Insecticidal and Synergistic Potential of Three Monoterpenoids against the Yellow Fever Mosquito, Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae), and the House Fly, Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Topical Dose Response
2.2. Co-Toxicity Assays
2.3. In Vitro Inhibition of Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Activity
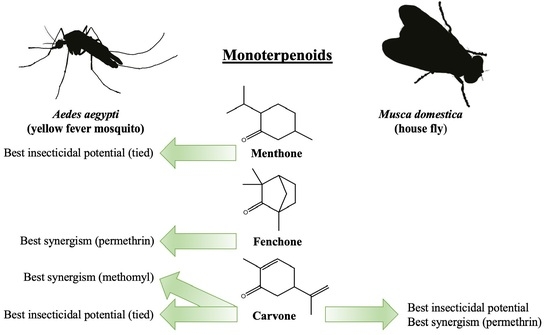
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Insects and Chemicals
4.2. Topical Dose Responses
4.3. Co-Toxicity Assays
4.4. In Vitro Inhibition of Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Activity
4.5. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Russell, R.J.; Claudianos, C.; Campbell, P.M.; Horne, I.; Sutherland, T.D.; Oakeshott, J.G. Two major classes of target site insensitivity mutations confer resistance to organophosphate and carbamate insecticides. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2004, 79, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, L. Pyrethroid resistance in mosquitoes. Insect Sci. 2006, 13, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, T.C.; Dripps, J.E.; Watson, G.B.; Paroonagian, D. Resistance and cross-resistance to the spinosyns—A review and analysis. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2012, 102, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossthwaite, A.J.; Rendine, S.; Stenta, M.; Slater, R. Target-site resistance to neonicotinoids. J. Chem. Biol. 2014, 7, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balmert, N.J.; Rund, S.S.; Ghazi, J.P.; Zhou, P.; Duffield, G.E. Time-of-day specific changes in metabolic detoxification and insecticide resistance in the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae. J. Insect Physiol. 2014, 64, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Li, M.; Gong, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, T. Cytochrome P450s–Their expression, regulation, and role in insecticide resistance. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 120, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres, M.; Santo-Orihuela, P.L.; Vassena, C.V. Evaluation of Resistance to Different Insecticides and Metabolic Detoxification Mechanism by Use of Synergist in the Common Bed Bug (Heteroptera: Cimicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2019, 56, 1324–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.; Zhou, Y.; Mo, J. The clone of laccase gene and its potential function in cuticular penetration resistance of Culex pipiens pallens to fenvalerate. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2009, 93, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balabanidou, V.; Grigoraki, L.; Vontas, J. Insect cuticle: A critical determinant of insecticide resistance. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2018, 27, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathantriphop, S.; Thanispong, K.; Sanguanpong, U.; Achee, N.; Bangs, M.; Chareonviriyaphap, T. Comparative Behavioral Responses of Pyrethroid–Susceptible and –Resistant Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) Populations to Citronella and Eucalyptus Oils. J. Med. Entomol. 2014, 51, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, K.; Doggett, S.L.; Singham, G.V.; Lee, C.-Y. Insecticide resistance and resistance mechanisms in bed bugs, Cimex spp. (Hemiptera: Cimicidae). Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machani, M.G.; Ochomo, E.; Amimo, F.; Mukabana, W.R.; Githeko, A.K.; Yan, G.; Afrane, Y.A. Behavioral responses of pyrethroid resistant and susceptible Anopheles gambiae mosquitoes to insecticide treated bed net. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, A.; Potter, M.F.; Haynes, K.F. Evaluation of Piperonyl Butoxide as a Deltamethrin Synergist for Pyrethroid-Resistant Bed Bugs. J. Econ. Entomol. 