The Effects of Structural Alterations in the Polyamine and Amino Acid Moieties of Philanthotoxins on Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Inhibition in the Locust, Schistocerca gregaria
Abstract
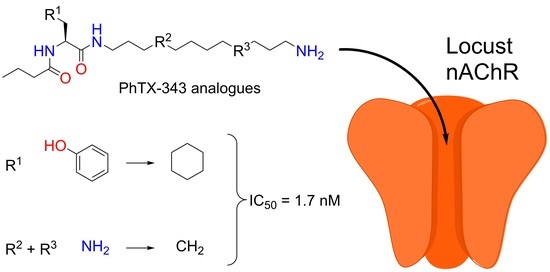
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Synthesis of Cha-PhTX-12
2.2. Characterisation of Whole-Cell Current Responses to ACh in Locust Neurons
2.3. The Impact of Modification to the Polyamine Region
2.4. The Effect of Replacing the Tyrosyl Moiety
2.5. The Effect of Combined Modification in the Polyamine and Amino Acid Moieties
2.6. Low Concentrations of PhTX-343 and Cha-PhTX-343 Potentiate Responses to ACh in Some Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Philanthotoxin Analogues
4.2. Locust Neuron Preparation and Cell Culture
4.3. Whole-Cell Patch-Clamp of Locust Neurons
4.4. Concentration–Inhibition Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Stromgaard, K.; Jensen, L.S.; Vogensen, S.B. Polyamine toxins: Development of selective ligands for ionotropic receptors. Toxicon 2005, 45, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stromgaard, K.; Piazzi, L.; Olsen, C.A.; Franzyk, H.; Jaroszewski, J.W. Protolytic properties of polyamine wasp toxin analogues studied by C-13 NMR spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2006, 44, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brier, T.J.; Mellor, I.R.; Tikhonov, D.B.; Neagoe, I.; Shao, Z.Y.; Brierley, M.J.; Stromgaard, K.; Jaroszewski, J.W.; Krogsgaard-Larsen, P.; Usherwood, P.N.R. Contrasting actions of philanthotoxin-343 and philanthotoxin (12) on human muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 64, 954–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mellor, I.R.; Brier, T.J.; Pluteanu, F.; Stromgaard, K.; Saghyan, A.; Eldursi, N.; Brierley, M.J.; Anderson, K.; Jaroszewski, J.W.; Krogsgaard-Larsen, P.; et al. Modification of the philanthotoxin-343 polyamine moiety results in different structure-activity profiles at muscle nicotinic ACh, NMDA and AMPA receptors. Neuropharmacology 2003, 44, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachel, H.S.; Franzyk, H.; Mellor, I.R. Philanthotoxin Analogues That Selectively Inhibit Ganglionic Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors with Exceptional Potency. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 6214–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachel, H.S.; Patel, R.N.; Franzyk, H.; Mellor, I.R. Block of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors by philanthotoxins is strongly dependent on their subunit composition. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Nakazawa, K.; Inoue, K.; Ohno, Y. Potent and voltage-dependent block by philanthotoxin-343 of neuronal nicotinic receptor/channels in PC12 cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 122, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozental, R.; Scoble, G.T.; Albuquerque, E.X.; Idriss, M.; Sherby, S.; Sattelle, D.B.; Nakanishi, K.; Konno, K.; Eldefrawi, A.T.; Eldefrawi, M.E. Allosteric Inhibition of Nicotinic Acetylcholine-Receptors of Vertebrates and Insects by Philanthotoxin. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1989, 249, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Nauen, R.; Jeschke, P.; Velten, R.; Beck, M.E.; Ebbinghaus-Kintscher, U.; Thielert, W.; Wolfel, K.; Haas, M.; Kunz, K.; Raupach, G. Flupyradifurone: A brief profile of a new butenolide insecticide. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 850–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeschke, P.; Nauen, R.; Beck, M.E. Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Agonists: A Milestone for Modern Crop Protection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 9464–9485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thany, S.H.; Tricoire-Leignel, H. Emerging Pharmacological Properties of Cholinergic Synaptic Transmission: Comparison between Mammalian and Insect Synaptic and Extrasynaptic Nicotinic Receptors. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2011, 9, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.G.; Kayser, H.; Maienfisch, P.; Casida, J.E. Insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: Conserved neonicotinoid specificity of [H-3]imidacloprid binding site. J. Neurochem. 2000, 75, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Delso, N.; Amaral-Rogers, V.; Belzunces, L.P.; Bonmatin, J.M.; Chagnon, M.; Downs, C.; Furlan, L.; Gibbons, D.W.; Giorio, C.; Girolami, V.; et al. Systemic insecticides (neonicotinoids and fipronil): Trends, uses, mode of action and metabolites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 5–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, C.; Denholm, I.; Williamson, M.S.; Nauen, R. The global status of insect resistance to neonicotinoid insecticides. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 121, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, S.Q.; Hu, X.P.; Li, M.N.; Jiang, X.Q.; Xu, X.Y.; Cheng, J.G.; Qian, X.H. Discovery of novel iminosydnone compounds with insecticidal activities based on the binding mode of triflumezopyrim. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 46, 34015502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihara, M.; Buckingham, S.D.; Matsuda, K.; Sattelle, D.B. Modes of Action, Resistance and Toxicity of Insecticides Targeting Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 2925–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.J.; Li, Q.X.; Song, B.A. Recent Research Progress in and Perspectives of Mesoionic Insecticides: Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Inhibitors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11039–11053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna-Hernández, S.A.; Bonilla-Landa, I.; Reyes-Luna, A.; Rodríguez-Hernández, A.; Cuapio-Muñoz, U.; Ibarra-Juárez, L.A.; Suarez-Mendez, G.; Barrera-Méndez, F.; Pérez-Landa, I.D.; Enríquez-Medrano, F.J.; et al. Synthesis and Insecticidal Evaluation of Chiral Neonicotinoids Analogs: The Laurel Wilt Case. Molecules 2021, 26, 4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, M.; Casida, J.E. Neonicotinoid insecticide toxicology: Mechanisms of selective action. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. 2005, 45, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eldefrawi, M.E.; Anis, N.A.; Eldefrawi, A.T. Glutamate Receptor Inhibitors as Potential Insecticides. Arch. Insect. Biochem. 1993, 22, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, N.; Sherby, S.; Goodnow, R.; Niwa, M.; Konno, K.; Kallimopoulos, T.; Bukownik, R.; Nakanishi, K.; Usherwood, P.; Eldefrawi, A.; et al. Structure-Activity-Relationships of Philanthotoxin Analogs and Polyamines on N-Methyl-D-Aspartate and Nicotinic Acetylcholine-Receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1990, 254, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benson, J.A.; Kaufmann, L.; Hue, B.; Pelhate, M.; Schurmann, F.; Gsell, L.; Piek, T. The Physiological Action of Analogs of Philanthotoxin-4.3.3 at Insect Nicotinic Acetylcholine-Receptors. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 1993, 105, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, M.; Stromgaard, K.; Mellor, I.; Jaroszewski, J.; Krogsgaard-Larsen, P.; Usherwood, P. Philanthotoxin analogues containing ether groups distinguish between nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and ionotropic quisqualate receptors. J. Neurochem. 1999, 73, S144. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, L.S.; Bolcho, U.; Egebjerg, J.; Stromgaard, K. Design, synthesis, and pharmacological characterization of polyamine toxin derivatives: Potent ligands for the pore-forming region of AMPA receptors. Chemmedchem 2006, 1, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, C.A.; Mellor, I.R.; Wellendorph, P.; Usherwood, P.N.R.; Witt, M.; Franzyk, H.; Jaroszewski, J.W. Tuning wasp toxin structure for nicotinic receptor antagonism: Cyclohexylalanine-containing analogues as potent and voltage-dependent blockers. Chemmedchem 2006, 1, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stromgaard, K.; Brier, T.J.; Andersen, K.; Mellor, I.R.; Saghyan, A.; Tikhonov, D.; Usherwood, P.N.R.; Krogsgaard-Larsen, P.; Jaroszewski, J.W. Solid-phase synthesis and biological evaluation of a combinatorial library of philanthotoxin analogues. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 43, 4526–4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stromgaard, K.; Brierley, M.J.; Andersen, K.; Slok, F.A.; Mellor, I.R.; Usherwood, P.N.R.; Krogsgaard-Larsen, P.; Jaroszewski, J.W. Analogues of neuroactive polyamine wasp toxins that lack inner basic sites exhibit enhanced antagonism toward a muscle-type mammalian nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 5224–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piek, T.; Hue, B. Philanthotoxins, a New Class of Neuroactive Polyamines, Block Nicotinic Transmission in the Insect Cns. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 1989, 93, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonov, D.B.; Mellor, I.R.; Usherwood, P.N.R. Modeling noncompetitive antagonism of a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Biophys. J. 2004, 87, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlin, A. Emerging structure of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stromgaard, K.; Mellor, I.R.; Andersen, K.; Neagoe, I.; Pluteanu, F.; Usherwood, P.N.R.; Krogsgaard-Larsen, P.; Jaroszewski, J.W. Solid-phase synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of analogues of PhTX-12—A potent and selective nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 1159–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.Y.; Mellor, I.R.; Brierley, M.J.; Harris, J.; Usherwood, P.N.R. Potentiation and inhibition of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors by spermine in the TE671 human muscle cell line. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 286, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wellendorph, P.; Jaroszewski, J.W.; Hansen, S.H.; Franzyk, H. A sequential high-yielding large-scale solution-method for synthesis of philanthotoxin analogues. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 38, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Compound | IC50 (95% CI), μM | Peak/1 s Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peak Current | 1 s Current | ||
| PhTX-343 (n = 15) | 39.8 (12.0–132) | 0.80 (0.48–1.34) | 50 ++++ |
| PhTX-12 (n = 19) | 1.17 (0.72–1.92) **** | 0.13 (0.08–0.21) **** | 9.0 ++++ |
| Cha-PhTX-343 (n = 10) | 1.75 (0.83–3.68) **** | 0.44 (0.22–0.89) | 4.0 ++ |
| Cha-PhTX-12 (n = 7) | 0.0075 (0.0042–0.013) **** | 0.0017 (0.0008–0.0035) **** | 4.4 ++ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luck, V.L.; Richards, D.P.; Shaikh, A.Y.; Franzyk, H.; Mellor, I.R. The Effects of Structural Alterations in the Polyamine and Amino Acid Moieties of Philanthotoxins on Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Inhibition in the Locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Molecules 2021, 26, 7007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26227007
Luck VL, Richards DP, Shaikh AY, Franzyk H, Mellor IR. The Effects of Structural Alterations in the Polyamine and Amino Acid Moieties of Philanthotoxins on Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Inhibition in the Locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Molecules. 2021; 26(22):7007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26227007
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuck, Victoria L., David P. Richards, Ashif Y. Shaikh, Henrik Franzyk, and Ian R. Mellor. 2021. "The Effects of Structural Alterations in the Polyamine and Amino Acid Moieties of Philanthotoxins on Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Inhibition in the Locust, Schistocerca gregaria" Molecules 26, no. 22: 7007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26227007
APA StyleLuck, V. L., Richards, D. P., Shaikh, A. Y., Franzyk, H., & Mellor, I. R. (2021). The Effects of Structural Alterations in the Polyamine and Amino Acid Moieties of Philanthotoxins on Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Inhibition in the Locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Molecules, 26(22), 7007. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26227007