Formation of Tetrahydrofurano-, Aryltetralin, and Butyrolactone Norlignans through the Epoxidation of 9-Norlignans
Abstract
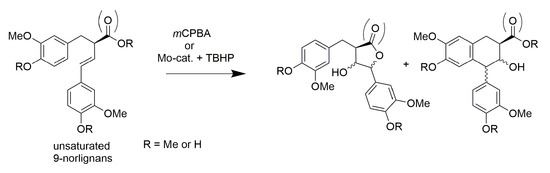
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. m-CPBA-Mediated Epoxidation
2.2. Mo-Catalyzed Epoxidation with TBHP
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Prilezhaev Reaction (mCPBA)
4.2.2. Mo-Catalyzed Epoxidation by TBHP
4.2.3. Analytical Methods
4.2.4. Isolation of Products
4.3. Experimental Data
4.3.1. Product 1A
4.3.2. Product 1B
4.3.3. Product 2A
4.3.4. Product 2B
4.3.5. Products 3A
Isomer 1 of 3A (7-(R) 8-(R)):
Isomer 2 of 3A (7-(S) 8-(R)):
Isomer 3 of 3A (7-(R) 8-(S)):
Isomer 4 of 3A (7-(S) 8-(S)):
4.3.6. Products 3B
Isomer 1 of 3B:
Isomer 2 of 3B
4.3.7. Products 4B
Major Isomer of Product 4B:
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haworth, R.D. natural resins. Ann. Rep. Prog. Chem. 1936, 33, 266–279. [Google Scholar]
- Francenia Santos-Sánchez, N.; Salas-Coronado, R.; Hernández-Carlos, B.; Villanueva-Cañongo, C. Shikimic Acid Pathway in Biosynthesis of Phenolic Compounds. In Plant Physiological Aspects of Phenolic Compounds; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Willför, S.M.; Ahotupa, M.O.; Hemming, J.E.; Reunanen, M.H.T.; Eklund, P.C.; Sjöholm, R.E.; Eckerman, C.S.E.; Suvi, P.; Pohjamo, A.; Holmbom, B.R. Antioxidant Activity of Knotwood Extractives and Phenolic Compounds of Selected Tree Species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 7600–7606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, P.C.; Långvik, O.K.; Wärnå, J.P.; Salmi, T.O.; Willför, S.M.; Sjöholm, R.E. Chemical studies on antioxidant mechanisms and free radical scavenging properties of lignans. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2005, 3, 3336–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlercreutz, H. Lignans and Human Health. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2007, 44, 483–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, C.; Siani, F.; Mus, L.; Ghezzi, C.; Cerri, S.; Pacchetti, B.; Bigogno, C.; Blandini, F. Neuroprotective effects of lignan 7-hydroxymatairesinol (HMR/lignan) in a rodent model of Parkinson’s disease. Nutrition 2020, 69, 110494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-García, C.; Sánchez-Quesada, C.; Toledo, E.; Delgado-Rodríguez, M.; Gaforio, J. Naturally Lignan-Rich Foods: A Dietary Tool for Health Promotion? Molecules 2019, 24, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, S.; Umezawa, T. Biosynthesis of lignans and norlignans. J. Wood Sci. 2007, 53, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, P.; Raitanen, J.-E. 9-Norlignans: Occurrence, Properties and Their Semisynthetic Preparation from Hydroxymatairesinol. Molecules 2019, 24, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holmbom, B.; Eckerman, C.; Eklund, P.; Hemming, J.; Nisula, L.; Reunanen, M.; Sjöholm, R.; Sundberg, A.; Sundberg, K.; Willför, S. Knots in trees – A new rich source of lignans. Phytochem. Rev. 2003, 2, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, I.; Yus, M. Asymmetric Ring Opening of Epoxides. Curr. Org. Chem. 2005, 9, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swern, D. Organic peroxides, Vol. 2; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1971; ISBN 0471839612. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, E.; Andrioletti, B.; Zrig, S.; Quelquejeu-Ethève, M. Enantioselective epoxidation of olefins with chiral metalloporphyrin catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2005, 34, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plesnicar, B. Oxidation in Organic C. In Organic Chemistry, Volume 5-C; Trahanovsky, W., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1978; ISBN 9780323152433. [Google Scholar]
- Runeberg, P.A.; Brusentsev, Y.; Rendon, S.M.K.; Eklund, P.C.; Runeberg, P.A.; Brusentsev, Y.; Rendon, S.M.K.; Eklund, P.C. Oxidative Transformations of Lignans. Molecules 2019, 24, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Linker, T.; Engelhardt, U.; Sarkar, A. Kinetic Resolution by Jacobsen Epoxidation as an Easy Route to Podophyllotoxin Analoga. In Peroxide Chemistry; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; ISBN 9783527600397. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon, R.A. Molybdenum-catalysed epoxidation of olefins with alkyl hydroperoxides I. Kinetic and product studies. Recl. des Trav. Chim. des Pays-Bas 1973, 92, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Jiang, P.; Wai, P.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, P.; Wai, P.T.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, W. Recent Progress in Application of Molybdenum-Based Catalysts for Epoxidation of Alkenes. Catalysts 2019, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morlot, J.; Uyttebroeck, N.; Agustin, D.; Poli, R. Solvent-Free Epoxidation of Olefins Catalyzed by “[MoO 2 (SAP)]”: A New Mode of tert -Butylhydroperoxide Activation. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Vanderbeeken, T.; Agustin, D.; Poli, R. Tridentate ONS vs. ONO salicylideneamino(thio)phenolato [MoO2L] complexes for catalytic solvent-free epoxidation with aqueous TBHP. Catal. Commun. 2015, 63, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Guerrero, T.; Merecias, S.R.; García-Ortega, H.; Santillan, R.; Daran, J.-C.; Farfán, N.; Agustin, D.; Poli, R. Substituent effects on solvent-free epoxidation catalyzed by dioxomolybdenum(VI) complexes supported by ONO Schiff base ligands. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2015, 431, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cindrić, M.; Pavlović, G.; Katava, R.; Agustin, D. Towards a global greener process: from solvent-less synthesis of molybdenum(vi) ONO Schiff base complexes to catalyzed olefin epoxidation under organic-solvent-free conditions. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Agustin, D.; Poli, R. Influence of ligand substitution on molybdenum catalysts with tridentate Schiff base ligands for the organic solvent-free oxidation of limonene using aqueous TBHP as oxidant. Mol. Catal. 2017, 443, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loubidi, M.; Agustin, D.; Benharref, A.; Poli, R. Solvent-free epoxidation of himachalenes and their derivatives by TBHP using [MoO2(SAP)]2 as a catalyst. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2014, 17, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeds, A.I.; Češková, I.; Eklund, P.C.; Willför, S.M. Identification of new lignans in Norway spruce knotwood extracts. Holzforschung 2012, 66, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassner, A.; Reuss, R.H.; Pinnick, H.W. Synthetic methods. VIII. Hydroxylation of carbonyl compounds via silyl enol ethers. J. Org. Chem. 1975, 40, 3427–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldoveanu, S.C.; David, V. Derivatization Methods in GC and GC/MS. In Gas Chromatography - Derivatization, Sample Preparation, Application; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |








| Entry | Subs. | Pre-cat (mol%) | Oxidant (equiv.) | Temp. (°C) | Time (h) | Conv [%] | Distribution of Products * | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | Others a | |||||||
| 1 | 1 | - | TBHP (10) | 80 | 24 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | 1 | [MoO2(SAP)]2 (0.5) | TBHP (5) | 80 | 3 | 100 | 37 | 4 | 2 | - | 57 |
| 3 | 1 | [MoO2(SATP)]2 (0.5) | TBHP (5) | 80 | 3 | 100 | 37 | 4 | 2 | - | 57 |
| 4 | 1 | - | mCPBA (1) | 25 | 0.5 | 100 | 74 | 20 | - | - | 6 |
| 5 | 2 | [MoO2(SAP)]2 (0.5) | TBHP (5) | 80 | 8 | 100 | 29 | 18 | 5 | - | 48 |
| 6 | 2 | [MoO2(SATP)]2 (0.5) | TBHP (5) | 80 | 3.66 | 100 | 37 | 26 | 7 | - | 30 |
| 7 | 2 | - | mCPBA (1) | 25 | 0.33 | 100 | 48 | 52 | - | - | - |
| 8 | 3 | [MoO2(SAP)]2 (2.5) | TBHP (2) | 80 | 1.66 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 9 | 3 | [MoO2(SAP)]2 (1.5) | TBHP (5) | 80 | 2.5 | 100 | 1 | 1 | - | - | 98 |
| 10 | 3 | [MoO2(SATP)]2 (2.5) | TBHP (2) | 80 | 1.5 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 11 | 3 | [MoO2(SATP)]2 (0.5) | TBHP (5) | 80 | 20 | 99 | 1 | 1 | - | - | 97 |
| 12 | 3 | - | mCPBA (1) | 25 | 0.5 | 96 | 71 | 24 | - | - | 1 |
| 13 | 4 | [MoO2(SAP)]2 (0.5) | TBHP (2) | 80 | 24 | 0- | - | - | - | - | - |
| 14 | 4 | [MoO2(SAP)]2 (1.5) | TBHP (5) | 80 | 21 | 93 | - | 14 | 2 | - | 84 |
| 15 | 4 | [MoO2(SATP)]2 (1.5) | TBHP (5) | 80 | 2 | 80 | - | 19 | 4 | - | 77 |
| 16 | 4 | - | mCPBA (1) | 25 | 0.5 | 83 | - | 32 | - | 51 | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Runeberg, P.A.; Agustin, D.; Eklund, P.C. Formation of Tetrahydrofurano-, Aryltetralin, and Butyrolactone Norlignans through the Epoxidation of 9-Norlignans. Molecules 2020, 25, 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25051160
Runeberg PA, Agustin D, Eklund PC. Formation of Tetrahydrofurano-, Aryltetralin, and Butyrolactone Norlignans through the Epoxidation of 9-Norlignans. Molecules. 2020; 25(5):1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25051160
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuneberg, Patrik A., Dominique Agustin, and Patrik C. Eklund. 2020. "Formation of Tetrahydrofurano-, Aryltetralin, and Butyrolactone Norlignans through the Epoxidation of 9-Norlignans" Molecules 25, no. 5: 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25051160
APA StyleRuneberg, P. A., Agustin, D., & Eklund, P. C. (2020). Formation of Tetrahydrofurano-, Aryltetralin, and Butyrolactone Norlignans through the Epoxidation of 9-Norlignans. Molecules, 25(5), 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25051160