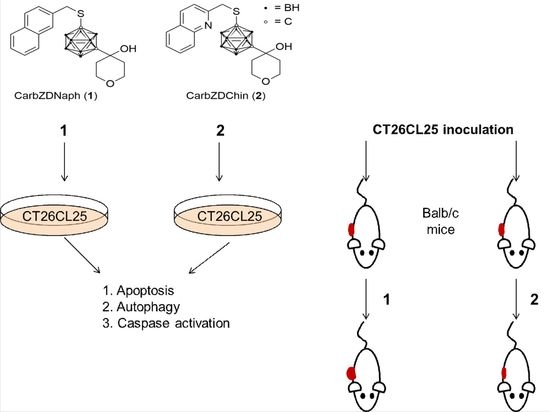
Carborane-Based Analog of Rev-5901 Attenuates Growth of Colon Carcinoma In Vivo
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Compounds 1 and 2 Induce Apoptosis, Activate Caspases and Cytoprotective Autophagy
2.2. Intracellular Signaling of 1 Activates MAPK, While 2 Activates the PI3K/Akt Pathway
2.3. Compound 2 Has an In Vivo Potency for Tumor Reduction
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Cells
4.2. Animals
4.3. Annexin V/Propidium Iodide Staining
4.4. Activation of Caspases
4.5. Detection of Autophagy
4.6. Western Blot
4.7. Induction of Colon Carcinoma and Animal Treatment
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Funk, C.D. Prostaglandins and Leukotrienes: Advances in Eicosanoid Biology. Science 2001, 294, 1871–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Samuelsson, B.; Dahlén, S.E.; Lindgren, J.A.; Rouzer, C.A.; Serhan, C.N. Leukotrienes and Lipoxins: Structures, Biosynthesis, and Biological Effects. Science 1987, 237, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, C.N. A Search for Endogenous Mechanisms of Anti-Inflammation Uncovers Novel Chemical Mediators: Missing Links to Resolution. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 122, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijón, M.A.; Spencer, D.M.; Kaiser, A.L.; Leslie, C.C. Role of Phosphorylation Sites and the C2 Domain in Regulation of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 145, 1219–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters-Golden, M.; Brock, T.G. Intracellular Compartmentalization of Leukotriene Synthesis: Unexpected Nuclear Secrets. FEBS Lett. 2001, 487, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montuschi, P. Leukotrienes, Antileukotrienes and Asthma. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werz, O.; Steinhilber, D. Therapeutic Options for 5-Lipoxygenase Inhibitors. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 112, 701–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Srivastava, M.; Ahmad, N.; Sakamoto, K.; Bostwick, D.G.; Mukhtar, H. Lipoxygenase-5 Is Overexpressed in Prostate Adenocarcinoma. Cancer 2001, 91, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, R.; Ding, X.Z.; Tong, W.G.; Schneider, M.B.; Standop, J.; Friess, H.; Büchler, M.W.; Pour, P.M.; Adrian, T.E. 5-Lipoxygenase and Leukotriene B(4) Receptor Are Expressed in Human Pancreatic Cancers but Not in Pancreatic Ducts in Normal Tissue. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 161, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohd, J.F.; Nielsen, C.K.; Campbell, J.; Landberg, G.; Löfberg, H.; Sjölander, A. Expression of the Leukotriene D4 Receptor CysLT1, COX-2, and Other Cell Survival Factors in Colorectal Adenocarcinomas. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, R.; Matsuyama, M.; Tsuchida, K.; Kawahito, Y.; Sano, H.; Nakatani, T. Expression of Lipoxygenase in Human Bladder Carcinoma and Growth Inhibition by Its Inhibitors. J. Urol. 2003, 170, 1994–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, M.; Yoshimura, R.; Mitsuhashi, M.; Tsuchida, K.; Takemoto, Y.; Kawahito, Y.; Sano, H.; Nakatani, T. 5-Lipoxygenase Inhibitors Attenuate Growth of Human Renal Cell Carcinoma and Induce Apoptosis through Arachidonic Acid Pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2005, 14, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, R.; Matsuyama, M.; Mitsuhashi, M.; Takemoto, Y.; Tsuchida, K.; Kawahito, Y.; Sano, H.; Nakatani, T. Relationship between Lipoxygenase and Human Testicular Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2004, 13, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasilewicz, M.P.; Kołodziej, B.; Bojułko, T.; Kaczmarczyk, M.; Sulzyc-Bielicka, V.; Bielicki, D.; Ciepiela, K. Overexpression of 5-Lipoxygenase in Sporadic Colonic Adenomas and a Possible New Aspect of Colon Carcinogenesis. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2010, 25, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, M.; Das, S.; Janarthan, M.; Ramachandran, H.K.; Chatterjee, M. Role of 5-Lipoxygenase in Resveratrol Mediated Suppression of 7,12-Dimethylbenz(α)Anthracene-Induced Mammary Carcinogenesis in Rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 668, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, M.; Shekhar, S.; Rai, N.; Kaur, P.; Parshad, R.; Dey, S. Serum 5-LOX: A Progressive Protein Marker for Breast Cancer and New Approach for Therapeutic Target. Carcinogenesis 2016, 37, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, J.F.; Ferguson, A.D.; Mosley, R.T.; Hutchinson, J.H. What’s All the FLAP about? 