney, J.W. Brain lesions, obesity, and other disturbances in mice treated with monosodium glutamate. Science 1969, 164, 719–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanika, R.I.; Pivovarova, N.B.; Brantner, C.A.; Watts, C.A.; Winters, C.A.; Andrews, S.B. Coupling diverse routes of calcium entry to mitochondrial dysfunction and glutamate excitotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9854–9859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, T.H.; Miyamoto, M.; Sastre, A.; Schnaar, R.L.; Coyle, J.T. Glutamate toxicity in a neuronal cell line involves inhibition of cystine transport leading to oxidative stress. Neuron 1989, 2, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.B.; Maher, P. Protein kinase C activation inhibits glutamate-induced cytotoxicity in a neuronal cell line. Brain Res. 1994, 652, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, D.; Kimura, H.; Maher, P. Growth factors and vitamin E modify neuronal glutamate toxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 8264–8267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.J.; Reynolds, I.J. Mitochondria and Na+/Ca2+ exchange buffer glutamate-induced calcium loads in cultured cortical neurons. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 1318–1328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rizzuto, R. Intracellular Ca2+ pools in neuronal signalling. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2001, 11, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zucker, R.S. Mitochondrial involvement in post-tetanic potentiation of synaptic transmission. Neuron 1997, 18, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szydlowska, K.; Tymianski, M. Calcium, ischemia and excitotoxicity. Cell Calcium 2010, 47, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirnagl, U. Bench to bedside: The quest for quality in experimental stroke research. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2006, 26, 1465–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiga, S.; García-Segura, L.M.; Azcoitia, I. The neuroprotective properties of sex steroids and neurosteroids. Rev. Neurol. 2004, 39, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simpkins, J.W.; Rajakumar, G.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Simpkins, C.E.; Greenwald, D.; Yu, C.J.; Bodor, N.; Day, A.L. Estrogens may reduce mortality and ischemic damage caused by middle cerebral artery occlusion in the female rat. J. Neurosurg. 1997, 87, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behl, C.; Skutella, T.; Lezoualc’h, F.; Post, A.; Widmann, M.; Newton, C.J.; Holsboer, F. Neuroprotection against oxidative stress by estrogens: Structure-activity relationship. Mol. Pharmacol. 1997, 51, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Behl, C.; Widmann, M.; Trapp, T.; Holsboer, F. 17-β estradiol protects neurons from oxidative stress-induced cell death in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 216, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, P.S.; Gordon, K.; Simpkins, J.W. Phenolic A ring requirement for the neuroprotective effects of steroids. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1997, 63, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosmann, B.; Behl, C. The antioxidant neuroprotective effects of estrogens and phenolic compounds are independent from their estrogenic properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 8867–8872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokai, L.; Prokai-Tatrai, K.; Perjesi, P.; Zharikova, A.D.; Perez, E.J.; Liu, R.; Simpkins, J.W. Quinol-based cyclic antioxidant mechanism in estrogen neuroprotection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11741–11746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Brown, C.M.; Wise, P.M. Neuroprotective effects of estrogens following ischemic stroke. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2009, 30, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpkins, J.W.; Singh, M.; Brock, C.; Etgen, A.M. Neuroprotection and estrogen receptors. Neuroendocrinology 2012, 96, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vegeto, E.; Ghisletti, S.; Meda, C.; Etteri, S.; Belcredito, S.; Maggi, A. Regulation of the lipopolysaccharide signal transduction pathway by 17β-estradiol in macrophage cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 91, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamid, R.; Luo, J.; VandeVrede, L.; Kundu, I.; Michalsen, B.; Litosh, V.A.; Schiefer, I.T.; Gherezghiher, T.; Yao, P.; Qin, Z.; et al. Benzothiophene Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators Provide Neuroprotection by a novel GPR30-dependent Mechanism. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2011, 2, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronnekleiv, O.K.; Malyala, A.; Kelly, M.J. Membrane-initiated signaling of estrogen in the brain. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2007, 25, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, C.E., Jr.; Park-Chung, M.; Gibbs, T.T.; Farb, D.H. 17β-Estradiol protects against NMDA-induced excitotoxicity by direct inhibition of NMDA receptors. Brain Res. 1997, 761, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, M.; Kuller, L.H.; Prentice, R.; Rodabough, R.J.; Psaty, B.M.; Stafford, R.S.; Sidney, S.; Rosendaal, F.R. Estrogen plus progestin and risk of venous thrombosis. JAMA 2004, 292, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inagaki, T.; Etgen, A.M. Neuroprotective action of acute estrogens: Animal models of brain ischemia and clinical implications. Steroids 2013, 78, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perron, F.; Albizati, K.F. Chemistry of spiroketals. Chem. Rev. 1989, 89, 1617–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, K.; Sheth, N.; Ranpariya, V.; Parmar, S. Anticonvulsant activity of solasodine isolated from Solanum sisymbriifolium fruits in rodents. Pharm. Biol. 2011, 49, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecanu, L.; Hashim, A.I.; McCourty, A.; Giscos-Douriez, I.; Dinca, I.; Yao, W.; Vicini, S.; Szabo, G.; Erdélyi, F.; Greeson, J.; et al. The naturally occurring steroid solasodine induces neurogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Neuroscience 2011, 183, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpkins, J.W.; Yang, S.H.; Liu, R.; Perez, E.; Cai, Z.Y.; Covey, D.F.; Green, P.S. Estrogen-like compounds for ischemic neuroprotection. Stroke 2004, 35, 2648–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, A.Z.; Tacoronte, J.E.; Mancha, F. C.; de la Paz, L.A.; Cabrera, M.T. Ecdysteroid analogs based on steroidal sapogenins I. Synthesis of bromo-derivatives from diosgenin. Preliminary study of their biological activity. Rev. CENIC. Cienc. Quím. 2002, 33, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- SciFinder. Chemical Abstracts Service. Columbus 2015. Available online: https://scifinder.cas.org/scifinder/ (accesed on 30 January 2015).
- Rivera, D.G.; León, F.; Coll, F.; Davison, G.P. Novel 5β-hydroxyspirostan-6-ones ecdysteroid antagonists: Synthesis and biological testing. Steroids 2006, 71, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shawakfeh, K.Q.; Al-Said, N.H. Synthesis of new symmetrical bis-steroidal pyrazine analogues from diosgenin. Steroids 2011, 76, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhavnani, B.R.; Berco, M.; Binkley, J. Equine estrogens differentially prevent neuronal cell death induced by glutamate. J. Soc. Gynecol. Investig. 2003, 10, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, L.A.; Tischler, A.S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 2424–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kritis, A.A.; Stamoula, E.G.; Paniskaki, K.A.; Vavilis, T.D. Researching glutamate—Induced cytotoxicity in different cell lines: A comparative/collective analysis/study. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, M.D.; Vanden Heuvel, J.P.; Isom, G.E.; Schwarz, R.D. Differential expression of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) in the rat pheochromocytoma cell line PC12: Role of nerve growth factor and ras. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 252, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajta, M.; Budziszewska, B.; Marszał, M.; Lasoń, W. Effects of 17-β estradiol and estriol on NMDA-induced toxicity and apoptosis in primary cultures of rat cortical neurons. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2001, 52, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Behl, C. Estrogen can protect neurons: Modes of action. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 83, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, H.; Ibi, M.; Kihara, T.; Urushitani, M.; Akaike, A.; Shimohama, S. Estradiol protects mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons from oxidative stress-induced neuronal death. J. Neurosci. Res. 1998, 54, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.H.; Perez, E.; Cutright, J.; Liu, R.; He, Z.; Day, A.L.; Simpkins, J.W. Testosterone increases neurotoxicity of glutamate in vitro and ischemia-reperfusion injury in an animal model. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 92, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fanaei, H.; Sadeghipour, H.R.; Karimian, S.M.; Hassanzade, G. Flutamide Enhances Neuroprotective Effects of Testosterone during Experimental Cerebral Ischemia in Male Rats. ISRN Neurol. 2013, 2013, 592398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macrae, I.M.; Carswell, H.V. Oestrogen and stroke: The potential for harm as well as benefit. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2006, 34, 1362–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.L.; Kim, C.K.; Cho, J.-H.; Lee, K.-H.; Ahn, J.-Y. Neuroprotection signaling pathway of nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor against staurosporine induced apoptosis in hippocampal H19-7/IGF-IR [corrected]. Exp. Mol. Med. 2010, 42, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillion, J.A.; Li, Y.; Maric, D.; Takanohashi, A.; Klimanis, D.; Barker, J.L.; Hallenbeck, J.M. Involvement of Akt in preconditioning-induced tolerance to ischemia in PC12 cells. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2006, 26, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Lu, C.; Han, Q.; Li, J.; Du, Z.; Liao, L.; Zhao, R.C. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect PC12 cells from glutamate excitotoxicity-induced apoptosis by upregulation of XIAP through PI3-K/Akt activation. Toxicology 2011, 279, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.; Howson, P.A.; Xia, Z.; Zhou, S.; Wu, E.; Xia, Z.; Hu, Y. Smilagenin attenuates beta amyloid (25-35)-induced degeneration of neuronal cells via stimulating the gene expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Neuroscience 2012, 210, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce-Keller, A.J.; Keeling, J.L.; Keller, J.N.; Huang, F.F.; Camondola, S.; Mattson, M.P. Antiinflammatory effects of estrogen on microglial activation. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 3646–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vegeto, E.; Bonincontro, C.; Pollio, G.; Sala, A.; Viappiani, S.; Nardi, F.; Brusadelli, A.; Viviani, B.; Ciana, P.; Maggi, A. Estrogen prevents the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in microglia. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.M.; Dela Cruz, C.D.; Yang, E.; Wise, P.M. Inducible nitric oxide synthase and estradiol exhibit complementary neuroprotective roles after ischemic brain injury. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 210, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, R.; Perez, E.; Yi, K.D.; Koulen, P.; Simpkins, J.W. Estrogen attenuates nuclear factor-kappa B activation induced by transient cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2004, 1008, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marty, M.S.; O’Connor, J.C. Key learnings from the Endocrine Disruptor Screening Program (EDSP) Tier 1 rodent uterotrophic and Hershberger assays. Birth Defects Res. B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 2014, 101, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Pupo, L.; Nuñez, F.Y.; Tacoronte, M.J.E.; Delgado, H.R. Efecto sobre la viabilidad celular de una nueva serie de espirosteroides sintéticos en células PC12. Rev. Cuba. Farm. 2013, 47, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, J.P.; Rees, S.; Kalindjian, S.B.; Philpott, K.L. Principles of early drug discovery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussaud, S.; Draheim, H.J. A new method to isolate microglia from adult mice and culture them for an extended period of time. J. Neurosci. Methods 2010, 187, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds S9 and S15 are available from the authors.





© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Pupo, L.; Zaldo-Castro, A.; Exarchou, V.; Tacoronte-Morales, J.E.; Pieters, L.; Vanden Berghe, W.; Nuñez-Figueredo, Y.; Delgado-Hernández, R. In Vitro Neuroprotective and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Natural and Semi-Synthetic Spirosteroid Analogues. Molecules 2016, 21, 992. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21080992
García-Pupo L, Zaldo-Castro A, Exarchou V, Tacoronte-Morales JE, Pieters L, Vanden Berghe W, Nuñez-Figueredo Y, Delgado-Hernández R. In Vitro Neuroprotective and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Natural and Semi-Synthetic Spirosteroid Analogues. Molecules. 2016; 21(8):992. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21080992
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Pupo, Laura, Armando Zaldo-Castro, Vassiliki Exarchou, Juan Enrique Tacoronte-Morales, Luc Pieters, Wim Vanden Berghe, Yanier Nuñez-Figueredo, and René Delgado-Hernández. 2016. "In Vitro Neuroprotective and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Natural and Semi-Synthetic Spirosteroid Analogues" Molecules 21, no. 8: 992. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21080992
APA StyleGarcía-Pupo, L., Zaldo-Castro, A., Exarchou, V., Tacoronte-Morales, J. E., Pieters, L., Vanden Berghe, W., Nuñez-Figueredo, Y., & Delgado-Hernández, R. (2016). In Vitro Neuroprotective and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Natural and Semi-Synthetic Spirosteroid Analogues. Molecules, 21(8), 992. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21080992