Oxidation of Isoeugenol by Salen Complexes with Bulky Substituents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of Sulfosalen and Phosphosalen
2.2. Optimization of Polymerization Conditions
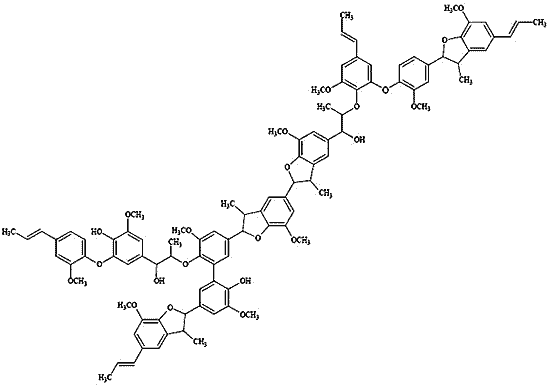
2.3. Polymer Characterization
2.4. Radical Scavenging Activity
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. General Procedure for Oxidative Coupling of Isoeugenol
3.3. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
3.4. Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC)
3.5. Statistical Analyses of Data
3.6. 13C-NMR and 31P-NMR Studies
3.7. LC-MS
3.8. Estimation of Radical Scavenging Activity
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- Joo, H; Chae, HJ; Yeo, JS; Yoo, Y. Depolymerization of Phenolic Polymers Using Horseradish Peroxidase in Organic Solvent. J. Proc. Biochem 1997, 32, 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Kurek, B; Artaud, I; Pollet, B; Lapierre, C; Monties, B. Oxidative Degradation of in Situ and Isolated Spruce Lignins by Water-Soluble Hydrogen Peroxide Resistant Pentafluorophenyl Porphyrin. J. Agric. Food Chem 1996, 44, 1953–1959. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer, P; Breith, E; Lűbbe, E; Tsumaki, T. Tricyclic Ortho-Condensed Partial Valence Rings. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem 1933, 503, 84–130. [Google Scholar]
- Minutolo, F; Pini, D; Petri, A; Salvatori, P. Heterogeneous Asymmetric Epoxidation of Unfunctionalized Olefins Catalyzed by Polymer-Bound (Salen)Manganese Complexes. Tetrahedron: Asym 1996, 7, 2293–2302. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon, R; Kochi, JK. Metal-Catalysed Oxidations of Organic Compounds; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Haikarainen, A; Sipila, J; Pietikainen, P; Pajunen, A; Mutikainen, I. Synthesis and Characterization of Bulky Salen-Type Complexes of Co, Cu, Fe, Mn and Ni with Amphiphilic Solubility Properties. J Chem Soc., Dalton Trans 2001, 991–995. [Google Scholar]
- Haikarainen, A; Sipila, J; Pietikainen, P; Pajunen, A; Mutikainen, I. Salen Complexes with Bulky Substituents as Useful Tools for Biomimetic Phenol Oxidation Research. Bioorg. Medicin. Chem 2001, 9, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar]
- Sipila, J; Haikarainen, A; Brunow, G. Oxidative Delignification Chemistry, Fundamental and Catalysis; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Canevali, C; Orlandi, M; Pardi, L; Rindone, B; Scotti, R; Sipila, J; Morazzoni, F. Oxidative Degradation of Monomeric and Dimeric Phenylpropanoids: Reactivity and Mechanism Investigation. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans 2002, 15, 3007–3014. [Google Scholar]
- Boerjan, W; Ralph, J; Baucher, M. Lignin Biosynthesis. Annu. Rev. Plant. Biol 2003, 54, 519–546. [Google Scholar]
- Terashima, N; Atalla, RH; Ralph, J; Landucci, LL; La Pierre, C; Monties, B. New Preparation of Lignin Polymer Models under Condition that Approximate Cell Wall Lignification. Synthesis of Novel Lignin Polymer Models and their Structural Characterization by 13C-NMR. Holzforschung 1995, 49, 521–527. [Google Scholar]
