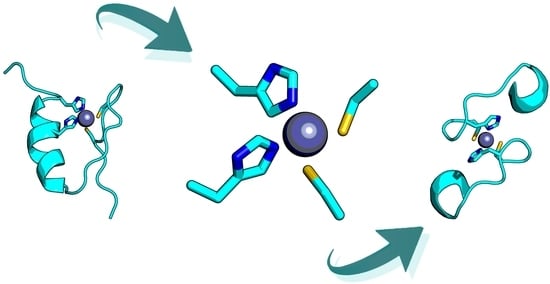
Unravelling the Structure of the Tetrahedral Metal-Binding Site in METP3 through an Experimental and Computational Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Design
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. Metal Binding Properties
2.4. CD Spectroscopy
2.5. NMR Analysis
2.6. Retrostructural Analysis of Pseudo-Symmetric Dimers Containing CXXHX Motif
2.7. Dimer Selection and Model Validation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Instrumentations
4.2. Peptide Synthesis and Purification
4.3. Metal-Binding Experiments
4.4. UV-Visible (UV-Vis) Spectroscopy
4.5. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectroscopy
4.6. NMR Spectroscopy
4.7. Analysis of the Protein Structure Database
4.8. METP3 Model Refinement
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crichton, R.R. Biological Inorganic Chemistry: A New Introduction to Molecular Structure and Function, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bertini, I.; Gray, H.B.; Stiefel, E.I.; Valentine, J.S. Biological Inorganic Chemistry: Structure and Reactivity; University Science Books: Sausalito, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, C.M.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Protein Folding and Metal Ions: Mechanisms, Biology and Disease; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Andreini, C.; Bertini, I.; Cavallaro, G.; Holliday, G.L.; Thornton, J.M. Metal Ions in Biological Catalysis: From Enzyme Databases to General Principles. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 13, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglio, O.; Nastri, F.; Lombardi, A. Structural and Functional Aspects of Metal Binding Sites in Natural and Designed Metalloproteins. In Ionic Interactions in Natural and Synthetic Macromolecules; Ciferri, A., Perico, A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 361–450. [Google Scholar]
- Nastri, F.; D’Alonzo, D.; Leone, L.; Zambrano, G.; Pavone, V.; Lombardi, A. Engineering Metalloprotein Functions in Designed and Native Scaffolds. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2019, 44, 1022–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluska, K.; Adamczyk, J.; Krężel, A. Metal Binding Properties, Stability and Reactivity of Zinc Fingers. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 367, 18–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Henarejos, S.A.; Alcaraz, L.A.; Donaire, A. Blue Copper Proteins: A Rigid Machine for Efficient Electron Transfer, a Flexible Device for Metal Uptake. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 584, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascella, M.; Magistrato, A.; Tavernelli, I.; Carloni, P.; Rothlisberger, U. Role of Protein Frame and Solvent for the Redox Properties of Azurin from Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19641–19646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dudev, T.; Lim, C. Metal Binding Affinity and Selectivity in Metalloproteins: Insights from Computational Studies. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2008, 37, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirts, E.N.; Bhagi-Damodaran, A.; Lu, Y. Understanding and Modulating Metalloenzymes with Unnatural Amino Acids, Non-Native Metal Ions, and Non-Native Metallocofactors. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortmayer, M.; Fisher, K.; Basran, J.; Wolde-Michael, E.M.; Heyes, D.J.; Levy, C.; Lovelock, S.L.; Anderson, J.L.R.; Raven, E.L.; Hay, S.; et al. Rewiring the “Push-Pull” Catalytic Machinery of a Heme Enzyme Using an Expanded Genetic Code. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 2735–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zastrow, M.L.; Pecoraro, V.L. Designing Functional Metalloproteins: From Structural to Catalytic Metal Sites. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 2565–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chino, M.; Maglio, O.; Nastri, F.; Pavone, V.; DeGrado, W.F.; Lombardi, A. Artificial Diiron Enzymes with a De Novo Designed Four-Helix Bundle Structure. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 2015, 3371–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lombardi, A.; Pirro, F.; Maglio, O.; Chino, M.; DeGrado, W.F. De Novo Design of Four-Helix Bundle Metalloproteins: One Scaffold, Diverse Reactivities. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 1148–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grayson, K.J.; Anderson, J.L.R. Designed for Life: Biocompatible de Novo Designed Proteins and Components. J. R. Soc. Interface 2018, 15, 20180472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakkis, A.; Gagnon, D.; Esselborn, J.; Britt, R.D.; Tezcan, F.A. Metal-Templated Design of Chemically Switchable Protein Assemblies with High-Affinity Coordination Sites. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 21940–21944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basler, S.; Studer, S.; Zou, Y.; Mori, T.; Ota, Y.; Camus, A.; Bunzel, H.A.; Helgeson, R.C.; Houk, K.N.; Jiménez-Osés, G.; et al. Efficient Lewis Acid Catalysis of an Abiological Reaction in a de Novo Protein Scaffold. Nat. Chem. 2021, 13, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slope, L.N.; Hill, M.G.; Smith, C.F.; Teare, P.; de Cogan, F.J.; Britton, M.M.; Peacock, A.F.A. Tuning Coordination Chemistry through the Second Sphere in Designed Metallocoiled Coils. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 3729–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, H.F.; Branco, R.J.F.; Leite, F.A.S.; Matzapetakis, M.; Roque, A.C.A.; Iranzo, O. Hydrolytic Zinc Metallopeptides Using a Computational Multi-State Design Approach. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 6723–6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, A.; Bhattacharjya, S. De Novo-Designed β-Sheet Heme Proteins. Biochemistry 2021, 60, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chino, M.; Leone, L.; Zambrano, G.; Pirro, F.; D’Alonzo, D.; Firpo, V.; Aref, D.; Lista, L.; Maglio, O.; Nastri, F.; et al. Oxidation Catalysis by Iron and Manganese Porphyrins within Enzyme-like Cages. Biopolymers 2018, 109, e23107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepi, M.; Oliva, R.; Petraccone, L.; Vecchio, P.D.; Ricca, E.; Isticato, R.; Lanzilli, M.; Maglio, O.; Lombardi, A.; Leone, L.; et al. Fluorescent Peptide DH3w: A Sensor for Environmental Monitoring of Mercury (II). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bos, J.; Roelfes, G. Artificial Metalloenzymes for Enantioselective Catalysis. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2014, 19, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soler, M.; Feliu, L.; Planas, M.; Ribas, X.; Costas, M. Peptide-Mediated Vectorization of Metal Complexes: Conjugation Strategies and Biomedical Applications. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 12970–12982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leone, L.; D’Alonzo, D.; Maglio, O.; Pavone, V.; Nastri, F.; Lombardi, A. Highly Selective Indole Oxidation Catalyzed by a Mn-Containing Artificial Mini-Enzyme. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 9407–9417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijano-Rubio, A.; Yeh, H.-W.; Park, J.; Lee, H.; Langan, R.A.; Boyken, S.E.; Lajoie, M.J.; Cao, L.; Chow, C.M.; Miranda, M.C.; et al. De Novo Design of Modular and Tunable Protein Biosensors. Nature 2021, 591, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrando, J.; Solomon, L.A. Recent Progress Using De Novo Design to Study Protein Structure, Design and Binding Interactions. Life 2021, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, S.E.J.; Bridwell-Rabb, J.; Drennan, C.L. Metalloprotein Crystallography: More than a Structure. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polizzi, N.F.; DeGrado, W.F. A Defined Structural Unit Enables de Novo Design of Small-Molecule–Binding Proteins. Science 2020, 369, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala, D.; Musiani, F.; Rosato, A. Application of Molecular Dynamics to the Investigation of Metalloproteins Involved in Metal Homeostasis. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 2018, 4661–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylemans, B.; Killian, T.; Vandebroek, L.; Van Meervelt, L.; Tame, J.R.H.; Parac-Vogt, T.N.; Voet, A.R.D. Crystal Structures of Scone: Pseudosymmetric Folding of a Symmetric Designer Protein. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. Struct. Biol. 2021, 77, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-Q.; Chino, M.; Liu, L.; Tang, Y.; Hu, X.; DeGrado, W.F.; Lombardi, A. De Novo Design of Tetranuclear Transition Metal Clusters Stabilized by Hydrogen-Bonded Networks in Helical Bundles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olson, T.L.; Espiritu, E.; Edwardraja, S.; Simmons, C.R.; Williams, J.C.; Ghirlanda, G.; Allen, J.P. Design of Dinuclear Manganese Cofactors for Bacterial Reaction Centers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA - Bioenerg. 2016, 1857, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirts, E.N.; Petrik, I.D.; Hosseinzadeh, P.; Nilges, M.J.; Lu, Y. A Designed Heme-[4Fe-4S] Metalloenzyme Catalyzes Sulfite Reduction like the Native Enzyme. Science 2018, 361, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chino, M.; Leone, L.; Maglio, O.; Lombardi, A. Designing Covalently Linked Heterodimeric Four-Helix Bundles. Methods Enzymol. 2016, 580, 471–499. [Google Scholar]
