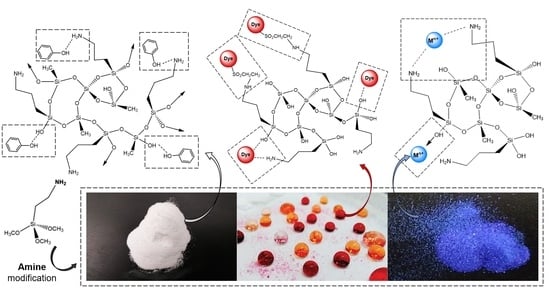
Amine Modification of Silica Aerogels/Xerogels for Removal of Relevant Environmental Pollutants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Aerogels Selection Based on Preliminary Adsorption Tests
2.2. Properties of the Adsorbents
2.3. Adsorption of Pollutants
2.3.1. Adsorption Equilibrium
2.3.2. Adsorption Kinetics
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Silica Aerogels
3.2.1. Synthesis of VOC Adsorbents
3.2.2. Synthesis of Heavy Metal Adsorbents
3.2.3. Synthesis of Dye Adsorbents
3.3. Characterization
3.4. Adsorption Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, C.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Fan, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, R. Compressive, ultralight and fire-resistant lignin-modified graphene aerogels as recyclable absorbents for oil and organic solvents. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 350, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Syed, Z.; Brighu, U.; Gupta, A.B.; Ram, C. Adsorption of textile wastewater on alkali-activated sand. J.Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourmoradi, H.; Khiadani, M.; Nikaeen, M. Multi-Component Adsorption of Benzene, Toluene, Ethylbenzene, and Xylene from Aqueous Solutions by Montmorillonite Modified with Tetradecyl Trimethyl Ammonium Bromide. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuana, R.A.; Okieimen, F.E. Heavy Metals in Contaminated Soils: A Review of Sources, Chemistry, Risks and Best Available Strategies for Remediation. Isrn Ecol. 2011, 2011, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lima, L.F.; de Andrade, J.R.; da Silva, M.G.C.; Vieira, M.G.A. Fixed Bed Adsorption of Benzene, Toluene, and Xylene (BTX) Contaminants from Monocomponent and Multicomponent Solutions Using a Commercial Organoclay. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 6326–6336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, C.M.C.; Matias, T.; Durães, L.; Valente, A.J.M. Efficient simultaneous removal of petroleum hydrocarbon pollutants by a hydrophobic silica aerogel-like material. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 520, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Mazumder, M.A.J.; Al-Attas, O.; Husain, T. Heavy metals in drinking water: Occurrences, implications, and future needs in developing countries. Sci. Total Env. 2016, 569–570, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA. Heavy Metal Emissions; Indicator code: AIR 001; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- You, L.; Wu, Z.; Kim, T.; Lee, K. Kinetics and thermodynamics of bromophenol blue adsorption by a mesoporous hybrid gel derived from tetraethoxysilane and bis(trimethoxysilyl)hexane. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 300, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Xu, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, X.; Li, X. Preparation and adsorption properties of nano magnetite silica gel for methylene blue from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 546, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H.M. Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomis, D.; Guyton, K.Z.; Grosse, Y.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Vilahur, N.; Mattock, H.; Straif, K. Carcinogenicity of benzene. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1574–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, W.; Lee, J.; Raza, N.; Luo, Y.; Kim, K.-H.; Yang, J. Removal of phenolic compounds from industrial waste water based on membrane-based technologies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 71, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.S.; Choppala, G.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Park, J.; Naidu, R. Microbial Transformation of Trace Elements in Soils in Relation to Bioavailability and Remediation. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Whitacre, M.D., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Chary, N.S.; Fernandez-Alba, A.R. Determination of volatile organic compounds in drinking and environmental waters. TracTrends Anal. Chem. 2012, 32, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damjanović, L.; Rakić, V.; Rac, V.; Stošić, D.; Auroux, A. The investigation of phenol removal from aqueous solutions by zeolites as solid adsorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayemiwo, O.; Daramola, M.; Moothi, K. BTEX compounds in water—future trends and directions for water treatment. Water Sa 2017, 43, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirpichtchikova, T.A.; Manceau, A.; Spadini, L.; Panfili, F.; Marcus, M.A.; Jacquet, T. Speciation and solubility of heavy metals in contaminated soil using X-ray microfluorescence, EXAFS spectroscopy, chemical extraction, and thermodynamic modeling. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 2163–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vareda, J.P.; Valente, A.J.; Durães, L. Heavy metals in Iberian soils: Removal by current adsorbents/amendments and prospective for aerogels. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 237, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K. Green Chemistry for Dyes Removal from Waste Water: Research Trends and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.M.; Carr, C.M. A critical review on recent advancements of the removal of reactive dyes from dyehouse effluent by ion-exchange adsorbents. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirirerkratana, K.; Kemacheevakul, P.; Chuangchote, S. Color removal from wastewater by photocatalytic process using titanium dioxide-coated glass, ceramic tile, and stainless steel sheets. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, P.V.; Schulz, P.C. Adsorption of reactive dyes on titania–silica mesoporous materials. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 299, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vareda, J.P.; Valente, A.J.M.; Durães, L. Assessment of heavy metal pollution from anthropogenic activities and remediation strategies: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashim, M.A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Sahu, J.N.; Sengupta, B. Remediation technologies for heavy metal contaminated groundwater. J. Env. Manag. 2011, 92, 2355–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Liu, H.; Xu, A.; Tang, K.; Huang, Y.; Lu, C. In situ reduced and assembled three-dimensional graphene aerogel for efficient dye removal. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 714, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadi, A.; Rafati, A.A. Preparation of silica mesoporous nanoparticles functionalized with β-cyclodextrin and its application for methylene blue removal. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 209, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini Hashemi, M.S.; Eslami, F.; Karimzadeh, R. Organic contaminants removal from industrial wastewater by CTAB treated synthetic zeolite Y. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 233, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burakov, A.E.; Galunin, E.V.; Burakova, I.V.; Kucherova, A.E.; Agarwal, S.; Tkachev, A.G.; Gupta, V.K. Adsorption of heavy metals on conventional and nanostructured materials for wastewater treatment purposes: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, H. Recent advances in aerogels for environmental remediation applications: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 98–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durães, L.; Maleki, H.; Vareda, J.P.; Lamy-Mendes, A.; Portugal, A. Exploring the Versatile Surface Chemistry of Silica Aerogels for Multipurpose Application. Mrs Adv. 2017, 2, 3511–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Wei, W.; Jiang, Z.; Lu, J.; Zhu, J.; Xie, J. Removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution by adsorption onto hydrophobic/hydrophilic silica aerogel. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 509, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhu, J.; Wei, W.; Ma, L.; Zhu, J.; Xie, J. Comparative study of modified/non-modified aluminum and silica aerogels for anionic dye adsorption performance. Rsc Adv. 2018, 8, 29129–29140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Štandeker, S.; Novak, Z.; Knez, Ž. Adsorption of toxic organic compounds from water with hydrophobic silica aerogels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 310, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, G.; Yao, Y.; Wei, W.; Zhang, T. Preparation of hydrophobic granular silica aerogels and adsorption of phenol from water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 280, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štandeker, S.; Veronovski, A.; Novak, Z.; Knez, Ž. Silica aerogels modified with mercapto functional groups used for Cu(II) and Hg(II) removal from aqueous solutions. Desalination 2011, 269, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouretedal, H.R.; Kazemi, M. Characterization of modified silica aerogel using sodium silicate precursor and its application as adsorbent of Cu2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+ ions. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2012, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihian, H.; Nourmoradi, H.; Shokouhi, M. Performance of silica aerogels modified with amino functional groups in Pb(II) and Cd(II) removal from aqueous solutions. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2012, 14, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihian, H.; Nourmoradi, H.; Shokouhi, M. Removal of copper (II) and nickel (II) from aqueous media using silica aerogel modified with amino propyl triethoxysilane as an adsorbent: Equilibrium, kinetic, and isotherms study. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 52, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.; Khan, A.; Ahmad, R. The use of functionalized aerogels as a low level chromium scavenger. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 203, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaonan, D.; Genggeng, Q.; Peng, W.; Giannelis, E.P. A Highly Efficient and Selective Polysilsesquioxane Sorbent for Heavy Metal Removal. ChemPhysChem 2012, 13, 2536–2539. [Google Scholar]
- Vareda, J.P.; Durães, L. Functionalized silica xerogels for adsorption of heavy metals from groundwater and soils. J. Sol.-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 84, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vareda, J.P.; Durães, L. Efficient adsorption of multiple heavy metals with tailored silica aerogel-like materials. Env. Technol. 2019, 40, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Hu, H.; Ji, X.; Yan, Z.; Sun, W.; Xie, J. Selective adsorption of organic dyes by porous hydrophilic silica aerogels from aqueous system. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Shan, J.; Lai, Z.; Lei, W.; Ding, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H. Facile Synthesis of Flexible Methylsilsesquioxane Aerogels with Surface Modifications for Sound—Absorbance, Fast Dye Adsorption and Oil/Water Separation. Molecules 2018, 23, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguado, J.; Arsuaga, J.M.; Arencibia, A.; Lindo, M.; Gascón, V. Aqueous heavy metals removal by adsorption on amine-functionalized mesoporous silica. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfarra, A.; Frackowiak, E.; Béguin, F. The HSAB concept as a means to interpret the adsorption of metal ions onto activated carbons. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 228, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.Y.; McKay, G.; Yeung, K.L. Selective Adsorbents from Ordered Mesoporous Silica. Langmuir 2003, 19, 3019–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; McLaughlin, E.; Pfeffer, R.; Lin, Y.S. Adsorption of Organic Compounds in Vapor, Liquid, and Aqueous Solution Phases on Hydrophobic Aerogels. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 12177–12185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, V. Funcionalização de aerogéis de sílica para adsorção de corantes têxteis. Master’s Thesis, Chemical Engineering, University of Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal, 2017. (In Portuguese). [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, D. Aerogéis compósitos de nanotubos de carbono/sílica para remediação ambiental. Master’s Thesis, Chemical Engineering, University of Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal, 2019. (In Portuguese). [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, M. Xerogéis de Sílica Funcionalizados como Adsorventes não Seletivos de Metais Pesados. Master’s Thesis, Thesis in Chemical Engineering. University of Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal, 2018. (In Portuguese). [Google Scholar]
