Selenium Speciation in the Fountain Creek Watershed (Colorado, USA) Correlates with Water Hardness, Ca and Mg Levels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of the Se-Levels and Speciation in the Fountain Creek
2.2. Se, Ca and Mg Levels and Hardness in the Fountain Creek Water
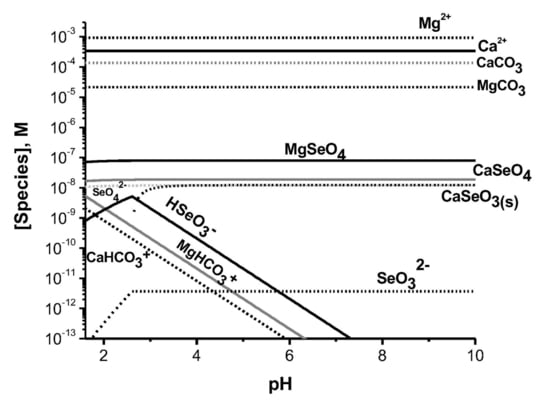
2.3. Speciation Profile for Sites with Low and High Levels of Se
2.4. Exploration of Other Physical Parameters and Their Impact on the Speciation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Fountain Creek Sampling
3.3. Analysis for Se, Ca and Mg
3.4. Alkalinity
3.5. Statistical Calculations
3.6. Speciation Calculations
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United States Environmental Protection Agency National Recommended Water Quality Criteria-Aquatic Life Criteria Table. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/wqc/national-recommended-water-quality-criteria-aquatic-life-criteria-table (accessed on 18 April 2016).
- Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment. The Basic Standards and Methodologies for Surface Water; Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment Water Quality Control Commission: Denver, CO, USA, 2013; Volume 31, p. 218.
- Divine, C.E.; Gates, T.K. Sources and Occurrence of Selenium in the Arkansas River and Fountain Creek near Pueblo, Colorado; Arcadis G&M, Inc.: Highlands Ranch, CO, USA, 2006; pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Edelmann, P.; Ferguson, S.A.; Stogner, R.W., Sr.; August, M.; Payne, W.F.; Bruce, J.F. Evaluation of Water Quality, Suspended Sediment, and Stream Morphology with an Emphasis on Effects of Stormflow on Fountain and Monument Creek Basins, Colorado Spring and Vicinity, Colorado, 1981 Through 2001; United States Geological Survey: Denver, CO, USA, 2005.
- Bird, S.M.; Ge, H.; Uden, P.C.; Tyson, J.F.; Block, E.; Denoyer, E. High-Performance liquid chromatography of selenoamino acids and organo selenium compounds. Speciation by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 1997, 789, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, S.M.; Tyson, J.F. Speciation of selenoamino acids and organoselenium compounds in selenium-Enriched yeast using high-Performance liquid chromatography–Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 1997, 12, 785–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, E.; Booker, S.J.; Flores-Penalba, S.; George, G.N.; Gundala, S.; Landgraf, B.J.; Liu, J.; Lodge, S.N.; Pushie, M.J.; Rozovsky, S.; et al. Trifluoroselenomethionine: A New Unnatural Amino Acid. Chembiochem 2016, 17, 1738–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combs, G.F., Jr.; Gray, W.P. Chemopreventive agents: Selenium. Pharmacol. Ther. 1998, 79, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, S.A.; O’Connor, L.; Rossman, T.G.; Block, E. Pro-Angiogenesis action of arsenic and its reversal by selenium-Derived compounds. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weekley, C.M.; Harris, H.H. Which form is that? The importance of selenium speciation and metabolism in the prevention and treatment of disease. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8870–8894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Draft Aquatic Life Ambient Water Quality Criterion for Selenium–Freshwater 2015; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; pp. 1–740.
