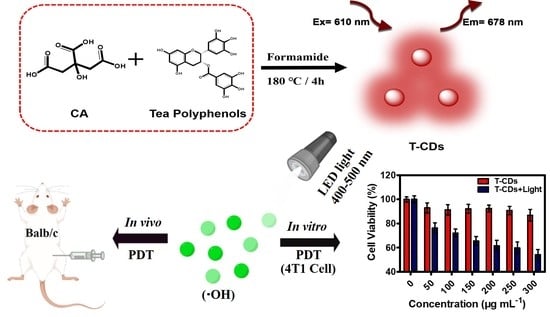
Carbon Dots Derived from Tea Polyphenols as Photosensitizers for Photodynamic Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of the T−CDs
2.2. Optical Properties of the T−CDs
2.3. ROS Production of the T−CDs
2.4. Biosafety Testing of the T−CDs
2.5. Photodynamic Application of the T−CDs
2.6. Biological Imaging Application of the T−CDs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of T−CDs
3.3. Characterization
3.4. Detection of the Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
3.5. Cell Culture and Cell Experiment
3.5.1. Cytotoxicity Test
3.5.2. Biological Imaging Stained with the T−CDs
3.5.3. Hemolysis Test
3.6. Animal Culture and Animal Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Dolmans, D.E.; Fukumura, D.; Jain, R.K. Photodynamic therapy for cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Li, B.; Li, C.; Fan, J.; Lei, Q.; Li, C.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X. Carbon−dot−decorated carbon nitride nanoparticles for enhanced photodynamic therapy against hypoxic tumor via water splitting. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 8715–8722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chilakamarthi, U.; Giribabu, L. Photodynamic therapy: Past, present and future. Chem. Rec. 2017, 17, 775–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Zheng, X.; Liu, S.; Zheng, M.; Xie, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yu, M.; Shuai, X. Diketopyrrolopyrrole−based carbon dots for photodynamic therapy. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 10991–10998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Choi, W.; Jangili, P.; Ge, Y.; Xu, Y.; Kang, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, B.; Xie, Z.; et al. Overcoming barriers in photodynamic therapy harnessing nano−formulation strategies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 9152–9201. [Google Scholar]
- Garin, C.; Alejo, T.; Vanesa, P.; Prieto, M.; Mendoza, G.; Arruebo, M.; Sebastian, V.; Rezusta, A.J. Chalcogenide nanoparticles and organic photosensitizers for synergetic antimicrobial photodynamic therapy. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 6246–6259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Guo, D. Type I photodynamic therapy by organic–inorganic hybrid materials: From strategies to applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 395, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, R.; Sibata, C. Oncologic photodynamic therapy photosensitizers: A clinical review. Photodiagn. Photodyn. 2010, 7, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Ham, X.; Li, S.; Abdulrahman, O.; Abdulaziz, S.; Mohammad, S.; Leblanc, R. Carbon dots: Biomacromolecule interaction, bioimaging and nanomedicine. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 343, 256–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Xu, N.; Fan, J.; Sun, W.; Peng, X. Carbon dots for in vivo bioimaging and theranostics. Small 2019, 15, 1805087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liang, Q.; Li, Z.; Osipov, V.; Lin, Y.; Ge, B.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Bi, H. Rational synthesis of solid−state ultraviolet B emitting carbon dots via acetic acid−promoted fractions of sp3 bonding strategy. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2200011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Lan, M.; Zhou, B.; Liu, W.; Guo, L.; Wang, H.; Jia, Q.; Niu, G.; Huang, X.; Zhou, H.; et al. A graphene quantum dot photodynamic therapy agent with high singlet oxygen generation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, Q.; Ge, J.; Liu, W.; Guo, L.; Zheng, X.; Chen, S.; Chen, M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; et al. Self−assembled carbon dot nanosphere: A robust, near−infrared light−responsive, and vein injectable photosensitizer. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Abbas, K.; Huang, X.; Zhang, R.; Tedesco, A.; Bi, H. F,N−Doped carbon dots as efficient Type I photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Ma, M.; Liang, Q.; Wu, X.; Abbas, K.; Zhu, J.; Xu, Q.; Tedesco, A.; Bi, H. Single−atom manganese anchored on carbon dots for promoting mitochondrial targeting and photodynamic effect in cancer treatment. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 6679–6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Chen, J.; Jiang, K.; Tang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Wu, A.; Lin, H. Ce6−modified carbon dots for multimodal−imaging−guided and single−NIR−laser−triggered photothermal/photodynamic synergistic cancer therapy by reduced irradiation power. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 5791–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Q.; Ge, J.; Liu, W.; Zheng, X.; Chen, S.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P. A magnetofluorescent carbon dot assembly as an acidic H2O2−driven oxygenerator to regulate tumor hypoxia for simultaneous bimodal imaging and enhanced photodynamic therapy. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, Q.; Landis, K.; Chen, D.; Huo, C.; Wan, S.; Chan, T. Green tea polyphenols as a natural tumour cell proteasome inhibitor. Inflammopharmacology 2008, 16, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Liang, Y.; Shiau, S. Cancer chemoprevention by tea polyphenols through mitotic signal transduction blockade. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 58, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, Y. (−)−Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) enhances the sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells to 5−FU by inhibiting GRP78/NF−κB/miR−155−5p/MDR1 pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2510–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.; Chen, P.; Ou, C.; Chang, H.; Chang, H. Extremely high inhibition activity of photoluminescent carbon nanodots toward cancer cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, X.; Ma, C.; Ge, C.; Yan, M.