Role of Bcl-2 Family Proteins in Photodynamic Therapy Mediated Cell Survival and Regulation
Abstract
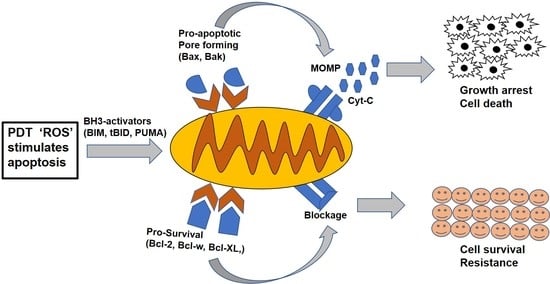
:1. Introduction
2. The Bcl-2 Family Proteins
3. Functions and Regulation of Bcl-2 Family Protein
4. Death and Survival Functions of Pro-Apoptotic Bcl-2 Proteins
5. Intramitochondrial Functions of Bcl-2 Family Proteins
6. Photodynamic Therapy and Drug Resistance
7. Challenges of Drug Resistance and Photosensitizer Uptake
8. Expression of Bcl-2 Family Proteins after PDT Treatment
9. Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis
10. Death-Receptor-Mediated Apoptosis
11. Bcl-2 Family Proteins in Autophagic Response to Photodynamic Therapy
12. Conclusions
13. Future Perspectives
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antonsson, B.; Conti, F.; Ciavatta, A.; Montessuit, S.; Lewis, S.; Martinou, I.; Bernasconi, L.; Bernard, A.; Mermod, J.-J.; Mazzei, G. Inhibition of Bax channel-forming activity by Bcl-2. Science 1997, 277, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yuan, J. Caspases in apoptosis and beyond. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6194–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinou, J.-C.; Youle, R.J. Mitochondria in apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Venosa, G.; Perotti, C.; Batlle, A.; Casas, A. The role of cytoskeleton and adhesion proteins in the resistance to photodynamic therapy. Possible therapeutic interventions. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2015, 14, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etminan, N.; Peters, C.; Ficnar, J.; Anlasik, S.; Bünemann, E.; Slotty, P.J.; Hänggi, D.; Steiger, H.-J.; Sorg, R.V.; Stummer, W. Modulation of migratory activity and invasiveness of human glioma spheroids following 5-aminolevulinic acid–based photodynamic treatment. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 115, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, A.; Di Venosa, G.; Vanzulli, S.; Perotti, C.; Mamome, L.; Rodriguez, L.; Simian, M.; Juarranz, A.; Pontiggia, O.; Hasan, T. Decreased metastatic phenotype in cells resistant to aminolevulinic acid-photodynamic therapy. Cancer Lett. 2008, 271, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vaux, D.L.; Cory, S.; Adams, J.M. Bcl-2 gene promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to immortalize pre-B cells. Nature 1988, 335, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.M.; Cory, S. The Bcl-2 protein family: Arbiters of cell survival. Science 1998, 281, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oltval, Z.N.; Milliman, C.L.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programed cell death. Cell 1993, 74, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, Y. Role of Bcl-2 family proteins in apoptosis: Apoptosomes or mitochondria? Genes Cells 1998, 3, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.; Zha, J.; Jockel, J.; Boise, L.H.; Thompson, C.B.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Bad, a heterodimeric partner for Bcl-XL and Bcl-2, displaces Bax and promotes cell death. Cell 1995, 80, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sattler, M.; Liang, H.; Nettesheim, D.; Meadows, R.P.; Harlan, J.E.; Eberstadt, M.; Yoon, H.S.; Shuker, S.B.; Chang, B.S.; Minn, A.J. Structure of Bcl-xL-Bak peptide complex: Recognition between regulators of apoptosis. Science 1997, 275, 983–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamas-Din, A.; Kale, J.; Leber, B.; Andrews, D.W. Mechanisms of action of Bcl-2 family proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chittenden, T.; Flemington, C.; Houghton, A.B.; Ebb, R.G.; Gallo, G.J.; Elangovan, B.; Chinnadurai, G.; Lutz, R.J. A conserved domain in Bak, distinct from BH1 and BH2, mediates cell death and protein binding functions. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 5589–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.C.; Adams, J.M.; Cory, S. The conserved N-terminal BH4 domain of Bcl-2 homologues is essential for inhibition of apoptosis and interaction with CED-4. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimizu, S.; Tsujimoto, Y. Proapoptotic BH3-only Bcl-2 family members induce cytochrome c release, but not mitochondrial membrane potential loss, and do not directly modulate voltage-dependent anion channel activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cory, S.; Huang, D.C.; Adams, J.M. The Bcl-2 family: Roles in cell survival and oncogenesis. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8590–8607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kale, J.; Osterlund, E.J.; Andrews, D.W. BCL-2 family proteins: Changing partners in the dance towards death. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lomonosova, E.; Chinnadurai, G. BH3-only proteins in apoptosis and beyond: An overview. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leber, B.; Lin, J.; Andrews, D.W. Embedded together: The life and death consequences of interaction of the Bcl-2 family with membranes. Apoptosis 2007, 12, 897–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Czabotar, P.E.; Westphal, D.; Dewson, G.; Ma, S.; Hockings, C.; Fairlie, W.D.; Lee, E.F.; Yao, S.; Robin, A.Y.; Smith, B.J. Bax crystal structures reveal how BH3 domains activate Bax and nucleate its oligomerization to induce apoptosis. Cell 2013, 152, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korsmeyer, S.J.; Shutter, J.R.; Veis, D.J.; Merry, D.E.; Oltvai, Z.N. Bcl-2/Bax: A rheostat that regulates an anti-oxidant pathway and cell death. Semin. Cancer Biol. 1993, 4, 327–332. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Chanvorachote, P.; Toledo, D.; Stehlik, C.; Mercer, R.R.; Castranova, V.; Rojanasakul, Y. Peroxide is a key mediator of Bcl-2 down-regulation and apoptosis induction by cisplatin in human lung cancer cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 73, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roufayel, R. Regulation of stressed-induced cell death by the Bcl-2 family of apoptotic proteins. Mol. Membr. Biol. 2016, 33, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fannjiang, Y.; Kim, C.-H.; Huganir, R.L.; Zou, S.; Lindsten, T.; Thompson, C.B.; Mito, T.; Traystman, R.J.; Larsen, T.; Griffin, D.E. BAK alters neuronal excitability and can switch from anti-to pro-death function during postnatal development. Dev. Cell 2003, 4, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hardwick, J.M.; Soane, L. Multiple functions of BCL-2 family proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rolland, S.G.; Lu, Y.; David, C.N.; Conradt, B. The BCL-2–like protein CED-9 of C. elegans promotes FZO-1/Mfn1, 2–and EAT-3/Opa1–dependent mitochondrial fusion. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 186, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karbowski, M.; Lee, Y.-J.; Gaume, B.; Jeong, S.-Y.; Frank, S.; Nechushtan, A.; Santel, A.; Fuller, M.; Smith, C.L.; Youle, R.J. Spatial and temporal association of Bax with mitochondrial fission sites, Drp1, and Mfn2 during apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 159, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whelan, R.S.; Konstantinidis, K.; Wei, A.-C.; Chen, Y.; Reyna, D.E.; Jha, S.; Yang, Y.; Calvert, J.W.; Lindsten, T.; Thompson, C.B. Bax regulates primary necrosis through mitochondrial dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6566–6571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alavian, K.N.; Li, H.; Collis, L.; Bonanni, L.; Zeng, L.; Sacchetti, S.; Lazrove, E.; Nabili, P.; Flaherty, B.; Graham, M. Bcl-x L regulates metabolic efficiency of neurons through interaction with the mitochondrial F 1 FO ATP synthase. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, A.l.F.; De Almeida, D.R.Q.; Terra, L.F.; Baptista, M.C.S.; Labriola, L. Photodynamic therapy in cancer treatment-an update review. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buytaert, E.; Dewaele, M.; Agostinis, P. Molecular effectors of multiple cell death pathways initiated by photodynamic therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2007, 1776, 86–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroz, P.; Hashmi, J.T.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Lange, N.; Hamblin, M.R. Stimulation of anti-tumor immunity by photodynamic therapy. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 7, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plaetzer, K.; Krammer, B.; Berlanda, J.; Berr, F.; Kiesslich, T. Photophysics and photochemistry of photodynamic therapy: Fundamental aspects. Lasers Med. Sci. 2009, 24, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowis, D.; Szokalska, A.; Makowski, M.; Winiarska, M.; Golab, J. Improvement of anti-tumor activity of photodynamic therapy through inhibition of cytoprotective mechanism in tumor cells. In Photodynamic Therapy: Back to the Future; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2009; p. 73804F. [Google Scholar]
