Beneficial Effects of Naringenin in Cigarette Smoke-Induced Damage to the Lung Based on Bioinformatic Prediction and In Vitro Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
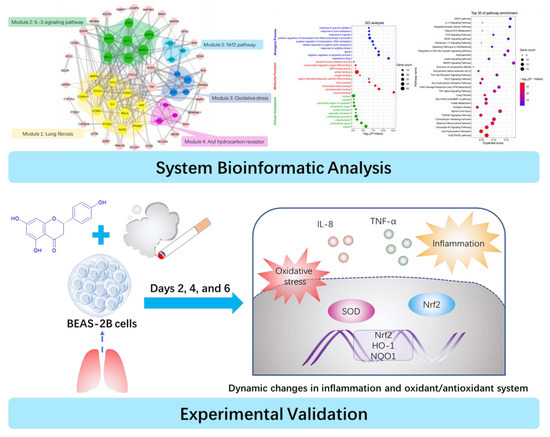
2.1. PPI Network and Function Module Analysis
2.2. GO and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
2.3. Effects of CSE and Naringenin on Cell Viability
2.4. Effect of Naringenin on CSE-Induced IL-8 and TNF-α Levels
2.5. Effect of Naringenin on CSE-Induced Nrf2 mRNA and Protein Expression
2.6. Effects of Naringenin on CSE-Induced mRNA Expression of HO-1 and NQO1
2.7. Effect of Naringenin on CSE-Induced SOD Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Sources and Search Strategy
4.2. Network Construction and Analysis
4.3. Gene Ontologies and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
4.4. Reagents
4.5. Cigarette Smoke Extract Preparation
4.6. Cell Viability Assay
4.7. Cell Treatment
4.8. Measurement of IL-8, TNF-α, and SOD Levels
4.9. RT-qPCR
4.10. Western Blotting Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bousquet, J.; Dahl, R.; Khaltaev, N. Global alliance against chronic respiratory diseases. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 29, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferkol, T.; Schraufnagel, D. The global burden of respiratory disease. Ann. Am. Thorac Soc. 2014, 11, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamdar, A.C.; Inamdar, A.A. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in lung disorders: Pathogenesis of lung diseases and mechanism of action of mesenchymal stem cell. Exp. Lung Res. 2013, 39, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schluger, N.W.; Koppaka, R. Lung disease in a global context. A call for public health action. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2014, 11, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantin, A.M.; Richter, M.V. Cigarette Smoke-induced proteostasis imbalance in obstructive lung diseases. Curr. Mol. Med. 2012, 12, 836–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelak, A.; Ratajczak, A.; Adamiec, A.; Feleszko, W. Tobacco smoke induces and alters immune responses in the lung triggering inflammation, allergy, asthma and other lung diseases: A mechanistic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Campos, J.L.; Tan, W.; Soriano, J.B. Global burden of COPD. Respirology 2016, 21, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattab, Y.; Alhassan, S.; Balaan, M.; Lega, M.; Singh, A.C. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Crit. Care Nurs. Q. 2016, 39, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzikhan, N.; Verhamme, K.M.; Hofman, A.; Stricker, B.H.; Brusselle, G.G.; Lahousse, L. Prevalence and incidence of COPD in smokers and non-smokers: The Rotterdam Study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 31, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hecht, S.S. Lung carcinogenesis by tobacco smoke. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 2724–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.M.; Chen, H.; Chan, Y.L.; Wang, G.; Oliver, B.G. Why Do Intrauterine exposure to air pollution and cigarette smoke increase the risk of asthma? Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnes, P.J. New anti-inflammatory targets for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.Y.; Stone, K.; Pryor, W.A. Detection of free radicals in aqueous extracts of cigarette tar by electron spin resonance. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1995, 19, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.; Kulkarni, Y.A.; Wairkar, S. Pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and formulations aspects of naringenin: An update. Life Sci. 2018, 215, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podder, B.; Song, H.-Y.; Kim, Y.-S. Naringenin exerts cytoprotective effect against paraquat-induced toxicity in human bronchial epithelial BEAS-2B cells through NRF2 activation. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, R.; Pan, T.; Zhu, A.L.; Zhang, M.H. Anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic properties of naringenin via attenupation of NF-kappaB and activation of the heme oxygenase HO-1/related factor 2 pathway. Pharm. Rep. 2017, 69, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, L.H.; Hon, C.M.; Chellappan, D.K.; Chellian, J.; Madheswaran, T.; Zeeshan, F.; Awasthi, R.; Aljabali, A.A.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Dureja, H.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of action of naringenin in chronic airway diseases. Eur. J. Pharm. 