Advancements in Portable Voltammetry: A Promising Approach for Iron Speciation Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthetic Solutions
2.2. Certified Reference Material
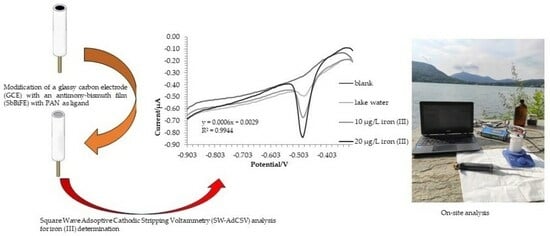
2.3. Water Samples
3. Material and Method
3.1. Instruments
3.2. Reagents
3.3. Preparation of –SbBiFE-GCE
3.4. Parameters for Iron Determination
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagajyoti, P.C.; Lee, K.D.; Sreekanth, T.V.M. Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2010, 8, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statham, P.J.; Jacobson, Y.; Van Den Berg, C.M.G. The measurement of organically complexed FeII in natural waters using competitive ligand reverse titration. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 743, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopwood, M.J.; Birchill, A.J.; Gledhill, M.; Achterberg, E.P.; Klar, J.K.; Milne, A. A Comparison between Four Analytical Methods for the Measurement of Fe(II) at Nanomolar Concentrations in Coastal Seawater. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Rees, N.V.; Kabakaev, A.S.; Compton, R.G. Determination of Iron: Electrochemical Methods. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 1693–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Millero, F.J. The solubility of iron in seawater. Mar. Chem. 2002, 77, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowie, A.R.; Maldonado, M.T.; Frew, R.D.; Croot, P.L.; Achterberg, E.P.; Mantoura, R.C.; Worsfold, P.J.; Law, C.S.; Boyd, P.W. The fate of added iron during a mesoscale fertilisation experiment in the Southern Ocean. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2001, 48, 2703–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, M.L. The level of iron enrichment required to initiate diatom blooms in HNLC waters. Mar. Chem. 2003, 82, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, P.W.; Ellwood, M.J. The biogeochemical cycle of iron in the ocean. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecca, L.; Youdim, M.B.H.; Riederer, P.; Connor, J.R.; Crichton, R.R. Iron, brain ageing and neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.J.; Zucca, F.A.; Duyn, J.H.; Crichton, R.R.; Zecca, L. The role of iron in brain ageing and neurodegenerative disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-L.; Fan, Y.-G.; Yang, Z.-S.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Guo, C. Iron and Alzheimer’s Disease: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Implications. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasiecki, J.; Targońska, M.; Wasąg, B. The Role of Butyrylcholinesterase and Iron in the Regulation of Cholinergic Network and Cognitive Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.; Lee, H.J. Redox-Active Metal Ions and Amyloid-Degrading Enzymes in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baringer, S.L.; Simpson, I.A.; Connor, J.R. Brain iron acquisition: An overview of homeostatic regulation and disease dysregulation. J. Neurochem. 2023, 165, 625–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, X.; Geng, X.; Wang, F. Meta-analysis of iron metabolism markers levels of Parkinson’s disease patients determined by fluid and MRI measurements. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2023, 78, 127190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laglera, L.M.; Monticelli, D. Iron detection and speciation in natural waters by electrochemical techniques: A critical review. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2017, 3, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuculić, V.; Pižeta, I.; Branica, M. Voltammetry of Dissolved Iron(III)-Nitrilotriacetate-Hydroxide System in Water Solution. Electroanalysis 2005, 17, 2129–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualhaija, M.M.; Van Den Berg, C.M.G. Chemical speciation of iron in seawater using catalytic cathodic stripping voltammetry with ligand competition against salicylaldoxime. Mar. Chem. 2014, 164, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, E.; Göktug, Ö.; İnam, R.; Doyduk, D. Development and characterization of iron (III) phthalocyanine modified carbon nanotube paste electrodes and application for determination of fluometuron herbicide as an electrochemical sensor. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 895, 115389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukosav, P.; Mlakar, M. Speciation of biochemically important iron complexes with amino acids: L-aspartic acid and L-aspartic acid—Glycine mixture. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 139, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Huis, A. Edible Insects: Future Prospects for Food and Feed Security. In FAO Forestry Paper, No. 171; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gledhill, M.; Van Den Berg, C.M.G. Measurement of the redox speciation of iron in seawater by catalytic cathodic stripping voltammetry. Mar. Chem. 2013, 50, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, H.; Fukushima, M.; Yamamoto, M. Determination of Labile Fe(II) Species Complexed with Seawater Extractable Organic Matter Under Seawater Conditions Based on the Kinetics of Ligand-exchange Reactions with Ferrozine. Anal. Sci. 2013, 29, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laglera, L.M.; Caprara, S.; Monticelli, D. Towards a zero-blank, preconcentration-free voltammetric method for iron analysis at picomolar concentrations in unbuffered seawater. Talanta 2016, 150, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanvito, F.; Pacileo, L.; Monticelli, D. Fostering and Understanding Iron Detection at the Ultratrace Level by Adsorptive Stripping Voltammetry with Catalytic Enhancement. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, M.M.; Hassanein, A.M.; Hammam, E.; Beltagi, A.M. Simultaneous determination of Cd, Pb, Cu, Sb, Bi, Se, Zn, Mn, Ni, Co and Fe in water samples by differential pulse stripping voltammetry at a hanging mercury drop electrode. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 2000, 367, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croot, P.L.; Johansson, M. Determination of Iron Speciation by Cathodic Stripping Voltammetry in Seawater Using the Competing Ligand 2-(2-Thiazolylazo)-p-cresol (TAC). Electroanalysis 2000, 12, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z. Determination of iron with chemically-modified carbon-paste electrodes. Talanta 1991, 38, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholivand, M.B.; Geravandi, B.; Parvin, M.H. Anodic Stripping Voltammetric Determination of Iron(II) at a Carbon Paste Electrode Modified with Dithiodianiline (DTDA) and Gold Nanoparticles (GNP). Electroanalysis 2011, 23, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugo, P.; Moretto, L.M.; De Boni, A.; Scopece, P.; Mazzocchin, G.A. Iron(II) and iron(III) determination by potentiometry and ion-exchange voltammetry at ionomer-coated electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 474, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stozhko, N.Y.; Inzhevatova, O.V.; Kolyadina, L.I. Determination of Iron in Natural and Drinking Waters by Stripping Voltammetry. J. Anal. Chem. 2005, 60, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.; Chaar, J.; Baldan, M.; Braga, N. Simultaneous voltammetric detection of Fe3+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Pb2+ e Cd2+ in fuel ethanol using anodic stripping voltammetry and boron-doped diamond electrodes. Fuel 2021, 291, 120104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, R.; Toral, M.I.; Arancibia, V. Determination of iron in water samples by adsorptive stripping voltammetry with a bismuth film electrode in the presence of 1-(2-piridylazo)-2-naphthol. Talanta 2008, 75, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobrowski, A.; Nowak, K.; Zarębski, J. Application of a bismuth film electrode to the voltammetric determination of trace iron using a Fe(III)–TEA–BrO3− catalytic system. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 382, 1691–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Zhuang, X.; Ni, S.; Luan, F.; Wu, X.; Yu, S. An Electrochemical Sensor Based on Gold and Bismuth Bimetallic Nanoparticles Decorated L-Cysteine Functionalized Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites for Sensitive Detection of Iron Ions in Water Samples. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shervedani, R.K.; Hatefi-Mehrjardi, A.; Asadi-Farsani, A. Sensitive determination of iron(III) by gold electrode modified with 2-mercaptosuccinic acid self-assembled monolayer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 601, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Yu, J.; Wei, L.; Zhao, Q.; Ren, L.; Hu, Z. Electrochemical sensor based on N-CQDs/AgNPs/β-CD nanomaterials: Application to simultaneous selective determination of Fe(II) and Fe(III) irons released from iron supplement in simulated gastric fluid. Talanta 2023, 253, 123959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statham, P.J.; Hart, V. Dissolved iron in the Cretan Sea (eastern Mediterranean). Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficiarà, E.; Boschi, S.; Ansari, S.; D’Agata, F.; Abollino, O.; Caroppo, P.; Di Fede, G.; Indaco, A.; Rainero, I.; Guiot, C. Machine Learning Profiling of Alzheimer’s Disease Patients Based on Current Cerebrospinal Fluid Markers and Iron Content in Biofluids. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 607858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Test | Bi Concentration (mg L−1) | Sb Concentration (mg L−1) | Deposition Time (s) | Accuracy (% of Recovery) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 300 | 200 | 300 | 76.7 |
| 2 | 300 | 200 | 120 | n.d. |
| 3 | 300 | 200 | 30 | n.d. |
| 4 | 100 | 50 | 300 | 95.3 |
| 5 | 100 | 50 | 120 | 89.8 |
| 6 | 100 | 50 | 30 | 88.7 |
| 7 | 20 | 10 | 300 | 80.5 |
| 8 | 20 | 10 | 120 | n.d. |
| 9 | 20 | 10 | 30 | n.d. |
| WE | Analyte | Repeatability (RSD %, n = 3) | Linearity | LOD * (μg L−1) | LOQ * (μg L−1) | Accuracy (% Recovery) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SbBiFE | Iron (III) | 3.05 | y = 0.056x + 0.0308 R2 = 0.9978 | 0.54 | 1.78 | 95.4 |
| Analyte | Theoretical Concentration Prepared (μg L−1) | Results with ICP-OES (μg L−1) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iron (II) | 1000 | 1058 | 105.8 |
| Iron (III) | 1000 | 1034 | 103.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Inaudi, P.; Abollino, O.; Argenziano, M.; Malandrino, M.; Guiot, C.; Bertinetti, S.; Favilli, L.; Giacomino, A. Advancements in Portable Voltammetry: A Promising Approach for Iron Speciation Analysis. Molecules 2023, 28, 7404. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217404
Inaudi P, Abollino O, Argenziano M, Malandrino M, Guiot C, Bertinetti S, Favilli L, Giacomino A. Advancements in Portable Voltammetry: A Promising Approach for Iron Speciation Analysis. Molecules. 2023; 28(21):7404. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217404
Chicago/Turabian StyleInaudi, Paolo, Ornella Abollino, Monica Argenziano, Mery Malandrino, Caterina Guiot, Stefano Bertinetti, Laura Favilli, and Agnese Giacomino. 2023. "Advancements in Portable Voltammetry: A Promising Approach for Iron Speciation Analysis" Molecules 28, no. 21: 7404. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217404
APA StyleInaudi, P., Abollino, O., Argenziano, M., Malandrino, M., Guiot, C., Bertinetti, S., Favilli, L., & Giacomino, A. (2023). Advancements in Portable Voltammetry: A Promising Approach for Iron Speciation Analysis. Molecules, 28(21), 7404. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217404