Identification of Trace Components in Sauce-Flavor Baijiu by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Comparison of Trace Components Obtained from Mass Spectrometry
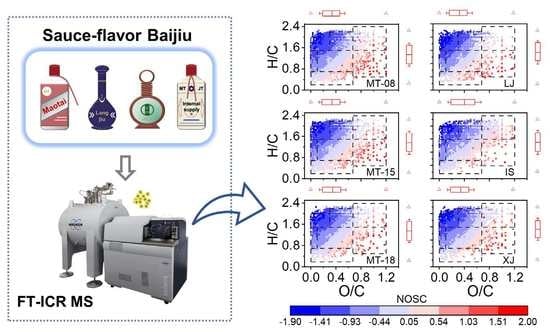
2.2. The General Characteristics of Sauce-Flavor Baijiu
2.3. Factor Analysis of Trace Components Characteristics of Sauce-Flavor Baijiu
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Samples
3.2. Mass Spectrometry
3.3. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, S.; Qian, S.; Zheng, J.; Li, Z.; Lin, H. A colorimetric sensor array for the discrimination of Chinese liquors. Analyst 2020, 145, 6968–6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, F.; Yi, B.; Shen, C.; Tao, F.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Xu, P. Chemical analysis of the Chinese liquor Luzhoulaojiao by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.L.; Yu, Y.; Ramaswamy, H.S.; Zhu, S.M. Characterization of Chinese liquor aroma components during aging process and liquor age discrimination using gas chromatography combined with multivariable statistics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, W.; Lin, W.; Chen, X.; Lian, X.; Shen, C.; Liu, M.; Lin, F.; Sun, X.; Xu, Y.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Reducing the background interference of liquid-liquid extraction method during Baijiu aroma analysis. Food Chem. 2022, 404 Pt A, 134557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, L.; Xu, Y. Yeast community associated with the solid state fermentation of traditional Chinese Maotai-flavor liquor. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 166, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-W.; Han, B.-Z. Baijiu (白酒), Chinese liquor: History, classification and manufacture. J. Ethn. Foods 2016, 3, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Chen, L.; Yang, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, L. Yeasts and their importance to the flavour of traditional Chinese liquor: A review. J. Inst. Brew. 2019, 125, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Tian, W.; Zhao, D. Research progress of trace components in sesame-aroma type of baijiu. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.-R.; Meng, Q.-H.; Qi, P.-F.; Jing, T. A Hand-Held Electronic Nose System for Rapid Identification of Chinese Liquors. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 2006411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Qian, M.C. Headspace Solid Phase Microextraction and Gas Chromatography−Olfactometry Dilution Analysis of Young and Aged Chinese “Yanghe Daqu” Liquors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 7931–7938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Qian, M.C. Characterization of Aroma Compounds of Chinese “Wuliangye” and “Jiannanchun” Liquors by Aroma Extract Dilution Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2695–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Lu, X.; Ji, K.; Guo, K.; Li, Y.; Wu, C.; Xu, G. Characterization of flavor compounds in Chinese liquor Moutai by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 597, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, R.L.; Alexander, R.; Snaychuk, L.; Edwards, J.C.; Fitzgerald, N.; Gao, P.; Quan, D.; Douvris, C.; Vaughan, T.; Bussan, D.D. A Fast, Straightforward and Inexpensive Method for the Authentication of Baijiu Spirit Samples by Fluorescence Spectroscopy. Beverages 2021, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Ma, C.; Zhu, C.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, L. Year prediction and flavor classification of Chinese liquors based on fluorescence spectra. Measurement 2019, 134, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Li, Y.; Du, A.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, R.; Shi, L.; Luo, C.; Feng, K.; Chang, J.; Chu, X. Foodomics analysis of natural aging and gamma irradiation maturation in Chinese distilled Baijiu by UPLC-Orbitrap-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, H.J.; Marshall, A.G. Electrospray Ionization Fourier Transform Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Wine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 5710–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.S.; Vaz, B.G.; Corilo, Y.E.; Ramires, C.F.; Saraiva, S.A.; Sanvido, G.B.; Schmidt, E.M.; Maia, D.R.J.; Cosso, R.G.; Zacca, J.J.; et al. Whisky analysis by electrospray ionization-Fourier transform mass spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roullier-Gall, C.; Witting, M.; Moritz, F.; Gil, R.B.; Goffette, D.; Valade, M.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Gougeon, R.D. Natural oxygenation of Champagne wine during ageing on lees: A metabolomics picture of hormesis. Food Chem. 2016, 203, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kew, W.; Mackay, C.L.; Goodall, I.; Clarke, D.J.; Uhrin, D. Complementary Ionization Techniques for the Analysis of Scotch Whisky by High Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11265–11272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubert, J.; Lacina, O.; Fauhl-Hassek, C.; Hajslova, J. Metabolic fingerprinting based on high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry: A reliable tool for wine authentication? Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 6791–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kew, W.; Goodall, I.; Clarke, D.; Uhrin, D. Chemical Diversity and Complexity of Scotch Whisky as Revealed by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 28, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L.; Zhuang, H.; Yao, G.; Ren, H.; Liu, Y. A biomimetic olfactory recognition system for the discrimination of Chinese liquor aromas. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrow, M.P.; Peru, K.M.; Headley, J.V. An added dimension: GC atmospheric pressure chemical ionization FTICR MS and the Athabasca oil sands. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8281–8288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Xie, Q.; Wang, J.-J.; He, D.; Bao, H.; Fu, Q.-L.; Su, S.; Sheng, M.; Li, S.-L.; Volmer, D.A.; et al. Deciphering dissolved organic matter by Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (FT-ICR MS): From bulk to fractions and individuals. Carbon Res. 2022, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Fu, P.; Volmer, D.A. Analysis of natural organic matter via Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry: An overview of recent non-petroleum applications. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2022, 41, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Qi, Y.; Ma, C.; Ge, J.; Hu, Q.; Yue, F.J.; Li, S.L.; Volmer, D.A. Characterization of Lignin Compounds at the Molecular Level: Mass Spectrometry Analysis and Raw Data Processing. Molecules 2021, 26, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Ma, C.; Chen, S.; Ge, J.; Hu, Q.; Li, S.-L.; Volmer, D.A.; Fu, P. Online Liquid Chromatography and FT-ICR MS Enable Advanced Separation and Profiling of Organosulfates in Dissolved Organic Matter. ACS ES T Water 2021, 1, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Qi, Y.; Li, C.; Ma, J.; Yi, Y.; Hu, Q.; Mostofa, K.M.G.; Volmer, D.A.; Li, S.L. Fluorescence and molecular signatures of dissolved organic matter to monitor and assess its multiple sources from a polluted river in the farming-pastoral ecotone of northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 154575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zou, W.; Shen, C.H.; Yang, J.G. Basic flavor types and component characteristics of Chinese traditional liquors: A review. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 4096–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Fu, P.; Li, S.; Ma, C.; Liu, C.; Volmer, D.A. Assessment of molecular diversity of lignin products by various ionization techniques and high-resolution mass spectrometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, W.; Ge, J.; Hu, Q.; Ma, J.; Yuan, D.; Fu, X.; Qi, Y.; Volmer, D.A. An advanced LC-MS/MS protocol for simultaneous detection of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2023, 37, e9397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Junjun, H.E.; Chuxiang, L.; Chunlin, Z. Analysis of volatile flavor compounds from defective product of sauce-flavor Baijiu by GC×GC-TOF-MS. China Brew. 2019, 38, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Hertkorn, N.; Frommberger, M.; Witt, M.; Koch, B.P.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Perdue, E.M. Natural Organic Matter and the Event Horizon of Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 8908–8919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Andrilli, J.; Dittmar, T.; Koch, B.P.; Purcell, J.M.; Marshall, A.G.; Cooper, W.T. Comprehensive characterization of marine dissolved organic matter by Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry with electrospray and atmospheric pressure photoionization. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 24, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackburn, J.W.T.; Kew, W.; Graham, M.C.; Uhrin, D. Laser Desorption/Ionization Coupled to FTICR Mass Spectrometry for Studies of Natural Organic Matter. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 4382–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, C.; Fang, Z.; Li, Y.; Jiang, C.; Zhao, S.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Q. Ionization selectivity of electrospray and atmospheric pressure photoionization FT-ICR MS for petroleum refinery wastewater dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2021, 23, 1466–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roullier-Gall, C.; Signoret, J.; Hemmler, D.; Witting, M.A.; Kanawati, B.; Schafer, B.; Gougeon, R.D.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P. Usage of FT-ICR-MS Metabolomics for Characterizing the Chemical Signatures of Barrel-Aged Whisky. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merder, J.; Freund, J.A.; Feudel, U.; Hansen, C.T.; Hawkes, J.A.; Jacob, B.; Klaproth, K.; Niggemann, J.; Noriega-Ortega, B.E.; Osterholz, H.; et al. ICBM-OCEAN: Processing Ultrahigh-Resolution Mass Spectrometry Data of Complex Molecular Mixtures. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 6832–6838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRowe, D.E.; Van Cappellen, P. Degradation of natural organic matter: A thermodynamic analysis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 2030–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Ge, J.; Yi, Y.; Ma, C.; Qi, Y.; Volmer, D.A. Fractionation and characterization of dissolved organic matter using solid-phase extraction followed by Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry with electrospray, atmospheric pressure photoionization, and laser desorption ionization. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 36, e9364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, B.P.; Dittmar, T. From mass to structure: An aromaticity index for high-resolution mass data of natural organic matter. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, T.; Biester, H.; Dittmar, T. Molecular fractionation of dissolved organic matter with metal salts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4419–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Type | No. of Assigned Formulas | m/zwa | Cwa | Hwa | Owa | Nwa | Swa | H/Cwa | O/Cwa | DBEwa | NOSCwa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESI+ | MT-08 | 3051 | 368.8 | 17.7 | 26.7 | 4.3 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 5.9 | −0.7 |
| MT-15 | 2432 | 374.5 | 18.0 | 27.4 | 4.1 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 0.2 | 5.9 | −0.7 | |
| MT-18 | 2346 | 355.6 | 16.7 | 24.9 | 4.1 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 5.8 | −0.6 | |
| LJ | 1481 | 375.0 | 19.3 | 28.7 | 3.6 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 1.6 | 0.2 | 6.5 | −0.8 | |
| IS | 1691 | 395.3 | 18.3 | 25.0 | 5.8 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 7.4 | −0.4 | |
| XJ | 2375 | 363.0 | 18.0 | 27.9 | 4.3 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 5.6 | −0.8 | |
| ESI− | MT-08 | 3741 | 333.8 | 16.4 | 22.0 | 5.8 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 1.4 | 0.4 | 6.6 | −0.5 |
| MT-15 | 2562 | 313.2 | 15.6 | 21.0 | 5.2 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 1.4 | 0.4 | 6.3 | −0.5 | |
| MT-18 | 2375 | 304.1 | 15.1 | 21.0 | 5.2 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 5.7 | −0.6 | |
| LJ | 1628 | 291.0 | 14.4 | 20.1 | 4.8 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 5.5 | −0.6 | |
| IS | 1658 | 387.9 | 16.5 | 22.9 | 9.5 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 1.6 | 0.7 | 6.3 | −0.1 | |
| XJ | 2783 | 326.0 | 16.5 | 24.9 | 5.3 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 5.2 | −0.7 | |
| MT-08 | MT-15 | MT-18 | LJ | IS | XJ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | ESI+ | 2193 | 1851 | 1751 | 1217 | 1442 | 1774 |
| ESI− | 2883 | 1981 | 1780 | 1364 | 1389 | 2182 | |
| Common | 858 | 581 | 595 | 264 | 269 | 601 | |
| Abund. | ESI+ | 61.9% | 68.7% | 70.6% | 81.3% | 78.8% | 59.9% |
| ESI− | 66.4% | 73.0% | 70.2% | 85.1% | 65.9% | 76.3% | |
| Common | 38.1%; 33.6% | 31.3%; 27.0% | 29.4%; 29.8% | 18.7%; 14.9% | 21.2%; 34.1% | 40.1%; 23.7% | |
| MT-08 | MT-15 | MT-18 | LJ | IS | XJ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C16H26N2OS2 | C16H26N2OS2 | C16H26N2OS2 | C6H12O3 | C15H28O14 | C6H12O3 |
| C6H12O3 | C15H27N3O5S2 | C14H26N2O2S3 | C15H28N2OS3 | C12H24O12 | C16H26N2OS2 |
| C15H27N3O5S2 | C17H13N3 | C15H27N3O5S2 | C16H26N2OS2 | C9H18O9 | C15H27N3O5S2 |
| C9H12N2OS | C6H12O3 | C6H12O3 | C12H10OS | C16H26N2OS2 | C20H36O5 |
| C20H38O5 | C14H26N2O2S3 | C9H12N2OS | C17H13N3 | C6H10O5 | C9H12N2OS |
| C14H26N2O2S3 | C9H12N2OS | C20H38O5 | C13H24N2OS3 | C23H20O7S | C24H46O5 |
| C19H18O5S3 | C20H38O5 | C17H13N3 | C15H27N3O5S2 | C18H32O16 | C16H24O7 |
| C17H13N3 | C22H40O4 | C12H22N2O2S3 | C9H12N2OS | C18H34O17 | C17H13N3 |
| C12H22N2O2S3 | C12H22N2O2S3 | C11H22O6 | C14H26N2O2S3 | C37H36N2O11 | C12H10OS |
| C13H26N2OS3 | C12H10OS | C13H26N2OS3 | C24H24O4 | C9H12N2OS | C14H26N2O2S3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, J.; Qi, Y.; Yao, W.; Yuan, D.; Hu, Q.; Ma, C.; Volmer, D.A.; Liu, C.-Q. Identification of Trace Components in Sauce-Flavor Baijiu by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2023, 28, 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031273
Ge J, Qi Y, Yao W, Yuan D, Hu Q, Ma C, Volmer DA, Liu C-Q. Identification of Trace Components in Sauce-Flavor Baijiu by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031273
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Jinfeng, Yulin Qi, Wenrui Yao, Daohe Yuan, Qiaozhuan Hu, Chao Ma, Dietrich A. Volmer, and Cong-Qiang Liu. 2023. "Identification of Trace Components in Sauce-Flavor Baijiu by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry" Molecules 28, no. 3: 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031273
APA StyleGe, J., Qi, Y., Yao, W., Yuan, D., Hu, Q., Ma, C., Volmer, D. A., & Liu, C. -Q. (2023). Identification of Trace Components in Sauce-Flavor Baijiu by High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Molecules, 28(3), 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031273