- Shiba, T; Ling, X; Miyakoshi, T; Chen, CL. Oxidation of Isoeugenol and Coniferyl Alcohol Catalyzed by Laccases Isolated from Rhus Vernicifera Stokes and Pycnoporus Coccineus. J. Molecul. Catalysis B: Enzym 2000, 10, 605–615. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H; Ho, SH. Insecticidal Properties of Eugenol, Isoeugenol and Methyleugenol and their Effects on Nutrition of Sitophilus Zeamais Motsch. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) and Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). J. Stored Product. Res 2002, 38, 403–412. [Google Scholar]
- Evliya, H; Olcay, A. Oxidative Polymerization of Isoeugenol and Mild Oxidation of Synthetic Polymers with Alkaline Cupric Hydroxide. Holzforschung 1974, 130–135. [Google Scholar]
- Quideau, S; Ralph, JA. Biomimetic Route to Lignin Model Compounds via Silver (I) Oxide Oxidation. Holzforschung 1994, 48, 124–132. [Google Scholar]
- Orlandi, M; Agozzino, P; Donato, DI; Giachi, G; Toppa, EL; Zoia, L. Consolidation of Waterlogged Woods by in-situ Polymerisation of Isoeugenol; Conservation Science; Joyce, T, Ed.; Archetype Publications: London, UK, 2007; pp. 262–268. [Google Scholar]
- Elegir, G; Kindl, A; Sadocco, P; Orlandi, M. Development of Antimicrobial Cellulose Packaging through Laccase-Mediated Grafting of Phenolic Compounds. Enzyme Microb. Technol 2008, 43, 84–92. [Google Scholar]
- Sippola, V; Vilijava, TR; Vilonen, K; Krause, O. New Method to Follow the Dimerization Reaction Occurring During Oxidation of 4-Ethylguaiacol. Holzforschung 2002, 56, 601–606. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkanen, KV. Lignin Precursors and their Polymerization. In Lignins: Occurrence, Formation, Structure, and Reactions; Sarkanen, KV, Ludwing, CH, Eds.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1971; pp. 95–163. [Google Scholar]
- Canevali, C; Orlandi, M; Zoia, L; Scotti, R; Tolppa, EL; Agnoli, F; Morazzoni, F. Radicalization of Lignocellulosic Fibers, Related Structural and Morphological Changes. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1592–1601. [Google Scholar]
- Bortolomeazzi, R; Verardo, G; Liessi, A; Callea, A. Formation of Dehydrodiisoeugenol and Dehydrodieugenol from the Reaction of Isoeugenol and Eugenol with DPH Radical and their Role in the Radical Scavenging Activity. Food Chem 2010, 118, 256–265. [Google Scholar]
- Granata, A; Argyropoulos, DS. 2-Chloro-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaphospholane, a Reagent for the Accurate Determination of the Uncondensed and Condensed Phenolic Moieties in Lignins. J. Agric. Food Chem 1995, 43, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar]
- Reale, S; di Tullio, A; Spetri, N; de Angelis, F. Mass Spectroscopy in the Biosynthetic and Structural Investigation of Lignins. Mass Spec. Rev 2004, 23, 87–126. [Google Scholar]
- Evtuguin, D; Amado, F. Application of Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry to Elucidation of the Primary Structure of Lignin. Macromol. Biosci 2003, 3, 339–343. [Google Scholar]
- Evliya, H. Carbon-13 NMR Studies of a Dehydropolymer (DHP) from Isoeugenol; Comparison with Spruce Lignin. Holzforschung 1989, 43, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Nenadis, N; Zhang, HY; Tsimidou, MZ. Structure–Antioxidant Activity Relationship of Ferulic Acid Derivatives: Effect of Carbon Side Chain Characteristic Groups. J. Agric. Food Chem 2003, 51, 1874–1879. [Google Scholar]
