Neobaicalein Inhibits Th17 Cell Differentiation Resulting in Recovery of Th17/Treg Ratio through Blocking STAT3 Signaling Activation
Abstract
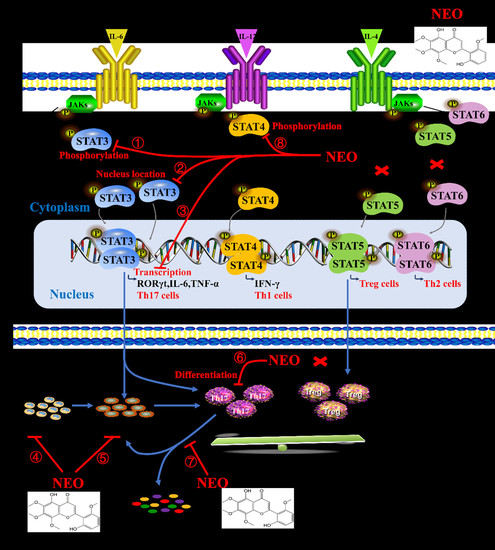
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. IL-17 Signaling Pathway Regulated by NEO Was Discovered Both RA, IBD and MS
2.2. NEO Significantly Inhibited ConA-Stimulated CD4+ T Proliferation
2.3. NEO Blocked CD4+ T Activation through Decreasing CD25 and CD69 Expression
2.4. NEO Restricted the Differentiation of CD4+ T Cells to Th17 Cells
2.5. NEO Extinguished Cytokine Secretion in the Process of Differentiation of CD4+ T Cells to Th17 Cells
2.6. NEO at a High Dose Reduced Treg Cell Differentiation
2.7. NEO Inhibited Phosphorylation of STAT3 and STAT3 Nucleus Translocation
2.8. ADME Properties and Drug-Likeness of NEO
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Network Pharmacology-Based Study
4.3. CCK8 Assay
4.4. Splenocytes Proliferation Assay
4.5. Splenocytes Activation Assay
4.6. T Cells Differentiation Assay
4.7. Cytometric Bead Array (CBA) Assay
4.8. Western Blot
4.9. Immunocytochemistry
4.10. Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.11. ADME and BBB Assay
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DMSO | Dimethylsulfoxide |
| FACS | Fluorescence Activating Cell Sorter |
| IBD | Inflammatory Bowel Disease |
| MMPs | Matrix Metalloproteinases |
| MS | Multiple Sclerosis |
| NEO | Neobaicalein |
| PBS | Phosphate Buffered Saline |
| RA | Rheumatoid Arthritis |
| RORγt | Retinoic acid receptor-related orphan nuclear receptor |
| STAT3 | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 |
| Th17 | T helper 17 |
| Treg | Regulatory T cells |
References
- Balasa, R.; Barcutean, L.; Balasa, A.; Motataianu, A.; Roman-Filip, C.; Manu, D. The action of TH17 cells on blood brain barrier in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Hum. Immunol. 2020, 81, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, F.S.; Gershwin, M.E. Human autoimmune diseases: A comprehensive update. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 278, 369–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuzawa-Carballeda, J.; Vargas-Rojas, M.I.; Cabral, A.R. Autoimmune inflammation from the Th17 perspective. Autoimmun. Rev. 2007, 6, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, T.; Su, R.; Wu, R.; Xue, H.; Wang, Y.; Su, R.; Gao, C.; Li, X.; Wang, C. Frontiers of Autoantibodies in Autoimmune Disorders: Crosstalk Between Tfh/Tfr and Regulatory B Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 641013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolff, S.; Witzke, O.; Wilde, B. Th17 cells in renal inflammation and autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffold, A.; Bacher, P. Anti-fungal T cell responses in the lung and modulation by the gut-lung axis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2020, 56, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wan, Y. Molecular control of pathogenic Th17 cells in autoimmune diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 80, 106187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, A.N.; Noorbakhsh, S.M.; Hamedifar, H.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Yazdani, R.; Bautista, J.M.; Azizi, G. A role for Th1-like Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and autoimmune disorders. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 105, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunte, K.; Beikler, T. Th17 Cells and the IL-23/IL-17 Axis in the Pathogenesis of Periodontitis and Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Lin, F.; Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xing, Y.; Deng, Z.; Yao, Z.; Tsun, A.; Li, B. FOXP3 and RORgammat: Transcriptional regulation of Treg and Th17. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oo, Y.H.; Banz, V.; Kavanagh, D.; Liaskou, E.; Withers, D.R.; Humphreys, E.; Reynolds, G.M.; Lee-Turner, L.; Kalia, N.; Hubscher, S.G.; et al. CXCR3-dependent recruitment and CCR6-mediated positioning of Th-17 cells in the inflamed liver. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tabarkiewicz, J.; Pogoda, K.; Karczmarczyk, A.; Pozarowski, P.; Giannopoulos, K. The Role of IL-17 and Th17 Lymphocytes in Autoimmune Diseases. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2015, 63, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kunwar, S.; Dahal, K.; Sharma, S. Anti-IL-17 therapy in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Rheumatol. Int. 2016, 36, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.K.; Chen, Z.; Larjo, A.; Kanduri, K.; Nousiainen, K.; Äijo, T.; Ricaño-Ponce, I.; Hrdlickova, B.; Tuomela, S.; Laajala, E.; et al. Genome-wide Analysis of STAT3-Mediated Transcription during Early Human Th17 Cell Differentiation. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1888–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Gholami, M.H.; Mirzaei, S.; Zabolian, A.; Haddadi, A.; Farahani, M.V.; Kashani, S.H.; Hushmandi, K.; Najafi, M.; Zarrabi, A.; et al. Dual relationship between long non-coding RNAs and STAT3 signaling in different cancers: New insight to proliferation and metastasis. Life Sci. 2021, 270, 119006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, G.R.; Cheon, H.; Wang, Y. Responses to Cytokines and Interferons that Depend upon JAKs and STATs. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a028555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parsafar, S.; Nayeri, Z.; Aliakbari, F.; Shahi, F.; Mohammadi, M.; Morshedi, D. Multiple neuroprotective features of Scutellaria pinnatifida-derived small molecule. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayarani-Najarani, Z.; Asili, J.; Parsaee, H.; Mousavi, S.H.; Mashhadian, N.V.; Mirzaee, A.; Emami, S.A. Wogonin and neobaicalein from Scutellaria litwinowii roots are apoptotic for HeLa cells. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2012, 22, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Lv, D.; Chen, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Hong, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Hu, X.; Cao, Y.; et al. Biosensor-Based Active Ingredients Recognition System for Screening STAT3 Ligands from Medical Herbs. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 8936–8945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano-Zaragoza, J.F.; Romo-Martínez, E.J.; Durán-Avelar, M.; García-Magallanes, N.; Vibanco-Pérez, N. Th17 cells in autoimmune and infectious diseases. Int. J. Inflam. 2014, 2014, 651503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.A.; Liu, M.; Nixon, B.G.; Kang, D.; Toure, A.; Bivona, M.; Li, M.O. Foxp3-independent mechanism by which TGF-beta controls peripheral T cell tolerance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7536–E7544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheng, W.; Yang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, H.; Low, P.Y.; Kemeny, D.M.; Tan, P.; Moh, A.; Kaplan, M.H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. STAT5 programs a distinct subset of GM-CSF-producing T helper cells that is essential for autoimmune neuroinflammation. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 1387–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dardalhon, V.; Korn, T.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Anderson, A.C. Role of Th1 and Th17 cells in organ-specific autoimmunity. J. Autoimmun. 2008, 31, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, L.; Xu, Y.; Yang, M.; Xu, Y.; Komaniecki, G.P.; Kosciuk, T.; Chen, X.; Lu, X.; Zou, X.; et al. A STAT3 palmitoylation cycle promotes TH17 differentiation and colitis. Nature 2020, 586, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Niu, Y.; Ren, R.; Su, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Ma, X. Beneficial effects of mijianchangpu decoction on ischemic stroke through components accessing to the brain based on network pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 285, 114882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Chang, D.; Zhuang, S.; Xu, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Nan, L.; et al. Effect of dendrobium mixture in alleviating diabetic cognitive impairment associated with regulating gut microbiota. