Structure Elucidation and Cholinesterase Inhibition Activity of Two New Minor Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
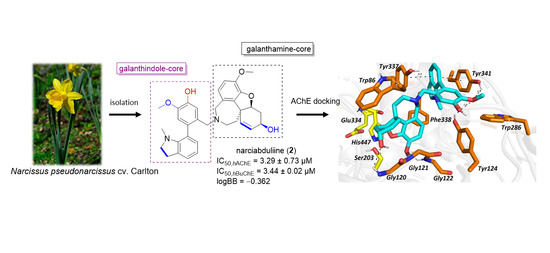
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Isolation of Compound 1
3.3. Isolation of Compound 2
3.4. hAChE and hBuChE Inhibition Assay
3.5. Molecular Modeling Studies
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Cahlíková, L.; Kawano, I.; Řezáčová, M.; Blunden, G.; Hulcová, D.; Havelek, R. The Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids Haemanthamine, Haemanthidine and Their Semisynthetic Derivatives as Potential Drugs. Phytochem. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalecká, M.; Havelek, R.; Královec, K.; Brůčková, L.; Cahlíková, L. Amaryllidaceae Family Alkaloids as Potential Drugs for Cancer Treatment. Chem. Listy 2013, 107, 701–708. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z. Amaryllidaceae and Sceletium Alkaloids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2016, 33, 1318–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, J.J.; Wilhelm, A.; Bonnet, S.L.; van Staden, J. Antibacterial Constituents of the Plant Family Amaryllidaceae. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 4943–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, J.J.; van Staden, J. Antifungal Activity Based Studies of Amaryllidaceae Plant Extracts. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2017, 12, 1953–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konrath, E.L.; Passos, C.D.; Klein, L.C.; Henriques, A.T. Alkaloids as a Source of Potential Anticholinesterase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 65, 1701–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Mamun, A.; Maříková, J.; Hulcová, D.; Janoušek, J.; Šafratová, M.; Nováková, L.; Kučera, T.; Hrabinová, M.; Kuneš, J.; Korábečný, J.; et al. Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids of Belladine-Type from Narcissus pseudonarcissus cv. Carlton as New Selective Inhibitors of Butyrylcholinesterase. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohelová, E.; Maříková, J.; Korábečný, J.; Hulcová, D.; Kučera, T.; Jun, D.; Chlebek, J.; Jenčo, J.; Šafratová, M.; Hrabinová, M.; et al. Alkaloids of Zephyranthes citrina (Amaryllidaceae) and Their Implication to Alzheimer’s Disease: Isolation, Structural Elucidation and Biological Activity. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 107, 104567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clardy, J.; Chan, J.A.; Wildman, W.C. The Structure of Lycorenine and the 7-Hydroxy Alkaloids Derived from the [2]Benzopyrano[3,4-g]indole Nucleus. J. Org. Chem. 1972, 37, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulcová, D.; Maříková, J.; Korábečný, J.; Hošťálková, A.; Jun, D.; Kuneš, J.; Chlebek, J.; Opletal, L.; De Simone, A.; Nováková, L.; et al. Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids from Narcissus pseudonarcissus L. cv. Dutch Master as Potential Drugs in Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Phytochemistry 2019, 165, 112055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šafratová, M.; Hošťálková, A.; Hulcová, D.; Breiterová, K.; Hrabcová, V.; Machado, M.; Fontinha, D.; Prudêncio, M.; Kuneš, J.; Chlebek, J.; et al. Alkaloids from Narcissus poeticus cv. Pink Parasol of Various Structural Types and Their Biological Activity. Arch. Pharmacal. Res. 2018, 41, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, J.; Rudolph, M.J.; Burshteyn, F.; Cassidy, M.S.; Gary, E.G.; Love, J.; Franklin, M.C.; Height, J.J. Structures of Human Acetylcholinesterase in Complex with Pharmacologically Important Ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 10282–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachon, F.; Carletti, E.; Ronco, C.; Trovaslet, M.; Nicolet, Y.; Jean, L.; Renard, P.Y. Crystal Structures of Human Cholinesterases in Complex with Huprine W and Tacrine: Elements of Specificity for Anti-Alzheimer’s Drugs Targeting Acetyl- and Butyryl-Cholinesterase. Biochem. J. 2013, 453, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saxena, A.; Redman, A.M.G.; Jiang, X.; Lockridge, O.; Doctor, B.P. Differences in Active Site Gorge Dimensions of Cholinesterases Revealed by Binding of Inhibitors to Human Butyrylcholinesterase. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 14642–14651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muehlbacher, M.; Spitzer, G.M.; Liedl, K.R.; Kornhuber, J. Qualitative Prediction of Blood-brain Barrier Permeability on a Large and Refined Dataset. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2011, 25, 1095–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al Shammari, L.; Hulcová, D.; Maříková, J.; Kučera, T.; Šafratová, M.; Nováková, L.; Schmidt, M.; Pulkrábková, L.; Janoušek, J.; Soukup, O.; et al. Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids from Hippeastrum X hybridum CV. Ferrari, and Preparation of Vittatine Derivatives as Potential Ligands for Alzheimer´s Disease. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 136, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maříková, J.; Ritomská, A.; Korábečný, J.; Peřinová, R.; Al Mamun, A.; Kučera, T.; Kohelová, E.; Hulcová, D.; Kobrlová, T.; Kuneš, J.; et al. Aromatic Esters of the Crinane Amaryllidaceae Alkaloid Ambelline as Selective Inhibitors of Butyrylcholinesterase. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostalkova, A.; Marikova, J.; Opletal, L.; Korabecny, J.; Hulcova, D.; Kunes, J.; Novakova, L.; Perez, D.I.; Jun, D.; Kucera, T.; et al. Isoquinoline Alkaloids from Berberis vulgaris as Potential Lead Compounds for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A Visualization System for Exploratory Research and Analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated Docking with Selective Receptor Flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panek, D.; Więckowska, A.; Wichur, T.; Bajda, M.; Godyń, J.; Jończyk, J.; Mika, K.; Janockova, J.; Soukup, O.; Knez, D.; et al. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of new Phthalimide and Saccharin Derivatives with Alicyclic Amines Targeting Cholinesterases, Beta-secretase and Amyloid Beta Aggregation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 125, 676–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svobodova, B.; Mezeiova, E.; Hepnarova, V.; Hrabinova, M.; Muckova, L.; Kobrlova, T.; Jun, D.; Soukup, O.; Jimeno, M.L.; Marco-Contelles, J.; et al. Exploring Structure-Activity Relationship in Tacrine-Squaramide Derivatives as Potent Cholinesterase Inhibitors. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An Open Chemical Toolbox. J. Cheminf. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Compound | % Inhibition hAChE ± SEM a | IC50, hAChE ± SEM (µM) b | % Inhibition hBuChE ± SEM a | IC50, hBuChE ± SEM (µM) b | logBB c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9-O-demethyllycorenine (1) | 3.1 ± 1.2 | >100 | 30.2 ± 0.8 | >100 | n.c. |
| narciabduliine (2) | 94.7 ± 0.7 | 3.29 ± 0.73 | 94.1 ± 0.2 | 3.44 ± 0.02 | −0.36 |
| galantamine d | 98.8 ± 1.1 | 2.01 ± 0.14 | 68.2 ± 1.2 | 29.31 ± 3.49 | 0.05 |
| eserine d | 99.8 ± 0.6 | 0.20 ± 0.0.01 | 99.9 ± 0.5 | 0.30 ± 0.01 | −0.18 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maříková, J.; Mamun, A.A.; Shammari, L.A.; Korábečný, J.; Kučera, T.; Hulcová, D.; Kuneš, J.; Malaník, M.; Vašková, M.; Kohelová, E.; et al. Structure Elucidation and Cholinesterase Inhibition Activity of Two New Minor Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids. Molecules 2021, 26, 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051279
Maříková J, Mamun AA, Shammari LA, Korábečný J, Kučera T, Hulcová D, Kuneš J, Malaník M, Vašková M, Kohelová E, et al. Structure Elucidation and Cholinesterase Inhibition Activity of Two New Minor Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids. Molecules. 2021; 26(5):1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051279
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaříková, Jana, Abdullah Al Mamun, Latifah Al Shammari, Jan Korábečný, Tomáš Kučera, Daniela Hulcová, Jiří Kuneš, Milan Malaník, Michaela Vašková, Eliška Kohelová, and et al. 2021. "Structure Elucidation and Cholinesterase Inhibition Activity of Two New Minor Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids" Molecules 26, no. 5: 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051279
APA StyleMaříková, J., Mamun, A. A., Shammari, L. A., Korábečný, J., Kučera, T., Hulcová, D., Kuneš, J., Malaník, M., Vašková, M., Kohelová, E., Nováková, L., Cahlíková, L., & Pour, M. (2021). Structure Elucidation and Cholinesterase Inhibition Activity of Two New Minor Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids. Molecules, 26(5), 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051279