- Lamy-Mendes, A.; Girão, A.V.; Silva, R.F.; Durães, L. Polysilsesquioxane-based silica aerogel monoliths with embedded CNTs. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 288, 109575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswara Rao, A.; Bhagat, S.D.; Hirashima, H.; Pajonk, G.M. Synthesis of flexible silica aerogels using methyltrimethoxysilane (MTMS) precursor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 300, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüsing, N.; Schubert, U.; Mezei, R.; Fratzl, P.; Riegel, B.; Kiefer, W.; Kohler, D.; Mader, W. Formation and Structure of Gel Networks from Si(OEt)4/(MeO)3Si(CH2)3NR‘2 Mixtures (NR‘2 = NH2 or NHCH2CH2NH2). Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Oweini, R.; El-Rassy, H. Synthesis and characterization by FTIR spectroscopy of silica aerogels prepared using several Si(OR)4 and R′′Si(OR′)3 precursors. J. Mol. Struct. 2009, 919, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woignier, T.; Phalippou, J. Skeletal density of silica aerogels. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1987, 93, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, T.; Marques, J.; Conceição, F.; Maleki, H.; Quina, M.J.; Gando-Ferreira, L.; Valente, A.J.M.; Portugal, A.; Durães, L. Towards improved adsorption of phenolic compounds by surface chemistry tailoring of silica aerogels. J. Sol.-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 84, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, I.; Rodriguez-Iglesias, J.; Maranon, E.; Castrillon, L.; Alvarez, M. Removal of residual phenols from coke wastewater by adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bahdod, A.; El Asri, S.; Saoiabi, A.; Coradin, T.; Laghzizil, A. Adsorption of phenol from an aqueous solution by selected apatite adsorbents: Kinetic process and impact of the surface properties. Water Res. 2009, 43, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouallal, H.; Dehmani, Y.; Moussout, H.; Messaoudi, L.; Azrour, M. Kinetic, isotherm and mechanism investigations of the removal of phenols from water by raw and calcined clays. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perdigoto, M.L.N.; Martins, R.C.; Rocha, N.; Quina, M.J.; Gando-Ferreira, L.; Patrício, R.; Durães, L. Application of hydrophobic silica based aerogels and xerogels for removal of toxic organic compounds from aqueous solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 380, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channa, A.M.; Baytak, S.; Memon, S.Q.; Talpur, M.Y. Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies of removal of phenol from aqueous solution using surface engineered chemistry. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Lu, M.; Wang, H.; Pei, Y.; Rao, H.; Du, X. Three-dimensional graphene aerogels–mesoporous silica frameworks for superior adsorption capability of phenols. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 153, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, I. Hydrated metal ions in aqueous solution: How regular are their structures? Pure Appl. Chem. 2010, 82, 1901–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, B.; Guo, Y.; Huang, W. Synthesis of chitosan-functionalized MCM-41-A and its performance in Pb(II) removal from synthetic water. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 71, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, F.; Xu, R.; Wei, S.; Li, G. Synthesis of thiol-functionalized MCM-41 mesoporous silicas and its application in Cu(II), Pb(II), Ag(I), and Cr(III) removal. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 2111–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.P.; Oliveira, J.T.; Oliveira, A.G.; Sousa, F.W.; Abdala Neto, E.F.; Vidal, C.B.; de Keukeleire, D.; dos Santos, A.B.; Nascimento, R.F. Treatment of Sulfonated Azo Dye Reactive Red 198 by UV/H2O2. J. Chem. 2014, 2014, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prechtl, F.; Patsch, M. Reactive dyes with a combination anchor. U.S. Patent US6410698B1, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jesionowski, T. Synthesis of organic–inorganic hybrids via adsorption of dye on an aminosilane-functionalised silica surface. Dye. Pigment. 