- Kimani, S.G.; Phillips, J.B.; Bruce, J.I.; MacRobert, A.J.; Golding, J.P. Antioxidant inhibitors potentiate the cytotoxicity of photodynamic therapy. Photochem. Photobiol. 2012, 88, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brancaleon, L.; Moseley, H. Laser and non-laser light sources for photodynamic therapy. Lasers Med. Sci. 2002, 17, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Li, L.-B.; Wang, L.-W.; Song, X.-D.; Yow, C.M.; Lei, X.; Musani, A.I.; Luo, R.-C.; Day, B.J. Photodynamic therapy of cancer—Challenges of multidrug resistance. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2015, 8, 1530002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castano, A.P.; Demidova, T.N.; Hamblin, M.R. Mechanisms in photodynamic therapy: Part one—photosensitizers, photochemistry and cellular localization. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2004, 1, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juzeniene, A.; Nielsen, K.P.; Moan, J. Biophysical aspects of photodynamic therapy. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2006, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, R.R.; Sibata, C.H. Oncologic photodynamic therapy photosensitizers: A clinical review. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2010, 7, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayhew, S.; Vernon, D.I.; Schofield, J.; Griffiths, J.; Brown, S.B. Investigation of Cross-resistance to a Range of Photosensitizers, Hyperthermia and UV Light in Two Radiation-induced Fibrosarcoma Cell Strains Resistant to Photodynamic Therapy In Vitro. Photochem. Photobiol. 2001, 73, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella, M.A.M.; Capella, L.S. A light in multidrug resistance: Photodynamic treatment of multidrug-resistant tumors. J. Biomed. Sci. 2003, 10, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, A.; Di Venosa, G.; Hasan, T.; Batlle, A. Mechanisms of resistance to photodynamic therapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 2486–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonker, J.W.; Buitelaar, M.; Wagenaar, E.; Van Der Valk, M.A.; Scheffer, G.L.; Scheper, R.J.; Plösch, T.; Kuipers, F.; Elferink, R.P.O.; Rosing, H. The breast cancer resistance protein protects against a major chlorophyll-derived dietary phototoxin and protoporphyria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15649–15654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsunoda, Y.; Usuda, J.; Imai, K.; Kubota, M.; Maehara, S.; Ohtani, K. The expression of BCRP/ABCG2 causes resistance to Photofrin-PDT. Jpn. J. Laser Surg. Med. 2008, 28, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pustogarov, N.; Panteleev, D.; Goryaynov, S.A.; Ryabova, A.V.; Rybalkina, E.Y.; Revishchin, A.; Potapov, A.A.; Pavlova, G. Hiding in the shadows: CPOX expression and 5-ALA induced fluorescence in human glioma cells. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 5699–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurumi, H.; Kanda, T.; Kawaguchi, K.; Yashima, K.; Koda, H.; Ogihara, K.; Matsushima, K.; Nakao, K.; Saito, H.; Fujiwara, Y. Protoporphyrinogen oxidase is involved in the fluorescence intensity of 5-aminolevulinic acid-mediated laser-based photodynamic endoscopic diagnosis for early gastric cancer. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2018, 22, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usuda, J.; Tsunoda, Y.; Ichinose, S.; Ishizumi, T.; Ohtani, K.; Maehara, S.; Ono, S.; Tsutsui, H.; Ohira, T.; Okunaka, T. Breast cancer resistant protein (BCRP) is a molecular determinant of the outcome of photodynamic therapy (PDT) for centrally located early lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2010, 67, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, P.; Ross, D.D.; Nakanishi, T.; Bailey-Dell, K.; Zhou, S.; Mercer, K.E.; Sarkadi, B.; Sorrentino, B.P.; Schuetz, J.D. The stem cell marker Bcrp/ABCG2 enhances hypoxic cell survival through interactions with heme. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 24218–24225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srivastava, M.; Ahmad, N.; Gupta, S.; Mukhtar, H. Involvement of Bcl-2 and Bax in photodynamic therapy-mediated apoptosis antisense Bcl-2 oligonucleotide sensitizes RIF 1 cells to photodynamic therapy apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 15481–15488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kessel, D. Death pathways associated with photodynamic therapy. Med. Laser Appl. 2006, 21, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, X.Y.; Zacal, N.; Singh, G.; Rainbow, A.J. Alterations in Mitochondrial and Apoptosis-regulating Gene Expression in Photodynamic Therapy-resistant Variants of HT29 Colon Carcinoma Cells. Photochem. Photobiol. 2005, 81, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granville, D.; Jiang, H.; An, M.; Levy, J.; McManus, B.; Hunt, D. Bcl-2 overexpression blocks caspase activation and downstream apoptotic events instigated by photodynamic therapy. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 79, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koukourakis, M.I.; Corti, L.; Skarlatos, J.; Giatromanolaki, A.; Krammer, B.; Blandamura, S.; Piazza, M.; Verwanger, T.; Schnitzhofer, G.; Kostandelos, J. Clinical and experimental evidence of Bcl-2 involvement in the response to photodynamic therapy. Anticancer Res. 2001, 21, 663–668. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.-Y.; Chiu, S.-M.; Oleinick, N.L. Photochemical destruction of the Bcl-2 oncoprotein during photodynamic therapy with the phthalocyanine photosensitizer Pc 4. Oncogene 2001, 20, 3420–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Usuda, J.; Azizuddin, K.; Chiu, S.M.; Oleinick, N.L. Association between the Photodynamic Loss of Bcl-2 and the Sensitivity to Apoptosis Caused by Phthalocyanine Photodynamic Therapy. Photochem. Photobiol. 2003, 78, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, P.; Bovey, R.; Tardy, S.; Sahli, R.; Sordat, B.; Costa, J. Induction of apoptosis by wild-type p53 in a human colon tumor-derived cell line. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 4495–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sionov, R.V.; Haupt, Y. The cellular response to p53: The decision between life and death. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6145–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fisher, A.M.; Danenberg, K.; Banerjee, D.; Bertino, J.R.; Danenberg, P.; Gomer, C.J. Increased photosensitivity in HL60 cells expressing wild-type p53. Photochem. Photobiol. 1997, 66, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Naka, N.; Okishio, K.; Atagi, S.; Ogawara, M.; Hosoe, S.; Kawahara, M.; Furuse, K. Immunohistochemical analysis of Bcl-2 protein in early squamous cell carcinoma of the bronchus treated with photodynamic therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 82, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zawacka-Pankau, J.; Krachulec, J.; Grulkowski, I.; Bielawski, K.P.; Selivanova, G. The p53-mediated cytotoxicity of photodynamic therapy of cancer: Recent advances. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 232, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.V.; Paczulla, A.M.; Klonisch, T.; Dimgba, F.N.; Rao, S.B.; Roberg, K.; Schweizer, F.; Lengerke, C.; Davoodpour, P.; Palicharla, V.R. Interconnections between apoptotic, autophagic and necrotic pathways: Implications for cancer therapy development. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2013, 17, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.-P.; Lu, Y.-Y.; Ji, L.-N.; Mao, Z.