- Hamilton, S.J.; Holley, K.M.; Buhl, K.J.; Bullard, F.A. Selenium impacts on razorback sucker, Colorado: Colorado River: III. Larvae. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 61, 168–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, S.J.; Holley, K.M.; Buhl, K.J.; Bullard, F.A. Selenium impacts on razorback sucker, Colorado River, Colorado II. Eggs. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 61, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, S.J.; Holley, K.M.; Buhl, K.J.; Bullard, F.A.; Ken Weston, L.; McDonald, S.F. Selenium impacts on razorback sucker, Colorado River, Colorado I. Adults. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 61, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mast, M.A.; Mills, T.J.; Paschke, S.S.; Keith, G.; Linard, J.I. Mobilization of selenium from the Mancos Shale and associated soils in the lower Uncompahgre River Basin, Colorado. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 48, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, C.J.; McDonald, L.E.; Loveridge, R.; Strosher, M.M. The effect of bioaccumulated selenium on mortalities and deformities in the eggs, larvae, and fry of a wild population of cutthroat trout (Oncorhynchus clarki lewisi). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 39, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemly, A.D. A teratogenic deformity index for evaluating impacts of selenium on fish populations. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1997, 37, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Presser, T.S.; Sylvester, M.A.; Low, W.H. Bioaccumulation of selenium from natural geologic sources in western states and its potential consequences. Environ. Manag. 1994, 18, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, S.J.; Turner, J.A.; Carsella, J.S.; Lehmpuhl, D.W.; Nimmo, D.R. Bioaccumulation of selenium by the Bryophyte Hygrohypnum ochraceum in the Fountain Creek Watershed, Colorado. Environ. Manag. 2012, 50, 1111–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathews, T.J.; Fortner, A.M.; Jett, R.T.; Morris, J.; Gable, J.; Peterson, M.J.; Carriker, N. Selenium bioaccumulation in fish exposed to coal ash at the Tennessee Valley Authority Kingston spill site. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 2273–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carsella, J.S.; Melnykov, I.; Bonetti, S.J.; Sánchez-Lombardo, I.; Crans, D.C. Selenium speciation in the Fountain Creek watershed and its effects on fish diversity. J. Biol. Inorg.Chem. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, I.; Beath, O.A. Selenium: Geobotany, Biochemistry, Toxicity, and Nutrition; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1964; p. 411. [Google Scholar]
- Block, E. Fifty years of smelling sulfur. J. Sulfur Chem. 2013, 34, 158–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crans, D.C. Antidiabetic, Chemical, and Physical Properties of Organic Vanadates as Presumed Transition-State Inhibitors for Phosphatases. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 11899–11915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crans, D.C.; Woll, K.A.; Prusinskas, K.; Johnson, M.D.; Norkus, E. Metal speciation in health and medicine represented by iron and vanadium. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 12262–12275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doucette, K.A.; Hassell, K.N.; Crans, D.C. Selective speciation improves efficacy and lowers toxicity of platinum anticancer and vanadium antidiabetic drugs. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2016, 165, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, T.; Jakusch, T.; Hollender, D.; Dörnyei, Á.; Enyedy, É.A.; Pessoa, J.C.; Sakurai, H.; Sanz-Medel, A. Biospeciation of antidiabetic VO(IV) complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2008, 252, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Odani, A. Demonstration of the importance of metal ion speciation in bioactive systems. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 80, 1691–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawell, J.K.; Combs, G.F. Guidelines for drinking-water quality. In Selenium in Drinking Water: Background Document for Development of WHO Guidlines for Dinking Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; Volume 2011, p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg, P.; Bingefors, S. Selenium levels of forages and soils in different regions of Sweden. Acta Agric. Scand. 1970, 20, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.C.; Voegeli, P.T. Radiochemical Analyses of Ground and Surface Water in Colorado, 1954–1961; Colorado Water Conservation Board: Denver, CO, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.; Westfall, B. Further field studies on the selenium problem in relation to public health. Public Health Rep. (1896–1970) 1937, 52, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulp, T.R.; Pratt, L.M. Speciation and weathering of selenium in Upper Cretaceous chalk and shale from South Dakota and Wyoming, USA. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 3687–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.; Pintos, V.; Domínguez, S.; Kremer, C.; Kremer, E. Selenite and selenate speciation in natural waters: Interaction with divalent metal ions. J. Solut. Chem. 2010, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.; Pintos, V.; Gonzatto, L.; Domínguez, S.; Kremer, C.; Kremer, E. Selenium chemical speciation in natural waters: Protonation and complexation behavior of selenite and selenate in the presence of environmentally relevant cations. Chem. Geol. 2011, 288, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baes, C.F.; Mesmer, R.E. Hydrolysis of Cations; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1976; p. 489. [Google Scholar]
- Nimmo, D.R.; Herrmann, S.J.; Carsella, J.S.; McGarvy, C.M.; Foutz, H.P.; Herrmann-Hoesing, L.M.; Gregorich, J.M.; Turner, J.A.; Vanden Heuvel, B.D. Mercury and selenium in fish of Fountain Creek, Colorado (USA): Possible sources and implications. Springerplus 2016, 5, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Geological Survey National Water Information System: Web Interface. USGS Site 07106500. Available online: http://waterdata.usgs.gov/co/nwis/uv/?site_no=07106500 (accessed on 26 January 2017).