2020, 879, 173139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yao, J.; Zhang, J. Naringenin attenuates inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in cigarette smoke induced mouse model and involves suppression of NF-kappaB. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nymark, P.; Rieswijk, L.; Ehrhart, F.; Jeliazkova, N.; Tsiliki, G.; Sarimveis, H.; Evelo, C.T.; Hongisto, V.; Kohonen, P.; Willighagen, E.; et al. A Data Fusion Pipeline for Generating and Enriching Adverse Outcome Pathway Descriptions. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 162, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottin, V.; Wollin, L.; Fischer, A.; Quaresma, M.; Stowasser, S.; Harari, S. Fibrosing interstitial lung diseases: Knowns and unknowns. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2019, 28, 180100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Inflammatory mechanisms in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kandasamy, K.; Mohan, S.S.; Raju, R.; Keerthikumar, S.; Kumar, G.S.; Venugopal, A.K.; Telikicherla, D.; Navarro, J.D.; Mathivanan, S.; Pecquet, C.; et al. NetPath: A public resource of curated signal transduction pathways. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janssen, W.J.; Yunt, Z.X.; Muldrow, A.; Kearns, M.T.; Kloepfer, A.; Barthel, L.; Bratton, D.L.; Bowler, R.P.; Henson, P.M. Circulating hematopoietic progenitor cells are decreased in COPD. COPD 2014, 11, 277–289. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.S.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, Y.C. Impact of oxidative stress on lung diseases. Respirology 2009, 14, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of asthma and COPD. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 1541–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, K.W.; Kim, Y.O.; Andrade, J.E.; Burgess, J.R.; Kim, Y.C. Dietary naringenin increases hepatic peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor alpha protein expression and decreases plasma triglyceride and adiposity in rats. Eur. J. Nutr. 2011, 50, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, T.; Uchi, H.; Yasukawa, F.; Furue, M. Role of the arylhydrocarbon receptor in lung disease. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 155, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamer, C.A.; Shepherd, D.M. Role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in lung inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2013, 35, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borger, P.; Oliver, B.; Heijink, I.; Hardavella, G. Beyond the Immune System: The Role of Resident Cells in Asthma and COPD. J Allergy 2012, 2012, 968039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiba, T.; Chihara, J.; Furue, M. Role of the Arylhydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) in the Pathology of Asthma and COPD. J. Allergy 2012, 2012, 372384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.K.; Yeh, C.H.; Iwamoto, T.; Satsu, H.; Shimizu, M.; Totsuka, M. Dietary flavonoid naringenin induces regulatory T cells via an aryl hydrocarbon receptor mediated pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2171–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutten, A.; Goven, D.; Artaud-Macari, E.; Boczkowski, J.; Bonay, M. NRF2 targeting: A promising therapeutic strategy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Cha, Y.N.; Surh, Y.J. A protective role of nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2 (Nrf2) in inflammatory disorders. Mutat. Res. 2010, 690, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumura, K.; Maruoka, S.; Shimizu, T.; Gon, Y. Role of Nrf2 in the pathogenesis of respiratory diseases. Respir. Investig. 2020, 58, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korytina, G.F.; Akhmadishina, L.Z.; Aznabaeva, Y.G.; Kochetova, O.V.; Zagidullin, N.S.; Kzhyshkowska, J.G.; Zagidullin, S.Z.; Viktorova, T.V. Associations of the NRF2/KEAP1 pathway and antioxidant defense gene polymorphisms with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Gene 2019, 692, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goven, D.; Boutten, A.; Lecon-Malas, V.; Marchal-Somme, J.; Amara, N.; Crestani, B.; Fournier, M.; Leseche, G.; Soler, P.; Boczkowski, J.; et al. Altered Nrf2/Keap1-Bach1 equilibrium in pulmonary emphysema. Thorax 2008, 63, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malhotra, D.; Thimmulappa, R.; Navas-Acien, A.; Sandford, A.; Elliott, M.; Singh, A.; Chen, L.; Zhuang, X.; Hogg, J.; Pare, P. Decline in NRF2-regulated antioxidants in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease lungs due to loss of its positive regulator, DJ-1. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 592–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Rangasamy, T.; Thimmulappa, R.K.; Lee, H.; Osburn, W.O.; Brigelius-Flohé, R.; Kensler, T.W.; Yamamoto, M.; Biswal, S. Glutathione peroxidase 2, the major cigarette smoke–inducible isoform of GPX in lungs, is regulated by Nrf2. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 35, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Betsuyaku, T.; Ito, Y.; Nagai, K.; Nasuhara, Y.; Kaga, K.; Kondo, S.; Nishimura, M. Down-regulated NF-E2-related factor 2 in pulmonary macrophages of aged smokers and patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 39, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasini, A.M.F.; Ferrari, M.; Stranieri, C.; Vallerio, P.; Mozzini, C.; Garbin, U.; Zambon, G.; Cominacini, L. Nrf2 expression is increased in peripheral blood mononuclear cells derived from mild-moderate ex-smoker COPD patients with persistent oxidative stress. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2016, 11, 1733–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasini, A.M.F.; Stranieri, C.; Ferrari, M.; Garbin, U.; Cazzoletti, L.; Mozzini, C.; Spelta, F.; Peserico, D.; Cominacini, L. Oxidative stress and Nrf2 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells derived from COPD patients: An observational longitudinal study. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eapen, M.S.; Myers, S.; Walters, E.H.; Sohal, S.S. Airway inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): A true paradox. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2017, 11, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Khor, T.O.; Cheung, K.L.; Li, W.; Wu, T.Y.; Huang, Y.; Foster, B.A.; Kan, Y.W.; Kong, A.N. Nrf2 expression is regulated by epigenetic mechanisms in prostate cancer of TRAMP mice. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Davies, K.J.A.; Forman, H.J. Oxidative stress response and Nrf2 signaling in aging. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 314–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebrahimi, K.B.; Cano, M.; Rhee, J.; Datta, S.; Wang, L.; Handa, J.T. Oxidative stress induces an interactive decline in wnt and Nrf2 signaling in degenerating retinal pigment epithelium. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 29, 389–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhang, C.; Kong, A.N. Epigenetic regulation of Keap1-Nrf2 signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q. Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharm. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, D.; Liu, X.S.B.J.; Zhang, G.X.; Ming, Z.H.; Wang, T.J. Isoliquiritigenin Inhibits Cigarette Smoke-Induced COPD by Attenuating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress via the Regulation of the Nrf2 and NF-kappa B Signaling Pathways. Front. Pharm. 2018, 9, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gu, X.; Yu, M.; Zi, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Xiang, L. Effects of ginsenoside Rb1 on oxidative stress injury in rat spinal cords by regulating the eNOS/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Exp. Med. 2018, 16, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zoja, C.; Benigni, A.; Remuzzi, G. The Nrf2 pathway in the progression of renal disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, i19–i24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goncalves, P.B.; Romeiro, N.C. Multi-target natural products as alternatives against oxidative stress in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 163, 911–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despotovic, M.; Stoimenov, T.J.; Stankovic, I.; Pavlovic, D.; Sokolovic, D.; Cvetkovic, T.; Kocic, G.; Basic, J.; Veljkovic, A.; Djordjevic, B. Gene polymorphisms of tumor necrosis factor alpha and antioxidant enzymes in bronchial asthma. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 24, 251–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.W.; Kim, S.K.; Han, Y.R.; Hong, D.; Chon, J.; Chung, J.H.; Hong, S.J.; Park, M.S.; Ban, J.Y. Promoter polymorphism (-308G/A) of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) gene and asthma risk: An updated meta-analysis. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2019, 23, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.X.; Lu, L.W.; Liu, W.J.; Huang, M. Plasma inflammatory cytokine IL-4, IL-8, IL-10, and TNF-alpha levels correlate with pulmonary function in patients with asthma-chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) overlap syndrome. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 2800–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawayama, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Matsunaga, K.; Kobayashi, A.; Hayamizu, T.; Johnson, M.; Hoshino, T. Responsiveness of blood and sputum inflammatory cells in Japanese COPD patients, non-COPD smoking controls, and non-COPD nonsmoking controls. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2016, 11, 295–303. [Google Scholar]