2009, 102, 2310–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carvalho, C.C.C.R.; Da Fonseca, M.M.R. Carvone: Why and how should one bother to produce this terpene. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.K.; Prajapati, V.; Kumar, S. Bioactivities of l-carvone, d-Carvone, and Dihydrocarvone Toward Three Stored Product Beetles. J. Econ. Entomol. 2003, 96, 1594–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nukenine, E.N.; Adler, C.; Reichmuth, C. Bioactivity of fenchone and Plectranthus glandulosus oil against Prostephanus truncatus and two strains of Sitophilus zeamais. J. Appl. Entomol. 2010, 134, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, L.C.; Edman, J.D.; Scott, T.W. Why Do Female Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) Feed Preferentially and Frequently on Human Blood? J. Med. Entomol. 2001, 38, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, T.W.; Amerasinghe, P.H.; Morrison, A.C.; Lorenz, L.H.; Clark, G.G.; Strickman, D.; Kittayapong, P.; Edman, J.D. Longitudinal studies of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) in Thailand and Puerto Rico: Blood feeding frequency. J. Med. Entomol. 2000, 37, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleton, N.; Koopmans, M.; Reimerink, J.; Godeke, G.-J.; Reusken, C. Come fly with me: Review of clinically important arboviruses for global travelers. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 55, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vontas, J.; Kioulos, E.; Pavlidi, N.; Morou, E.; Della Torre, A.; Ranson, H. Insecticide resistance in the major dengue vectors Aedes albopictus and Aedes aegypti. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2012, 104, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estep, A.S.; Sanscrainte, N.D.; Waits, C.M.; Bernard, S.J.; Lloyd, A.M.; Lucas, K.J.; Buckner, E.A.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Morreale, R.; Conti, L.A.; et al. Quantification of permethrin resistance and kdr alleles in Florida strains of Aedes aegypti (L.) and Aedes albopictus (Skuse). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Issa, R. Musca domestica acts as transport vector hosts. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2019, 43, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olsen, A.R.; Hammack, T.S. Isolation of Salmonella spp. from the housefly, Musca domestica L., and the dump fly, Hydrotaea aenescens (Wiedemann) (Diptera: Muscidae), at caged-layer houses. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 958–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chuang, H.-L.; Chiu, C.-C.; Yeh, K.-S.; Chang, C.-C.; Hsuan, S.-L.; Lin, W.-H.; Chen, T.-H. Transmission of Salmonella between swine farms by the housefly (Musca domestica). J. Food Prot. 2011, 74, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geden, C.J.; Nayduch, D.; Scott, J.G.; Burgess, E.R.; Gerry, A.C.; E Kaufman, P.; Thomson, J.; Pickens, V.; Machtinger, E.T. House Fly (Diptera: Muscidae): Biology, Pest Status, Current Management Prospects, and Research Needs. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2021, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winpisinger, K.A.; Ferketich, A.K.; Berry, R.L.; Moeschberger, M.L. Spread of Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae), from Two Caged Layer Facilities to Neighboring Residences in Rural Ohio. J. Med. Entomol. 2005, 42, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, J.C.; Ross, D.H.; Scott, J.G. Insecticide resistance monitoring of house fly populations from the United States. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 158, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, G.J.; Denholm, I. An unconventional use of piperonyl butoxide for managing the cotton whitefly, Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 1998, 88, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, N.A.; Eldefrawi, M.E.; Toppozada, A.; Zeid, M. Toxicological Studies on the Egyptian Cotton Leaf worm, Prodenia litura. VI. Potentiation and Antagonism of Organophosphorus and Carbamate Insecticides. J. Econ. Entomol. 