Recent Advances in Food-Packing, Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications of Zein and Zein-Based Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
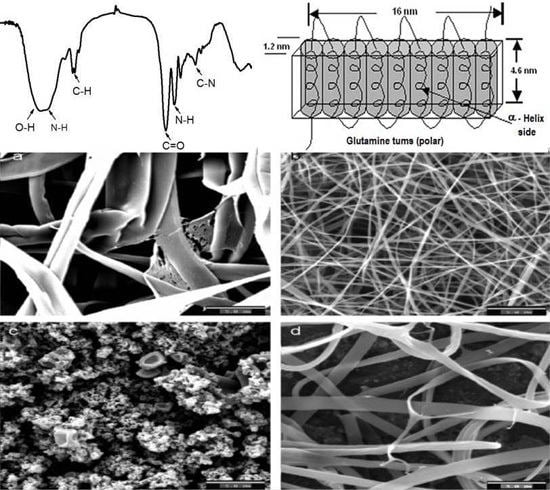
1.1. Composition and Structure of Zein


1.2. General Properties of Zein
| Physical Form | Amorphous Powder |
|---|---|
| Glass transition temperature | 165 °C |
| Thermal degradation point | 280 °C |
| Molecular weight | 21–25 kDa |
| Degree of polymerization | 210–245 |
| Isoelectric point | pH 6.2 |
| Partial specific volume | 0.771 |
1.3. Film-Forming Capability of Zein and Zein-Based Materials
1.4. Fibers of Zein and Zein-Based Materials
1.5. Fibers of Zein by Electrospinning Process

2. Mixing or Blends Based on Zein Aimed at Biomaterial Applications
2.1. Blends of Zein with Polymers
2.2. Zein-Blended Nanofibers Performed through Electrospinning
2.3. Mixing Zein or Zein-Blends with Non-Polymer Moieties
3. Some Methods for Chemical Modifying Zein
4. Biodegradation of Zein and Degradation of Zein and Zein-Based Materials
4.1. Biodegradation of Zein
4.2. Degradation of Zein and Zein-Based Materials
5. Biomedical Applications of Zein-Based Materials
5.1. As Drug Carriers for Drug Delivery


5.2. As Scaffolds in Tissue Engineering
5.3. As Enzymatic Hydrolysate Peptides for Reducing Blood Pressure
5.4. As Nutraceutical Zein Colloidal Particles
5.5. As Non-Conventional Biomaterial
6. Future Trends for Technological Applications of Zein-Based Materials
- (i)
- There are still few studies evaluating the influence of a chemical modifying process on the biodegradability of chemically-modified zein derivatives. Much of the works in the literature assume that the chemical modification of zein does not alter its biodegradability (or doing so at a very small scale, but neglected in deeper studies). In some cases, such an assumption might not be true;
- (ii)
- The high biocompatibility (inexistence of toxicity) of neat zein can be affected after the plasticization process or by blending with other polymers. A quick search made in the ISI (Web of Science©) database using simultaneously the keywords “zein”, “plasticization” (or “blending”) and “cytotoxicity” revealed the inexistence of studies correlating the effects of plasticization (or blending) of zein to biocompatibility. Therefore, more cytotoxicity studies in this direction are needed.
- (iii)
- The influence of the size and geometries on the biodegradability of zein and zein-based materials is an open issue. For instance, in the case of nanofibers or nanoparticles, the large exposed area may increase the rate of zein degradability, in an enzymatic environment.
- (iv)
- According to a very recent publication [5], the authors pointed out zein-based nanocomposites with inorganic nanocrystal materials. The authors stated that these materials “…will undoubtedly draw more attention. These nanocomposites-based delivery systems are beginning to demonstrate their superior capability to encapsulate and control the release of drugs for a wide variety of applications…”. This statement is true. The incorporation of inorganic particles as encapsulated materials in zein-based nanocomposites (particles, nanofibers) opens the window for identifying/tuning different properties of zein and zein-based materials.
