Modeling of Solid–Liquid Equilibria in Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Parameter Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theory
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Parameter Study on a Hypothetical Binary System
3.1.1. Melting Properties of Pure Components
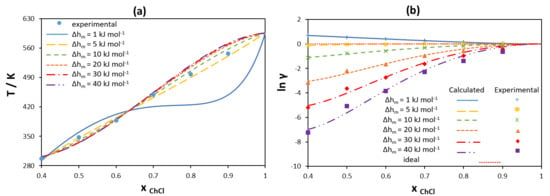
3.1.2. Non-Ideality of Components in Liquid Phase
3.2. Parameter Study on Real Binary Systems
3.2.1. [Ch]Cl-Based Binary Systems
3.2.2. Quaternary Ammonium Chloride Salts/Fatty Acids DES
4. Method
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Row, K. Recent developments in deep eutectic solvents in chemical sciences. Mon. Chem. 2013, 144, 1427–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; De Oliveira Vigier, K.; Royer, S.; Jerome, F. Deep eutectic solvents: Syntheses, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Hao, J.-W.; Mo, L.-P.; Zhang, Z.-H. Recent advances in the application of deep eutectic solvents as sustainable media as well as catalysts in organic reactions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 48675–48704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Ahmed, E.I.; Prasad, K.; Qader, I.B.; Ryder, K.S. Liquid pharmaceuticals formulation by eutectic formation. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2017, 448, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroso, I.M.; Craveiro, R.; Rocha, Â.; Dionísio, M.; Barreiros, S.; Reis, R.L.; Paiva, A.; Duarte, A.R.C. Design of controlled release systems for THEDES—Therapeutic deep eutectic solvents, using supercritical fluid technology. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 492, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroso, I.M.; Silva, J.C.; Mano, F.; Ferreira, A.S.; Dionísio, M.; Sá-Nogueira, I.; Barreiros, S.; Reis, R.L.; Paiva, A.; Duarte, A.R.C. Dissolution enhancement of active pharmaceutical ingredients by therapeutic deep eutectic systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 98, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayyan, A.; Ali Hashim, M.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hayyan, M.; AlNashef, I.M. A novel phosphonium-based deep eutectic catalyst for biodiesel production from industrial low grade crude palm oil. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 92, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayyan, A.; Hashim, M.A.; Hayyan, M.; Mjalli, F.S.; AlNashef, I.M. A novel ammonium based eutectic solvent for the treatment of free fatty acid and synthesis of biodiesel fuel. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 46, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadj-Kali, M.K.; Mulyono, S.; Hizaddin, H.F.; Wazeer, I.; El-Blidi, L.; Ali, E.; Hashim, M.A.; AlNashef, I.M. Removal of Thiophene from Mixtures with n-Heptane by Selective Extraction Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 8415–8423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.; Rodríguez-Juan, E.; Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, G.; Rios, J.J.; Fernández-Bolaños, J. Extraction of phenolic compounds from virgin olive oil by deep eutectic solvents (DESs). Food Chem. 2016, 197, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Duan, M.-H.; Yao, X.-H.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Zhao, C.-J.; Zu, Y.-G.; Fu, Y.-J. Green extraction of five target phenolic acids from Lonicerae japonicae Flos with deep eutectic solvent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 157, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, N.R.; Ferre Guell, J.; Kroon, M.C. Glycerol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents as Extractants for the Separation of MEK and Ethanol via Liquid–Liquid Extraction. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2016, 61, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, K.; Li, N.; Wen, Q.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, Y. Ternary and binary deep eutectic solvents as a novel extraction medium for protein partitioning. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 8196–8207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Namieśnik, J. Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Mixtures: Sustainable Solvents for Extraction Processes. Chem. Sus. Chem. 2014, 7, 1784–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehrer, S.; Bezold, F.; Garcia, E.M.; Minceva, M. Deep eutectic solvents in countercurrent and centrifugal partition chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1434, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezold, F.; Weinberger, M.E.; Minceva, M. Assessing solute partitioning in deep eutectic solvent-based biphasic systems using the predictive thermodynamic model COSMO-RS. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2017, 437, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezold, F.; Weinberger, M.E.; Minceva, M. Computational solvent system screening for the separation of tocopherols with centrifugal partition chromatography using deep eutectic solvent-based biphasic systems. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1491, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezold, F.; Minceva, M. A water-free solvent system containing an L-menthol-based deep eutectic solvent for centrifugal partition chromatography applications. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1587, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atilhan, M.; Aparicio, S. Behavior of Deep Eutectic Solvents under External Electric Fields: A Molecular Dynamics Approach. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Das, S.; Biswas, R. Fast fluctuations in deep eutectic melts: Multi-probe fluorescence measurements and all-atom molecular dynamics simulation study. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2013, 581, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Das, S.; Biswas, R. Density relaxation and particle motion characteristics in a non-ionic deep eutectic solvent (acetamide + urea): Time-resolved fluorescence measurements and all-atom molecular dynamics simulations. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 142, 034505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, E.S.C.; Voroshylova, I.V.; Pereira, C.M.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S. Improved Force Field Model for the Deep Eutectic Solvent Ethaline: Reliable Physicochemical Properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 10124–10137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, G.; Atilhan, M.; Aparicio, S. The impact of charges in force field parameterization for molecular dynamics simulations of deep eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 211, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, O.S.; Bowron, D.T.; Edler, K.J. Liquid structure of the choline chloride-urea deep eutectic solvent (reline) from neutron diffraction and atomistic modelling. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 2736–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrow, T.I.; Maginn, E.J. Density, local composition and diffusivity of aqueous choline chloride solutions: A molecular dynamics study. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2004, 217, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, S.L.; Painter, P.; Colina, C.M. Experimental and computational studies of choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2014, 59, 3652–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, G. Theoretical study on the structures and properties of mixtures of urea and choline chloride. J. Mol. Model. 2013, 19, 2433–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahn, S. Deep eutectic solvents: Similia similibus solvuntur? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 4041–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, G.; Atilhan, M.; Aparicio, S. An approach for the rationalization of melting temperature for deep eutectic solvents from DFT. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2015, 634, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, M.; Moura, L.M.; Turner, A.H.; Swadźba-Kwaśny, M.; Callear, S.K.; McCune, J.A.; Scherman, O.A.; Holbrey, J.D. A comparison of choline:urea and choline:oxalic acid deep eutectic solvents at 338 K. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 148, 193823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashworth, C.R.; Matthews, R.P.; Welton, T.; Hunt, P.A. Doubly ionic hydrogen bond interactions within the choline chloride-urea deep eutectic solvent. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 18145–18160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanovic, R.; Ludwig, M.; Webber, G.B.; Atkin, R.; Page, A.J. Nanostructure, hydrogen bonding and rheology in choline chloride deep eutectic solvents as a function of the hydrogen bond donor. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 3297–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainberger, S.; Kindlein, M.; Bezold, F.; Elts, E.; Minceva, M.; Briesen, H. Deep eutectic solvent formation: A structural view using molecular dynamics simulations with classical force fields. Mol. Phys. 2017, 115, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, V. Properties and Applications of Deep Eutectic Solvents and Low-Melting Mixtures Dissertation. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Regensburg, Regensburg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, A.P.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed between Choline Chloride and Carboxylic Acids: Versatile Alternatives to Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, H.G.; Sun, C.C.; Neervannan, S. Characterization of thermal behavior of deep eutectic solvents and their potential as drug solubilization vehicles. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 378, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, M.A.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; AlNashef, I.M. Phosphonium-Based Ionic Liquids Analogues and Their Physical Properties. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2010, 55, 4632–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Hou, Y.; Ren, S.; Tian, S.; Wu, W. Formation of Deep Eutectic Solvents by Phenols and Choline Chloride and Their Physical Properties. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2013, 58, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Ballerat-Busserolles, K.; Husson, P.; Andanson, J.-M. Impact of water on the melting temperature of urea + choline chloride deep eutectic solvent. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 4492–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, L.P.; Fernandez, L.; Conceição, J.H.F.; Martins, M.A.R.; Sosa, A.; Ortega, J.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Design and Characterization of Sugar-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents Using Conductor-like Screening Model for Real Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 10724–10734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, M.A.R.; Crespo, E.A.; Pontes, P.V.A.; Silva, L.P.; Bülow, M.; Maximo, G.J.; Batista, E.A.C.; Held, C.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Tunable Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvents Based on Terpenes and Monocarboxylic Acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 8836–8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, E.A.; Silva, L.P.; Martins, M.A.R.; Bülow, M.; Ferreira, O.; Sadowski, G.; Held, C.