1966, 59, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, E.R.; Geden, C.J.; Lohmeyer, K.H.; King, B.H.; Machtinger, E.T.; Scott, J.G. Toxicity of fluralaner, a companion animal insecticide, relative to industry-leading agricultural insecticides against resistant and susceptible strains of filth flies. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J. Sax’s Dangerous Properties of Industrial Materials, 9th ed.; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Volume 1–3, p. 2109. [Google Scholar]
- NLM. RTECS (Registry of Toxic Effects of Chemical Substances); Record Nos. 53328, 53329; NLM: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Opdyke, D.L.J. Fragrance raw materials monograph: Fenchone. Food Cosmet. Toxicol. 1976, 14, 769–771. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA Scientific Committee. Scientific opinion on the safety assessment of carvone, considering all sources of exposure. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlin, C.D.S. The Pesticide Manual: A World Compendium, 14th ed.; British Crop Production Council: Alton, UK, 2006; pp. 813–814. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Pesticide Residues in Food, Toxicological Evaluations; Food and Agriculture Organization of the Unites Nations: Rome, Italy; World Health Organization: Rome, Italy, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Royal Society of Chemistry Information Services. The Agrochemicals Handbook, 3rd ed.; Kidd, H., James, D.R., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry Information Services: Cambridge, UK, 1991; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Isman, M.B. Plant essential oils for pest and disease management. Crop Prot. 2000, 19, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhou, W.; Bian, C.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, B. Degradation and Pathways of Carvone in Soil and Water. Molecules 2022, 27, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imgrund, H. Environmental Fate of Permethrin; California Department of Pesticide Regulation, Environmental Monitoring Branch: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, P.H. Handbook of Environmental Fate and Exposure Data for Organic Chemicals: Pesticides; Lewis: Chelsea, MI, USA, 1991; pp. 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hummelbrunner, L.A.; Isman, M.B. Acute, Sublethal, Antifeedant, and Synergistic Effects of Monoterpenoid Essential Oil Compounds on the Tobacco Cutworm, Spodoptera litura (Lep., Noctuidae). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Slowing and Combating Pest Resistance to Pesticides; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- B-Bernard, C.; Philogène, B.J.R. Insecticide synergists: Role, importance, and perspectives. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 1993, 38, 199–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Thomas, A.; Sahgal, A.; Verma, A.; Samuel, T.; Pillai, M. Effect of the synergist, piperonyl butoxide, on the development of deltamethrin resistance in yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti L. (Diptera: Culicidae). Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2002, 50, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seixas, G.; Grigoraki, L.; Weetman, D.; Vicente, J.L.; Silva, A.C.; Pinto, J.; Vontas, J.; Sousa, C.A. Insecticide resistance is mediated by multiple mechanisms in recently introduced Aedes aegypti from Madeira Island (Portugal). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, O.; Oishi, S.; Fujitani, T.; Tanaka, T.; Yoneyama, M. Chronic Toxicity Studies of Piperonyl Butoxide in F344 Rats: Induction of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Fundam. Appl. Toxicol. 1994, 22, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiden, M.H.J. Toxicity of carbamates to insects. Bull. World Health Organ. 1971, 44, 203. [Google Scholar]
