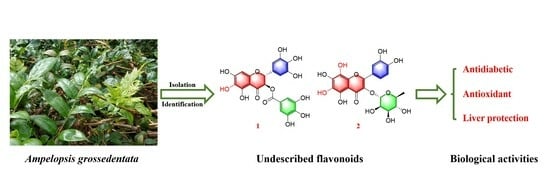
Chemical Constituents and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory, Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Activities of Ampelopsis grossedentata
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structure Elucidation
2.2. α-Glucosidase Inhibition Assay
2.3. Antioxidant Effect
2.4. Hepatoprotective Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Chemicals and Reagents
3.3. Plant Material
3.4. Extraction and Isolation
3.5. α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Assay
3.6. Measurement of Antioxidant Activity
3.6.1. DPPH Assay
3.6.2. ABTS Assay
3.6.3. FRAP Assay
3.7. Hepatoprotective Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, D.; Ouyang, W.; Yao, R.; He, S.; Li, S. Research Progress on chemical constituents and anti-infective effects of the traditional Chinese medicine vine tea (Ampelopsis grossedentata). Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. Mater. Medica World Sci. Technol. 2021, 23, 2012–2022. [Google Scholar]
- Carneiro, R.C.; Ye, L.; Baek, N.; Teixeira, G.H.; O’Keefe, S.F. Vine tea (Ampelopsis grossedentata): A review of chemical composition, functional properties, and potential food applications. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 76, 104317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; He, X.; Chen, K.; Chen, J.; Sakao, K.; Hou, D. Antioxidant properties of a traditional vine tea, Ampelopsis grossedentata. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Ma, W.; Zhao, S.; Liu, R.; Rong, J.; Li, X. Antioxidant properties of the extracts of vine tea (Ampelopsis grossedentata) with the different color characteristics and inhibition of rapeseed and sunflower oil oxidation. LWT 2021, 136, 110292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, H.; Yang, H.; Lin, A.; Xia, H.; Cheng, X.; Liu, H. Vine tea (Ampelopsis grossedentata) extract attenuates CCl4-induced liver injury by restoring gut microbiota dysbiosis in mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, 2100892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Sun, Y.; Ming, Q.; Tian, Z.; Yang, H.; Liu, C. Ampelopsin attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced mouse liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell activation associated with the SIRT1/TGF-β1/Smad3 and autophagy pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 77, 105984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Zou, J.; Gao, K. α-Glucosidase inhibition and antihyperglycemic activity of flavonoids from Ampelopsis grossedentata and the flavonoid derivatives. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Wang, X.; Lang, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Qin, Y. Ampelopsis grossedentata supplementation effectively ameliorates the glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, N. Ampelopsin inhibits human glioma through inducing apoptosis and autophagy dependent on ROS generation and JNK pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 116, 108524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shu, F.; Liang, X.; Chang, H.; Shi, L.; Peng, X.; Mi, M. Ampelopsin induces cell growth inhibition and apoptosis in breast cancer cells through ROS generation and endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Wang, H.; Yu, H.; Ge, G. Flavonoids in Ampelopsis grossedentata as covalent inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro: Inhibition potentials, covalent binding sites and inhibitory mechanisms. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 187, 976–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Tong, Q.; Wang, W.; Shi, C.; Xiong, W.; Chen, J.; Fang, J. Suppression of inflammatory responses by dihydromyricetin, a flavonoid from Ampelopsis grossedentata, via inhibiting the activation of NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Wang, F.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Yi, X. Antibacterial activity and mode of action of dihydromyricetin from Ampelopsis grossedentata leaves against food-borne bacteria. Molecules 2019, 24, 2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Peng, C.; Sheng, W.; Liu, X.; Chen, C.; Gong, L.; Zhou, X. Chemical constituents of Artemisia frigida. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2022, 58, 735–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, C.; Zheng, X.; Gong, L.; Zeng, K.; Wang, W.; Tu, P. Dibenzocyclooctadiene lignans from Artemisia sieversiana and their anti-inflammatory activities. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 75, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, G.; Sun, C.; Peng, F.; Yu, L.; Chen, Y.; Tan, Y.; Cao, X.; Tang, Y.; Xie, F.; et al. Chemistry, pharmacokinetics, pharmacological activities, and toxicity of Quercitrin. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 1545–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Xiong, W.; Perumalla, S.R.; Fang, J.; Sun, C.C. Solid-state characterization of optically pure (+) Dihydromyricetin extracted from Ampelopsis grossedentata leaves. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessada, S.M.; Barreira, J.C.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.; Oliveira, M.B.P. Phenolic profile and antioxidant activity of Coleostephus myconis (L.) Rchb. f.: An underexploited and highly disseminated species. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 89, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, W.; Song, B.A.; Zhao, H.J.; Qi, X.B.; Huang, Y.J.; Liu, X.H. Novel myricetin derivatives: Design, synthesis and anticancer activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.G.; Li, Y.X.; Yuan, M.Q. Isolation, purification and identification of etiolation substrate from fresh-cut Chinese water-chestnut (Eleocharis tuberosa). Food Chem. 2015, 186, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Mai, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; He, X. Health benefits of the flavonoids from onion: Constituents and their pronounced antioxidant and anti-neuroinflammatory capacities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Wu, B.; Zhuang, Y.; Ding, L.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, F. Chemical constitutes of fresh celery. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2009, 34, 1512–1515. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Fan, J.; Ruan, L.; Bi, J.; Yan, Y.; Wang, T.; Gao, H.; Yao, X.; Cheng, K.; Zhang, W. Semi-preparative separation of dihydromyricetin enantiomers by supercritical fluid chromatography and determination of anti-inflammatory activities. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1606, 460386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, M.; Su, H.; Hu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yang, T.; Shu, G. Chemical composition of total flavonoids from Salvia chinensia Benth and their pro-apoptotic effect on hepatocellular carcinoma cells: Potential roles of suppressing cellular NF-κB signaling. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabbi, F.; Zada, A.; Nisar, A.; Sohail, M.; Khalil, S.K.; Shah, W.A. Bioassay-guided isolation, identification of compounds from Sterculia diversifolia and investigation of their anti-glycation and antioxidant activities. Pharm. Chem. J. 2020, 53, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsimo, S.J.N.; Tamokou, J.D.D.; Havyarimana, L.; Csupor, D.; Forgo, P.; Hohmann, J.; Tane, P. Antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of kaempferol rhamnoside derivatives from Bryophyllum pinnatum. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Guo, Y.; Fu, C.; Li, J.; Li, Z. Simultaneous separation and purification of total polyphenols, chlorogenic acid and phlorizin from thinned young apples. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Li, Y.; Yi, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, Y. Three new acylphloroglucinol glucosides from the roots of Lysidice rhodostegia and their antioxidant activities. Carbohydr. Res. 2020, 492, 108012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Tong, Q.; Dong, W.; Yang, G.; Hou, X.; Xiong, W.; Wang, W. Tissue distribution, excretion, and metabolic profile of dihydromyricetin, a flavonoid from vine tea (Ampelopsis grossedentata) after oral administration in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4597–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kumar, S.; Rani, P. Pharmacophore modeling and 3D-QSAR studies on flavonoids as α-glucosidase inhibitors. Der Pharma Chem. 2010, 2, 324–335. [Google Scholar]
- Şöhretoğlu, D.; Sari, S.; Barut, B.; Özel, A. Discovery of potent α-glucosidase inhibitor flavonols: Insights into mechanism of action through inhibition kinetics and docking simulations. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 79, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proença, C.; Freitas, M.; Ribeiro, D.; Oliveira, E.F.; Sousa, J.L.; Tome, S.M.; Fernandes, E. α-Glucosidase inhibition by flavonoids: An in vitro and in silico structure–activity relationship study. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 1216–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, S.; Zhi, Z.; Cheng, H.; Chen, S.; Ye, X. Antioxidant and pancreatic lipase inhibitory effects of flavonoids from different citrus peel extracts: An in vitro study. Food Chem. 2020, 326, 126785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, R.; Li, L.; Yuan, T.; Seeram, N.P. α-Glucosidase inhibitory hydrolyzable tannins from Eugenia jambolana seeds. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1505–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zar, P.P.K.; Morishita, A.; Hashimoto, F.; Sakao, K.; Fujii, M.; Wada, K.; Hou, D.X. Anti-inflammatory effects and molecular mechanisms of loquat (Eriobotrya japonica) tea. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 6, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, K.; Charles, A.L. In Vitro antioxidant activity of Kyoho grape extracts in DPPH and ABTS assays: Estimation methods for EC50 using advanced statistical programs. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.; Xue, J.; Abbas, S.; Feng, B.; Zhang, X.; Xia, S. Liposome as a delivery system for carotenoids: Comparative antioxidant activity of carotenoids as measured by ferric reducing antioxidant power, DPPH assay and lipid peroxidation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 6726–6735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Cong, X.; Zheng, L.; Xu, L.; Yin, L.; Peng, J. Dioscin, a natural steroid saponin, shows remarkable protective effect against acetaminophen-induced liver damage in vitro and in vivo. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 214, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| No. | 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC | δH | δC | δH | |
| 2 | 82.9 | 5.31, d, (11.4) | 159.3 | -- |
| 3 | 74.2 | 5.84, d, (11.4) | 136.2 | -- |
| 4 | 193.4 | -- | 179.6 | -- |
| 5 | 165.4 | -- | 163.1 | -- |
| 6 | 164.2 | -- | 166.3 | -- |
| 7 | 169.9 | -- | 166.3 | -- |
| 8 | 96.6 | 5.96, s | 158.6 | -- |
| 9 | 169.1 | -- | 158.5 | -- |
| 10 | 102.1 | -- | 105.8 | -- |
| 1′ | 127.9 | -- | 122.9 | -- |
| 2′ | 107.8 | 6.52, s | 116.9 | 7.33, d (2.1) |
| 3′ | 147.0 | -- | 146.4 | -- |
| 4′ | 135.1 | -- | 149.8 | -- |
| 5′ | 147.0 | -- | 116.4 | 6.91, d (8.3) |
| 6″ | 107.8 | 6.52, s | 122.8 | 7.31, dd (8.3, 2.1) |
| 1″ | 120.4 | -- | 103.5 | 5.35, d (1.7) |
| 2″ | 110.4 | 6.97, s | 71.9 | 4.22, dd (3.4, 1.7) |
| 3″ | 146.4 | -- | 72.1 | 3.75, dd (9.6, 3.4) |
| 4″ | 140.2 | -- | 73.2 | 3.34, t (9.6) |
| 5″ | 146.4 | -- | 72.0 | 3.42, dq (9.6, 6.1) |
| 6″ | 110.4 | 6.97, s | 17.7 | 0.94, d (6.1) |
| 7″ | 166.8 | -- |
| Compound | IC50 a (μM) | Compound | IC50 a (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 11 | 6.04 ± 0.26 |
| 2 | >20 | 12 | >20 |
| 3 | >20 | 13 | >20 |
| 4 | 1.88 ± 0.08 | 14 | >20 |
| 5 | 1.83 ± 0.05 | 15 | >20 |
| 6 | >20 | 16 | 10.91 ± 0.51 |
| 7 | 2.90 ± 0.12 | 17 | 4.18 ± 0.11 |
| 8 | 10.32 ± 0.31 | 18 | >20 |
| 9 | 9.42 ± 0.51 | 19 | 1.59 ± 0.03 |
| 10 | 1.69 ± 0.05 | Acarbose b | 0.06 ± 0.01 |
| Compound | Antioxidant Activity | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| DPPH Assay IC50 a (μM) | ABTS Assay IC50 a (μM) | FRAP Assay a (μMOL/ML) | |
| 1 | 32.52 ± 0.16 | 4.43 ± 0.02 | 1.70 ± 0.00 |
| 2 | 44.42 ± 0.63 | 6.73 ± 0.03 | 1.96 ± 0.01 |
| 3 | 28.26 ± 0.38 | 5.91 ± 0.11 | 1.71 ± 0.01 |
| 4 | 25.54 ± 0.63 | 2.76 ± 0.04 | 2.67 ± 0.01 |
| 5 | 29.75 ± 0.59 | 3.39 ± 0.07 | 1.72 ± 0.01 |
| 6 | >80 | >20 | 0.07 ± 0.00 |
| 7 | >80 | 19.91 ± 0.46 | 0.85 ± 0.01 |
| 8 | >80 | >20 | 0.13 ± 0.01 |
| 9 | >80 | >20 | 0.09 ± 0.00 |
| 10 | 43.50 ± 0.36 | 5.01 ± 0.11 | 1.43 ± 0.01 |
| 11 | >80 | >20 | 0.15 ± 0.00 |
| 12 | 39.21 ± 0.18 | 7.36 ± 0.08 | 1.32 ± 0.01 |
| 13 | 35.03 ± 0.28 | 6.88 ± 0.13 | 1.69 ± 0.02 |
| 14 | >80 | >20 | 0.07 ± 0.00 |
| 15 | >80 | >20 | 0.17 ± 0.01 |
| 16 | >80 | >20 | 0.24 ± 0.01 |
| 17 | 43.05 ± 0.94 | 10.25 ± 0.13 | 1.18 ± 0.01 |
| 18 | 63.51 ± 0.97 | 9.96 ± 0.16 | 1.35 ± 0.02 |
| 19 | 17.31 ± 0.31 | 2.19 ± 0.01 | 2.79 ± 0.01 |
| ascorbic acid b | 77.93 ± 0.87 | 19.01 ± 0.31 | 0.57 ± 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Q.-J.; Zhou, W.-C.; Liu, X.-Y.; Li, Y.-J.; Xie, Q.-L.; Wang, B.; Liu, C.; Wang, W.-M.; Wang, W.; Zhou, X.-D. Chemical Constituents and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory, Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Activities of Ampelopsis grossedentata. Molecules 2023, 28, 7956. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28247956
Luo Q-J, Zhou W-C, Liu X-Y, Li Y-J, Xie Q-L, Wang B, Liu C, Wang W-M, Wang W, Zhou X-D. Chemical Constituents and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory, Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Activities of Ampelopsis grossedentata. Molecules. 2023; 28(24):7956. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28247956
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Qu-Jing, Wen-Chao Zhou, Xin-Yi Liu, Ya-Jie Li, Qing-Ling Xie, Bin Wang, Chao Liu, Wen-Mao Wang, Wei Wang, and Xu-Dong Zhou. 2023. "Chemical Constituents and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory, Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Activities of Ampelopsis grossedentata" Molecules 28, no. 24: 7956. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28247956
APA StyleLuo, Q. -J., Zhou, W. -C., Liu, X. -Y., Li, Y. -J., Xie, Q. -L., Wang, B., Liu, C., Wang, W. -M., Wang, W., & Zhou, X. -D. (2023). Chemical Constituents and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory, Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Activities of Ampelopsis grossedentata. Molecules, 28(24), 7956. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28247956