Synthesis of 9-Hydroxystearic Acid Derivatives and Their Antiproliferative Activity on HT 29 Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of 9-HSA Derivatives
2.2. Biological Activity
2.2.1. Preliminary Biological Activity of (R)-2, 3, (S)-4, and (S)-5
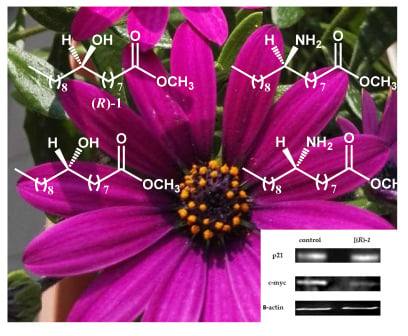
2.2.2. Effect of Methyl (9R)-9-hydroxystearate [(R)-1], Methyl (9S)-9-hydroxystearate [(S)-1], Methyl (9R)-9-aminostearate [(R)-5] and Methyl (9S)-9-aminostearate [(S)-5] on Proliferation of HT29
2.2.3. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.2.4. Effect of (R)-1 on Histone Acetylation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical Syntheses
3.1.1. Synthesis of Methyl (9R)-9-hydroxyoctadecanoate [(R)-1]
3.1.2. Synthesis of Methyl (R)-9-(tosyloxy)octadecanoate [(R)-2]
3.1.3. Synthesis of Methyl 9-MethoxyOctadecanoate (3)
3.1.4. Synthesis of Methyl (9S)-9-azidooctadecanoate [(S)-4]
3.1.5. Synthesis of Methyl (9S)-9-aminooctadecanoate [(S)-5]
3.1.6. Synthesis of (S)-2-Chloro-2-oxo-1-phenylethyl Methyl Carbonate (7)
3.1.7. Methyl (9S)-9-{[(2S)-2-(Acetyloxy)-2-Phenylacetyl]amino}octadecanoate [(S,S)-8] and Methyl (9R)-9-{[(2S)-2-(Acetyloxy)-2-Phenylacetyl]amino}octadecanoate [(R,S)-8]
3.2. Cell Culture and Treatments
3.2.1. MTT Assay
3.2.2. Cell Cycle Analysis by Flow Cytometry
3.2.3. Histone Extraction and Western Blot
3.2.4. Total Protein Extraction and Western Blot
3.2.5. Quantitative Real Time-PCR Analysis
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masotti, L.; Casali, E.; Gesmundo, N.; Sartor, G.; Galeotti, T.; Borrello, S.; Piretti, M.V.; Pagliuca, G. Lipid peroxidation in cancer cells: Chemical and physical studies. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1989, 551, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masotti, L.; Casali, E.; Gesmundo, N. Influence of hydroxystearic acid on in vitro cell proliferation. Mol. Aspects Med. 1993, 14, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertucci, C.; Hudaib, M.; Boga, C.; Calonghi, N.; Cappadone, C.; Masotti, L. Gas chromatography/ mass apectrometry assay of endogenous cellular lipid peroxidation products: Quantitative analysis of 9- and 10-hydroxystearic acids. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2002, 16, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calonghi, N.; Cappadone, C.; Pagnotta, E.; Farruggia, G.; Buontempo, F.; Boga, C.; Brusa, G.L.; Santucci, M.A.; Masotti, L. 9-Hydroxystearic acid upregulates p21WAF1 in HT29 cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 314, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calonghi, N.; Pagnotta, E.; Parolin, C.; Molinari, C.; Boga, C.; Dal Piaz, F.; Brusa, G.L.; Santucci, M.A.; Masotti, L. Modulation of apoptotic signalling by 9-hydroxystearic acid in osteosarcoma cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Mol. Cell. Biol. Lipids 2007, 1771, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boanini, E.; Torricelli, P.; Boga, C.; Micheletti, G.; Cassani, M.C.; Fini, M.; Bigi, A. (9R)-9-Hydroxystearate-Functionalized Hydroxyapatite as Anti-Proliferative and Cytotoxic Agent towards Osteosarcoma Cells. Langmuir 2016, 32, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calonghi, N.; Cappadone, C.; Pagnotta, E.; Boga, C.; Bertucci, C.; Fiori, J.; Tasco, G.; Casadio, R.; Masotti, L. Histone deacetylase 1: A target of 9-hydroxystearic acid in the inhibition of cell growth in human colon cancer. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 1596–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calonghi, N.; Pagnotta, E.; Parolin, C.; Tognoli, C.; Boga, C.; Masotti, L. 9-Hydroxystearic acid interferes with EGF signalling in a human colon adenocarcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 342, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.C.; Johnstone, R.W. New and emerging HDAC inhibitors for cancer treatment. J. Clin. Invest. 2014, 124, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Earle, F.R.; Mikolajczak, K.L.; Wolff, I.A.; Barclay, A.S. Search for new industrial oils. X. Seed oils of the calenduleae. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1964, 41, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolin, C.; Calonghi, N.; Presta, E.; Boga, C.; Caruana, P.; Naldi, M.; Andrisano, V.; Masotti, L.; Sartor, G. Mechanism and stereoselectivity of HDAC I inhibition by (R)-9-hydroxystearic acid in colon cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 1334–1340. [Google Scholar]