- Chino, M.; Leone, L.; Maglio, O.; D’Alonzo, D.; Pirro, F.; Pavone, V.; Nastri, F.; Lombardi, A. A De Novo Heterodimeric Due Ferri Protein Minimizes the Release of Reactive Intermediates in Dioxygen-Dependent Oxidation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15580–15583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocny, C.S.; Pecoraro, V.L. De Novo Protein Design as a Methodology for Synthetic Bioinorganic Chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 2388–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mutter, A.C.; Tyryshkin, A.M.; Campbell, I.J.; Poudel, S.; Bennett, G.N.; Silberg, J.J.; Nanda, V.; Falkowski, P.G. De Novo Design of Symmetric Ferredoxins That Shuttle Electrons in Vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 14557–14562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leone, L.; Chino, M.; Nastri, F.; Maglio, O.; Pavone, V.; Lombardi, A. Mimochrome, a Metalloporphyrin-Based Catalytic Swiss Knife†. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2020, 67, 495–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiella, M.; Maglio, O.; Nastri, F.; Lombardi, A.; Lista, L.; Hagen, W.R.; Pavone, V. De Novo Design, Synthesis and Characterisation of MP3, A New Catalytic Four-Helix Bundle Hemeprotein. Chem.–Eur. J. 2012, 18, 15960–15971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caserta, G.; Chino, M.; Firpo, V.; Zambrano, G.; Leone, L.; D’Alonzo, D.; Nastri, F.; Maglio, O.; Pavone, V.; Lombardi, A. Enhancement of Peroxidase Activity in Artificial Mimochrome VI Catalysts through Rational Design. ChemBioChem 2018, 19, 1823–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, L.; D’Alonzo, D.; Balland, V.; Zambrano, G.; Chino, M.; Nastri, F.; Maglio, O.; Pavone, V.; Lombardi, A. Mn-Mimochrome VI*a: An Artificial Metalloenzyme with Peroxygenase Activity. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, G.; Ruggiero, E.; Malafronte, A.; Chino, M.; Maglio, O.; Pavone, V.; Nastri, F.; Lombardi, A. Artificial Heme Enzymes for the Construction of Gold-Based Biomaterials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zambrano, G.; Nastri, F.; Pavone, V.; Lombardi, A.; Chino, M. Use of an Artificial Miniaturized Enzyme in Hydrogen Peroxide Detection by Chemiluminescence. Sensors 2020, 20, 3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maglio, O.; Chino, M.; Vicari, C.; Pavone, V.; Louro, R.O.; Lombardi, A. Histidine Orientation in Artificial Peroxidase Regioisomers as Determined by Paramagnetic NMR Shifts. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, J.M.; Alachouzos, G.; Chino, M.; Frontier, A.J.; Lombardi, A.; Bren, K.L. Tuning Mechanism through Buffer Dependence of Hydrogen Evolution Catalyzed by a Cobalt Mini-Enzyme. Biochemistry 2020, 59, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, A.; Marasco, D.; Maglio, O.; Di Costanzo, L.; Nastri, F.; Pavone, V. Miniaturized Metalloproteins: Application to Iron–Sulfur Proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11922–11927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benson, D.E.; Wisz, M.S.; Liu, W.; Hellinga, H.W. Construction of a Novel Redox Protein by Rational Design: Conversion of a Disulfide Bridge into a Mononuclear Iron−Sulfur Center. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 7070–7076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinas, E.; Regan, L. The de Novo Design of a Rubredoxin-like Fe Site. Protein Sci. 1998, 7, 1939–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, V.; Rosenblatt, M.M.; Osyczka, A.; Kono, H.; Getahun, Z.; Dutton, P.L.; Saven, J.G.; DeGrado, W.F. De Novo Design of a Redox-Active Minimal Rubredoxin Mimic. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5804–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tebo, A.G.; Pinter, T.B.J.; García-Serres, R.; Speelman, A.L.; Tard, C.; Sénéque, O.; Blondin, G.; Latour, J.