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Mittal, G. Biodegradable protein-based films from plant resources: A review. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2010, 29, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Cheryan, M. Zein: The industrial protein from corn. Ind. Crops Prod. 2001, 13, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, M.I.; Tomka, I.; Waysek, E. Physico-chemical characterization of zein as a film coating polymer—A direct comparison with ethyl cellulose. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 141, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Dumont, M.-J. Review: Bio-based films from zein, keratin, pea, and rapeseed protein feedstocks. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 1915–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, Q. Zein-based micro- and nano-particles for drug and nutrient delivery: A review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Li, X.; Song, T. Electrospinning and crossfinking of Zein nanofiber mats. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Giner, S.; Gimenez, E.; Lagarona, J.M. Characterization of the morphology and thermal properties of zein prolamine nanostructures obtained by electrospinning. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, T.; Toyohara, K.; Minematsu, H. Preparation of ultrafine fibrous zein membranes via electrospinning. Polym. Int. 2005, 54, 1187–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lopes, F.; Geil, P.; Padua, G.W. Effects of processing on the structure of zein/oleic acid films investigated by X-ray diffraction. Macromol. Biosci. 2005, 5, 1200–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selling, G.W.; Sessa, D.J.; Palmquist, D.E. Effect of water and tri(ethylene) glycol on the rheological properties of zein. Polymer 2004, 45, 4249–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.; Yang, Y. Thermoplastic films from plant proteins. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Chen, J.X.; Dai, F.; Wu, F.B.; Yang, J.M.; Zhang, G.P. Protein fractions in barley grains as affected by some agronomic factors and their relationships to malt quality. Cereal Res. Commun. 2007, 35, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbetti, M.G.M. Handbook on Sourdough Biotechnology, 1st ed.; EUA: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–298.s. [Google Scholar]
- Magoshi, J.; Nakamura, S.; Murakami, K.I. Structure and physical-properties of seed proteins.1. Glass-transition and crystallization of zein protein from corn. J. Appl. Polymer Sci. 1992, 45, 2043–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.J.; Lamsal, B.P. Zein extraction from corn, corn products, and coproducts and modifications for various applications: A review. Cereal Chem. 2011, 88, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamla, M.C. The chemistry of cereal proteins—Lasztity, R. Bull. Et Mem. De La Societe D Anthropol. De Paris 1984, 11, 354–354. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Geraghty, D.; Peifer, M.A.; Rubenstein, I.; Messing, J. The primary structure of a plant-storage protein—Zein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981, 9, 5163–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabra, V.; Arreguin, R.; Galvez, A.; Quirasco, M.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R.; Farres, A. Characterization of a 19 kDa alpha-zein of high purity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, G.I.; Hoeller, U.; Schierle, J.; Neuringer, M.; Johnson, E.J.; Schalch, W. Metabolism of lutein and zeaxanthin in rhesus monkeys: Identification of (3R,6'R)- and (3R,6'S)-3'-dehydro-lutein as common metabolites and comparison to humans. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B-Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 151, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.W.; Myers, D.J.; Johnson, L.A. Factors affecting yield and composition of zein extracted from commercial corn gluten meal. Cereal Chem. 1997, 74, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, L.C.; Dallmer, M.F.; Radewonuk, E.R.; Parris, N.; Kurantz, M.; Craig, J.C. Zein batch extraction from dry-milled corn: Cereal disintegration by dissolving fluid shear. Cereal Chem. 1998, 75, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.J.; Lamsal, B.P. Development of new method for extraction of alpha-zein from corn gluten meal using different solvents. Cereal Chem. 2011, 88, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Cheryan, M.; deVor, R.E. Solvent extraction of zein from dry-milled corn. Cereal Chem. 2000, 77, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esen, A. Separation of alcohol-soluble proteins (zeins) from maize into 3 fractions by differential solubility. Plant Physiol. 1986, 80, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.M. Multiple zeins from maize endosperms characterized by reversed-phase high-performance liquid-chromatography. Plant Physiol. 1991, 95, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wroblewitz, S.; Huether, L.; Manderscheid, R.; Weigel, H.