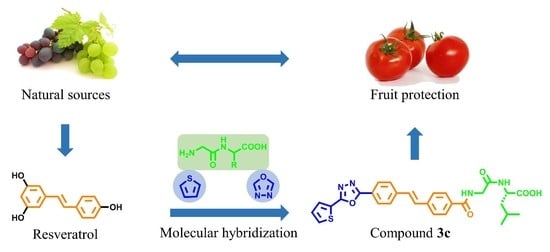
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Dipeptide-Based Stilbene Derivatives Bearing a Biheterocyclic Moiety as Potential Fungicides
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. In Vitro Antifungal Activities
2.3. Effect on Gray Mold of Tomatoes
2.4. Optical Microscopy Analysis
2.5. Effect on Cell Membrane Permeability
2.6. Effect on Mycelial Respiration
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Instrumentation
3.2. In Vitro Antifungal Test
3.3. In Vivo Assay against Tomato Gray Mold
3.4. Optical Microscopy of Hyphal Morphology of B. cinerea
3.5. Assessment of Cell Membrane Permeability
3.6. Determination of Oxygen Consumption
3.7. General Method for the Synthesis of Carboxylic Acid 2
3.8. General Method for the Synthesis of the Target Compounds
3.8.1. (E)-4-(4-(5-(Thiophen-2-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)styryl)benzoic acid (2)
3.8.2. (E)-(4-(4-(5-(Thiophen-2-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)styryl)benzoyl)glycylglycine (3a)
3.8.3. (E)-(4-(4-(5-(Thiophen-2-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)styryl)benzoyl)glycyl-L-methionine (3b)
3.8.4. (E)-(4-(4-(5-(Thiophen-2-yl)-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)styryl)benzoyl)glycyl-L-leucine (3c)
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Horbach, R.; Navarro-Quesada, A.R.; Knogge, W.; Deising, H.B. When and how to kill a plant cell: Infection strategies of plant pathogenic fungi. J. Plant Physiol. 2011, 168, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, R.; Van Kan, J.A.L.; Pretorius, Z.A.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; Di Pietro, A.; Spanu, P.D.; Rudd, J.J.; Dickman, M.; Kahmann, R.; Ellis, J.; et al. The Top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Zheng, X.J.; Khaskheli, M.I.; Sun, X.F.; Chang, X.L.; Gong, G.S. Identification of Colletotrichum species associated with blueberry anthracnose in Sichuan, China. Pathogens. 2020, 9, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noor, N.M.; Zakaria, L. Identification and characterization of Colletotrichum spp. associated with chili anthracnose in peninsular Malaysia. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2018, 151, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, E.; Gladieux, P.; Giraud, T. The ‘Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde fungus’: Noble rot versus gray mold symptoms of Botrytis cinerea on grapes. Evol. Appl. 2013, 6, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.H.; Song, M.H.; Keum, Y.S. Effects of azole fungicides on secreted metabolomes of Botrytis cinerea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 5309–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloukas, T.; Markoglou, A.N.; Karaoglanidis, G.S. Differential effect of SdhB gene mutations on the sensitivity to SDHI fungicides in Botrytis cinerea. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chambers, J.E.; Greim, H.; Kendall, R.J.; Segner, H.; Sharpe, R.M.; Van Der Kraak, G. Human and ecological risk assessment of a crop protection chemical: A case study with the azole fungicide epoxiconazole. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2014, 44, 176–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Wang, X.N.; Lou, H.X. Natural stilbenes: An overview. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 916–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Mendonsa, R.; Koli, M.; Subramanian, M.; Nayak, S.K. Antibacterial activity of resveratrol structural analogues: A mechanistic evaluation of the structure-activity relationship. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 367, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roupe, K.A.; Remsberg, C.M.; Yanez, J.A.; Davies, N.M. Pharmacometrics of stilbenes: Seguing towards the clinic. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 1, 81–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.D.; Deng, Y.Z.; Han, T.Y.; Jiang, L.Q.; Xi, P.G.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, Z.D.; Gao, L.W. In vitro and in vivo effectiveness of phenolic compounds for the control of postharvest gray mold of table grapes. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 139, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabaston, J.; Richard, T.; Biais, B.; Waffo-Teguo, P.; Pedrot, E.; Jourdes, M.; Corio-Costet, M.F.; Mérillon, J.M. Stilbenes from common spruce (Picea abies) bark as natural antifungal agent against downy mildew (Plasmopara viticola). Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 103, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Catana, F.; Yang, Y.N.; Roderick, R.; van Breemen, R.B. An LC-MS method for analyzing total resveratrol in grape juice, cranberry juice, and in wine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippis, B.; Ammazzalorso, A.; Amoroso, R.; Giampietro, L. Stilbene derivatives as new perspective in antifungal medicinal chemistry. Drug Dev. Res. 2019, 80, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbaghi, M.; Jeandet, P.; Bessis, R.; Leroux, P. Degradation of stilbene-type phytoalexins in relation to the pathogenicity of Botrytis cinerea to grapevines. Plant Pathol. 1996, 45, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.Q.; Liu, L.W.; Wang, P.Y.; Long, Q.S.; Zhao, Y.L.; Jin, L.H.; Xu, W.M.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, S. Synthesis and in vitro and in vivo biological activity evaluation and quantitative proteome profiling of oxadiazoles bearing flexible heterocyclic patterns. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7626–7639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.J.; Li, C.S.; Cui, M.Y.; Song, Z.W.; Bai, X.Q.; Liang, C.W.; Wan-g, H.Y.; Zhang, T.Y. Synthesis, biological evaluation of benzothiazole derivatives bearing a 1,3,4-oxadiazole moiety as potential anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Kumar, R.; Angeli, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Sharma, P.K. Tail approach synthesis of novel benzenesulfonamides incorporating 1,3,4-oxadiazole hybrids as potent inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase I, II, IX, and XII isoenzymes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 193, 112219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutani, R.; Pathak, D.P.; Kapoor, G.; Husain, A.; Iqbal, M.A. Novel hybrids of benzothiazole-1,3,4-oxadiazole-4-thiazolidinone: Synthesis, in silico ADME study, molecular docking and in vivo anti-diabetic assessment. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 83, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverio, M.R.S.; Espindola, L.S.; Lopes, N.P.; Vieira, P.C. Plant natural products for the control of Aedes aegypti: The main vector of important arboviruses. Molecules 2020, 25, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.T.; Wu, H.B.; Jiang, H.Y. Thiophenes from Echinops grijsii as a preliminary approach to control disease complex of root-knot nematodes and soil-borne fungi: Isolation, activities, and structure-nonphototoxic activity relationship analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 6160–6168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.L.; Shi, Y.X.; Zhan, Y.Z.; Zhang, L.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.H.; Li, Z.M.; Li, B.J. Synthesis and biological activity of novel furan/thiophene and piperazine-containing (bis)1,2,4-triazole Mannich bases. Chin. J. Chem. 2015, 33, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezugwu, J.A.; Okoro, U.C.; Ezeokonkwo, M.A.; Bhimapaka, C.R.; Okafor, S.N.; Ugwu, D.I.; Ekoh, O.C.; Attah, S.I. Novel Leu-Val based dipeptide as antimicrobial and antimalarial agents: Synthesis and molecular docking. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 583926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, T.; Greenfield, S.A. Bioactivity of a peptide derived from acetylcholinesterase in hippocampal organotypic cultures. Exp. Brain Res. 2004, 155, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, J.L.; Dunn, M.K. Therapeutic peptides: Historical perspectives, current development trends, and future directions. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2700–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudasheva, T.A. Theoretical grounds and technologies for dipeptide drug development. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2015, 64, 2012–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.Y.; Guo, H.X.; Chen, F.L.; Zhao, L.C.; He, L.P.; Ou, Y.W.; Huang, M.M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, B.Y.; Cao, Y.; et al. Antibacterial effects of a cell-pe-netrating peptide isolated from Kefir. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3234–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tareq, F.S.; Lee, M.A.