-M.; Penner-Hahn, J.; Lehnert, N.; et al. Development of a Rubredoxin-Type Center Embedded in a de Dovo-Designed Three-Helix Bundle. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 2308–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertini, I.; Luchinat, C. High Spin Cobalt(II) as a Probe for the Investigation of Metalloproteins. Adv. Inorg. Biochem. 1984, 6, 71–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reddi, A.R.; Guzman, T.R.; Breece, R.M.; Tierney, D.L.; Gibney, B.R. Deducing the Energetic Cost of Protein Folding in Zinc Finger Proteins Using Designed Metallopeptides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 12815–12827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besold, A.N.; Widger, L.R.; Namuswe, F.; Michalek, J.L.; Michel, S.L.; Goldberg, D.P. Revisiting and Re-Engineering the Classical Zinc Finger Peptide: Consensus Peptide-1 (CP-1). Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanZile, M.L.; Cosper, N.J.; Scott, R.A.; Giedroc, D.P. The Zinc Metalloregulatory Protein Synechococcus PCC7942 SmtB Binds a Single Zinc Ion per Monomer with High Affinity in a Tetrahedral Coordination Geometry. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 11818–11829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmer, D.R.; Krauss, M. Ab Initio Quantum Chemical Study of the Cobalt D-d Spectroscopy of Several Substituted Zinc Enzymes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 10247–10257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan, L.; Clarke, N.D. A Tetrahedral Zinc(II)-Binding Site Introduced into a Designed Protein. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 10878–10883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizek, B.A.; Merkle, D.L.; Berg, J.M. Ligand Variation and Metal Ion Binding Specificity in Zinc Finger Peptides. Inorg. Chem. 1993, 32, 937–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreerama, N.; Woody, R.W. Estimation of Protein Secondary Structure from Circular Dichroism Spectra: Comparison of CONTIN, SELCON, and CDSSTR Methods with an Expanded Reference Set. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 287, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roccatano, D.; Colombo, G.; Fioroni, M.; Mark, A.E. Mechanism by Which 2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol/Water Mixtures Stabilize Secondary-Structure Formation in Peptides: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12179–12184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, G.; Neuhaus, D.; Wörgötter, E.; Vašák, M.; Kägi, J.H.R.; Wüthrich, K. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Identification of “Half-Turn” and 310-Helix Secondary Structure in Rabbit Liver Metallothionein-2. J. Mol. Biol. 1986, 187, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüthrich, K. NMR of Proteins and Nucleic Acids; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Karplus, M. Contact Electron-Spin Coupling of Nuclear Magnetic Moments. J. Chem. Phys. 1959, 30, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, A.; Nastri, F.; Marasco, D.; Maglio, O.; Sanctis, G.D.; Sinibaldi, F.; Santucci, R.; Coletta, M.; Pavone, V. Design of a New Mimochrome with Unique Topology. Chem.–Eur. J. 2003, 9, 5643–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, D.E.; DeGrado, W.F. Amino Acid Propensities Are Position-Dependent throughout the Length of α-Helices. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 337, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavone, V.; Gaeta, G.; Lombardi, A.; Nastri, F.; Maglio, O.; Isernia, C.; Saviano, M. Discovering Protein Secondary Structures: Classification and Description of Isolated α-Turns. Biopolymers 1996, 38, 705–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, C.; Nataraj, D.V. Energy Minimization Studies on α-Turns. J. Pept. Sci. 1998, 4, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreini, C.; Bertini, I.; Cavallaro, G. Minimal Functional Sites Allow a Classification of Zinc Sites in Proteins. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ireland, S.M.; Martin, A.C.R. ZincBind—the Database of Zinc Binding Sites. Database 2019, 2019, baz006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.J.; Headd, J.J.; Moriarty, N.W.; Prisant, M.G.; Videau, L.L.; Deis, L.N.; Verma, V.; Keedy, D.A.; Hintze, B.J.; Chen, V.B.; et al. MolProbity: More and Better Reference Data for Improved All-atom Structure Validation. Protein Sci. Publ. Protein Soc. 2018, 27, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.B.; Raleigh, D.P.; Lombardi, A.; DeGrado, W.F. De Novo Design of Helical Bundles as Models for Understanding Protein Folding and Function. Acc. Chem. Res. 2000, 33, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.-C.; Casey, P.J.; Fierke, C.A. Evidence for a Catalytic Role of Zinc in Protein Farnesyltransferase: Spectroscopy of Co2+ - Farnesyltransferase Indicates Metal Coordination of the Substrate Thiolate*. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taylor, J.S.; Lau, C.Y.; Applebury, M.L.; Coleman, J.E. Escherichia Coli Co (II) Alkaline Phosphatase Absorption, Circular Dichroism, and Magnetic Circular Dichroism of the d-d Electronic Transitions. J. Biol. Chem. 1973, 248, 6216–6220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallee, W.M.B.L. Cobalt as Probe and Label of Proteins. In Methods in Enzymology; Metallobiochemistry Part C: Spectroscopic and Physical Methods for Probing Metal Ion Environments in Metalloenzymes and Metalloproteins; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1993; Volume 226, pp. 52–71. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Gupta, Y.K. Natural Zinc Ribbon HNH Endonucleases and Engineered Zinc Finger Nicking Endonuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haag, F.; Ahmed, L.; Reiss, K.; Block, E.; Batista, V.S.; Krautwurst, D. Copper-Mediated Thiol Potentiation and Mutagenesis-Guided Modeling Suggest a Highly Conserved Copper-Binding Motif in Human OR2M3. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 2157–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guérineau, M.; Bessa, L.; Moriau, S.; Lescop, E.; Bontems, F.; Mathy, N.; Guittet, E.; Bischerour, J.; Bétermier, M.; Morellet, N. The Unusual Structure of the PiggyMac Cysteine-Rich Domain Reveals Zinc Finger Diversity in PiggyBac-Related Transposases. Mob. DNA 2021, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, K.C. Prediction and Classification of Alpha-Turn Types. Biopolymers 1997, 42, 837–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohage, E.C.; Graml, W.; Walter, M.M.; Steinbacher, S.; Steipe, B. Beta-Turn Propensities as Paradigms for the Analysis of Structural Motifs to Engineer Protein Stability. Protein Sci. 1997, 6, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.-J.; Chang, H.-J.; Peng, H.-P.; Huang, S.-S.; Lin, M.-Y.; Yang, A.-S. Assessing Computational Amino Acid Beta-Turn Propensities with a Phage-Displayed Combinatorial Library and Directed Evolution. Struct. Lond. Engl. 1993 2006, 14, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar]
- Laitaoja, M.; Valjakka, J.; Jänis, J. Zinc Coordination Spheres in Protein Structures. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 10983–10991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maret, W.; Li, Y. Coordination Dynamics of Zinc in Proteins. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4682–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J.M.; Merkle, D.L. On the Metal Ion Specificity of Zinc Finger Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 3759–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, D. An Introduction to Biological NMR Spectroscopy *. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2013, 12, 3006–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, W.R.P.; Hunenberger, P.H.; Tironi, I.G.; Mark, A.E.; Billeter, S.R.; Fennen, J.; Torda, A.E.; Huber, T.; Kruger, P.; van Gunsteren, W.F. The GROMOS biomolecular simulation program package. J. Phys. Chem. A 1999, 103, 3596–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, S.; Rohl, A.L.; Shi, S.; Freeman, C.M.; O’Hare, D. Molecular Mechanics Study of Oligomeric Models for Poly(Ferrocenylsilanes) Using the Extensible Systematic Forcefield (ESFF). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 7578–7592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifson, S.; Hagler, A.T.; Dauber, P. Consistent Force Field Studies of Intermolecular Forces in Hydrogen-Bonded Crystals. 1. Carboxylic Acids, Amides, and the C:O.Cntdot..Cntdot..Cntdot.H- Hydrogen Bonds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1979, 101, 5111–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.R.; Brooks, C.L.; Mackerell, A.D.; Nilsson, L.; Petrella, R.J.; Roux, B.; Won, Y.; Archontis, G.; Bartels, C.; Boresch, S.; et al. CHARMM: The Biomolecular Simulation Program. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 1545–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Compound | Wavelength [nm] (ε × 10−3 [M−1cm−1]) | Coordination Site | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| METP3 | 308 (2.10) | 564 (0.313) | 624 (0.470) | 649 (0.440) | Cys2His2 |