-J.; Waetzig, H.; Daenicke, S. Effect of rising atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration on the protein composition of cereal grain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 6616–6625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton, J.W. Zein: A history of processing and use. Cereal Chem. 2002, 79, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraman, I.; Lamsal, B.P. Recovery and characterization of alpha-zein from corn fermentation coproducts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3071–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forato, L.A.; Bernardes, R.; Colnago, L.A. Protein structure in KBr pellets by infrared spectroscopy. Anal. Biochem. 1998, 259, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argos, P.; Pedersen, K.; Marks, M.D.; Larkins, B.A. A structural model for maize zein proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 9984–9990. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsushima, N.; Danno, G.; Takezawa, H.; Izumi, Y. Three-dimensional structure of maize alpha-zein proteins studied by small-angle X-ray scattering. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta-Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1997, 1339, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, E. Desenvolvimento de blendas poliméricas de zeína e amido de milho. Ph.D. Dissertation, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, SP, Brazil, 26 January 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Xian, W.; Li, S.; Liu, C.; Padua, G.W. Topography and biocompatibility of patterned hydrophobic/hydrophilic zein layers. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton, J.W. Viscoelasticity of zein-starch doughs. Cereal Chem. 1992, 69, 351–355. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.C.; Liu, Z.D.; An, H.J.; Li, M.Q.; Hu, J. Nano-structure and properties of maize zein studied by atomic force microscopy. J. Cereal Sci. 2005, 41, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmambux, M.N.; Stading, M. In situ tensile deformation of zein films with plasticizers and filler materials. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parris, N.; Coffin, D.R. Composition factors affecting the water vapor permeability and tensile properties of hydrophilic zein films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.M.; Padua, G.W. Water vapor barrier properties of zein films plasticized with oleic acid. Cereal Chem. 1998, 75, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Rakotonirainy, A.M.; Padua, G.W. Thermal behavior of zein-based biodegradable films. Starch-Starke 2003, 55, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.M.; Padua, G.W.; Wei, L.S. Properties and microstructure of zein sheets plasticized with palmitic and stearic acids. Cereal Chem. 1997, 74, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuq, B.; Gontard, N.; Guilbert, S. Proteins as agricultural polymers for packaging production. Cereal Chem. 1998, 75, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Padua, G.W. Tensile properties of extruded Zein sheets and extrusion blown films. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2003, 288, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, E.; de Medeiros, E.S.; Carvalho, A.J.F.; Curvelo, A.A.S.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Mechanical and morphological characterization of starch/zein blends plasticized with glycerol. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 101, 4133–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selling, G.W. The effect of extrusion processing on Zein. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 2241–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Geil, P.; Padua, G. Role of hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions in structure development of zein films. J. Polym. Environ. 2004, 12, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.; Sampath, S. Adsorption of zein on surfaces with controlled wettability and thermal stability of adsorbed zein films. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2120–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, H.M.; Padua, G.W. Properties and microstructure of plasticized zein films. Cereal Chem. 1997, 74, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, J.F.; Geil, P.H.; Padua, G.W. Zein adsorption to hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces investigated by surface plasmon resonance. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1356–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, K.; Kokini, J.L.; Huang, Q. Engineering zein films with controlled surface morphology and hydrophilicity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 2186–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcan, I.; Yemenicioglu, A. Incorporating phenolic compounds opens a new perspective to use zein films as flexible bioactive packaging materials. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croston, C.B.; Evans, C.D.; Smith, A.K. Zein fibers preparation by wet spinning. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1945, 37, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uy, W.C. Zein Corn-Protein Fibre Production for Use in Clothing Fabrics|Involves Dry Spinning from a Volatile Solvent System, and Avoids Use of Environmentally Hazardous Alkaline Solutions and Acid Coagulating Baths. US5750064-A, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Pelosi, L.F. Crosslinked Zein Prepn.