Effect of Enzyme Modified Soymilk on Rennet Induced Gelation of Skim Milk
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Protein Structural Characteristics
2.2. Rheological Properties
2.3. Physical and Chemical Indicators
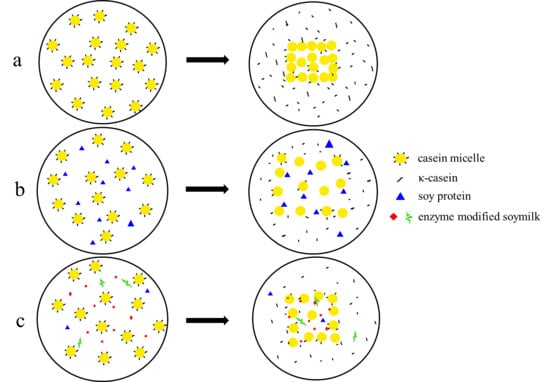
2.4. Microstructure
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Skim Milk Preparation
4.2. Enzyme Modified Soymilk Preparation
4.3. Electrophoresis
4.4. Mixture Preparation
4.5. Curd Making
4.6. Rheological Properties
4.7. Microstructure Determination
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schaafsma, G. The protein digestibility-corrected amino acid score (pdcaas)—A concept for describing protein quality in foods and food ingredients: A critical review. J. Aoac Int. 2005, 88, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lucey, J.A.; Singh, H. Formation and physical properties of acid milk gels: A review. Food Res. Int. 1997, 30, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgleish, D.G. Proteolysis and aggregation of casein micelles treated with immobilized or soluble chymosin. J. Dairy Res. 1979, 46, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.; Dalgleish, D.G. Application of transmission diffusing wave spectroscopy to the study of gelation of milk by acidification and rennet. Colloid. Surface B 2004, 38, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poysa, V.; Woodrow, L. Stability of soybean seed composition and its effect on soymilk and tofu yield and quality. Food Res. Int. 2002, 35, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesch, R.; Juneja, M.; Monagle, C.; Corredig, M. Aggregation of soy/milk mixes during acidification. Food Res. Int. 2004, 37, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grygorczyk, A.; Alexander, M.; Corredig, M. Combined acid- and rennet-induced gelation of a mixed soya milk–cow’s milk system. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 2306–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Hill, A.; Corredig, M. Gelation of mixtures of soymilk and reconstituted skim milk subjected to combined acid and rennet. J. Texture Stud. 2012, 43, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahnoud, M.I. Physicochemical and functional properties of protein hydrolysates in nutritional products. Food Technol. 1994, 48, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz, S.E.M.; Wagner, J.R. Hydrolysates of native and modified soy protein isolates: Structural characteristics, solubility and foaming properties. Food Res. Int. 2001, 35, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achouri, A.; Zhang, W. Effect of succinylation on the physicochemical properties of soy protein hydrolysate. Food Res. Int. 2001, 34, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumura, K.; Saito, T.; Tsuge, K.; Ashida, N.; Kugimiya, W.; Inouye, K. Functional properties of soy protein hydrolysates obtained by selective proteolysis. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 38, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Were, L.; Hettiarachchy, N.S.; Kalapathy, U. Modified soy proteins with improved foaming and water hydration properties. J. Food Sci. 1997, 62, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suro´wka, K.; Zmudzin´ski, D.; Suro´wka, J. Enzymic modification of extruded soy protein concentrates as a method of obtaining new functional food components. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2004, 15, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldoni, A.N.; Palatnik, D.R.; Zaritzky, N.; Campderrós, M.E. Soft cheese-like product development enriched with soy protein concentrates. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 55, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Cao, X.; Lin, J.; Xie, J.; Xu, X. Optimization of process of analog Mozzarella cheese containing limit hydrolyzed soy milk. Food Sci Technol. 2010, 35, 94–100. [Google Scholar]