2002, 55, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, F.C.F.; Wu, T.Y.; Teh, C.Y.; Juan, J.C.; Balasubramanian, N. Investigation into photocatalytic decolorisation of CI Reactive Black 5 using titanium dioxide nanopowder. Coloration Technol. 2012, 128, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yang, R.; Li, M. Liquid adsorption of basic dye using silica aerogels with different textural properties. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2010, 356, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Multimodel inference: Understanding AIC and BIC in model selection. Sociol. Methods Res. 2004, 33, 261–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazerolle, M. Improving data analysis in herpetology: Using Akaike’s Information Criterion (AIC) to assess the strength of biological hypotheses. Amphib. -Reptil. 2006, 27, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, T.; Marques, J.; Quina, M.J.; Gando-Ferreira, L.; Valente, A.J.M.; Portugal, A.; Durães, L. Silica-based aerogels as adsorbents for phenol-derivative compounds. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 480, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saad, N.; Al-Mawla, M.; Moubarak, E.; Al-Ghoul, M.; El-Rassy, H. Surface-functionalized silica aerogels and alcogels for methylene blue adsorption. Rsc Adv. 2015, 5, 6111–6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhamou, A.; Baudu, M.; Derriche, Z.; Basly, J.-P. Aqueous heavy metals removal on amine-functionalized Si-MCM-41 and Si-MCM-48. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-S.; Fan, Y.-H.; Zhang, S.-W.; Qi, S.-H. Enhanced adsorption removal of anionic dyes via a facile preparation of amino-functionalized magnetic silica. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durães, L.; Maia, A.; Portugal, A. Effect of additives on the properties of silica based aerogels synthesized from methyltrimethoxysilane (MTMS). J. Supercrit. Fluids 2015, 106, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.B.; Vareda, J.P.; Lamy-Mendes, A.; Durães, L. Effect of different silylation agents on the properties of ambient pressure dried and supercritically dried vinyl-modified silica aerogels. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 147, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriano, D.C. Trace Elements in Terrestrial Environments: Biogeochemistry, Bioavailability, and Risks of Metals. 2nd Edition ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Cheng, S.; Li, H.Y. Adsorption of Pb(II) and Cu(II) metal ions on functionalized large-pore mesoporous silica. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Lu, C.; Hu, S. Adsorption of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and p-xylene by NaOCl-oxidized carbon nanotubes. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 353, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, D.A.; Scholz, M. Textile dye wastewater characteristics and constituents of synthetic effluents: A critical review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1193–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, A.M.; Goh, P.S.; Abdullah, M.S.; Ng, B.C.; Ismail, A.F. Adsorptive nanocomposite membranes for heavy metal remediation: Recent progresses and challenges. Chemosphere 2019, 232, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, N. Facile synthesis of porous carbons from silica-rich rice husk char for volatile organic compounds (VOCs) sorption. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markandeya, S.; Kisku, G. Linear and non-linear kinetic modeling for adsorption of disperse dye in batch process. Res. J. Environ. Toxicol. 2015, 9, 320–331. [Google Scholar]