-W. Metallomics insights into the programmed cell death induced by metal-based anticancer compounds. Metallomics 2014, 6, 978–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edinger, A.L.; Thompson, C.B. Death by design: Apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2004, 16, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Berghe, T.V.; Vanlangenakker, N.; Buettner, S.; Eisenberg, T.; Vandenabeele, P.; Madeo, F.; Kroemer, G. Programmed necrosis: From molecules to health and disease. In International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 289, pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ortel, B.; Shea, C.R.; Calzavara-Pinton, P. Molecular mechanisms of photodynamic therapy. Front. Biosci. 2009, 14, 4157–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tait, S.W.; Green, D.R. Mitochondria and cell death: Outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, H.K.; Susin, S.A. Therapeutic potential of AIF-mediated caspase-independent programmed cell death. Drug Resist. Updates 2007, 10, 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, P.-S.; He, P.; Shin, J.-I.; Hwang, H.-J.; Lee, S.J.; Ahn, J.-C. Photodynamic therapy with 9-hydroxypheophorbide α on AMC-HN-3 human head and neck cancer cells: Induction of apoptosis via photoactivation of mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, M.; Kornbluth, S. Caspases and kinases in a death grip. Cell 2009, 138, 838–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghavami, S.; Hashemi, M.; Ande, S.R.; Yeganeh, B.; Xiao, W.; Eshraghi, M.; Bus, C.J.; Kadkhoda, K.; Wiechec, E.; Halayko, A.J. Apoptosis and cancer: Mutations within caspase genes. J. Med. Genet. 2009, 46, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Renault, T.T.; Manon, S. Bax: Addressed to kill. Biochimie 2011, 93, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.-O.; Ha, K.-S. New insights into the mechanisms for photodynamic therapy-induced cancer cell death. In International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 295, pp. 139–174. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, R.D.; Manadas, B.J.; Carvalho, A.P.; Duarte, C.B. Intracellular signaling mechanisms in photodynamic therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2004, 1704, 59–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oleinick, N.L.; Morris, R.L.; Belichenko, I. The role of apoptosis in response to photodynamic therapy: What, where, why, and how. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2002, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Degterev, A.; Yuan, J. Expansion and evolution of cell death programmes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinkel, S.S.; Hurov, K.E.; Ong, C.; Abtahi, F.M.; Gross, A.; Korsmeyer, S.J. A role for proapoptotic BID in the DNA-damage response. Cell 2005, 122, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaufmann, T.; Tai, L.; Ekert, P.G.; Huang, D.C.; Norris, F.; Lindemann, R.K.; Johnstone, R.W.; Dixit, V.M.; Strasser, A. The BH3-only protein bid is dispensable for DNA damage-and replicative stress-induced apoptosis or cell-cycle arrest. Cell 2007, 129, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kodama, T.; Takehara, T.; Hikita, H.; Shimizu, S.; Shigekawa, M.; Li, W.; Miyagi, T.; Hosui, A.; Tatsumi, T.; Ishida, H. BH3-only activator proteins Bid and Bim are dispensable for Bak/Bax-dependent thrombocyte apoptosis induced by Bcl-xL deficiency molecular requisites for the mitochondrial pathway to apoptosis in platelets. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 13905–13913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zha, J.; Weiler, S.; Oh, K.J.; Wei, M.C.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Posttranslational N-myristoylation of BID as a molecular switch for targeting mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 2000, 290, 1761–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Roskams, T.; Xu, Y.; Agostinis, P.; de Witte, P.A. Photodynamic therapy with hypericin induces vascular damage and apoptosis in the RIF-1 mouse tumor model. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 98, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, N.; Gupta, S.; Feyes, D.K.; Mukhtar, H. Involvement of Fas (APO-1/CD-95) during photodynamic-therapy-mediated apoptosis in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 115, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yokota, T.; Ikeda, H.; Inokuchi, T.; Sano, K.; Koji, T. Enhanced cell death in NR-S1 tumor by photodynamic therapy: Possible involvement of Fas and Fas ligand system. Lasers Surg. Med. Off. J. Am. Soc. Laser Med. Surg. 2000, 26, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penning, L.; Rasch, M.; Ben-Hur, E.; Dubbelman, T.; Havelaar, A.; Van der Zee, J.; Van Steveninck, J. A role for the transient increase of cytoplasmic free calcium in cell rescue after photodynamic treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1992, 1107, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Singh, G.; Rainbow, A.J. Sustained activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway protects cells from photofrin-mediated photodynamic therapy. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 5528–5535. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.Y.; Chiu, S.M.; Azizuddin, K.; Joseph, S.; Oleinick, N.L. The death of human cancer cells following photodynamic therapy: Apoptosis competence is necessary for Bcl-2 protection but not for induction of autophagy. Photochem. Photobiol. 2007, 83, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Marani, M.; Yu, J.; Nan, B.; Roth, J.A.; Kagawa, S.; Fang, B.; Denner, L.; Marcelli, M. Adenovirus-mediated Bax overexpression for the induction of therapeutic apoptosis in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 186–191. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.; Fletcher, G.C.; Tolkovsky, A.M. Autophagy is activated by apoptotic signalling in sympathetic neurons: An alternative mechanism of death execution. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 1999, 14, 180–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman-Antosiewicz, A.; Johnson, D.E.; Singh, S.V. Sulforaphane causes autophagy to inhibit release of cytochrome C and apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5828–5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lockshin, R.A.; Zakeri, Z. Apoptosis, autophagy, and more. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 2405–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, S.; Kanaseki, T.; Mizushima, N.; Mizuta, T.; Arakawa-Kobayashi, S.; Thompson, C.B.; Tsujimoto, Y. Role of Bcl-2 family proteins in a non-apoptotic programmed cell death dependent on autophagy genes. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattingre, S.; Levine, B. Bcl-2 inhibition of autophagy: A new route to cancer? Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 2885–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, M.-F.; Chen, M.-W.; Chen, K.-C.; Lou, P.-J.; Lin, S.Y.-F.; Hung, S.-C.; Hsiao, M.; Yao, C.-J.; Shieh, M.-J. Autophagy promotes resistance to photodynamic therapy-induced apoptosis selectively in colorectal cancer stem-like cells. Autophagy 2014, 10, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, K.; Deng, L.; Wang, H. Combination of an Autophagy Inducer and an Autophagy Inhibitor: A Smarter Strategy Emerging in Cancer Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domagala, A.; Stachura, J.; Gabrysiak, M.; Muchowicz, A.; Zagozdzon, R.; Golab, J.; Firczuk, M. Inhibition of autophagy sensitizes cancer cells to Photofrin-based photodynamic therapy. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, J.; Letai, A. Why do BCL-2 inhibitors work and where should we use them in the clinic? Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aniogo, E.C.; George, B.P.A.; Abrahamse, H. Role of Bcl-2 Family Proteins in Photodynamic Therapy Mediated Cell Survival and Regulation. Molecules 2020, 25, 5308. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225308
Aniogo EC, George BPA, Abrahamse H. Role of Bcl-2 Family Proteins in Photodynamic Therapy Mediated Cell Survival and Regulation. Molecules. 2020; 25(22):5308. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225308
Chicago/Turabian StyleAniogo, Eric Chekwube, Blassan Plackal Adimuriyil George, and Heidi Abrahamse. 2020. "Role of Bcl-2 Family Proteins in Photodynamic Therapy Mediated Cell Survival and Regulation" Molecules 25, no. 22: 5308. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225308
APA StyleAniogo, E. C., George, B. P. A., & Abrahamse, H. (2020). Role of Bcl-2 Family Proteins in Photodynamic Therapy Mediated Cell Survival and Regulation. Molecules, 25(22), 5308. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225308