On-Chip Antifouling Gel-Integrated Microelectrode Arrays for In Situ High-Resolution Quantification of the Nickel Fraction Available for Bio-Uptake in Natural Waters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Influence of Nioxime Concentration and pH on the Voltammetric Response
2.2. Sensor Sensitivity and Limit of Detection
2.3. Temperature Correction Factor for In Situ Measurements
2.4. Evaluation and Validation of the Analytical Method
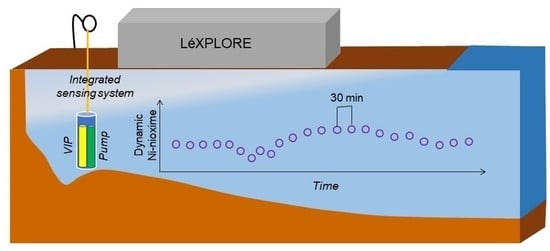
2.5. Field Application in Lake Geneva
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical and Instrumentation
3.2. Design and Preparation of the Hg-GIME
3.3. Apparatus and Operating Conditions
3.4. Field Test Area and Sample Collection
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cempel, M.; Nikel, G. Nickel: A Review of Its Sources and Environmental Toxicology. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2006, 15, 375–382. [Google Scholar]
- Dupont, C.L.; Buck, K.N.; Palenik, B.; Barbeau, K. Nickel Utilization in Phytoplankton Assemblages from Contrasting Oceanic Regimes. Deep Sea Res. Part Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2010, 57, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.A.; Strzepek, R.; Willis, A.; Ferderer, A.; Bach, L.T. Investigating the Effect of Nickel Concentration on Phytoplankton Growth to Assess Potential Side-Effects of Ocean Alkalinity Enhancement. Biogeosciences 2022, 19, 3683–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WFD-2013/39/EU. Directive 2013/39/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 August 2013 Amending Directives 2000/60/EC and 2008/105/EC as Regards Priority Substances in the Field of Water Policy. Off. J. Eur. Union 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Anzeec, A. Australian and New Zealand Guidelines for Fresh and Marine Water Quality. Natl. Water Qual. Manag. Strategy 2000, 1, 1–314. [Google Scholar]
- Brix, K.V.; Schlekat, C.E.; Garman, E.R. The Mechanisms of Nickel Toxicity in Aquatic Environments: An Adverse Outcome Pathway Analysis: Adverse Outcome Pathway for Ni. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tercier-Waeber, M.-L.; Stoll, S.; Slaveykova, V. Trace metal behavior in surface waters: Emphasis on dynamic speciation, sorption processes and bioavailability. Arch. Sci. 2012, 65, 119–142. [Google Scholar]
- Abdou, M.; Tercier-Waeber, M.-L.; Dutruch, L.; Bossy, C.; Pougnet, F.; Coynel, A.; Bakker, E.; Blanc, G.; Schäfer, J. Estuarine Dissolved Speciation and Partitioning of Trace Metals: A Novel Approach to Study Biogeochemical Processes. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdou, M.; Tercier-Waeber, M.-L. New Insights into Trace Metal Speciation and Interaction with Phytoplankton in Estuarine Coastal Waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 181, 113845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layglon, N.; Abdou, M.; Massa, F.; Castellano, M.; Bakker, E.; Povero, P.; Tercier-Waeber, M.-L. Speciation of Cu, Cd, Pb and Zn in a Contaminated Harbor and Comparison to Environmental Quality Standards. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tercier-Waeber, M.-L.; Confalonieri, F.; Abdou, M.; Dutruch, L.; Bossy, C.; Fighera, M.; Bakker, E.; Graziottin, F.; van der Wal, P.; Schäfer, J. Advanced Multichannel Submersible Probe for Autonomous High-Resolution in Situ Monitoring of the Cycling of the Potentially Bioavailable Fraction of a Range of Trace Metals. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tercier-Waeber, M.-L.; Hezard, T.; Masson, M.; Schäfer, J. In Situ Monitoring of the Diurnal Cycling of Dynamic Metal Species in a Stream under Contrasting Photobenthic Biofilm Activity and Hydrological Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7237–7244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmont-Hebert, C.; Tercier, M.L.; Buffle, J.; Fiaccabrino, G.C.; Rooij, N.F.; Koudelka-Hep, M. Gel-Integrated Microelectrode Arrays for Direct Voltammetric Measurements of Heavy Metals in Natural Waters and Other Complex Media. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 2949–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tercier, M.-L.; Buffle, J. Antifouling Membrane-Covered Voltammetric Microsensor for in Situ Measurements in Natural Waters. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 3670–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tercier-Waeber, M.-L.; Fighera, M.; Abdou, M.; Bakker, E.; van der Wal, P. Newly Designed Gel-Integrated Nanostructured Gold-Based Interconnected Microelectrode Arrays for Continuous in Situ Arsenite Monitoring in Aquatic Systems. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 328, 128996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tercier-Waeber, M.-L.; Abdou, M.; Fighera, M.; Kowal, J.; Bakker, E.; van der Wal, P. In Situ Voltammetric Sensor of Potentially Bioavailable Inorganic Mercury in Marine Aquatic Systems Based on Gel-Integrated Nanostructured Gold-Based Microelectrode Arrays. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touilloux, R.; Tercier-Waeber, M.L.; Bakker, E. Antifouling Membrane Integrated Renewable Gold Microelectrode for in Situ Detection of As (III). Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 7503–7510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tercier-Waeber, M.L.; Taillefert, M. Remote in situ voltammetric techniques to characterize the biogeochemical cycling of trace metals in aquatic systems. J. Environ. Monit. 2008, 10, 30–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illuminati, S.; Annibaldi, A.; Truzzi, C.; Tercier-Waeber, M.L.; Noel, S.; Braungardt, C.B.; Achterberg, E.P.; Howell, K.A.; Turner, D.; Marini, M.; et al. In-Situ Trace Metal (Cd, Pb, Cu) Speciation along the Po River Plume (Northern Adriatic Sea) Using Submersible Systems. Mar. Chem. 2019, 212, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, M.; Tercier-Waeber, M.L. Trace Metal Speciation at the Sediment-Water Interface of Vidy Bay: Influence of Contrasting Sediment Characteristics. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 76, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buffle, J.; Tercier-Waeber, M.-L. Voltammetric Environmental Trace-Metal Analysis and Speciation: From Laboratory to in Situ Measurements. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2005, 24, 172–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tercier-Waeber, M.L.; Buffle, J.; Koudelka-Hep, M.; Graziottin, F. Submersible Voltammetric Probes for In Situ Real-Time Trace Element Monitoring in Natural Aquatic Systems. In Environmental Electrochemistry: Analysis of Trace Element Biogeochemistry; American Chemical Society Symposium Series No. 811; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; Chapter 2, 16–39. [Google Scholar]
- Buffle, J.; Tercier-Waeber, M.-L. In situ Voltammetry: Concepts and Practice for Trace Analysis and Speciation. In In-Situ Monitoring of Aquatic Systems: Chemical Analysis and Speciation; Buffle, J., Horvai, G., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2000; Chapter 9, 279–405. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, J.; Pathirathna, P.; Hashemi, P. Novel Frontiers in Voltammetric Trace Metal Analysis: Towards Real Time, on-Site, in Situ Measurements. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 111, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layglon, N.; Creffield, S.; Bakker, E.; Tercier-Waeber, M.-L. On-Field High-Resolution Quantification of the Cobalt Fraction Available for Bio-Uptake in Natural Waters Using Antifouling Gel-Integrated Microelectrode Arrays. Rev. Mar. Pollut. Bull.