- Ebert, C.; Felluga, F.; Forzato, C.; Foscato, M.; Gardossi, L.; Nitti, P.; Pitacco, G.; Boga, C.; Caruana, P.; Micheletti, G. Enzymatic kinetic resolution of hydroxystearic acids: A combined experimental and molecular modelling investigation. J. Molec. Catal. B: Enzymatic 2012, 83, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayley, H.; Standring, D.N.; Knowles, J.R. Propane-1,3-di-thiol: A selective reagent for the efficient reduction of alkyl and aryl azides to amines. Tetrahedron Lett. 1978, 39, 3633–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boga, C.; Drioli, S.; Forzato, C.; Micheletti, G.; Nitti, P.; Prati, F. Easy route to enantiomerically enriched 7- and 8-hydroxy-stearic acids by olefin-metathesis-based approach. Synlett 2016, 27, 1354–1358. [Google Scholar]
- Richon, V.M.; Sandhoff, T.W.; Rifkind, R.A.; Marks, P.A. Histone deacetylase inhibitor selectively induces p21WAF1 expression and gene-associated histone acetylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10014–10019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, K.; Mizuno, T.; Sowa, Y.; Orita, T.; Yoshino, T.; Okuyama, Y.; Fujita, T.; Ohtani-Fujita, N.; Matsukawa, Y.; Tokino, T.; et al. Butyrate activates the WAF1/Cip1 gene promoter through Sp1 sites in a p53-negative human colon cancer cell line. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 22199–22206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Sowa, Y.; Sakai, T.; Pardee, A.B. Activation of the p21WAF1/CIP1 promoter independent of p53 by the histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) through the Sp1 sites. Oncogene 2000, 19, 5712–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dang, C.V. MYC, metabolism, cell growth, and tumorigenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a014217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, E.R.; Soucek, L.; Brown-Swigart, L.; Shchors, K.; Bialucha, C.U.; Evan, G.I. Reversible kinetic analysis of Myc targets in vivo provides novel insights into Myc-mediated tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 4591–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodir, N.M.; Swigart, L.B.; Karnezis, A.N.; Hanahan, D.; Evan, G.I.; Soucek, L. Endogenous Myc maintains the tumor microenvironment. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolfer, A.; Wittner, B.S.; Irimia, D.; Flavin, R.J.; Lupien, M.; Gunawardane, R.N.; Meyer, C.A.; Lightcap, E.S.; Tamayo, P.; Mesirov, J.P.; et al. MYC regulation of a “poor-prognosis” metastatic cancer cell state. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3698–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochrane, C.; Harwood, H.J. Phase properties of mixtures of 9- and 10-oxo-octadecanoic acids and of 9- and 10-hydroxyoctadecanoic acids. J. Org. Chem. 1961, 26, 1278–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busi, A.; Aluigi, A.; Guerrini, A.; Boga, C.; Sartor, G.; Calonghi, N.; Sotgiu, G.; Posati, T.; Corticelli, F.; Fiori, J.; et al. Unprecedented behavior of (9R)-9-hydroxystearic acid loaded keratin nanoparticles on cancer cell cycle. Mol. Pharmaceutics 2019, 16, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amellem, O.; Stokke, T.; Sandvik, J.A.; Pettersen, E.O. The retinoblastoma gene product is reversibly dephosphorylated and bound in the nucleus in S and G2 phases during hypoxic stress. Exp. Cell Res. 1996, 227, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |











© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calonghi, N.; Boga, C.; Telese, D.; Bordoni, S.; Sartor, G.; Torsello, C.; Micheletti, G. Synthesis of 9-Hydroxystearic Acid Derivatives and Their Antiproliferative Activity on HT 29 Cancer Cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 3714. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203714
Calonghi N, Boga C, Telese D, Bordoni S, Sartor G, Torsello C, Micheletti G. Synthesis of 9-Hydroxystearic Acid Derivatives and Their Antiproliferative Activity on HT 29 Cancer Cells. Molecules. 2019; 24(20):3714. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203714
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalonghi, Natalia, Carla Boga, Dario Telese, Silvia Bordoni, Giorgio Sartor, Chiara Torsello, and Gabriele Micheletti. 2019. "Synthesis of 9-Hydroxystearic Acid Derivatives and Their Antiproliferative Activity on HT 29 Cancer Cells" Molecules 24, no. 20: 3714. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203714
APA StyleCalonghi, N., Boga, C., Telese, D., Bordoni, S., Sartor, G., Torsello, C., & Micheletti, G. (2019). Synthesis of 9-Hydroxystearic Acid Derivatives and Their Antiproliferative Activity on HT 29 Cancer Cells. Molecules, 24(20), 3714. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203714