- El-Zemity, S.R. Synthesis and molluscicidal activity of novel N-methyl carbamates derivatives based on naturally occurring monoterpenoids. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2006, 2, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Norris, E.J.; Gross, A.D.; Dunphy, B.M.; Bessette, S.; Bartholomay, L.; Coats, J.R. Comparison of the Insecticidal Characteristics of Commercially Available Plant Essential Oils Against Aedes aegypti and Anopheles gambiae (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2015, 52, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Norris, E.J.; Bloomquist, J.R. Co-Toxicity Factor Analysis Reveals Numerous Plant Essential Oils Are Synergists of Natural Pyrethrins against Aedes aegypti Mosquitoes. Insects 2021, 12, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L.K.; Courtney, D.; Andres, V., Jr.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finney, D.J. Probit Analysis: A Statistical Treatment of the Sigmoid Response Curve, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Ritz, C.; Baty, F.; Streibig, J.C.; Gerhard, D. Dose-Response Analysis Using R. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0146021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| n | LD10 (95% CI) 1 | LD50 (95% CI) 1 | LD90 (95% CI) 1 | Slope (SE) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ae. aegypti | |||||
| Carvone | 220 | 3900 (1900–5200) b | 7300 (6700–7900) c | 14,200 (11,000–26,600) c | 8.9 (1.6) |
| Menthone | 220 | 5000 (1000–6300) b | 7100 (4100–8300) c | 10,000 (8500–13,100) c | 8.6 (3.3) |
| Fenchone | 220 | 7600 (5000–9500) b | 11,300 (10,200–53,400) d | 42,000 (28,800–94,900) d | 11.2 (5.1) |
| Methomyl | 280 | 0.97 (0.27–1.6) a | 2.7 (1.6–4.3) b | 7.55 (4.7–22.5) b | 2.9 (0.7) |
| Permethrin | 350 | 0.23 (0.12–0.33) a | 0.58 (0.45–0.71) a | 1.41 (1.08–2.24) a | 3.5 (1.4) |
| M. domestica | |||||
| Carvone | 480 | 3300 (3100–3400) b | 4300 (4200–4400) b | 5600 (5300–5900) b | 11.3 (0.9) |
| Menthone | 1280 | 5300 (5100–5400) c | 6800 (6700–7000) c | 8800 (8400–9400) c | 7.2 (0.5) |
| Fenchone | 600 | 8800 (8100–9400) d | 13,200 (12,600–13,800) d | 19,900 (18,600–21,600) d | 11.4 (0.8) |
| Methomyl | - | - | - | - | - |
| Permethrin | 580 | 0.46 (0.37–0.56) a | 0.84 (0.79–0.93) a | 1.5 (1.4–1.7) a | 5.2 (0.6) |
| 1-h% Mean Knockdown ± SEM | 24-h% Mean Mortality ± SEM | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Permethrin Alone | Synergist Alone | Mixture | Co-Toxicity Factor a | Permethrin Alone | Synergist Alone | Mixture | Co-Toxicity Factor a | |
| Ae. Aegypti * | ||||||||
| Control (ethanol) | NA | 0 ± 0 | NA | NA | NA | 0.3 ± 0.1 | NA | NA |
| PBO | 87.5 ± 6.3 | 7.5 ± 2.5 | 52.5 ± 7.5 | −44.7 | 27.5 ± 4.8 | 12.5 ± 6.3 | 50 ± 5.77 | 25 |
| Carvone | 76 ± 9.2 | 5 ± 5 | 100 ± 0 | 23.5 | 36 ± 6 | 5 ± 2.9 | 75 ± 5 | 83 |
| Menthone | 76 ± 9.2 | 7.5 ± 4.8 | 100 ± 0 | 19.8 | 36 ± 6 | 5 ± 2.9 | 95 ± 5 | 132 |
| Fenchone | 76 ± 9.2 | 0 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 32.0 | 36 ± 6 | 2.5 ± 2.5 | 100 ± 0 | 160 |
| Ae. Aegypti ** | ||||||||
| Control (ethanol) | NA | 0 ± 0 | NA | NA | NA | 0.3 ± 0.1 | NA | NA |
| PBO | 76 ± 9.2 | 22.5 ± 4.8 | 60 ± 14.7 | −39 | NA | 72.5 ± 8.5 | NA | NA |
| Carvone | 76 ± 9.2 | 20 ± 5.8 | 100 ± 0 | 4 | 36 ± 6 | 7.5 ± 2.5 | 90 ± 10 | 76 |
| Menthone | 76 ± 9.2 | 12.5 ± 4.8 | 100 ± 0 | 13 | 36 ± 6 | 15 ± 5 | 85 ± 5 | 83 |
| Fenchone | 76 ± 9.2 | 10 ± 4.1 | 100 ± 0 | 16 | 36 ± 6 | 2.5 ± 2.5 | 85 ± 15 | 121 |
| M. domestica *** | ||||||||