- Ikonen, T.; Ruottinen, O.; Syväoja, E.L.; Saarinen, K.; Pahkala, E.; Ojala, M. Effect of milk coagulation properties of herd bulk milks on yield and composition of Emmental cheese. Agric. Food Sci. 1999, 8, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.K.; Ramaswamy, H.S.; Stgelais, D. Water-holding capacity and gel strength of rennet curd as affected by high-pressure treatment of milk. Food Res. Int. 2000, 33, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Tong, Q.; Luo, J.; Xu, Y.; Ren, F. Effect of carrageenan on physicochemical and functional properties of low-fat colby cheese. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, E1949–E1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, D.W.; Deman, J.M. Structural and mechanical properties of textured proteins. J. Texture Stud. 1978, 9, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, J.A. Formation and physical properties of milk protein gels. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, M.A.; Hill, A.R.; Corredig, M. Rheological properties of rennet gels containing milk protein concentrates. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haratifar, S.; Corredig, M. Interactions between tea catechins and casein micelles and their impact on renneting functionality. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, A.; Leis, A.; Li, D.; Øiseth, S.K.; Puvanenthiran, A.; Augustin, M.A. Rennet gelation properties of milk: Influence of natural variation in milk fat globule size and casein micelle size. Int. Dairy J. 2014, 46, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Ren, F. Effects of size and stability of native fat globules on the formation of milk gel induced by rennet. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdy, A.; Xia, W.; Zhang, G. Effect of soy protein supplementation on the quality of ripening Cheddar-type cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 57, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, R.K.; Tamime, A.Y. The role of protein in yoghurt. In Developments in Food Proteins; Hudson, B.J.F., Ed.; Elsevier Applied Science Publishers LTD: London, UK, 1986; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Martindiana, A.B.; Janer, C.; Pelaez, C.; Requena, T. Development of a fermented goat’s milk containing probiotic bacteria. Int. Dairy J. 2003, 13, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, A.M.; Requena, T. The effect of supplementing goats milk with whey protein concentrate on textural properties of set-type yoghurt. Int. J. Food Sci Tech. 2006, 41, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsumi, S.; Matsumura, Y.; Mori, T. Structure-function relationships of soy proteins. In Food Proteins and Their Applications; Damodaran, S., Paraf, A., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 257–291. [Google Scholar]
- Domagała, J.; Najgebauer-Lejko, D.D.; Wieteska-Śliwa, I.; Sady, M.; Wszołek, M.; Bonczar, G.; Filipczak-Fiutak, M. The influence of milk protein cross-linking by transglutaminase on the rennet coagulation time and the gel properties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 96, 3500–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingrassia, R.; Costa, J.P.; Hidalgo, M.E.; Canales, M.M.; Castellini, H.; Riquelme, B.; Risso, P. Application of a digital image procedure to evaluate microstructure of caseinate and soy protein acid gels. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 53, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hrckova, M.; Rusnakova, M.; Zemanovic, J. Enzymatic hydrolysis of defatted soy flour by three different proteases and their effect on the functional properties of resulting protein hydrolysates. Czech. J. Food Sci. 2002, 20, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Luo, J.; Guo, H.; Zeng, S.; Ren, F. Effect of proteolysis and calcium equilibrium on functional properties of natural cheddar cheese during ripening and the resultant processed cheese. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, E248–E253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullin, W.J.; Fregeau-Reid, J.A.; Butler, M.; Poysa, V.; Woodrow, L.; Jessop, D.B.; Raymond, D. An interlaboratory test of a procedure to assess soybean quality for soymilk and tofu production. Food Res. Int. 2001, 34, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awolumate, E.O. Accumulation and quality of storage protein in developing cowpea, mung bean and soya bean seeds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 34, 1351–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamsal, B.P.; Jung, S.; Johnson, L.A. Rheological properties of soy protein hydrolysates obtained from limited enzymatic hydrolysis. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Luo, J.; Lv, X.; Guo, H.; Ren, F. Effect of carrageenan on the formation of rennet-induced casein micelle gels. Food Hydrocolloid. 2014, 36, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato-Calleros, C.; Robles-Martinez, J.C.; Caballero-Perez, J.F.; Vernon-Carter, E.J.; Aguirre-Mandujano, E. Fat replacers in low-fat mexican manchego cheese. J. Texture Stud. 2001, 32, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of skim milk and soymilk/enzyme modified soymilk are available from the authors. |




| Sample Number | G’60min 1 (Pa) | Gelation Time 2 (min) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 96.26 ± 1.56 k | 0.36 ± 0.13 a |
| S1 | 80.33 ± 1.86 i | 1.07 ± 0.16 c |
| S2 | 20.49 ± 1.40 b | 8.14 ± 0.15 i |
| S3 | 3.53 ± 0.95 a | 16.28 ± 0.11 j |
| L1 | 111.85 ± 1.68 m | 0.78 ± 0.08 b |
| L2 | 88.86 ± 1.77 j | 1.02 ± 0.20 bc |
| L3 | 75.32 ± 1.33 h | 1.53 ± 0.13 d |
| L4 | 58.14 ± 1.94 f | 2.28 ± 0.14 e |
| L5 | 47.88 ± 1.40 d | 3.04 ± 0.17 g |
| H1 | 102.47 ± 1.46 l | 0.83 ± 0.09 bc |
| H2 | 81.74 ± 1.24 i | 1.07 ± 0.13 c |
| H3 | 65.84 ± 0.88 g | 1.72 ± 0.13 d |
| H4 | 52.31 ± 1.78 e | 2.68 ± 0.11 f |
| H5 | 45.14 ± 1.18 c | 3.55 ± 0.18 h |
| Sample Number | Moisture Content (%) | Curd Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 75.25 ± 3.17 a | 13.52 ± 0.32 a |
| S1 | 78.78 ± 0.78 cd | 15.20 ± 0.20 de |
| S2 | 78.70 ± 0.51 cd | 15.71 ± 0.12 f |
| S3 | 78.01 ± 0.65 bcd | 15.40 ± 0.15 ef |
| L1 | 75.16 ± 1.37 a | 14.34 ± 0.17 bc |
| L2 | 75.90 ± 1.74 ab | 14.99 ± 0.34 d |
| L3 | 76.42 ± 0.84 abc | 15.61 ± 0.18 f |
| L4 | 77.24 ± 1.40 abcd | 16.50 ± 0.18 g |
| L5 | 78.74 ± 0.94 cd | 17.06 ± 0.28 h |
| H1 | 76.89 ± 0.19 abc | 14.05 ± 0.12 b |
| H2 | 75.76 ± 0.31 ab | 14.58 ± 0.11 c |
| H3 | 77.52 ± 0.49 abcd | 15.51 ± 0.21 ef |
| H4 | 77.68 ± 1.49 abcd | 16.41 ± 0.22 g |
| H5 | 79.87 ± 2.29 d | 16.34 ± 0.25 g |
| Mass Ratio | Soymilk | Low Degree of Hydrolysis of Soymilk | High Degree of Hydrolysis of Soymilk |
|---|---|---|---|
| 95:5 | S1 | L1 | H1 |
| 90:10 | S2 | L2 | H2 |
| 85:15 | S3 | L3 | H3 |
| 80:20 | - | L4 | H4 |
| 75:25 | - | L5 | H5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, K.; Yang, J.; Tong, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, F. Effect of Enzyme Modified Soymilk on Rennet Induced Gelation of Skim Milk. Molecules 2018, 23, 3084. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123084
Li K, Yang J, Tong Q, Zhang W, Wang F. Effect of Enzyme Modified Soymilk on Rennet Induced Gelation of Skim Milk. Molecules. 2018; 23(12):3084. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123084
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Kaixin, Jianjun Yang, Qigen Tong, Wei Zhang, and Fang Wang. 2018. "Effect of Enzyme Modified Soymilk on Rennet Induced Gelation of Skim Milk" Molecules 23, no. 12: 3084. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123084
APA StyleLi, K., Yang, J., Tong, Q., Zhang, W., & Wang, F. (2018). Effect of Enzyme Modified Soymilk on Rennet Induced Gelation of Skim Milk. Molecules, 23(12), 3084. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123084