- Rittstieg, K; Suurnakki, A; Suortti, T; Kruus, K; Guebitz, G; Buchert. Investigations on the Laccase-Catalyzed Polymerization of Lignin Model Compounds Using Size-Exclusion HPLC. J. Enzyme Microb. Technol 2002, 31, 403–410. [Google Scholar]
- Himmel, ME; Tatsumoto, K; Oh, KK; Grohmann, K; Johnson, DK; Chum, HL. Molecular Weight Distribution of Aspen Lignins Estimated by Universal Calibration. In Lignin Properties and Materials; Glasser, WG, Sarkanen, S, Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1988; pp. 82–99. [Google Scholar]








| Catalyst | Oxidant | Mn | Mw | Mw/Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuSS | O2 | 850 | 1260 | 1.48 |
| CuSS | H2O2 | 1230 | 2840 | 2.30 |
| CoSS | O2 | 530 | 830 | 1.56 |
| MnSS | H2O2 | 510 | 620 | 1.22 |
| FeSS | H2O2 | 830 | 1350 | 1.62 |
| CuPS | O2 | 480 | 750 | 1.56 |
| CuPS | H2O2 | 925 | 1465 | 1.22 |
| CoPS | O2 | 380 | 505 | 1.36 |
| pH | Mn | Mw | Mw/Mn |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.5a | 843 | 1222 | 1.45 |
| 7b | 936 | 1537 | 1.82 |
| 9c | 1013 | 1748 | 1.72 |
| Method | Mn | Mw | Mw/Mn |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZT | 1230 | 3108 | 2.52 |
| ZL | 1076 | 2675 | 2.48 |
| Isoeugenol w/v% | Catalyst w/v% | Mn | Mw | Mw/Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.02 | 832 | 1487 | 1.79 |
| 1 | 0.05 | 981 | 1698 | 1.73 |
| 1 | 0.1 | 1190 | 2157 | 1.81 |
| 1 | 0.2 | 1522 | 3652 | 2.40 |
| 0.5 | 0.1 | 570 | 1100 | 1.92 |
| 1 | 0.1 | 1230 | 2840 | 2.30 |
| 5 | 0.1 | 1530 | 3390 | 2.21 |
| 10 | 0.1 | 1270 | 3010 | 2.37 |
| Oxidant Concentration (mol H2O2/mol isoeugenol) | Number of H2O2 aliquots | Mn | Mw | Mw/Mn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 1 | 2030 | 7600 | 3.75 |
| 5 | 4 | 1690 | 5570 | 3.31 |
| 5 | 8 | 1260 | 2650 | 2.10 |
| 5 | 16 | 1450 | 3500 | 2.41 |
| 10 | 1 | 1230 | 2840 | 2.30 |
| 10 | 4 | 2440 | 8460 | 3.46 |
| 10 | 8 | 1950 | 7760 | 3.98 |
| 10 | 16 | 1480 | 3250 | 2.19 |
| 15 | 1 | 1330 | 2700 | 2.03 |
| 15 | 4 | 1440 | 3260 | 2.19 |
| 15 | 8 | 1630 | 3430 | 2.11 |
| 15 | 16 | 1670 | 4120 | 2.47 |
| Phenol (AH) | IC50 (mg of AH/mg of DPPH♦) |
|---|---|
| isoeugenol | 0.195 |
| DHP | 1.41 |
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Salanti, A.; Orlandi, M.; Tolppa, E.-L.; Zoia, L. Oxidation of Isoeugenol by Salen Complexes with Bulky Substituents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 912-926. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11030912
Salanti A, Orlandi M, Tolppa E-L, Zoia L. Oxidation of Isoeugenol by Salen Complexes with Bulky Substituents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2010; 11(3):912-926. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11030912
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalanti, Anika, Marco Orlandi, Eeva-Liisa Tolppa, and Luca Zoia. 2010. "Oxidation of Isoeugenol by Salen Complexes with Bulky Substituents" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 11, no. 3: 912-926. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11030912
APA StyleSalanti, A., Orlandi, M., Tolppa, E. -L., & Zoia, L. (2010). Oxidation of Isoeugenol by Salen Complexes with Bulky Substituents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 11(3), 912-926. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11030912