|Comprises Heating in the Presence of Water. WO9610582-A; WO9610582-A1; US5596080-A, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bhushani, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Electrospinning and electrospraying techniques: Potential food based applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 38, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahatheeswaran, D.; Mathew, A.; Aswathy, R.G.; Nagaoka, Y.; Venugopal, K.; Yoshida, Y.; Maekawa, T.; Sakthikumar, D. Hybrid fluorescent curcumin loaded zein electrospun nanofibrous scaffold for biomedical applications. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lim, L.T.; Kakuda, Y. Electrospun Zein Fibers as Carriers to Stabilize (−)-Epigallocatechin Gallate. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, C233–C240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongsasulak, S.; Pathumban, S.; Yoovidhya, T. Effect of entrapped alpha-tocopherol on mucoadhesivity and evaluation of the release, degradation, and swelling characteristics of zein-chitosan composite electrospun fibers. J. Food Eng. 2014, 120, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Li, X.; Song, T. Fabrication of zein/hyaluronic acid fibrous membranes by electrospinning. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2007, 18, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habeych, E.; Dekkers, B.; van der Goot, A.J.; Boom, R. Starch-zein blends formed by shear flow. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2008, 63, 5229–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, E.; Carvalho, A.J.F.D.; Curvelo, A.A.D.S.; Agnelli, J.A.M.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Preparation and characterization of thermoplastic starch/zein blends. Mater. Res. 2007, 10, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeych, E.; van der Goot, A.J.; Boom, R. In situ compatibilization of starch-zein blends under shear flow. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 3516–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, E.; Jacquet, P.; Coativy, G.; Reguerre, A.L.; Lourdin, D. Compatibilization of starch-zein melt processed blends by an ionic liquid used as plasticizer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corradini, E.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Guedes, C.G.F.; Rosa, D.S. Mechanical, thermal and morphological properties of poly(epsilon-caprolactone)/zein blends. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2004, 15, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, D.J.; Woods, K.K.; Mohamed, A.A.; Palmquist, D.E. Melt-processed blends of zein with polyvinylpyrrolidone. Ind. Crops Prod. 2011, 33, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selling, G.W.; Biswas, A. Blends of zein and nylon-6. J. Polym. Environ. 2012, 20, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Lee, T.-C.; Huang, Q. Structure and physical properties of zein/pluronic F127 composite films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Subirade, M. Elaboration and characterization of soy/zein protein microspheres for controlled nutraceutical delivery. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 3327–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, F.F.O.; Luzardo-Alvarez, A.; Perez-Estevez, A.; Seoane-Prado, R.; Blanco-Mendez, J. Development of a novel AMX-loaded PLGA/zein microsphere for root canal disinfection. Biomed. Mater. 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, V.; Piai, J.F.; Fajardo, A.R.; Favaro, S.L.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Preparation and characterization of zein and zein-chitosan microspheres with great prospective of application in controlled drug release. J. Nanomater. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Li, X.; Song, T.; Li, Y.; Pu, Y. Biodegradable nanofibrous membrane of zein/silk fibroin by electrospinning. Polym. Int. 2009, 58, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Giner, S.; Jose Ocio, M.; Maria Lagaron, J. Novel antimicrobial ultrathin structures of zein/chitosan blends obtained by electrospinning. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L.-M. Co-electrospun nanofibrous membranes of collagen and zein for wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unnithan, A.R.; Gnanasekaran, G.; Sathishkumar, Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, C.S. Electrospun antibacterial polyurethane-cellulose acetate-zein composite mats for wound dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 102, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.-H.; Wang, H.-J.; Tang, T.-T.; Zhang, X.-L.; Wang, J.-Y.; Dai, K.-R. Evaluation of the zein/inorganics composite on biocompatibility and osteoblastic differentiation. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, A.; Oliviero, M.; di Maio, E.; Netti, P.A.; Rofani, C.; Colosimo, A.; Guida, V.; Dallapiccola, B.; Palma, P.; Procaccini, E.; et al. Design of novel three-phase PCL/TZ-HA biomaterials for use in bone regeneration applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, A.; Zeppetelli, S.; di Maio, E.; Iannace, S.; Netti, P.A. Novel 3D porous multi-phase composite scaffolds based on PCL, thermoplastic zein and ha prepared via supercritical CO2 foaming for bone regeneration. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 1838–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, A.; Zeppetelli, S.; Oliviero, M.; Battista, E.; di Maio, E.; Iannace, S.; Netti, P.A. Microstructure, degradation and in vitro MG63 cells interactions of a new poly(epsilon-caprolactone), zein, and hydroxyapatite composite for bone tissue engineering. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2012, 27, 210–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Wei, J.; Liu, C.; OʼNeill, B.; Ngothai, Y. Fabrication and properties of porous scaffold of zein/PCL biocomposite for bone tissue engineering. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2012, 43, 2192–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, K.E.; Jane, J.L.; Pometto, A.L. Dialdehyde starch and zein plastic—Mechanical-properties and biodegradability. J. Environ. Polym. Degrad. 1995, 3, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selling, G.W.; Woods, K.K.; Biswas, A.; Willett, J.L. Reactive extrusion of zein with glyoxal. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 1828–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Selling, G.W.; Woods, K.K.; Evans, K. Surface modification of zein films. Ind. Crops Prod. 2009, 30, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braeuer, S.; Meister, F.; Gottloeber, R.-P.; Nechwatal, A. Preparation and thermoplastic processing of modified plant proteins. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2007, 292, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senna, M.M.; Salmieri, S.; el-Naggar, A.-W.; Safrany, A.; Lacroix, M. Improving the compatibility of zein/poly(vinyl alcohol) blends by gamma irradiation and graft copolymerization of acrylic acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4470–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.X.; Sakabe, H.; Isobe, S. Studies on the toughness and water resistance of zein-based polymers by modification. Polymer 2003, 44, 3901–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Huang, Y.; Yu, H.; Lee, T.-C.; Huang, Q. Reducing the brittleness of zein films through chemical modification. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imam, S.H.; Gordon, S.H. Biodegradation of coproducts from industrially processed corn in a compost environment. J. Polym. Environ. 2002, 10, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briassoulis, D.; Dejean, C. Critical review of norms and standards for biodegradable agricultural plastics part I (TM). Biodegradation in soil. J. Polym. Environ. 2010, 18, 384–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado-Lopez, P.; Murdan, S. Zein microspheres as drug/antigen carriers: A study of their degradation and erosion, in the presence and absence of enzymes. J. Microencapsul. 2006, 23, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchalska, P.; Luisa Marina, M.; Concepcion Garcia, M. Development of a reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography analytical methodology for the determination of antihypertensive peptides in maize crops. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1234, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobbetti, M.; Smacchi, E.; Corsetti, A.; Bellucci, M. Inhibition of proteolytic enzymes from Pseudomonas fluorescens ATCC 948 and angiotensin I-converting enzyme by peptides from zein, hordein, and gluten hydrolysates. J. Food Protect. 1997, 60, 499–504. [Google Scholar]
- Mannheim, A.; Cheryan, M. Water-soluble zein by enzymatic modification in organic-solvents. Cereal Chem. 1993, 70, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Fujimaki, M.; Abe, M.; Arai, S. Degradation of zein during germination of corn. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1977, 41, 887–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobokalonov, J.T.; Kasimova, G.F.; Muhidinov, Z.K.; Jonmurodov, A.S.; Khalikov, D.K.; Liu, L. Kinetics of piroxicam release from low-methylated pectin/zein hydrogel microspheres. Pharm. Chem. J. 2012, 46, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.-N.; Mo, H.-Y.; Yu, D.-G. Electrospun drug-loaded core-sheath PVP/zein nanofibers for biphasic drug release. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 438, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.X.; Shi, Y.P. A novel zein-based dry coating tablet design for zero-order release. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 370, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Padua, G.W. AGFD 124-Controlled self-organization of zein nanostructures for encapsulation of active food ingredients. Abstr. Pap. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 233, 46–46. [Google Scholar]