- United States Geological Survey National Water Information System: Web Interface. USGS Site 07106200. Available online: http://waterdata.usgs.gov/co/nwis/uv/?site_no=07106200 (accessed on 26 January 2017).
- United States Geological Survey National Water Information System: Web Interface. USGS Site 07103755. Available online: http://waterdata.usgs.gov/co/nwis/uv/?site_no=07103755 (accessed on 26 January 2017).
- United States Geological Survey National Water Information System: Web Interface. USGS Site 07103970. Available online: http://waterdata.usgs.gov/co/nwis/uv/?site_no=07103970 (accessed on 26 January 2017).
- United States Geological Survey National Water Information System: Web Interface. USGS Site 07104000. Available online: http://waterdata.usgs.gov/co/nwis/uv/?site_no=07104000 (accessed on 26 January 2017).
- United States Geological Survey National Water Information System: Web Interface. USGS Site 07106300. Available online: http://waterdata.usgs.gov/co/nwis/uv/?site_no=07106300 (accessed on 26 January 2017).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Methods for Measuring the Acute Toxicity of Effluents to Freshwater and Marine Organisms, 3rd ed.; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1985.
- Herrmann, S.; Nimmo, D.; Carsella, J.; Herrmann-Hoesing, L.; Turner, J.; Gregorich, J.; Heuvel, B.V.; Nehring, R.; Foutz, H. Differential Accumulation of Mercury and Selenium in Brown Trout Tissues of a High-Gradient Urbanized Stream in Colorado, USA. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 70, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, S.J.; Sublette, J.E.; Helland, L.K.; Nimmo, D.W.R.; Carsella, J.S.; Herrmann-Hoesing, L.M.; Heuvel, B.D.V. Species richness, diversity, and ecology of Chironomidae (Diptera) in Fountain Creek: A Colorado Front Range sandy-Bottom watershed. West. N. Am. Nat. 2016, 76, 186–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayaam, F. Calcium Activity, Complex and Ion-Pair in Saturated CaCO3. Soil Sci. 1968, 106, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, F. Magnesium complex and ion-Pair in MgCO3–CO2 solution system. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1971, 16, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthi, S. Carbonate Chemistry and Calcium Carbonate Saturation State of Rural Water Supply Projects in Nepal. In Proceedings of the Seventh International Water Technology Conference, Cairo, Egypt, 1–3 April 2003; pp. 545–560. [Google Scholar]
- Wurts, W.A.; Durborow, R.M. Interactions of pH, carbon dioxide, alkalinity and hardness in fish ponds. SRAC Publ. 1992, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Castanier, S.; Le Métayer-Levrel, G.; Perthuisot, J.-P. Ca-Carbonates precipitation and limestone genesis—The microbiogeologist point of view. Sediment. Geol. 1999, 126, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, C.; Birringer, M.; Block, E.; Kotrebai, M.; Tyson, J.F.; Uden, P.C.; Lisk, D.J. Chemical speciation influences comparative activity of selenium-enriched garlic and yeast in mammary cancer prevention. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2062–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotrebai, M.; Birringer, M.; Tyson, J.F.; Block, E.; Uden, P.C. Selenium speciation in enriched and natural samples by HPLC–ICP–MS and HPLC-ESI-MS with perfluorinated carboxylic acid ion-Pairing agents. Analyst 2000, 125, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, D.E.; Groves, J.W.; Gherase, M.R.; George, G.N.; Pickering, I.J.; Ponomarenko, O.; Langan, G.; Spallholz, J.E.; Alauddin, M.; Ahsan, H. Soft tissue measurement of arsenic and selenium in an animal model using portable X-ray fluorescence. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2015, 116, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, T.C.; Korbas, M.; James, A.K.; Sylvain, N.J.; Hackett, M.J.; Nehzati, S.; Krone, P.H.; George, G.N.; Pickering, I.J. Interaction of mercury and selenium in the larval stage zebrafish vertebrate model. Metallomics 2015, 7, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, S.; Thomas, J.K.; Sylvain, N.J.; Ponomarenko, O.; Gordon, R.A.; Heald, S.M.; Janz, D.M.; Krone, P.H.; Coulthard, I.; George, G.N. Selenium preferentially accumulates in the eye lens following embryonic exposure: A confocal X-ray fluorescence imaging study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2255–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, Y.Z.; Bayakly, N.; Peipho, A.; Carlson, B. Accurate Potentiometric Studies of Chromium-Citrate and Ferric-Citrate Complexes in Aqueous Solutions at Physiological and Alkaline pH Values. Synth. React. Inorg. Met. Org. Nano Met. Chem. 2006, 36, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, M.J. Methods of Analysis by the US Geological Survey National Water Quality Laboratory; Determination of Inorganic and Organic Constituents in Water and Fluvial Sediments; U.S. Geological Survey: Denver, CO, USA, 1993.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. In Method 200.8 Determination of Trace Elements in Water and Wastes by Inductively Coupled Plasma–Mass Spectrometry; rev. 5.4; Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1994; pp. 1–57.
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Alderlghi, L.; Gans, P.; Ienco, A.; Peters, D.; Sabatini, A.; Vacca, A. Hyperquad simulation and speciation (HySS): A utility program for the investigation of equilibria involving soluble and partially soluble species. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1999, 184, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olin, Å.; Noläng, B.; Öhman, L.-O.; Osadchii, E.; Rosén, E. Chemical Thermodynamics of Selenium; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Not Available. |








| Sample Sites | Spring | Fall | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T (°C) | pH | Water Se (µg/L) | Std. Error Water Se | Water Ca (µg/L) | Std. Error Water Ca | Water Mg (µg/L) | Std. Error Water Mg | Alkalinity (mg CaCO3/L) | T (°C) | pH | Water Se (µg/L) | Std. Error Water Se | Water Ca (µg/L) | Std. Error Water Ca | Water Mg (µg/L) | Std. Error Water Mg | Alkalinity (mg CaCO3/L) | |
| UF-1 | 4.6 | 7.2 | 0.193 | 0.003 | 28,440 | 892.5 | 5354 | 140.2 | 72 | 5.8 | 8.2 | 0.063 | 0.007 | 19,307 | 582.3 | 5481 | 261.7 | 76 |
