Cytotoxicity of Phenol Red in Toxicity Assays for Carbon Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of CNPs
2.2. Adsorption of Phenol Red on CNPs
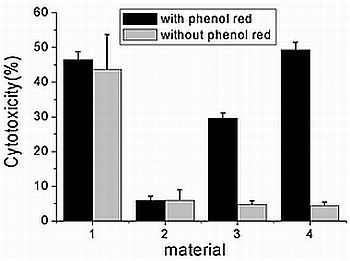
2.3. Effects of Phenol Red on Cytotoxicity
2.4. Cellular Uptake of Phenol Red and Its Dependence on Size of CBs
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Carbon Nanoparticles (CNPs)
3.2. Standard Curve Drawing of Phenol Red in Culture Medium
3.3. Determination of Adsorption Amounts of Phenol Red on CNPs
3.4. Assay for Phenol Red Concentration-Dependent Viability of Cells in Serum-Free Medium
3.5. Assay for Concentration-Dependent Cytotoxicity of Phenol Red in Serum-Free Medium with CNPs
3.6. Assay for Cytotoxicity of CNPs in Serum-Free Medium with or without Phenol Red
3.7. 125I Labeling of Phenol Red
3.8. Determination of Cellular Uptake of Phenol Red with Radiotracer Techniques
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
ijms-13-12336-s001.pdfAcknowledgements
References
- Nel, A.; Xia, T.; Madler, L.; Li, N. Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 2006, 311, 622–627. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.H.; Li, Q.N.; Wang, J.; Li, W.X.; Hu, J. Toxicology of Carbon Nanomaterials. In Nanotoxicology; Zhao, Y.L., Nalwa, H.S., Eds.; American Scientific Publishers: Stevenson Ranch, CA, USA, 2007; pp. 181–200. [Google Scholar]
- Dumortier, H.; Lacotte, S.; Pastorin, G.; Marega, R.; Wu, W.; Bonifazi, D.; Briand, J.P.; Prato, M.; Muller, S.; Bianco, A. Functionalized carbon nanotubes are non-cytotoxic and preserve the functionality of primary immune cells. Nano Lett 2006, 6, 1522–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Hurt, R.H.; Monthioux, M.; Kane, A. Toxicology of carbon nanomaterials: Status, trends, and perspectives on the special issue. Carbon 2006, 44, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Magrez, A.; Kasas, S.; Salicio, V.; Pasquier, N.; Seo, J.W.; Celio, M.; Catsicas, S.; Schwaller, B.; Forro, L. Cellular toxicity of carbon-based nanomaterials. Nano Lett 2006, 6, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar]
- Smart, S.K.; Cassady, A.I.; Lu, G.Q.; Martin, D.J. The biocompatibility of carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2006, 44, 1034–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Inman, A.O. Challenges for assessing carbon nanomaterial toxicity to the skin. Carbon 2006, 44, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Wörle-Knirsch, J.M.; Pulskamp, K.; Krug, H.F. Oops they did it again! Carbon nanotubes hoax scientists in viability assays. Nano Lett 2006, 6, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; von Dem Bussche, A.; Buechner, M.; Yan, A.; Kane, A.B.; Hurt, R.H. Adsorption of essential micronutrients by carbon nanotubes and the implications for nanotoxicity testing. Small 2008, 4, 721–727. [Google Scholar]
- Pantarotto, D.; Briand, J.P.; Prato, M.; Bianco, A. Translocation of bioactive peptides across cell membranes by carbon nanotubes. Chem. Commun. (Cambridge, UK) 2004, 1, 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, G.; Wang, H.; Yan, L.; Wang, X.; Pei, R.; Yan, T.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, X. Cytotoxicity of carbon nanomaterials: Single-wall nanotube, multi-wall nanotube, and fullerene. Environ. Sci. Technol 2005, 39, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar]
- Kostarelos, K.; Lacerda, L.; Pastorin, G.; Wu, W.; Wieckowski, S.; Luangsivilay, J.; Godefroy, S.; Pantarotto, D.; Briand, J.P.; Muller, S.; et al. Cellular uptake of functionalized carbon nanotubes is independent of functional group and cell type. Nat. Nanotechnol 2007, 2, 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, W.X.; Li, Q.N.; Li, Y.G.; Li, Y.F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Huang, Q. Effects of serum proteins on intracellular uptake and cytotoxicity of carbon nanoparticles. Carbon 2009, 47, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar]
- Parihar, S.; Sharon, M.; Sharon, M. Carbon nanomaterial shows drug delivery promise: Part 1—Selection of carbon nanomaterial and drug loading. Synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org 2006, 36, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, E.K.; Zhang, X.Q.; Chen, M.; Lam, R.; Robinson, E.; Huang, H.J.; Schaffer, D.; Osawa, E.; Goga, A.; Ho, D. Nanodiamond therapeutic delivery agents mediate enhanced chemoresistant tumor treatment. Sci. Transl. Med 2011, 3, 73ra21. [Google Scholar]