- Filho, C.M.C.; Bueno, P.V.A.; Matsushita, A.F.Y.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C.; Durães, L.; Murtinho, D.M.B.; Valente, A.J.M. Synthesis, characterization and sorption studies of aromatic compounds by hydrogels of chitosan blended with β-cyclodextrin- and PVA-functionalized pectin. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 14609–14622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of aerogels/xerogels used in this work are not available from the authors, due to the pursuing of the adsorption studies. |







| Adsorption Performance (mg/g) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorbent | Type of Material | Precursor system(a) | Initial concentration (mg/L) | Phenol | Benzene |
| M | Aerogel-like | 100% MTMS | 200 | 8.4 ± 0.8 | 51.0 ± 1.4 |
| MA | Aerogel-like | 90%MTMS/10%APTMS | 19.1 ± 0.9 | 15.4 ± 1.6 | |
| Copper | Lead | ||||
| Mt | Xerogel | 62.5%MTES/37.5%TEOS | 500 | 14.8 ± 10.1 | 23.3 ± 1.5 |
| A_Mt | Aerogel | 62.5%MTES/37.5%TEOS | (b) | 21.7 ± 0.6 | |
| MtA | Xerogel | 50%MTES/30%TEOS/20%APTMS | 124.2 ± 10.0 | 124.2 ± 2.5 | |
| A_MtA | Aerogel | 50%MTES/30%TEOS/20%APTMS | 115.6 ± 6.9 | 207.5 ± 2.1 | |
| Rubi Levafix | Methylene Blue | ||||
| T | Xerogel | 100%TMOS | 100 | (b) | 15.1 ± 0.3 |
| A_T | Aerogel | 100%TMOS | 5.4 ± 0.6 | 12.2 ± 0.5 | |
| TA | Xerogel | 65%TMOS/35%APTMS | 37.6 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | |
| A_TA | Aerogel | 65%TMOS/35%APTMS | 44.1 ± 0.1 | (b) | |
| Sample | Bulk Density/(kg/m3) | Skeletal Density/(kg/m3) | Porosity/(%) | SBET/(m2/g) | Dpore(a)/(nm) | Contact Angle/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M [54] | 75.3 ± 5.1 | 1610 ± 75 | 95.3 ± 0.1 | 458.1 ± 2.2 | 110.5 ± 6.9 | 162.9 ± 3.9 |
| MA [54] | 80.9 ± 7.2 | 1479 ± 52 | 94.5 ± 0.3 | 72.2 ± 1.3 | 647.4 ± 46.1 | 164.4 ± 10.1 |
| Mt | 1068 (b) | 1400 ± 17 | 23.8 | 758.9 ± 15.5 | 1.2 | 94.7 ± 3.2 |
| MtA | 1410 (b) | 1459 ± 30 | 3.4 | 27.9 ± 0.1 | 3.5 | (c) |
| A_T | 70.4 ± 5.3 | 1793 ± 80 | 96.1 ± 0.1 | 817.2 ± 7.3 | 66.8 ± 4.5 | (c) |
| A_TA | 99.4 ± 4.4 | 1588 ± 50 | 93.7 ± 0.1 | 191.6 ± 3.6 | 197.0 ± 8.9 | (c) |
| Sample | wt% Si + O (a) | wt% C | wt% H | wt% N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | Experimental | 74.60 | 20.30 ± 0.39 | 4.70 ± 0.04 | 0.41 ± 0.03 |
| Complete condensation | 77.6 | 17.90 | 4.51 | 0.00 | |
| Incomplete condensation 1OH | 78.93 | 15.78 | 5.30 | 0.00 | |
| Incomplete condensation 2OH | 79.97 | 14.11 | 5.92 | 0.00 | |
| MA | Experimental | 74.17 | 18.81 ± 0.35 | 5.05 ± 0.10 | 1.96 ± 0.02 |
| Complete condensation | 72.92 | 20.18 | 4.94 | 1.96 | |
| Incomplete condensation 1OH | 74.70 | 17.92 | 5.64 | 1.74 | |
| Incomplete condensation 2OH | 76.12 | 16.11 | 6.20 | 1.57 | |
| Mt | Experimental | 84.03 | 11.87 ± 0.17 | 3.52 ± 0.05 | 0.58 ± 0.03 |
| Complete condensation | 85.43 | 11.64 | 2.93 | 0.00 | |
| Incomplete condensation 1OH | 85.84 | 10.22 | 3.94 | 0.00 | |
| Incomplete condensation 2OH | 86.17 | 9.10 | 4.73 | 0.00 | |
| MtA | Experimental | 76.92 | 15.31 ± 1.12 | 4.47 ± 0.04 | 3.30 ± 0.06 |
| Complete condensation | 74.01 | 17.95 | 4.24 | 3.81 | |
| Incomplete condensation 1OH | 75.62 | 15.99 | 5.00 | 3.39 | |
| Incomplete condensation 2OH | 76.92 | 14.42 | 5.61 | 3.06 | |
| A_T | Experimental | 93.02 | 5.13 ± 0.07 | 1.68 ± 0.17 | 0.17 ± 0.08 |
| Complete condensation | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Incomplete condensation 1OH | 98.54 | 0.00 | 1.46 | 0.00 | |
| Incomplete condensation 2OH | 97.42 | 0.00 | 2.58 | 0.00 | |
| A_TA | Experimental | 73.16 | 17.40 ± 0.59 | 4.26 ± 0.09 | 5.18 ± 0.09 |
| Complete condensation | 74.07 | 16.25 | 3.64 | 6.32 | |
| Incomplete condensation 1OH | 75.36 | 14.56 | 4.42 | 5.66 | |
| Incomplete condensation 2OH | 76.63 | 13.19 | 5.06 | 5.13 |
| Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | RL | AIC(a) | 1/nF | KF ((mg/g) (L/mg)1/n) | AIC(a) | Maximum qe Experimental (mg/g) | |
| M_Phenol | 13 ± 4 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.23–0.86 | 21 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.7 | 24 | 10.0 ± 0.9 |
| MA_Phenol | 41 ± 8 | 0.005 ± 0.002 | 0.50–0.95 | 14 | 0.70 ± 0.03 | 0.54 ± 0.09 | 7 | 19.1 ± 0.9 |
| M_Benzene | (b) | (b) | (b) | -- | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 2.3 ± 1.0 | -- | 51.0 ± 0.6 |
| MA_Benzene | 20 ± 3 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.16–0.80 | 21 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 1.0 | 26 | 15.4 ± 0.2 |
