Chemical Synthesis and Characterization of an Equinatoxin II(1–85) Analogue
Abstract
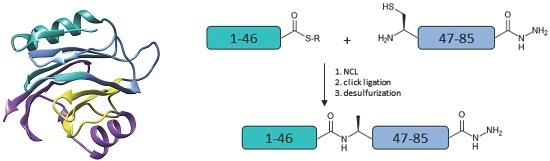
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Peptide Synthesis
3.3. Purification and Analysis
3.4. Native Chemical Ligation
3.5. CD Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rojko, N.; Dalla Serra, M.; Maček, P.; Anderluh, G. Pore formation by actinoporins, cytolysins from sea anemones. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1858, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, K.E.; Spielmann, T.; Hanssen, E.; Adisa, A.; Separovic, F.; Dixon, M.W.A.; Trenholme, K.R.; Hawthorne, P.L.; Gardiner, D.L.; Gilberger, T.; et al. Selective permeabilization of the host cell membrane of Plasmodium falciparum-infected red blood cells with streptolysin O and equinatoxin II. Biochem. J. 2007, 403, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanasiadis, A.; Anderluh, G.; Maček, P.; Turk, D. Crystal structure of the soluble form of equinatoxin II, a pore-forming toxin from the sea anemone Actinia equina. Structure 2001, 9, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, D.K.; Yao, S.; Rojko, N.; Anderluh, G.; Lybrand, T.P.; Downton, M.T.; Wagner, J.; Separovic, F. Characterization of the Lipid-Binding Site of Equinatoxin II by NMR and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Biophys. J. 2015, 108, 1987–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderluh, G.; Serra, M.D.; Viero, G.; Guella, G.; Macek, P.; Menestrina, G. Pore Formation by Equinatoxin II, a Eukaryotic Protein Toxin, Occurs by Induction of Nonlamellar Lipid Structures. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 45216–45223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojko, N.; Kristan, K.C.; Viero, G.; Zerovnik, E.; Macek, P.; Dalla Serra, M.; Anderluh, G. Membrane Damage by an -Helical Pore-forming Protein, Equinatoxin II, Proceeds through a Succession of Ordered Steps. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 23704–23715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belmonte, G.; Pederzolli, C.; Macek, P.; Menestrina, G. Pore formation by the sea anemone cytolysin equinatoxin II in red blood cells and model lipid membranes. J. Membr. Biol. 1993, 131, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, A.H.; Mobli, M.; Gooley, P.R.; King, G.F.; Mackay, J.P. Macromolecular NMR spectroscopy for the non-spectroscopist: Macromolecular NMR for the non-spectroscopists I. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drechsler, A.; Separovic, F. Solid-state NMR Structure Determination. IUBMB Life 2003, 55, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, B.; Tietze, D.; White, P.B.; Liao, S.Y.; Hong, M. Chemical ligation of the influenza M2 protein for solid-state NMR characterization of the cytoplasmic domain. Protein Sci. 2015, 24, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderluh, G.; Razpotnik, A.; Podlesek, Z.; Macek, P.; Separovic, F.; Norton, R.S. Interaction of the eukaryotic pore-forming cytolysin equinatoxin II with model membranes: 19F NMR studies. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 347, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, A.J.; Drechsler, A.; Kristan, K.; Anderluh, G.; Norton, R.S.; Wallace, B.A.; Separovic, F. The effects of lipids on the structure of the eukaryotic cytolysin equinatoxin II: A synchrotron radiation circular dichroism spectroscopic study. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1778, 2091–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miquel, V.-P.; Liu, Z.; Shah, N.H.; Willis, J.A.; Idoyaga, J.; Muir, T.W. Streamlined expressed protein ligation using split inteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 286–292. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, P.E.; Muir, T.W.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Kent, S.B.H. Synthesis of Proteins by Native Chermical Ligation. Science 1994, 266, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondalapati, S.; Jbara, M.; Brik, A. Expanding the chemical toolbox for the synthesis of large and uniquely modified proteins. Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M.; Kiuchi, T.; Nishihara, M.; Tezuka, K.; Okamoto, R.; Izumi, M.; Kajihara, Y. Chemical synthesis of erythropoietin glycoforms for insights into the relationship between glycosylation pattern and bioactivity. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1500678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.; Gao, S.; Zheng, Y.; Tan, X.; Lan, H.; Tan, X.; Sun, D.; Lu, L.; Wang, T.; Zheng, Q.; et al. Quasi-Racemic X-ray Structures of K27-Linked Ubiquitin Chains Prepared by Total Chemical Synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 7429–7435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstock, M.T.; Jacobsen, M.T.; Kay, M.S. Synthesis and folding of a mirror-image enzyme reveals ambidextrous chaperone activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11679–11684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, G.-M.; Li, Y.-M.; Shen, F.; Huang, Y.-C.; Li, J.-B.; Lin, Y.; Cui, H.-K.; Liu, L. Protein Chemical Synthesis by Ligation of Peptide Hydrazides. Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 7787–7791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.-M.; Wang, J.-X.; Liu, L. Convergent Chemical Synthesis of Proteins by Ligation of Peptide Hydrazides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10347–10350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, J.M.; Leadbeater, N.E. Microwave energy: A versatile tool for the biosciences. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, P.F.; Dogovski, C.; Dobson, R.C.J.; Bailey, M.F.; Goldie, K.N.; Karas, J.A.; Scanlon, D.B.; O’Hair, R.A.J.; Perugini, M.A. Aromatic residues in the C-terminal helix of human apoC-I mediate phospholipid interactions and particle morphology. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1384–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karas, J.A.; Boland, M.; Haigh, C.; Johanssen, V.; Hill, A.; Barnham, K.; Collins, S.; Scanlon, D. Microwave Synthesis of Prion Protein Fragments up to 111 Amino Acids in Length Generates Biologically Active Peptides. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2012, 18, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, S.C. The N Terminus of α-Synuclein Forms Cu II—Bridged Oligomers. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 7111–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Q.; Danishefsky, S.J. Free-Radical-Based, Specific Desulfurization of Cysteine: A Powerful Advance in the Synthesis of Polypeptides and Glycopolypeptides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 9248–9252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlström, A.; Undén, A. A new protecting group for aspartic acid that minimizes piperidine-catalyzed aspartimide formation in Fmoc solid phase peptide synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 4243–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drechsler, A.; Potrich, C.; Sabo, J.K.; Frisanco, M.; Guella, G.; Dalla Serra, M.; Anderluh, G.; Separovic, F.; Norton, R.S. Structure and activity of the N-terminal region of the eukaryotic cytolysin equinatoxin II. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2006, 45, 1818–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drechsler, A.; Miles, A.J.; Norton, R.S.; Wallace, B.A.; Separovic, F. Effect of lipid on the conformation of the N-terminal region of equinatoxin II: A synchrotron radiation circular dichroism spectroscopic study. Eur. Biophys. J. 2009, 39, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, Y.H.; Hung, A.; Norton, R.S.; Separovic, F.; Watts, A. Solid-state NMR and simulation studies of equinatoxin II N-terminus interaction with lipid bilayers. Proteins 2010, 78, 858–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |




© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karas, J.A.; Sani, M.-A.; Separovic, F. Chemical Synthesis and Characterization of an Equinatoxin II(1–85) Analogue. Molecules 2017, 22, 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22040559
Karas JA, Sani M-A, Separovic F. Chemical Synthesis and Characterization of an Equinatoxin II(1–85) Analogue. Molecules. 2017; 22(4):559. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22040559
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaras, John A., Marc-Antoine Sani, and Frances Separovic. 2017. "Chemical Synthesis and Characterization of an Equinatoxin II(1–85) Analogue" Molecules 22, no. 4: 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22040559
APA StyleKaras, J. A., Sani, M. -A., & Separovic, F. (2017). Chemical Synthesis and Characterization of an Equinatoxin II(1–85) Analogue. Molecules, 22(4), 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22040559