- Kam, N.W.S.; Liu, Z.; Dai, H.J. Carbon nanotubes as intracellular transporters for proteins and DNA: An investigation of the uptake mechanism and pathway. Angew. Chem 2005, 44, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, C.; Du, J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, Y.; Chai, Z.; Chen, C. Binding of blood proteins to carbon nanotubes reduces cytotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16968–16973. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Liang, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, N.; Sun, Y.; Chen, W.; Tai, R.; Fan, C.; Huang, Q. Excessive sodium ions delivered into cells by nanodiamonds: Implications for tumor therapy. Small 2012, 8, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Y.; Cai, X.; Li, W. The interaction and toxicity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with Stylonychia mytilus. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol 2006, 6, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Casey, A.; Davoren, M.; Herzog, E.; Lyng, F.M.; Byrne, H.J.; Chambers, G. Probing the interaction of single walled carbon nanotubes within cell culture medium as a precursor to toxicity testing. Carbon 2007, 45, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Casey, A.; Herzog, E.; Davoren, M.; Lyng, F.M.; Byrne, H.J.; Chambers, G. Spectroscopic analysis confirms the interactions between single walled carbon nanotubes and various dyes commonly used to assess cytotoxicity. Carbon 2007, 45, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, Y.; Yokoyama, A.; Shibata, K.; Akimoto, Y.; Ogino, S.; Nodasaka, Y.; Kohgo, T.; Tamura, K.; Akasaka, T.; Uo, M.; et al. Influence of length on cytotoxicity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes against human acute monocytic leukemia cell line THP-I in vitro and subcutaneous tissue of rats in vivo. Mol. BioSyst 2005, 1, 176–182. [Google Scholar]
- Chithrani, B.D.; Ghazani, A.A.; Chan, W.C.W. Determining the size and shape dependence of gold nanoparticle uptake into mammalian cells. Nano Lett 2006, 6, 662–668. [Google Scholar]
- Sohaebuddin, S.K.; Thevenot, P.T.; Baker, D.; Eaton, J.W.; Tang, L.P. Nanomaterial cytotoxicity is composition, size, and cell type dependent. Part. Fibre Toxicol 2010, 7, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.A.; Li, Q.N.; Xu, J.Y.; Li, J.; Cai, X.Q.; Liu, R.L.; Li, Y.J.; Ma, J.F.; Li, W.X. Comparative study on the acute pulmonary toxicity induced by 3 and 20 nm TiO2 primary particles in mice. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol 2007, 24, 239–244. [Google Scholar]
- Sager, T.M.; Castranova, V. Surface area of particle administered versus mass in determining the pulmonary toxicity of ultrafine and fine carbon black: Comparison to ultrafine titanium dioxide. Part. Fibre Toxicol 2009, 6, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Oberdorster, G. Toxicology of ultrafine particles: In vivo studies. Philos. Trans. Roy. Soc. A 2000, 358, 2719–2739. [Google Scholar]
- Muftuler, F.Z.B.; Unak, P.; Teksoz, S.; Acar, C.; Yolcular, S.; Yurekli, Y. I-131 labeling of tamoxifen and biodistribution studies in rats. Appl. Radiat. Isot 2008, 66, 178–187. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.Z.; Nie, L.; Wang, T.H.; Qin, Y.J.; Guo, Z.X.; Yang, D.L.; Yan, X.Y. Carbon nanotube delivery of the GFP gene into mammalian cells. ChemBioChem 2006, 7, 239–242. [Google Scholar]
- Kulamarva, A.; Bhathena, J.; Malhotra, M.; Sebak, S.; Nalamasu, O.; Ajayan, P.; Prakash, S. In vitro cytotoxicity of functionalized single walled carbon nanotubes for targeted gene delivery applications. Nanotoxicology 2008, 2, 184–188. [Google Scholar]
- Kam, N.W.S.; Jessop, T.C.; Wender, P.A.; Dai, H.J. Nanotube molecular transporters: Internalization of carbon nanotube-protein conjugates into mammalian cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2004, 126, 6850–6851. [Google Scholar]





| Medium composition | CNPs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MWNTs | PG | S160 | P90 | |
| Without serum | 2.36 ± 0.26 | 1.43 ± 0.16 | 3.81 ± 0.04 | 4.85 ± 0.02 |
| With serum | All data < 1.32 | |||
| Nanomaterials | Uptake quantities (ng 1000 cell−1) |
|---|---|
| Control | 0.31 ± 0.07 |
| MWNTs(−) | 2.33 ± 1.10 |
| PG(−) | 1.68 ± 0.36 |
| S160(−) | 7.10 ± 1.47 |
| P90(−) | 25.8 ± 1.9 |
| MWNTs(+) | 0.38 ± 0.06 |
| PG(+) | 0.33 ± 0.08 |
| S160(+) | 0.40 ± 0.15 |
| P90(+) | 0.52 ± 0.17 |
© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Fan, C.; Huang, Q. Cytotoxicity of Phenol Red in Toxicity Assays for Carbon Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 12336-12348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131012336
Zhu Y, Zhang X, Zhu J, Zhao Q, Li Y, Li W, Fan C, Huang Q. Cytotoxicity of Phenol Red in Toxicity Assays for Carbon Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(10):12336-12348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131012336
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Ying, Xiaoyong Zhang, Jianhua Zhu, Qunfen Zhao, Yuguo Li, Wenxin Li, Chunhai Fan, and Qing Huang. 2012. "Cytotoxicity of Phenol Red in Toxicity Assays for Carbon Nanoparticles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 10: 12336-12348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131012336
APA StyleZhu, Y., Zhang, X., Zhu, J., Zhao, Q., Li, Y., Li, W., Fan, C., & Huang, Q. (2012). Cytotoxicity of Phenol Red in Toxicity Assays for Carbon Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(10), 12336-12348. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131012336