5-Lipoxygenase-Activating Protein Inhibitors for Inflammatory Diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 29, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, B.; Steinhilber, D. 5-Lipoxygenase Inhibitors: A Review of Recent Patents (2010–2012). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2013, 23, 895–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leśnikowski, Z.J. Challenges and Opportunities for the Application of Boron Clusters in Drug Design. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 7738–7758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.G.; Ding, X.Z.; Adrian, T.E. The Mechanisms of Lipoxygenase Inhibitor-Induced Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 296, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.Z.; Kuszynski, C.A.; El-Metwally, T.H.; Adrian, T.E. Lipoxygenase Inhibition Induced Apoptosis, Morphological Changes, and Carbonic Anhydrase Expression in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 266, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennig, R.; Grippo, P.; Ding, X.Z.; Rao, S.M.; Buchler, M.W.; Friess, H.; Talamonti, M.S.; Bell, R.H.; Adrian, T.E. 5-Lipoxygenase, a Marker for Early Pancreatic Intraepithelial Neoplastic Lesions. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6011–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuhnert, R.; Sárosi, M.B.; George, S.; Lönnecke, P.; Hofmann, B.; Steinhilber, D.; Steinmann, S.; Schneider-Stock, R.; Murganić, B.; Mijatović, S.; et al. Carborane-Based Analogues of 5-Lipoxygenase Inhibitors Co-Inhibit Heat Shock Protein 90 in HCT116 Cells. ChemMedChem. 2019, 14, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.S.; Metzner, J.; Steinbrink, S.D.; Ulrich, S.; Angioni, C.; Geisslinger, G.; Steinhilber, D.; Maier, T.J. 5-Lipoxygenase Inhibitors Induce Potent Anti-Proliferative and Cytotoxic Effects in Human Tumour Cells Independently of Suppression of 5-Lipoxygenase Activity. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 161, 936–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Datta, K.; Biswal, S.S.; Kehrer, J.P. The 5-Lipoxygenase-Activating Protein (FLAP) Inhibitor, MK886, Induces Apoptosis Independently of FLAP. Biochem. J. 1999, 340, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhilber, D.; Fischer, A.S.; Metzner, J.; Steinbrink, S.D.; Roos, J.; Ruthardt, M.; Maier, T.J. 5-Lipoxygenase: Underappreciated Role of a pro-Inflammatory Enzyme in Tumorigenesis. Front. Pharmacol. 2010, 1, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mulugeta, S.; Suzuki, T.; Hernandez, N.T.; Griesser, M.; Boeglin, W.E.; Schneider, C. Identification and Absolute Configuration of Dihydroxy-Arachidonic Acids Formed by Oxygenation of 5S-HETE by Native and Aspirin-Acetylated COX-2. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Homewood, C.A.; Warhurst, D.C.; Peters, W.; Baggaley, V.C. Lysosomes, PH and the Anti-Malarial Action of Chloroquine. Nature 1972, 235, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Shishodia, S.; Sandur, S.K.; Pandey, M.K.; Sethi, G. Inflammation and Cancer: How Hot Is the Link? Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 1605–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboubi-Rabbani, M.; Zarghi, A. Lipoxygenase Inhibitors as Cancer Chemopreventives: Discovery, Recent Developments and Future Perspectives. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 1143–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.X.; Ding, X.L.; Wu, S.B.; Zhang, H.F.; Cao, W.; Qu, L.S.; Zhang, H. Inhibition of 5-Lipoxygenase Triggers Apoptosis in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoque, A.; Lippman, S.M.; Wu, T.T.; Xu, Y.; Liang, Z.D.; Swisher, S.; Zhang, H.; Cao, L.; Ajani, J.A.; Xu, X.C. Increased 5-Lipoxygenase Expression and Induction of Apoptosis by Its Inhibitors in Esophageal Cancer: A Potential Target for Prevention. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Melstrom, L.G.; Bentrem, D.J.; Salabat, M.R.; Kennedy, T.J.; Ding, X.-Z.; Strouch, M.; Rao, S.M.; Witt, R.C.; Ternent, C.A.; Talamonti, M.S.; et al. Overexpression of 5-Lipoxygenase in Colon Polyps and Cancer and the Effect of 5-LOX Inhibitors in Vitro and in a Murine Model. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6525–6530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuhnert, R.; Sárosi, M.B.; George, S.; Lönnecke, P.; Hofmann, B.; Steinhilber, D.; Murganic, B.; Mijatovic, S.; Maksimovic-Ivanic, D.; Hey-Hawkins, E. CarbORev-5901: The First Carborane-Based Inhibitor of the 5-Lipoxygenase Pathway. ChemMedChem. 2017, 12, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, I.; Park, S.; Cho, J.W.; Yigitkanli, K.; van Leyen, K.; Roth, J. Genetic Ablation and Short-Duration Inhibition of Lipoxygenase Results in Increased Macroautophagy. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 321, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Ghiso, J.A.; Estrada, Y.; Liu, D.; Ossowski, L. ERK(MAPK) Activity as a Determinant of Tumor Growth and Dormancy; Regulation by P38(SAPK). Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1684–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, Y.Y.; Fraga, M.; Mackenzie, G.G.; Waterhouse, A.L.; Cremonini, E.; Oteiza, P.I. The PI3K/Akt Pathway Is Involved in Procyanidin-Mediated Suppression of Human Colorectal Cancer Cell Growth. Mol. Carcinog. 2016, 55, 2196–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Wang, M.H.; Zhou, J.D.; Chi, Q. Upregulation of MiR-542-3p Inhibits the Growth and Invasion of Human Colon Cancer Cells through PI3K/AKT/Survivin Signaling. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 3545–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Zhi, X.; Shi, S.; Tao, R.; Chen, P.; Sun, S.; Bian, L.; Xu, Z.; Ma, L. SPOCK1 Is Up-Regulated and Promotes Tumor Growth via the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway in Colorectal Cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaei, M.J.; Baghery Saghchy Khorasani, A.; Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi, A.; Shahrokh, S.; Zali, M.R.; Bashash, D. The PI3K/Akt/MTOR Axis in Colorectal Cancer: Oncogenic Alterations, Non-Coding RNAs, Therapeutic Opportunities, and the Emerging Role of Nanoparticles. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 237, 1720–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, M.; Hirata, N.; Suizu, F. The Links between AKT and Two Intracellular Proteolytic Cascades: Ubiquitination and Autophagy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2014, 1846, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.; Shu, R.; Yu, C.; Fu, Z.; Li, Z. Mammalian AKT, the Emerging Roles on Mitochondrial Function in Diseases. Aging Dis. 2022, 13, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; Guo, Y. Deoxyschizandrin Inhibits the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Bladder Cancer Cells through ALOX5 Regulating PI3K-AKT Signaling Pathway. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 3079823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahnt, A.S.; Angioni, C.; Göbel, T.; Hofmann, B.; Roos, J.; Steinbrink, S.D.; Rörsch, F.; Thomas, D.; Geisslinger, G.; Zacharowski, K.; et al. Inhibitors of Human 5-Lipoxygenase Potently Interfere with Prostaglandin Transport. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 782584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paskaš, S.; Murganić, B.; Kuhnert, R.; Hey-Hawkins, E.; Mijatović, S.; Maksimović-Ivanić, D. Carborane-Based Analog of Rev-5901 Attenuates Growth of Colon Carcinoma In Vivo. Molecules 2022, 27, 4503. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144503
Paskaš S, Murganić B, Kuhnert R, Hey-Hawkins E, Mijatović S, Maksimović-Ivanić D. Carborane-Based Analog of Rev-5901 Attenuates Growth of Colon Carcinoma In Vivo. Molecules. 2022; 27(14):4503. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144503
Chicago/Turabian StylePaskaš, Svetlana, Blagoje Murganić, Robert Kuhnert, Evamarie Hey-Hawkins, Sanja Mijatović, and Danijela Maksimović-Ivanić. 2022. "Carborane-Based Analog of Rev-5901 Attenuates Growth of Colon Carcinoma In Vivo" Molecules 27, no. 14: 4503. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144503
APA StylePaskaš, S., Murganić, B., Kuhnert, R., Hey-Hawkins, E., Mijatović, S., & Maksimović-Ivanić, D. (2022). Carborane-Based Analog of Rev-5901 Attenuates Growth of Colon Carcinoma In Vivo. Molecules, 27(14), 4503. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27144503