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, J.S.; Hasan, C.M.; Islam, M.T.; Shin, H.J. Gageotetrins A-C, noncytotoxic antimicrobial linear lipopeptides from a marine bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 928–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.A.; Nasim, N.; Wang, Y.; Alhazmi, A.; Sanam, M.; Ul-Haq, Z.; Yalamati, D.; Ulanova, M.; Jiang, Z.H. Amphiphilic desmuramyl peptides for the rational design of new vaccine adjuvants: Synthesis, in vitro modulation of inflammatory response and molecular docking studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 209, 112863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Jia, C.; Gao, J.H.; Wang, R.D.; Zhang, L.X.; Sun, Q.; Huang, J.N. Structure-activity relationship and molecular docking analysis of cysteine-containing dipeptides as antioxidant and ACE inhibitory. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 2789–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, M.H.; Liu, H.C.; Yu, T.T.; Guo, P.; Liu, W.B.; Jin, X.B. Antimicrobial compounds were isolated from the secondary metabolites of gordonia, a resident of intestinal tract of Periplaneta americana. AMB Express 2021, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalaf, H.S.; Naglah, A.M.; Al-Omar, M.A.; Moustafa, G.O.; Awad, H.M.; Bakheit, A.H. Synthesis, docking, computational studies, and antimicrobial evaluations of new dipeptide derivatives based on nicotinoylglycylglycine hydrazide. Molecules 2020, 25, 3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Jian, W.L.; Shang, J.B.; He, D.H. Synthesis and antifungal activities of novel thiophene-based stilbene derivatives bearing an 1,3,4-oxadiazole unit. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monera, O.D.; Sereda, T.J.; Zhou, N.E.; Kay, C.M.; Hodges, R.S. Relationship of sidechain hydrophobicity and α-helical propensity on the stability of the single-stranded amphipathic α-helix. J. Pept. Sci. 1995, 1, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.S.; Zhang, S.; Yang, K.; Zhu, L.Z.; Lin, D.H. Toxicity of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoic acid to Escherichia coli: Membrane disruption, oxidative stress, and DNA damage induced cell inactivation and/or death. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serazetdinova, L.; Oldach, K.H.; Lörz, H. Expression of transgenic stilbene synthases in wheat causes the accumulation of unknown stilbene derivatives with antifungal activity. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 162, 985–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.J.; Liang, X.M.; Jin, S.H.; Lv, J.P.; Yu, C.X.; Qi, W.Y.; Li, B.J.; Yuan, H.Z.; Qi, S.H.; Shi, Y.X.; et al. Primary study on mode of action for macrocyclic fungicide candidates (7B3, D1) against Rhizoctonia solani Kühn. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2726–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, W.L.; He, D.H.; Xi, P.G.; Li, X.W. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel fluorine-containing stilbene derivatives as fungicidal agents against phytopathogenic fungi. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2015, 63, 9963–9969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Compound | Inhibition Rate (%) at 200 µg/mL a | EC50 (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| 3a | 73.0 ± 1.2 b | 119.6 |
| 3b | 74.8 ± 1.7 b | 116.3 |
| 3c | 79.6 ± 2.6 a | 106.1 |
| Carboxin | 77.9 ± 1.6 ab | 138.7 |
| Resveratrol b | 44.5 ± 1.2 c | 263.1 |
| Compound | Leision Length (mm) a | Control Efficacy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 3a | 24.7 ± 2.6 c | 55.2% |
| 3b | 24.3 ± 1.3 c | 56.1% |
| 3c | 23.0 ± 1.5 c | 59.1% |
| Carboxin | 30.5 ± 1.4 b | 42.0% |
| Resveratrol | 25.0 ± 2.2 c | 54.5% |
| CK b | 49.0 ± 1.0 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Lin, X.; Wen, L.; He, D. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Dipeptide-Based Stilbene Derivatives Bearing a Biheterocyclic Moiety as Potential Fungicides. Molecules 2022, 27, 8755. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248755
Zhu Y, Lin X, Wen L, He D. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Dipeptide-Based Stilbene Derivatives Bearing a Biheterocyclic Moiety as Potential Fungicides. Molecules. 2022; 27(24):8755. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248755
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yongchuang, Xingdong Lin, Lan Wen, and Daohang He. 2022. "Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Dipeptide-Based Stilbene Derivatives Bearing a Biheterocyclic Moiety as Potential Fungicides" Molecules 27, no. 24: 8755. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248755
APA StyleZhu, Y., Lin, X., Wen, L., & He, D. (2022). Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Dipeptide-Based Stilbene Derivatives Bearing a Biheterocyclic Moiety as Potential Fungicides. Molecules, 27(24), 8755. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248755