| Mt_Cu | (c) | (c) | (c) | (c) | (c) | (c) | (c) | 14.8 ± 10.1 |
| MtA_Cu | 149 ± 11 | 0.018 ± 0.005 | 0.10–0.84 | 35 | 0.38 ± 0.01 | 15.0 ± 0.6 | 9 | 124.2 ± 10.0 |
| Mt_Pb | 25 ± 1 | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 0.07–0.80 | 30 | 0.23 ± 0.08 | 6.1 ± 2.7 | 39 | 24.0 ± 0.4 |
| MtA_Pb | 128 ± 4 | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 0.02–0.48 | 27 | 0.144 ± 0.001 | 55.9 ± 0.4 | −11 | 124.2 ± 3.0 |
| A_T_Rubi | 12 ± 4 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.50–0.91 | 8 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 9 | 5.6 ± 0.5 |
| A_TA_Rubi | 53 ± 3 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.03–0.20 | 25 | 0.29 ± 0.02 | 21.5 ± 0.9 | 15 | 44.1 ± 0.1 |
| A_T_Blue | 13 ± 1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.04–0.32 | 29 | 0.22 ± 0.04 | 4.9 ± 0.7 | 24 | 12.7 ± 0.6 |
| A_TA_Blue | (c) | (c) | (c) | (c) | (c) | (c) | (c) | 0.2 ± 0.1 |
| Removal Efficiency (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| C0 = 50 mg/L | C0 = 100 mg/L | C0 = 200 mg/L | |
| M_Phenol | 17.9 ± 1.8 | 20.3 ± 0.9 | 8.4 ± 1.7 |
| MA_Phenol | 28.4 ± 0.4 | 24.3 ± 0.8 | 19.1 ± 1.8 |
| M_Benzene | 61.6 ± 0.3 | 64.1 ± 1.8 | 51.0 ± 1.3 |
| MA_Benzene | 32.5 ± 0.4 | 30.9 ± 0.2 | 15.4 ± 1.2 |
| Mt_Cu | (a) | (a) | (a) |
| MtA_Cu | 94.1 ± 0.4 | 86.0 ± 0.5 | 70.2 ± 3.0 |
| Mt_Pb | 34.0 ± 2.0 | 21.3 ± 2.1 | 24.0 ± 0.4 |
| MtA_Pb | 100.0 ± 0.0 | 100.0 ± 0.0 | 88.2 ± 0.5 |
| C0 = 25 mg/L | C0 = 50 mg/L | C0 = 100 mg/L | |
| A_T_Rubi | 14.2 ± 2.1 | 14.3 ±1.7 | 10.9 ± 1.3 |
| A_TA_Rubi | 99.4 ± 0.1 | 97.6 ± 0.2 | 88.14 ± 0.2 |
| A_T_Blue | 62.8 ± 0.8 | 41.0 ± 0.1 | 24.5 ± 0.9 |
| A_TA_Blue | (a) | (a) | (a) |
| Pseudo-First Order | Pseudo-Second Order | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | C0 (mg/L) | k1 (1/min) | qe (mg/g) | AIC (a) | k2 × 103 (g/(mg.min)) | qe (mg/g) | AIC (a) | qe (exp) (mg/g) |
| M_Phenol | 100 | 0.25 ± 0.04 | 10.5 ± 0.2 | −1 | 44.9 ± 11.4 | 10.8 ± 0.3 | −2 | 10.0 ± 0.9 |
| MA_Phenol | 100 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 16.1 ± 0.4 | 7 | 14.7 ± 3.2 | 16.9 ± 0.5 | 6 | 10.6 ± 0.6 |
| M_Benzene | 100 | 0.24 ± 0.03 | 37.1 ± 0.9 | 22 | 16.2 ± 7.2 | 38.1 ± 1.3 | 23 | 32.07 ± 0.03 |
| MA_Benzene | 100 | 0.35 ± 0.1 | 22.0 ± 0.5 | 13 | 38.7 ± 12.5 | 22.7 ± 0.4 | 6 | 15.5 ± 0.2 |
| MtA_Cu | 200 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 17.4 ± 1.5 | 31 | 1.6 ± 0.5 | 20.6 ± 1.6 | 27 | 70.2 ± 3.0 |
| Mt_Pb | 200 | 0.32 ± 0.03 | 23.7 ± 0.2 | 17 | 37.8 ± 5.8 | 24.2 ± 0.3 | 18 | 24.0 ± 0.4 |
| MtA_Pb | 200 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 26.0 ± 2.4 | 13 | 0.62 ± 0.2 | 33.0 ± 3.2 | 7 | 88.2 ± 0.5 |
| A_TA_Rubi | 50 | 0.19 ± 0.04 | 23.7 ± 0.7 | 18 | 12.7 ± 1.6 | 25.5 ± 0.4 | 8 | 24.40 ± 0.05 |
| A_T_Blue | 50 | 0.30 ± 0.05 | 10.7 ± 0.2 | 19 | 58.9 ± 6.0 | 11.3 ± 0.1 | 8 | 10.25 ± 0.04 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lamy-Mendes, A.; Torres, R.B.; Vareda, J.P.; Lopes, D.; Ferreira, M.; Valente, V.; Girão, A.V.; Valente, A.J.M.; Durães, L. Amine Modification of Silica Aerogels/Xerogels for Removal of Relevant Environmental Pollutants. Molecules 2019, 24, 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203701
Lamy-Mendes A, Torres RB, Vareda JP, Lopes D, Ferreira M, Valente V, Girão AV, Valente AJM, Durães L. Amine Modification of Silica Aerogels/Xerogels for Removal of Relevant Environmental Pollutants. Molecules. 2019; 24(20):3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203701
Chicago/Turabian StyleLamy-Mendes, Alyne, Rafael B. Torres, João P. Vareda, David Lopes, Marco Ferreira, Vanessa Valente, Ana V. Girão, Artur J. M. Valente, and Luísa Durães. 2019. "Amine Modification of Silica Aerogels/Xerogels for Removal of Relevant Environmental Pollutants" Molecules 24, no. 20: 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203701
APA StyleLamy-Mendes, A., Torres, R. B., Vareda, J. P., Lopes, D., Ferreira, M., Valente, V., Girão, A. V., Valente, A. J. M., & Durães, L. (2019). Amine Modification of Silica Aerogels/Xerogels for Removal of Relevant Environmental Pollutants. Molecules, 24(20), 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203701