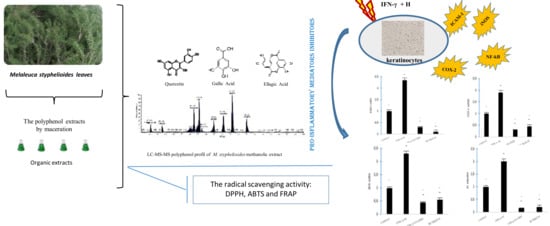
Melaleuca styphelioides Sm. Polyphenols Modulate Interferon Gamma/Histamine-Induced Inflammation in Human NCTC 2544 Keratinocytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Plant Material and Extracts Preparation
4.3. Phytochemical Analysis
4.3.1. The Phytochemical Screening
4.3.2. LC/MS-MS Analysis
4.4. Anti-Oxidant Activity Determination
4.5. Anti-Inflammatory Activity Evaluation
4.5.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.5.2. Cell Viability
4.5.3. RNA Extraction and RT-PCR
4.5.4. Western Blot
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| (H) | Histamine |
| (IFN-γ) | interferon gamma |
| (NF-κB) | nuclear factor kappa B |
| (ICAM-1) | inter-cellular adhesion molecule-1 |
| (iNOS) | nitric oxide synthase |
| (COX-2) | cyclooxygenase-2 |
| (DPPH) | 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| (ABTS) | 2,2′-azinobis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonate) |
| (E. hex) | hexane extract |
| (E. Et2O) | diethyl ether extract |
| (E. EtOAc) | ethyl acetate extract |
| (E. MeOH) | methanol extract |
| (M. MeOH) | Melaleuca styphelioides methanolic extract |
References
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köllisch, G.; Kalali, B.N.; Voelcker, V.; Wallich, R.; Behrendt, H.; Ring, J.; Bauer, S.; Jakob, T.; Mempel, M.; Ollert, M. Various members of the Toll-like receptor family contribute to the innate immune response of human epidermal keratinocytes. Immunology 2005, 114, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McInturff, J.E.; Modlin, R.L.; Kim, J. The role of toll-like receptors in the pathogenesis and treatment of dermatological disease. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 125, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastore, S.; Mascia, F.; Mariani, V.; Girolomoni, G. The epidermal growth factor receptor system in skin repair and inflammation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascia, F.; Mariani, V.; Girolomoni, G.; Pastore, S. Blockade of the EGF receptor induces a deranged chemokine expression in keratinocytes leading to enhanced skin inflammation. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkvliet, N.I. AHR-mediated immunomodulation: The role of altered gene transcription. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 77, 746–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pastore, S.; Mascia, F.; Mariotti, F.; Dattilo, C.; Mariani, V.; Girolomoni, G. ERK1/2 regulates epidermal chemokine expression and skin inflammation. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 5047–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essafi-Benkhadir, K.; Refai, A.; Riahi, I.; Fattouch, S.; Karoui, H.; Essafi, M. Quince (Cydonia oblonga Miller) peel polyphenols modulate LPS-induced inflammation in human THP-1-derived macrophages through NF-κB, p38MAPK and Akt inhibition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 418, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkina, L.G. Phenylpropanoids as naturally occurring antioxidants: From plant defense to human health. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2017, 53, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.J.; Kim, M.J.; Kang, S.; Moon, N.R.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, N.R.; Kim, K.S.; Park, S. Topical treatments of Saussurea costus root and Thuja orientalis L. synergistically alleviate atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions by inhibiting protease-activated receptor-2 and NF-κB signaling in HaCaT cells and Nc/Nga mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 199, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.O.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, C.Y. Vitamin C equivalent antioxidant capacity (VCEAC) of phenolic phytochemicals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3713–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkina, L.G.; Pastore, S.; De Luca, C.; Kostyuk, V.A. Metabolism of plant polyphenols in the skin: Beneficial versus deleterious effects. Curr. Drug Metab. 2008, 9, 710–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Kong, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yang, M.; Peng, X.; Efferth, T. In vitro antioxidant properties, DNA damage protective activity, and xanthine oxidase inhibitory effect of cajaninstilbene acid, a stilbene compound derived from pigeon pea [Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.] leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Salehi, B.; Varoni, E.M.; Sharopov, F.; Yousaf, Z.; Ayatollahi, S.A.; Kobarfard, F.