- Tercier, M.-L.; Buffle, J.; Graziottin, F. A Novel Voltammetric In-Situ Profiling System for ContinuousReal-Time Monitoring of Trace Elements in Natural Waters. Electroanalysis 1998, 10, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeloju, S.B.; Hadjichari, A. Simultaneous Determination of Nickel and Cobalt in Natural Water and Sediment Samples on an In-Situ Plated Mercury Film Electrode by Adsorptive Cathodic Stripping Voltammetry. Anal. Sci. 1999, 15, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, G.M.S.; Magalhães, J.M.C.S.; Soares, H.M.V.M. Simultaneous Determination of Nickel and Cobalt Using a Solid Bismuth Vibrating Electrode by Adsorptive Cathodic Stripping Voltammetry. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S. Metal-Metal Bonds and Physical Properties of Some Nickel (II)-Vic-Dioxime Complexes. Ph.D. Thesis, Iowa State University, Digital Repository, Ames, IA, USA, 1962; p. 6137117. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla, V.; Serrano, N.; Díaz-Cruz, J.M. Determination of Trace Levels of Nickel(II) by Adsorptive Stripping Voltammetry Using a Disposable and Low-Cost Carbon Screen-Printed Electrode. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tercier-Waeber, M.-L.; Confalonieri, F.; Koudelka-Hep, M.; Dessureault-Rompré, J.; Graziottin, F.; Buffle, J. Gel-Integrated Voltammetric Microsensors and Submersible Probes as Reliable Tools for Environmental Trace Metal Analysis and Speciation. Electroanalysis 2008, 20, 240–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penezic, A.; Tercier-Waeber, M.L.; Abdou, M.; Bossy, C.; Dutruch, L.; Bakker, E.; Schafer, J. Spatial Variability of Arsenic Speciation in the Gironde Estuary: Emphasis on Dynamic (Potentially Bioavailable) Inorganic Arsenite and Arsenate Fractions. Mar. Chem. 2020, 223, 103804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.J.; Janssen, F.; Polerecky, L.; Herlory, O.; de Beer, D. Phototrophic Biofilm Activity and Dynamics of Diurnal Cd Cycling in a Freshwater Stream. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7245–7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tercier, M.-L.; Parthasarathy, N.; Buffle, J. Reproducible, Reliable and Rugged Hg-Plated Ir-Based Microelectrode for in Situ Measurements in Natural Waters. Electroanalysis 1995, 7, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sensitivity (nA nM−1 min−1) | LOD 90 s (nM) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni(II) | Synthetic media (n = 3) | pH 8.5 | 1.42 ± 0.06 | 0.39 ± 0.04 |
| Freshwater (n = 3) | pH 8.5 | 1.75 ± 0.12 | 0.43 ± 0.06 | |
| Seawater (n = 3) | pH8.1 | 1.66 ± 0.15 | 0.34 ± 0.02 |
| ICP-MS Ni0.2 (nM) | Hg-GIME Ad-SWCSV | Ni0.2 Recovery Ad-SWCSV /ICP-MS (%) | NiDyn/Ni0.2 ICP-MS (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni0.2 (nM) | NiDyn (nM) | ||||
| Freshwater | 9.22 ± 0.02 | 10.00 ± 0.75 | 2.41 ± 0.09 | 108 ± 8 | 27 |
| Seawater | 7.27 ± 0.25 | 9.32 ± 0.86 | 0.94 ± 0.04 | 128 ± 7 | 13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Creffield, S.; Tercier-Waeber, M.-L.; Gressard, T.; Bakker, E.; Layglon, N. On-Chip Antifouling Gel-Integrated Microelectrode Arrays for In Situ High-Resolution Quantification of the Nickel Fraction Available for Bio-Uptake in Natural Waters. Molecules 2023, 28, 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031346
Creffield S, Tercier-Waeber M-L, Gressard T, Bakker E, Layglon N. On-Chip Antifouling Gel-Integrated Microelectrode Arrays for In Situ High-Resolution Quantification of the Nickel Fraction Available for Bio-Uptake in Natural Waters. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031346
Chicago/Turabian StyleCreffield, Sébastien, Mary-Lou Tercier-Waeber, Tanguy Gressard, Eric Bakker, and Nicolas Layglon. 2023. "On-Chip Antifouling Gel-Integrated Microelectrode Arrays for In Situ High-Resolution Quantification of the Nickel Fraction Available for Bio-Uptake in Natural Waters" Molecules 28, no. 3: 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031346
APA StyleCreffield, S., Tercier-Waeber, M. -L., Gressard, T., Bakker, E., & Layglon, N. (2023). On-Chip Antifouling Gel-Integrated Microelectrode Arrays for In Situ High-Resolution Quantification of the Nickel Fraction Available for Bio-Uptake in Natural Waters. Molecules, 28(3), 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031346