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. The Role of Polyfunctionality in the Formation of [Ch]Cl-Carboxylic Acid-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 11195–11209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, E.A.; Silva, L.P.; Martins, M.A.R.; Fernandez, L.; Ortega, J.; Ferreira, O.; Sadowski, G.; Held, C.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Characterization and Modeling of the Liquid Phase of Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Fatty Acids/Alcohols and Choline Chloride. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 12192–12202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pontes, P.V.A.; Crespo, E.A.; Martins, M.A.R.; Silva, L.P.; Neves, C.M.S.S.; Maximo, G.J.; Hubinger, M.D.; Batista, E.A.C.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; et al. Measurement and PC-SAFT modeling of solid–liquid equilibrium of deep eutectic solvents of quaternary ammonium chlorides and carboxylic acids. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2017, 448, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollau, L.J.B.M.; Vis, M.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Esteves, A.C.C.; Tuinier, R. Quantification of the liquid window of deep eutectic solvents. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 13351–13354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gamsjäger, H.; Lorimer John, W.; Scharlin, P.; Shaw David, G. Glossary of terms related to solubility (IUPAC Recommendations 2008). Pure Appl. Chem. 2008, 80, 233–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.A.R.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Insights into the Nature of Eutectic and Deep Eutectic Mixtures. J. Solut. Chem. 2018, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyykkö, P. Simple Estimates for Eutectic Behavior. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2019, 20, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prausnitz, J.M.; Lichtenthaler, R.N.; Azevedo, E.G.d. Molecular Thermodynamics of Fluid-Phase Equilibria; Prentice Hall PTR: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Katritzky, A.R.; Jain, R.; Lomaka, A.; Petrukhin, R.; Maran, U.; Karelson, M. Perspective on the Relationship between Melting Points and Chemical Structure. Cryst. Growth Des. 2001, 1, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.J.C.; Brown, R.F.C. Melting Point and Molecular Symmetry. J. Chem. Educ. 2000, 77, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavezzotti, A. Are Crystal Structures Predictable? Acc. Chem. Res. 1994, 27, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Yalkowsky, S.H. Estimation of Melting Points of Organic Compounds-II. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 2562–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, L.; Silva, L.P.; Martins, M.A.R.; Ferreira, O.; Ortega, J.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Indirect assessment of the fusion properties of choline chloride from solid–liquid equilibria data. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2017, 448, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicka, M.; Storoniak, P.; Błażejowski, J.; Rak, J. TG-FTIR, DSC, and Quantum-Chemical Studies on the Thermal Decomposition of Quaternary Ethylammonium Halides. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 5066–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawicka, M.; Storoniak, P.; Skurski, P.; Błażejowski, J.; Rak, J. TG-FTIR, DSC and quantum chemical studies of the thermal decomposition of quaternary methylammonium halides. Chem. Phys. 2006, 324, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples not available. |




 a(1) = −30;
a(1) = −30;  a(1) = −18;
a(1) = −18;  a(1) = −12;
a(1) = −12;  a(1) = 0.
a(1) = 0.
 a(1) = −30;
a(1) = −30;  a(1) = −18;
a(1) = −18;  a(1) = −12;
a(1) = −12;  a(1) = 0.
a(1) = 0.
 a(1) = −30;
a(1) = −30;  a(1) = −18;
a(1) = −18;  a(1) = −12;
a(1) = −12;  a(1) = 0.
a(1) = 0.
 a(1) = −30;
a(1) = −30;  a(1) = −18;
a(1) = −18;  a(1) = −12;
a(1) = −12;  a(1) = 0.
a(1) = 0.






| [N1111]Cl | [N2222]Cl | [N3333]Cl | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| xe,acid | Te | ΔTe | xe,acid | Te | ΔTe | xe,acid | Te | ΔTe | |
| Capric acid | 0.808 | 299.91 | 0.0161 | 0.614 | 297.40 | 0.0247 | 0.710 | 288.46 | 0.0565 |
| Lauric acid | 0.630 | 303.01 | 0.0478 | 0.640 | 301.44 | 0.0532 | 0.644 | 297.05 | 0.0688 |
| Myristic acid | 0.712 | 321.65 | 0.0167 | 0.658 | 317.88 | 0.0288 | 0.571 | 304.54 | 0.0738 |
| Palmitic acid | 0.615 | 328.51 | 0.0254 | 0.607 | 318.78 | 0.0567 | 0.483 | 303.56 | 0.1096 |
| Stearic acid | 0.634 | 337.89 | 0.0171 | 0.556 | 317.02 | 0.0841 | 0.562 | 322.82 | 0.0646 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alhadid, A.; Mokrushina, L.; Minceva, M. Modeling of Solid–Liquid Equilibria in Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Parameter Study. Molecules 2019, 24, 2334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122334
Alhadid A, Mokrushina L, Minceva M. Modeling of Solid–Liquid Equilibria in Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Parameter Study. Molecules. 2019; 24(12):2334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122334
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlhadid, Ahmad, Liudmila Mokrushina, and Mirjana Minceva. 2019. "Modeling of Solid–Liquid Equilibria in Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Parameter Study" Molecules 24, no. 12: 2334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122334
APA StyleAlhadid, A., Mokrushina, L., & Minceva, M. (2019). Modeling of Solid–Liquid Equilibria in Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Parameter Study. Molecules, 24(12), 2334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122334