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Afdjei, M.H.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; et al. Plants of the Melaleuca Genus as Antimicrobial Agents: From Farm to Pharmacy. Phyther. Res. 2017, 31, 1475–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sayed, E.; El-Lakkany, N.M.; Seif El-Din, S.H.; Sabra, A.N.A.; Hammam, O.A. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity of Melaleuca styphelioides on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sayed, E.; Esmat, A. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effect of ellagitannins and galloyl esters isolated from Melaleuca styphelioides on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in HepG2 cells. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, R.S.; Shalaby, A.S.; El-Baroty, G.A.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Ali, M.A.; Hassan, E.M. Chemical and Biological Evaluation of the Essential Oils of Different Melaleuca Species. Phyther. Res. 2004, 18, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amri, I.; Mancini, E.; de Martino, L.; Marandino, A.; Lamia, H.; Mohsen, H.; Bassem, J.; Scognamiglio, M.; Reverchon, E.; de Feo, V. Chemical composition and biological activities of the essential oils from three Melaleuca species grown in Tunisia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 16580–16591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Abd, N.M.; Mohamed Nor, Z.; Mansor, M.; Azhar, F.; Hasan, M.S.; Kassim, M. Antioxidant, antibacterial activity, and phytochemical characterization of Melaleuca cajuputi extract. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.V.; Bone, D.E.; Carrington, M.F. Antioxidant activity of dulse (Palmaria palmata) extract evaluated in vitro. Food Chem. 2005, 91, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albouchi, F.; Hassen, I.; Casabianca, H.; Hosni, K. Phytochemicals, antioxidant, antimicrobial and phytotoxic activities of Ailanthus altissima (Mill.) Swingle leaves. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2013, 87, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesjak, M.; Beara, I.; Simin, N.; Pintać, D.; Majkić, T.; Bekvalac, K.; Orčić, D.; Mimica-Dukić, N. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of quercetin and its derivatives. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 40, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziano, A.C.E.; Cardile, V.; Crascì, L.; Caggia, S.; Dugo, P.; Bonina, F.; Panico, A. Protective effects of an extract from Citrus bergamia against inflammatory injury in interferon-gamma and histamine exposed human keratinocytes. Life Sci. 2012, 90, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, W.L.; DeWitt, D.L.; Garavito, R.M. Cyclooxygenases: Structural, Cellular, and Molecular Biology. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000, 69, 145–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Decker, K.; Scholz, K.; Neufang, G.; Marks, F.; Fürstenberger, G. Localization of prostaglandin-H synthase-1 and -2 in mouse skin: Implications for cutaneous function. Exp. Cell Res. 1998, 242, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suschek, C.; Schnorr, O.; Kolb-Bachofen, V. The Role of iNOS in Chronic Inflammatory Processes In Vivo: Is it Damage-Promoting, Protective, or Active at all? Curr. Mol. Med. 2004, 4, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Takada, Y.; Boriek, A.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Nuclear factor-kappaB: Its role in health and disease. J. Mol. Med. 2004, 82, 434–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Mediavilla, V.; Crespo, I.; Collado, P.S.; Esteller, A.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; Tuñón, M.J.; González-Gallego, J. The anti-inflammatory flavones quercetin and kaempferol cause inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygenase-2 and reactive C-protein, and down-regulation of the nuclear factor kappaB pathway in Chang Liver cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 557, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Shi, D.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Xie, X.; Kang, T.; Deng, W. Quercetin suppresses cyclooxygenase-2 expression and angiogenesis through inactivation of P300 signaling. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Das, S.; Saha, A.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.K. Ellagic acid facilitates indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer healing via COX-2 up-regulation. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2012, 44, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahad, A.; Ganai, A.A.; Mujeeb, M.; Siddiqui, W.A. Ellagic acid, an NF-κB inhibitor, ameliorates renal function in experimental diabetic nephropathy. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 219, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Chen, F.; Wu, C.; Wang, X.; Chung, H.Y.; Jin, Z. Evaluation of antioxidant activity of Australian tea tree (Melaleuca alternifolia) oil and its components. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2849–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.C.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, D.S.; Jeon, Y.D.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.S.; Um, J.Y.; Hong, S.H. Vanillic acid inhibits inflammatory mediators by suppressing NF-κB in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated mouse peritoneal macrophages. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2011, 33, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.T.; Xiao, L.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Q.; Yan, T. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Apigenin in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory in Acute Lung Injury by Suppressing COX-2 and NF-kB Pathway. Inflammation 2014, 37, 2085–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ham, J.R.; Lee, H.-I.; Choi, R.-Y.; Sim, M.-O.; Seo, K.-I.; Lee, M.-K. Anti-steatotic and anti-inflammatory roles of syringic acid in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadioglu, O.; Nass, J.; Saeed, M.E.M.; Schuler, B.; Efferth, T. Kaempferol is an anti-inflammatory compound with activity towards NF-κB pathway proteins. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 2645–2650. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.; Ku, S.K.; Baek, Y.D.; Bae, J.S. Anti-inflammatory effects of rutin on HMGB1-induced inflammatory responses in vitro and in vivo. Inflamm. Res. 2014, 63, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, D.; Al-Sayed, E.; Albert, A.; Paul, E.; Singab, A.N.B.; Govindan Sadasivam, S.; Saso, L. Antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds from extracts of Eucalyptus globulus and Melaleuca styphelioides and their protective role on d-glucose-induced hyperglycemic stress and oxalate stress in NRK-49Fcells. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Euch, S.K.; Bouajila, J.; Bouzouita, N. Chemical composition, biological and cytotoxic activities of Cistus salviifolius flower buds and leaves extracts. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 76, 1100–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gutiérrez, N.; del MAguilera-Luiz, M.; Romero-González, R.; Vidal, J.L.M.; Garrido Frenich, A. Fast analysis of polyphenols in royal jelly products using automated TurboFlowTM-liquid chromatography-Orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2014, 973, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Standard Organization. ISO/IEC 17025 General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Laboratories; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Eurachem, a Laboratory Guide to Method Validation and Related Topics. 2014. Available online: http://www.eurachem.org/images/stories/Guides/pdf/valid.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2017).
- Lo Dico, G.M.; Cammilleri, G.; Macaluso, A. Simultaneous Determination of As, Cu, Cr, Se, Sn, Cd, Sb and Pb Levels in Infant Formulas by ICP-MS after Microwave-Assisted Digestion: Method Validation. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2015, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Man, H.; Behera, S.K.; Park, H.S. Optimization of operational parameters for ethanol production from korean food waste leachate. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziano, A.C.E.; Parenti, R.; Avola, R.; Cardile, V. Krabbe disease: Involvement of connexin43 in the apoptotic effects of sphingolipid psychosine on mouse oligodendrocyte precursors. Apoptosis 2016, 21, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avola, R.; Graziano, A.C.E.; Pannuzzo, G.; Albouchi, F.; Cardile, V. New insights on Parkinson’s disease from differentiation of SH-SY5Y into dopaminergic neurons: An involvement of aquaporin4 and 9. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 88, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avola, R.; Graziano, A.C.E.; Pannuzzo, G.; Cardile, V. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Adipose Tissue Differentiated into Neuronal or Glial Phenotype Express Different Aquaporins. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 8308–8320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |




| M. styphelioides Extracts | Total Phenolic mg GAE/g Dry Extract | Total Flavonoid mg QE/g Dry Extract | Total Tannins mg Eq Catéchine/g Dry Extract |
|---|---|---|---|
| E. MeOH | 142.7 ± 3.15 | 31.54 ± 1.99 | 15.2 ± 1.9 |
| E. EtOAc | 97.39 ± 7.69 | 26.8 ± 2.4 | 19.9 ± 2.9 |
| E. Et2O | 22.95 ± 0.4 | 7.83 ± 1.11 | 4.1 ± 1.3 |
| E. Hex | 3.27 ± 2.1 | nd | nd |
| C.A.S. Number | RT (min) | Mass (amu) [M − H−] | Fragments (m/z) | Compounds | Phenolic Family | Concentration (µg/kg DW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 327-97-9 | 0.59 | 353.8 | 191.20 | Chlorgenic Acid | Phenolic acids | 36 ± 7 |
| 149-91-7 | 1.28 | 169.01 | 125.00 | Gallic Acid | Phenolic acids | 1116 ± 127 |
| 1135-24-6 | 3.04 | 193.05 | 143.00 | Ferulic Acid | Phenolic acids | 86 ± 15 |
| 331-39-5 | 3.24 | 179.03 | 135.02 | Caffeic Acid | Phenolic acids | 92 ± 17 |
| 530-57-4 | 3.51 | 197.04 | 121.00 | Syringic Acid | Phenolic acids | 292 ± 35 |
| 207671-50-9 | 3.56 | 610.01 | 300.30 | Rutin | Flavonoids | 259 ± 31 |
| 520-26-3 | 3.59 | 609.20 | 301.00 | Hesperidina | Flavonoids | 177 ± 27 |
| 121-34-6 | 3.73 | 167.04 | 108.00 | Vanillic Acid | Phenolic acids | 359 ± 36 |
| 491-70-3 | 4.36 | 285.04 | 133.00 | Luteolin | Flavonoids | 56 ± 10 |
| 476-66-4 | 4.40 | 302.20 | 131.98 | Ellagic Acid | Phenolic acids | 522 ± 47 |
| 529-44-2 | 4.46 | 317.04 | 151.00 | Myricetin | Flavonoids | 160 ± 24 |
| 117-39-5 | 5.06 | 447.09 | 151.00 | Quercetin | Flavonoids | 4440 ± 355 |
| 67604-48-2 | 5.55 | 272.06 | 119.00 | Naringenin | Flavonoids | 23 ± 5 |
| 520-36-5 | 5.61 | 271.08 | 117.00 | Apigenin | Flavonoids | 336 ± 38 |
| 520-18-3 | 6.49 | 285.04 | 108.00 | Kaempferol | Flavonoids | 271 ± 35 |
| M. styphelioides Extracts | DPPH IC50 μg/mL | ABTS IC50 μg/mL | FRAP mM FeSO4/g DE |
|---|---|---|---|
| E. MeOH | 22.13 ± 2.17 | 21.39 ± 0.62 | 3.66 ± 0.014 |
| E. EtOAc | 119.15 ± 1.669 | 75.84 ± 1.22 | 0.85 ± 0.002 |
| E. Et2O | 73.24 ± 2.811 | 52.22 ± 1.40 | nd |
| E. Hexane | 229.9 ± 5.8 | 201.35 ± 9.4 | nd |
| Trolox IC50 | 13.69 ± 0.04 | 64.37 ± 1.28 | |
| BHT IC50 | 19.33 ± 0.32 |
| Primers | Forward (5′→3′) | Reverse (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| ICAM-1 | GGCCGGCCAGCTTATACAC | TAGACACTTGAGCTCGGGCA |
| iNOS | GTTCTCAAGGCACAGGTCTC | GCAGGTCACTTATGTCACTTATC |
| NF-κB | ATGGCTTCTATGAGGCTGAG | GTTGTTGTTGGTCTGGATGC |
| COX-2 | ATCATTCACCAGGCAAATTGC | GGCTTCAGCATAAAGCGTTTG |
| GAPDH | TCAACAGCGACACCCAC | GGGTCTCTCTCTTCCTCTTGTG |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albouchi, F.; Avola, R.; Dico, G.M.L.; Calabrese, V.; Graziano, A.C.E.; Abderrabba, M.; Cardile, V. Melaleuca styphelioides Sm. Polyphenols Modulate Interferon Gamma/Histamine-Induced Inflammation in Human NCTC 2544 Keratinocytes. Molecules 2018, 23, 2526. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102526
Albouchi F, Avola R, Dico GML, Calabrese V, Graziano ACE, Abderrabba M, Cardile V. Melaleuca styphelioides Sm. Polyphenols Modulate Interferon Gamma/Histamine-Induced Inflammation in Human NCTC 2544 Keratinocytes. Molecules. 2018; 23(10):2526. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102526
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbouchi, Ferdaous, Rosanna Avola, Gianluigi Maria Lo Dico, Vittorio Calabrese, Adriana Carol Eleonora Graziano, Manef Abderrabba, and Venera Cardile. 2018. "Melaleuca styphelioides Sm. Polyphenols Modulate Interferon Gamma/Histamine-Induced Inflammation in Human NCTC 2544 Keratinocytes" Molecules 23, no. 10: 2526. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102526
APA StyleAlbouchi, F., Avola, R., Dico, G. M. L., Calabrese, V., Graziano, A. C. E., Abderrabba, M., & Cardile, V. (2018). Melaleuca styphelioides Sm. Polyphenols Modulate Interferon Gamma/Histamine-Induced Inflammation in Human NCTC 2544 Keratinocytes. Molecules, 23(10), 2526. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102526