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Paulo, C.; Bi, H. Green synthesis of nitrogen−doped carbon dots from konjac flour with “off–on” fluorescence by Fe3+ and l−lysine for bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4631–4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Lv, X.; Qian, J.; Li, H.; Qian, Y.; Wang, X.; Meng, X.; Lin, W.; Wang, H. Graphitic carbon nitride quantum dots embedded in carbon nanosheets for near−infrared imaging−guided combined photo−chemotherapy. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 13304–13315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, K.; Wu, A.; Lin, H. Toward high−efficient red emissive carbon dots: Facile preparation, unique properties, and applications as multifunctional theranostic agents. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 8659–8668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, K.; Lin, H. Near−infrared emissive carbon dots for two−photon fluorescence bioimaging. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 17350–17356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Yang, S.; Song, Y.; Zhai, C.; Wang, Q.; Ding, G.; Kang, Z. Hydroxyl functionalized carbon dots with strong radical scavenging ability promote cell proliferation. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 065030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Tan, Z.; Fan, L.; Yang, S. Bright multicolor bandgap fluorescent carbon quantum dots for electroluminescent light-emitting diodes. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Meng, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhang, K.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, B. Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3953–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Liu, E.; Li, M.; Ushakova, E.; Kershaw, S.; Rogach, A.; Tang, Z.; Qu, S. Morphology control of luminescent carbon nanomaterials: From dots to rolls and belts. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yu, J.; Sui, L.; Zhu, S.; Tang, Z.; Yang, B.; Lu, S. Rational design of multi−color−emissive carbon dots in a single reaction system by hydrothermal. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2001453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Sui, L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, S.; Chen, A.; Jin, M.; Yang, B. Near−infrared photoluminescent polymer–carbon nanodots with two−photon fluorescence. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Ding, H.; Xu, M.; Hu, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Lu, S.; Tian, Y.; et al. UV–vis–NIR full−range responsive carbon dots with large multiphoton absorption cross sections and deep−red fluorescence at nucleoli and in vivo. Small 2020, 16, 2000680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shao, C.; Liu, T.; Chao, Z.; Chen, H.; Xiao, F.; He, H.; Wei, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. An NIR−II−emissive photosensitizer for hypoxia−tolerant photodynamic theranostics. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2003471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovic, Z.; Ristic, B.; Arsikin, K.; Klisic, D.; Trajkovic, L.; Markovic, B.; Kepic, D.; Stevovic, T.; Jovanovic, S.; Milenkovic, M.; et al. Graphene quantum dots as autophagy−inducing photodynamic agents. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7084–7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Wen, L.; Huang, R.; Wang, H.; Hu, X.; Xing, D. Mitochondrial specific photodynamic therapy by rare−earth nanoparticles mediated near−infrared graphene quantum dots. Biomaterials 2018, 153, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.W.; Bao, Y.; Zeng, J.; Wu, F. Nucleolus−targeted red emissive carbon dots with polarity−sensitive and excitation−independent fluorescence emission: High−resolution cell imaging and in vivo tracking. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 32647–32658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, R.; Tian, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, A.; Liu, R.; Liu, B.; Han, M.; Gao, X.; et al. Membrane−penetrating carbon quantum dots for imaging nucleic acid structures in live organisms. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.; Jia, C.; Wu, F.-G. Carbon Dots for Intracellular Sensing. Small Struct. 2022, 3, 2200033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Ding, H.; Li, Z.; Tedesco, A.C.; Bi, H. Carbon Dots Derived from Tea Polyphenols as Photosensitizers for Photodynamic Therapy. Molecules 2022, 27, 8627. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238627
Yang Y, Ding H, Li Z, Tedesco AC, Bi H. Carbon Dots Derived from Tea Polyphenols as Photosensitizers for Photodynamic Therapy. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8627. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238627
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yuxiang, Haizhen Ding, Zijian Li, Antonio Claudio Tedesco, and Hong Bi. 2022. "Carbon Dots Derived from Tea Polyphenols as Photosensitizers for Photodynamic Therapy" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8627. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238627
APA StyleYang, Y., Ding, H., Li, Z., Tedesco, A. C., & Bi, H. (2022). Carbon Dots Derived from Tea Polyphenols as Photosensitizers for Photodynamic Therapy. Molecules, 27(23), 8627. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238627