- Dall’Asta, M.; Derlindati, E.; Curella, V.; Mena, P.; Calani, L.; Ray, S.; Zavaroni, I.; Brighenti, F.; Del Rio, D. Effects of naringenin and its phase II metabolites on in vitro human macrophage gene expression. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 64, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Grondin, C.J.; Johnson, R.J.; Sciaky, D.; King, B.L.; McMorran, R.; Wiegers, J.; Wiegers, T.C.; Mattingly, C.J. The Comparative Toxicogenomics Database: Update 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D972–D978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Morris, J.H.; Cook, H.; Kuhn, M.; Wyder, S.; Simonovic, M.; Santos, A.; Doncheva, N.T.; Roth, A.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2017: Quality-controlled protein-protein association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D362–D368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruskovska, T.; Massaro, M.; Carluccio, M.A.; Arola-Arnal, A.; Muguerza, B.; Vanden Berghe, W.; Declerck, K.; Bravo, F.I.; Calabriso, N.; Combet, E.; et al. Systematic bioinformatic analysis of nutrigenomic data of flavanols in cell models of cardiometabolic disease. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 5040–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Chen, P.; Chen, Y.; He, S.; Ye, J.; Zhang, H.; Cao, J. Comparison between cigarette smoke-induced emphysema and cigarette smoke extract-induced emphysema. Tob. Induc. Dis. 2015, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, P.; Zhai, X.; Tian, F.; Li, W.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, W. Nano-carrier for gene delivery and bioimaging based on carbon dots with PEI-passivation enhanced fluorescence. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3604–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Su, W.W.; Zhu, Z.T.; Guan, M.Y.; Cheng, K.L.; Fan, W.Y.; Wei, G.Y.; Li, P.B.; Yang, Z.Y.; Yao, H.L. Regulation effects of naringin on diesel particulate matter-induced abnormal airway surface liquid secretion. Phytomedicine 2019, 63, 153004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, H.; Yao, J.; Chen, R.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, K.; Xie, Y.; Wan, T.; Ding, H. Apigenin exhibits protective effects in a mouse model of d-galactose-induced aging via activating the Nrf2 pathway. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 2331–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |









| Gene | Direction | Primer Sequences |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | Forward | CCTGTACGCCAACACAGTGC |
| Reverse | ATACTCCTGCTTGCTGATCC | |
| Nrf2 | Forward | CAGCCACTTTTATTCTTCCCC |
| Reverse | CAGCCACTTTTATTCTTCCCC | |
| HO-1 | Forward | CTGCAGGAACTGAGGATGCTG |
| Reverse | CCAGCAACAAAGTGCAAGATTC | |
| NQO1 | Forward | CGTTTCTTCCATCCTTCCAGG |
| Reverse | CGCAGACCTTGTGATATTCCAG |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, P.; Xiao, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Fan, W.; Su, W.; Li, P. Beneficial Effects of Naringenin in Cigarette Smoke-Induced Damage to the Lung Based on Bioinformatic Prediction and In Vitro Analysis. Molecules 2020, 25, 4704. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204704
Chen P, Xiao Z, Wu H, Wang Y, Fan W, Su W, Li P. Beneficial Effects of Naringenin in Cigarette Smoke-Induced Damage to the Lung Based on Bioinformatic Prediction and In Vitro Analysis. Molecules. 2020; 25(20):4704. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204704
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Pan, Ziting Xiao, Hao Wu, Yonggang Wang, Weiyang Fan, Weiwei Su, and Peibo Li. 2020. "Beneficial Effects of Naringenin in Cigarette Smoke-Induced Damage to the Lung Based on Bioinformatic Prediction and In Vitro Analysis" Molecules 25, no. 20: 4704. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204704
APA StyleChen, P., Xiao, Z., Wu, H., Wang, Y., Fan, W., Su, W., & Li, P. (2020). Beneficial Effects of Naringenin in Cigarette Smoke-Induced Damage to the Lung Based on Bioinformatic Prediction and In Vitro Analysis. Molecules, 25(20), 4704. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204704