| Control (acetone) | NA | 0 ± 0 | NA | NA | NA | 0.6 ± 0.6 | NA | NA |
| PBO | 80 ± 7.3 | 2 ± 2 | 96 ± 4 | 16.2 | 58 ± 10.1 | 6 ± 2.9 | 100 ± 0 | 55.9 |
| Carvone | 80 ± 7.3 | 16 ± 11.8 | 100 ± 0 | 3.2 | 58 ± 10.1 | 0 ± 0 | 96 ± 3.8 | 65.6 |
| Menthone | 80 ± 7.3 | 4 ± 2.4 | 95 ± 2.9 | 12.6 | 58 ± 10.1 | 0 ± 0 | 86 ± 6.6 | 48.4 |
| Fenchone | 80 ± 7.3 | 0 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 | 24.0 | 58 ± 10.1 | 0 ± 0 | 95 ± 2.9 | 63.4 |
| 1-h% Mean Knockdown ± SEM | 24-h% Mean Mortality ± SEM | 48-h% Mean Mortality ± SEM | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methomyl Alone | Synergist Alone | Mixture | Co-Toxicity Factor a | Methomyl Alone | Synergist Alone | Mixture | Co-Toxicity Factor a | Methomyl Alone | Synergist Alone | Mixture | Co-Toxicity Factor a | |
| 2 μg applied | ||||||||||||
| Control (ethanol) | NA | 0 ± 0 | NA | NA | NA | 0.3 ± 0.1 | NA | NA | NA | 0.5 ± 0.1 | NA | NA |
| PBO | 87.5 ± 9.5 | 7.5 ± 2.5 | 90 ± 10 | −5.3 | 57.5 ± 25.3 | 12.5 ± 6.3 | 80 ± 5.8 | 14.3 | 65 ± 21.8 | 15 ± 3.4 | 96.7 ± 3.3 | 20.9 |
| Carvone | 87.5 ± 9.5 | 5 ± 5 | 96.7 ± 3.3 | 4.5 | 57.5 ± 25.3 | 5 ± 2.9 | 76.7 ± 6.7 | 23 | 65 ± 21.8 | 5 ± 2.9 | 86.7 ± 3.3 | 24 |
| Menthone | 87.5 ± 9.5 | 7.5 ± 4.8 | 100 ± 0 | 0 | 57.5 ± 25.3 | 5 ± 2.9 | 73 ± 3.3 | 29 | 65 ± 21.8 | 7.5 ± 2.5 | 80 ± 5.8 | 7 |
| Fenchone | 87.5 ± 9.5 | 0 ± 0 | 83.3 ± 3.3 | −5 | 57.5 ± 25.3 | 2.5 ± 2.5 | 53.3 ± 17.6 | −11 | 65 ± 21.8 | 7.5 ± 4.8 | 60 ± 11.5 | −17 |
| 10 μg applied | ||||||||||||
| Control (ethanol) | NA | 0 ± 0 | NA | NA | NA | 0.3 ± 0.1 | NA | NA | NA | 0.5 ± 0.1 | NA | NA |
| PBO | ||||||||||||
| Carvone | 87.5 ± 9.5 | 20 ± 5.8 | 100 ± 0 | −7 | 57.5 ± 25.3 | 7.5 ± 2.5 | 83.3 ± 8.8 | 28 | 65 ± 21.8 | 15 ± 2.9 | 86.6 ± 8.8 | 8 |
| Menthone | 87.5 ± 9.5 | 12.5 ± 4.8 | 100 ± 0 | 0 | 57.5 ± 25.3 | 15 ± 5 | 93 ± 6.7 | 29 | 65 ± 21.8 | 22.5 ± 7.5 | 93.3 ± 6.7 | 7 |
| Fenchone | 87.5 ± 9.5 | 10 ± 4.1 | 93.3 ± 6.7 | −4 | 57.5 ± 25.3 | 2.5 ± 2.5 | 73.3 ± 12 | 22 | 65 ± 21.8 | 10 ± 4.1 | 80 ± 10 | 7 |
| Compound | Oral (Animal) | Dermal (Animal) | Citation |
| l-menthone | 500 (rt) | - | [31] |
| l-fenchone | 6160 (rt) | 5000 (rb) | [32,33] |
| l-carvone | 5400 (rt) | >4000 (rt) | [34] |
| Permethrin | 430–4000 (rt) | 2000 (rb) | [35,36] |
| Methomyl | 17–24 (rt) | 5880 (rb) | [37] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baker, O.S.; Norris, E.J.; Burgess, E.R., IV. Insecticidal and Synergistic Potential of Three Monoterpenoids against the Yellow Fever Mosquito, Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae), and the House Fly, Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae). Molecules 2023, 28, 3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073250
Baker OS, Norris EJ, Burgess ER IV. Insecticidal and Synergistic Potential of Three Monoterpenoids against the Yellow Fever Mosquito, Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae), and the House Fly, Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae). Molecules. 2023; 28(7):3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073250
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaker, Oshneil S., Edmund J. Norris, and Edwin R. Burgess, IV. 2023. "Insecticidal and Synergistic Potential of Three Monoterpenoids against the Yellow Fever Mosquito, Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae), and the House Fly, Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae)" Molecules 28, no. 7: 3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073250
APA StyleBaker, O. S., Norris, E. J., & Burgess, E. R., IV. (2023). Insecticidal and Synergistic Potential of Three Monoterpenoids against the Yellow Fever Mosquito, Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae), and the House Fly, Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae). Molecules, 28(7), 3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073250