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 149, 112891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tian, X.; Liu, W.; Wu, B.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, X.; et al. Importance of Gedunin in Antagonizing Rheumatoid Arthritis via Activating the Nrf2/ARE Signaling. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 6277760. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, G.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, B.; Zheng, W.; Ma, X.; Zheng, Y. 7-deacetyl-gedunin suppresses proliferation of Human rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblast through activation of Nrf2/ARE signaling. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 107, 108557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Meena, A.; Luqman, S.; Meena, A. Acacetin and pinostrobin as a promising inhibitor of cancer-associated protein kinases. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 151, 112091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.S.; Abbas, S.Q.; Ali, F.; Ishaq, M.; Bano, I.; Hassan, M.; Jin, H.-Z.; Bungau, S.G. A Comprehensive in silico exploration of pharmacological properties, bioactivities, molecular docking, and anticancer potential of vieloplain F from Xylopia vielana Targeting B-Raf Kinase. Molecules 2022, 27, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Properties | Parameters | Neobaicalein |
|---|---|---|
| Physicochemical Properties | MWa (g/mol) | 374.34 |
| Rotatable bonds | 5 | |
| H-Bond Acceptors | 8 | |
| H-Bond Donors | 2 | |
| Fraction Csp3 | 0.21 | |
| TPSA | 107.59 Ų | |
| Lipophilicity Log Po/w | iLOGP | 3.11 |
| XLOGP3 | 2.91 | |
| MLOGP | −0.12 | |
| Consensus | 2.4 | |
| Absorption | Water solubility | −4.10 |
| GI absorption | High | |
| Log Kp (skin permeation) cm/s | −6.52 | |
| Metabolism | CYP1A2 inhibitor | Yes |
| CYP2C9 inhibitor | Yes | |
| CYP2C19 inhibitor | No | |
| CYP3A4 inhibitor | Yes | |
| CYP2D6 inhibitor | No | |
| BBB | No | |
| P-gp substrate | No | |
| Drug-likeness | Lipinski | Yes |
| Ghose | Yes | |
| Veber | Yes | |
| Egan | Yes | |
| Muegge | Yes | |
| Bioavailability score | 0.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.-Y.; Yang, Y.-J.; Ma, X.-Q.; Cao, Q.; Wei, S.-S.; Pan, R.-R.; Nan, L.-H.; Liu, Y.-J.; Cao, Y.; Tian, X.-Y.; et al. Neobaicalein Inhibits Th17 Cell Differentiation Resulting in Recovery of Th17/Treg Ratio through Blocking STAT3 Signaling Activation. Molecules 2023, 28, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010018
Chen J-Y, Yang Y-J, Ma X-Q, Cao Q, Wei S-S, Pan R-R, Nan L-H, Liu Y-J, Cao Y, Tian X-Y, et al. Neobaicalein Inhibits Th17 Cell Differentiation Resulting in Recovery of Th17/Treg Ratio through Blocking STAT3 Signaling Activation. Molecules. 2023; 28(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jian-Yu, Ying-Jie Yang, Xue-Qin Ma, Qi Cao, Shan-Shan Wei, Rong-Rong Pan, Li-Hong Nan, Yao-Jun Liu, Yan Cao, Xiao-Yun Tian, and et al. 2023. "Neobaicalein Inhibits Th17 Cell Differentiation Resulting in Recovery of Th17/Treg Ratio through Blocking STAT3 Signaling Activation" Molecules 28, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010018
APA StyleChen, J. -Y., Yang, Y. -J., Ma, X. -Q., Cao, Q., Wei, S. -S., Pan, R. -R., Nan, L. -H., Liu, Y. -J., Cao, Y., Tian, X. -Y., Deng, S., Cheng, Z. -X., Wang, C. -J., Chen, T., Zheng, Y. -F., & Huang, M. -Q. (2023). Neobaicalein Inhibits Th17 Cell Differentiation Resulting in Recovery of Th17/Treg Ratio through Blocking STAT3 Signaling Activation. Molecules, 28(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010018