| GGG | 285 (3.4) | 550 (0.220) | 625 (0.500) | 660 (0.430) | Cys2His2 |
| CP-1 | 310 (2.50) | 570 (0.300) | 640 (0.900) | Cys3His | |
| METP | 353 (3.57) | 624 (0.420) | 685 (0.617) | 735 (0.582) | Cys4 |
| Metal Ion | KD (µM) METP a | KD (µM) METP3 |
|---|---|---|
| Co(II) | (53.5 ± 2.8) | (85 ± 4) |
| Zn(II) | (2.7 ± 0.1) | (5.6 ± 0.2) |
| Cd(II) | / | (5.0 ± 1.0) |
| Residue | X1 | X2 | X3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.25 | |
| C | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| D | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0.41 | 0.41 | 0 | |
| E | 6 | 6 | 8 |
| 2.20 | 2.20 | 2.93 | |
| F | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0.58 | 0.58 | |
| G | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| 0 | 0 | 2.17 | |
| H | 1 | 4 | 3 |
| 1.03 | 4.13 | 3.10 | |
| I | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| 0.41 | 1.23 | 0 | |
| K | 5 | 2 | 4 |
| 2.32 | 0.93 | 1.86 | |
| L | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 0.46 | 0 | 0.46 | |
| M | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| N | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| 1.21 | 1.81 | 1.21 | |
| P | 8 | 3 | 3 |
| 3.69 | 1.38 | 1.38 | |
| Q | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| 2.41 | 0 | 0 | |
| R | 6 | 3 | 1 |
| 2.34 | 1.17 | 0.39 | |
| S | 0 | 3 | 2 |
| 0 | 1.02 | 0.68 | |
| T | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| 1.23 | 1.23 | 1.23 | |
| V | 1 | 4 | 3 |
| 0.33 | 1.31 | 0.98 | |
| W | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1.75 | 1.75 | 0 | |
| Y | 0 | 4 | 4 |
| 0 | 3.16 | 3.16 |
| Cluster | ϕi+1 | ψi+1 | ϕi+2 | ψi+2 | ϕi+3 | ψi+3 | χ1 Cys | χ1 His |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (86) | −59 (5) | −37 (8) | −65 (7) | −47 (12) | −79 (18) | −21 (19) | 72 (4) | −75 (8) |
| 2 (16) | −63 (6) | −26 (11) | −91 (13) | −34 (12) | −116 (12) | 10 (32) | 177 (6) | −61 (6) |
| 3 (13) | −63 (3) | −31 (10) | −79 (3) | −41 (3) | −116 (7) | −6 (2) | 67 (3) | −53 (4) |
| 4 (11) | −62 (8) | −40 (11) | −83 (9) | −33 (13) | −119 (12) | 78 (9) | −178 (3) | −51 (6) |
| 5 (1) | −86 | −3 | −110 | −24 | −135 | 158 | −175 | 93 |
| 6 (1) | −58 | −48 | −59 | −54 | −63 | −45 | −177 | −81 |
| 7 (1) | −121 | −37 | −57 | −30 | −115 | 18 | 178 | −50 |
| Entry | #Clust. | Sequence | χ1 Cys a | χ1 His a | Sequence | χ1 Cys a | χ1 Cys a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2v0c_A | 4 | 176C-W-R-H-E180 | 174 | −59 | 159C-P-K-C-Q163 | 177 | −65 |
| 4ijd_A | 2 | 216C-A-A-H-G220 | 174 | −62 | 205C-E-M-C-Q209 | 179 | −61 |
| 4ijd_B | 2 | 216C-A-A-H-G220 | −176 | −56 | 205C-E-M-C-Q209 | 177 | −57 |
| 2au3_A | 5 | 35C-P-F-H-P39 | −175 | 93 | 56C-F-G-C-G60 | −172 | 67 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
La Gatta, S.; Leone, L.; Maglio, O.; De Fenza, M.; Nastri, F.; Pavone, V.; Chino, M.; Lombardi, A. Unravelling the Structure of the Tetrahedral Metal-Binding Site in METP3 through an Experimental and Computational Approach. Molecules 2021, 26, 5221. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175221
La Gatta S, Leone L, Maglio O, De Fenza M, Nastri F, Pavone V, Chino M, Lombardi A. Unravelling the Structure of the Tetrahedral Metal-Binding Site in METP3 through an Experimental and Computational Approach. Molecules. 2021; 26(17):5221. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175221
Chicago/Turabian StyleLa Gatta, Salvatore, Linda Leone, Ornella Maglio, Maria De Fenza, Flavia Nastri, Vincenzo Pavone, Marco Chino, and Angela Lombardi. 2021. "Unravelling the Structure of the Tetrahedral Metal-Binding Site in METP3 through an Experimental and Computational Approach" Molecules 26, no. 17: 5221. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175221
APA StyleLa Gatta, S., Leone, L., Maglio, O., De Fenza, M., Nastri, F., Pavone, V., Chino, M., & Lombardi, A. (2021). Unravelling the Structure of the Tetrahedral Metal-Binding Site in METP3 through an Experimental and Computational Approach. Molecules, 26(17), 5221. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175221