A Review on the Effect of High Pressure Processing (HPP) on Gelatinization and Infusion of Nutrients
Abstract
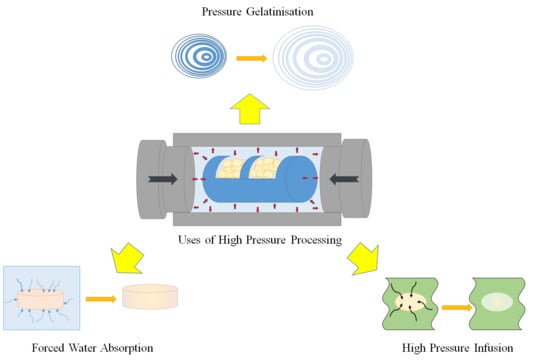
:1. Introduction
2. High Pressure Gelatinization
2.1. Starch Gelatinization
2.1.1. Gelatinization Mechanism
2.1.2. Properties of Pressure Gelatinized Starch
2.1.3. Influence of Additives on Gelatinization
2.1.4. Digestibility
2.1.5. Applications
2.2. Gelatinization of Collagen
3. Forced Water Absorption in Foods Using HPP
4. Pressure Assisted Infusion in Foods
4.1. Aroma Infusion
4.2. High Pressure Impregnation (HPI)
4.3. Flavour Infusion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martínez-Monteagudo, S.I.; Balasubramaniam, V.M. Fundamentals and applications of high-pressure processing technology. In High Pressure Processing of Food: Principles, Technology and Applications; Balasubramaniam, V.M., Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V., Lelieveld, H.L.M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzi, N.A.; Farid, M.M. High-pressure processing of Manuka honey: Brown pigment formation, improvement of antibacterial activity and hydroxymethylfurfural content. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, F.V.M.; Tan, E.K.; Farid, M. Bacterial spore inactivation at 45–65 °C using high pressure processing: Study of Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris in orange juice. Food Microbiol. 2012, 32, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaiman, A.; Farid, M.; Silva, F.V. Strawberry puree processed by thermal, high pressure, or power ultrasound: Process energy requirements and quality modeling during storage. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2017, 23, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghani, A.A.G.; Farid, M.M. Computational fluid dynamics analysis of high pressure processing of food. In Mathematical Modeling of Food Processing; Farid, M.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 537–557. [Google Scholar]
- Wazed, M.A.; Farid, M. Hypoallergenic and Low-Protein Ready-to-Feed (RTF) Infant Formula by High Pressure Pasteurization: A Novel Product. Foods 2019, 8, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.L.; Hu, X.S.; Shen, Q. Effect of high hydrostatic pressure on starches: A review. Starke 2010, 62, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallons, K.J.R.; Ryan, L.A.M.; Arendt, E.K. Pressure-Induced Gelatinization of Starch in Excess Water. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karwe, M.V.; Salvi, D.; Gosavi, N.S. High Pressure-Assisted Infusion in Foods. Ref. Modul. Food Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, T.S.; de Jesus, A.L.T.; Schmiele, M.; Tribst, A.A.L.; Cristianini, M. High pressure processing (HPP) of pea starch: Effect on the gelatinization properties. LWT 2017, 76, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, E.C.; Field, R.A. Underpinning Starch Biology with in vitro Studies on Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes and Biosynthetic Glycomaterials. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raguin, A.; Ebenhöh, O. Design starch: Stochastic modeling of starch granule biogenesis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2017, 45, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muhr, A.H.; Blanshard, J.M.V. Effect of hydrostatic pressure on starch gelatinisation. Carbohydr. Polym. 1982, 2, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevelein, J.M.; Van Assche, J.A.; Heremans, K.; Gerlsma, S.Y. Gelatinisation temperature of starch, as influenced by high pressure. Carbohydr. Res. 1981, 93, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Kawai, K.; Fukami, K.; Koseki, S. Pressure Gelatinization of Potato Starch. Food 2009, 3, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Chao, C.; Yu, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Copeland, L. New insights into starch gelatinization by high pressure: Comparison with heat-gelatinization. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, B.A.; Knorr, D. The impact of pressure, temperature and treatment time on starches: Pressure-induced starch gelatinisation as pressure time temperature indicator for high hydrostatic pressure processing. J. Food Eng. 2005, 68, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittadini, E.; Carini, E.; Chiavaro, E.; Rovere, P.; Barbanti, D. High pressure-induced tapioca starch gels: Physico-chemical characterization and stability. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 226, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douzals, J.P.; Perrier Cornet, J.M.; Gervais, P.; Coquille, J.C. High-Pressure Gelatinization of Wheat Starch and Properties of Pressure-Induced Gels. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 4824–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colussi, R.; Kaur, L.; Zavareze, E.R.; Dias, A.R.G.; Stewart, R.B.; Singh, J. High pressure processing and retrogradation of potato starch: Influence on functional properties and gastro-small intestinal digestion in vitro. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 75, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.D.; Ferreira, J.; Fidalgo, L.G.; Queirós, R.P.; Delgadillo, I.; Saraiva, J.A. Changes in maize starch water sorption isotherms caused by high pressure. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Li, T.; Gao, Q.; Liu, B.; Yu, S. Physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of high hydrostatic pressure treated waxy rice starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Al-Attar, H. Structural properties of high-pressure-treated chestnut flour dispersions. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buléon, A.; Colonna, P.; Planchot, V.; Ball, S. Starch granules: Structure and biosynthesis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1998, 23, 85–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Fan, H.; Cao, R.; Blanchard, C.; Wang, M. Physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of sorghum starch altered by high hydrostatic pressure. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, M.; Punia, S.; Sandhu, K.S.; Ahmed, J. Impact of high pressure processing on the rheological, thermal and morphological characteristics of mango kernel starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Bai, Y.; Mousaa, S.A.S.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, Q. Effect of High Hydrostatic Pressure on Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Rice Starch. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2012, 5, 2233–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider Teixeira, A.; Deladino, L.; García, M.A.; Zaritzky, N.E.; Sanz, P.D.; Molina-García, A.D. Microstructure analysis of high pressure induced gelatinization of maize starch in the presence of hydrocolloids. Food Bioprod. Process. 2018, 112, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamonte, G.; Jury, V.; de Lamballerie, M. Stabilizing emulsions using high-pressure-treated corn starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonin, H.; Guyon, C.; Orlowska, M.; de Lamballerie, M.; Le-Bail, A. Gelatinization of waxy starches under high pressure as influenced by pH and osmolarity: Gelatinization kinetics, final structure and pasting properties. LWT 2011, 44, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Banerji, A.; Lele, S.S.; Ananthanarayan, L. Starch digestibility and glycaemic index of selected Indian traditional foods: Effects of added ingredients. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 290–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, R.; Hayashida, A. Increased Amylase Digestibility of Pressure-treated Starch. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1989, 53, 2543–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colussi, R.; Kringel, D.; Kaur, L.; da Rosa Zavareze, E.; Dias, A.R.G.; Singh, J. Dual modification of potato starch: Effects of heat-moisture and high pressure treatments on starch structure and functionalities. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, M.; Jiang, B.; Cui, S.W.; Zhang, T.; Jin, Z. Slowly Digestible Starch—A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 1642–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorndech, W.; Tongta, S.; Blennow, A. Slowly Digestible- and Non-Digestible α-Glucans: An Enzymatic Approach to Starch Modification and Nutritional Effects. Starke 2018, 70, 1700145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deladino, L.; Schneider Teixeira, A.; Plou, F.J.; Navarro, A.S.; Molina-García, A.D. Effect of High Hydrostatic Pressure, alkaline and combined treatments on corn starch granules metal binding: Structure, swelling behavior and thermal properties assessment. Food Bioprod. Process. 2017, 102, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deladino, L.; Teixeira, A.S.; García, A.D.M.; Navarro, A.S. High-pressure-treated corn starch as an alternative carrier of molecules of nutritional interest for food systems. In New Polymers for Encapsulation of Nutraceutical Compounds; Ruiz, J.C.R., Campos, M.R.S., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2016; pp. 35–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcenilla, B.; Román, L.; Martínez, C.; Martínez, M.M.; Gómez, M. Effect of high pressure processing on batters and cakes properties. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 33, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, L.; Bao, Y.; Ren, R. Method for Preparing Resistant Starch by Treating B-Type Starch by Using High Static Pressure. CN Patent 1,056,938,70A, 22 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Stute, R. High-Pressure-Treated Starch. U.S. Patent 5,900,066A, 4 May 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kawai, K.; Fukami, K.; Yamamoto, K. State diagram of potato starch-water mixtures treated with high hydrostatic pressure. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 67, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ma, L.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Effects of pressure on gelatinization of collagen and properties of extracted gelatins. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 36, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, N.; Jaswir, I.; Jamal, P.; Jami, M.S. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA) of the jelly dessert prepared from halal gelatin extracted using High Pressure Processing (HPP). Malays. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 2019, 15, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, L.; Cai, L.; Zhou, M.; Li, J. Effects of acid concentration and the UHP pretreatment on the gelatinisation of collagen and the properties of extracted gelatins. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Endt, D.W.; Baker, M.T. The Chemistry of Filled Animal Glue Systems. Available online: https://cool.culturalheritage.org/albumen/library/c20/vonendt1991.html (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Ahromrit, A.; Ledward, D.A.; Niranjan, K. High pressure induced water uptake characteristics of Thai glutinous rice. J. Food Eng. 2006, 72, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakura, M.; Haraguchi, K.; Okadome, H.; Suzuki, K.; Tran, U.T.; Horigane, A.K.; Yoshida, M.; Homma, S.; Sasagawa, A.; Yamazaki, A.; et al. Effects of Soaking and High-Pressure Treatment on the Qualities of Cooked Rice. J. Appl. Glycosci. 2005, 52, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, S.M.; Hu, F.F.; Ramaswamy, H.S.; Yu, Y.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Q.T. Effect of High Pressure Treatment and Degree of Milling on Gelatinization and Structural Properties of Brown Rice. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2016, 9, 1844–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Goyal, S.K.; Alam, T.; Fatma, S.; Chaoruangrit, A.; Niranjan, K. Effect of high pressure soaking on water absorption, gelatinization, and biochemical properties of germinated and non-germinated foxtail millet grains. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 83, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, C.; Purohit, S.R.; Rao, P.S. High pressure induced water absorption and gelatinization kinetics of paddy. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 47, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallares, A.; Rousseau, S.; Chigwedere, C.M.; Kyomugasho, C.; Hendrickx, M.; Grauwet, T. Temperature-pressure-time combinations for the generation of common bean microstructures with different starch susceptibilities to hydrolysis. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Igura, N.; Shimoda, M.; Hayakawa, I. The synergistic effect of moderate heat and pressure on the physical properties and pectic substances of potato tissue. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigematsu, T.; Furukawa, N.; Takaoka, R.; Hayashi, M.; Sasao, S.; Ueno, S.; Nakajima, K.; Kido, M.; Nomura, K.; Iguchi, A. Effect of high pressure on the saccharification of starch in the tuberous root of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas). Biophys. Chem. 2017, 231, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ge, L.; Zhu, S.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, Q. Effect of presoaking high hydrostatic pressure on the cooking properties of brown rice. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 7904–7913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- George, J.M.; Senthamizh Selvan, T.; Rastogi, N.K. High-pressure-assisted infusion of bioactive compounds in apple slices. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 33, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Préstamo, G.; Arroyo, G. High Hydrostatic Pressure Effects on Vegetable Structure. J. Food Sci. 1998, 63, 878–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, S.; Nitin, N.; Salvi, D.; Karwe, M.V. High-Pressure Enhanced Infusion: Influence of Process Parameters. J. Food Process. Eng. 2015, 38, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błaszczak, W.; Misharina, T.A.; Yuryev, V.P.; Fornal, J. Effect of high pressure on binding aroma compounds by maize starches with different amylose content. LWT 2007, 40, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatankhah, H.; Ramaswamy, H.S. High pressure impregnation (HPI) of apple cubes: Effect of pressure variables and carrier medium. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulistyawati, I.; Dekker, M.; Fogliano, V.; Verkerk, R. Osmotic dehydration of mango: Effect of vacuum impregnation, high pressure, pectin methylesterase and ripeness on quality. LWT 2018, 98, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosavi, N.S.; Salvi, D.; Karwe, M.V. High Pressure-Assisted Infusion of Calcium into Baby Carrots Part I: Influence of Process Variables on Calcium Infusion and Hardness of the Baby Carrots. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2019, 12, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosavi, N.S.; Salvi, D.; Karwe, M.V. High Pressure-Assisted Infusion of Calcium into Baby Carrots Part II: Influence of Process Variables on β-carotene Extraction and Color of the Baby Carrots. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2019, 12, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatankhah, H.; Ramaswamy, H.S. High pressure impregnation of oil in water emulsions into selected fruits: A novel approach to fortify plant-based biomaterials by lipophilic compounds. LWT 2019, 101, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishna, A.K.; Farid, M. Enrichment of rice with natural thiamine using high-pressure processing (HPP). J. Food Eng. 2020, 110040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villacís, M.F.; Rastogi, N.K.; Balasubramaniam, V.M. Effect of high pressure on moisture and NaCl diffusion into turkey breast. LWT 2008, 41, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemus-Mondaca, R.; Zambra, C.; Marín, F.; Pérez-Won, M.; Tabilo-Munizaga, G. Mass Transfer Kinetic and Quality Changes During High-Pressure Impregnation (HPI) of Jumbo Squid (Dosidicus gigas) Slices. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2018, 11, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch, G.; Maglio, S.J. High Pressure Processing (HPP) for Infusing Flavor into Liquids Containing Alcohol. U.S. Patent 2,018,037,138,6A1, 27 December 2018. [Google Scholar]











| Type of Starch | Pressure | Temperature | Time | Property Assessed | Outcome | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tapioca | 600 MPa | 30–80 °C | 10–30 min |
|
| Vittadini et al. [18] |
| Wheat | 600 MPa | 25 °C | 15 min |
|
| Douzals et al. [19] |
| Wheat | 300–600 MPa | 25 °C | 10 min |
|
| Liu et al. [16] |
| Potato | 400 MPa (3 cycles) followed by 600 MPa (6 cycles) | 21 °C | Each cycle 10 min |
|
| Colussi et al. [20] |
| Maize | 300 MPa | 20 °C | 5–60 min | Moisture adsorption-desorption analysis |
| Santos et al. [21] |
| Waxy rice | 100–600 MPa | 25 °C | 20 min |
| With increase in pressure
| Li et al. [27] |
| Chestnut | 400–600 MPa | 35–38 °C | 10 min |
|
| Ahmed et al. [23] |
| Sorghum | 120–600 MPa | Room temperature | 20 min |
|
| Liu et al. [25] |
| Mango kernel | 300–600 MPa | 38 °C | 10 min |
|
| Kaur et al. [26] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balakrishna, A.K.; Wazed, M.A.; Farid, M. A Review on the Effect of High Pressure Processing (HPP) on Gelatinization and Infusion of Nutrients. Molecules 2020, 25, 2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102369
Balakrishna AK, Wazed MA, Farid M. A Review on the Effect of High Pressure Processing (HPP) on Gelatinization and Infusion of Nutrients. Molecules. 2020; 25(10):2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102369
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalakrishna, Akash Kaushal, Md Abdul Wazed, and Mohammed Farid. 2020. "A Review on the Effect of High Pressure Processing (HPP) on Gelatinization and Infusion of Nutrients" Molecules 25, no. 10: 2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102369
APA StyleBalakrishna, A. K., Wazed, M. A., & Farid, M. (2020). A Review on the Effect of High Pressure Processing (HPP) on Gelatinization and Infusion of Nutrients. Molecules, 25(10), 2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102369