| UF-2 | 4.9 | 7.2 | 0.140 | 0.017 | 28,867 | 1993.3 | 5474 | 341.9 | 50 | 5.7 | 8.1 | 0.000 | 0.007 | 13,003 | 1355.7 | 3481 | 450.2 | 63 |
| UF-3 | 5.7 | 7.6 | 0.673 | 0.090 | 34,863 | 2409.8 | 6890 | 456.9 | 81 | 6.0 | 8.1 | 0.043 | 0.009 | 13,897 | 291.7 | 4041 | 61.7 | 146 |
| UF-4 | 6.6 | 7.6 | 1.323 | 0.313 | 39,017 | 2989.2 | 10,134 | 1504.9 | 83 | 7.0 | 8.1 | 0.340 | 0.010 | 15,303 | 205.1 | 5490 | 109.3 | 154 |
| MC-1 | 4.2 | 7.4 | 0.207 | 0.012 | 12,227 | 357.3 | 1742 | 25.1 | 66 | 5.5 | 7.9 | 0.177 | 0.009 | 15,757 | 99.4 | 4772 | 102.3 | 86 |
| MC-2 | 3.9 | 7.5 | 0.277 | 0.007 | 19,380 | 875.6 | 3400 | 253.9 | 74 | 5.3 | 8.0 | 0.330 | 0.023 | 21,547 | 394.7 | 7599 | 223.0 | 89 |
| MC-3 | 4.1 | 7.2 | 0.343 | 0.017 | 21,623 | 1374.0 | 3818 | 283.5 | 73 | 4.5 | 8.1 | 0.597 | 0.038 | 22,450 | 283.6 | 8043 | 143.3 | 88 |
| MC-4 | 4.1 | 7.5 | 0.443 | 0.023 | 26,327 | 1978.4 | 4365 | 324.2 | 78 | 5.0 | 8.0 | 0.860 | 0.021 | 27,047 | 91.3 | 8450 | 26.5 | 86 |
| MC-5 | 4.8 | 7.4 | 1.863 | 0.216 | 38,503 | 3260.0 | 6712 | 538.8 | 110 | 6.4 | 8.1 | 5.283 | 0.269 | 41,080 | 172.1 | 13,217 | 416.0 | 105 |
| LF-1 | 7.7 | 7.5 | 2.050 | 0.202 | 42,303 | 2751.5 | 8135 | 538.8 | 104 | 9.9 | 8.1 | 2.970 | 0.072 | 29,947 | 312.5 | 10,960 | 573.0 | 108 |
| LF-2 | 12.2 | 7.2 | 2.780 | 0.008 | 53,465 | 698.1 | 14,540 | 714.4 | 141 | 15.2 | 8.1 | 3.773 | 0.060 | 38,537 | 520.7 | 18,177 | 137.8 | 179 |
| LF-3 | 10.6 | 7.6 | 3.290 | 0.125 | 64,447 | 2316.7 | 17,703 | 514.4 | 138 | 15.1 | 8.1 | 3.800 | 0.057 | 41,837 | 806.5 | 19,770 | 182.5 | 180 |
| LF-4 | 11.3 | 7.7 | 9.687 | 0.617 | 69,083 | 827.5 | 22,943 | 627.7 | 140 | 15.2 | 8.1 | 18.59 | 1.131 | 46,683 | 254.6 | 29,830 | 531.5 | 183 |
| LF-5 | 11.8 | 7.8 | 7.910 | 0.377 | 69,373 | 1624.5 | 23,183 | 793.0 | - | 15.8 | 8.2 | 14.05 | 0.677 | 47,137 | 542.6 | 29,900 | 517.3 | - |
| Ref. | b | [37] | [37] | b | b | b | [38,39,40,41,42,43] | b | [37] | [37] | b | b | [38,39,40,41,42,43] | |||||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carsella, J.S.; Sánchez-Lombardo, I.; Bonetti, S.J.; Crans, D.C. Selenium Speciation in the Fountain Creek Watershed (Colorado, USA) Correlates with Water Hardness, Ca and Mg Levels. Molecules 2017, 22, 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050708
Carsella JS, Sánchez-Lombardo I, Bonetti SJ, Crans DC. Selenium Speciation in the Fountain Creek Watershed (Colorado, USA) Correlates with Water Hardness, Ca and Mg Levels. Molecules. 2017; 22(5):708. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050708
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarsella, James S., Irma Sánchez-Lombardo, Sandra J. Bonetti, and Debbie C. Crans. 2017. "Selenium Speciation in the Fountain Creek Watershed (Colorado, USA) Correlates with Water Hardness, Ca and Mg Levels" Molecules 22, no. 5: 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050708
APA StyleCarsella, J. S., Sánchez-Lombardo, I., Bonetti, S. J., & Crans, D. C. (2017). Selenium Speciation in the Fountain Creek Watershed (Colorado, USA) Correlates with Water Hardness, Ca and Mg Levels. Molecules, 22(5), 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050708