- Regier, M.C.; Taylor, J.D.; Borcyk, T.; Yang, Y.; Pannier, A.K. Fabrication and characterization of DNA-loaded zein nanospheres. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2012, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parris, N.; Cooke, P.H.; Hicks, K.B. Encapsulation of essential oils in zein nanospherical particles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4788–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, S.-J.; Sun, S.-X.; Sun, Q.-S.; Wang, J.-Y.; Liu, X.-M.; Liu, G.-Y. Tablets based on compressed zein microspheres for sustained oral administration: Design, pharmacokinetics, and clinical study. J. Biomater. Appl. 2011, 26, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Carneado, J.; Kogan, M.J.; Castel, S.; Giralt, E. Potential peptide carriers: Amphipathic proline-rich peptides derived from the N-terminal domain of gamma-zein. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1811–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yu, D.-G.; Chen, K.; Wang, G.; Williams, G.R. Smooth preparation of ibuprofen/zein microcomposites using an epoxy-coated electrospraying head. Mater. Lett. 2013, 93, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Lin, C.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y. Preparation, characterization, and in vitro release investigation of lutein/zein nanoparticles via solution enhanced dispersion by supercritical fluids. J. Food Eng. 2012, 109, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccioni, G.; DʼOrazio, N.; Salvatore, C.; Franceschelli, S.; Pesce, M.; Speranza, L. Carotenoids and Vitamins C and E in the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2012, 82, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.M.; Sun, Q.S.; Wang, H.J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.Y. Microspheres of corn protein, zein, for an ivermectin drug delivery system. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, T.T.Y.; Teng, Z.; Chen, P.; Sun, J.; Wang, Q. Encapsulation of indole-3-carbinol and 3,3'-diindolylmethane in zein/carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles with controlled release property and improved stability. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, B.; Whent, M.; Yu, L.; Wang, Q. Preparation and characterization of zein/chitosan complex for encapsulation of alpha-tocopherol, and its in vitro controlled release study. Coll. Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2011, 85, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsmeyer, R.W.; Gurny, R.; Doelker, E.; Buri, P.; Peppas, N.A. Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1983, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.K.; Kaur, G.; Verma, A. Fabrication of plant protein microspheres for encapsulation, stabilization and in vitro release of multiple anti-tuberculosis drugs. Coll. Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 375, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Davidson, P.M.; Zhong, Q. Release and antilisterial properties of nisin from zein capsules spray-dried at different temperatures. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 1977–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Zhong, Q. In vitro release kinetics of nisin as affected by Tween 20 and glycerol co-encapsulated in spray-dried zein capsules. J. Food Eng. 2011, 106, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsasulak, S.; Puttipaiboon, N.; Yoovidhya, T. Fabrication, gastromucoadhesivity, swelling, and degradation of zein-chitosan composite ultrafine fibers. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, N926–N935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Fabrication and characterization of novel assembled prolamin protein nanofabrics with improved stability, mechanical property and release profiles. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 21592–21601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Cellulose nanowhiskers and fiber alignment greatly improve mechanical properties of electrospun prolamin protein fibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 1709–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitta, S.K.; Numata, K. Biopolymer-based nanoparticles for drug/gene delivery and tissue engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 1629–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-J.; Gong, S.-J.; Lin, Z.-X.; Fu, J.-X.; Xue, S.-T.; Huang, J.-C.; Wang, J.-Y. In vivo biocompatibility and mechanical properties of porous zein scaffolds. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 3952–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, A.; Zeppetelli, S.; di Maio, E.; Iannace, S.; Netti, P.A. Architecture and properties of bi-modal porous scaffolds for bone regeneration prepared via supercritical CO2 foaming and porogen leaching combined process. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2012, 67, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, F. Zein nanofibrous membranes as templates for biomineralization of hydroxyapatite crystallites. Polym. Compos. 2013, 34, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Han, H.; Sun, D. Preparation and evaluation of electrospun zein/HA fibers based on two methods of adding HA nanoparticles. J. Bionic Eng. 2014, 11, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, A.; di Maio, E.; Iannace, S.; Netti, P.A. Tuning the microstructure and biodegradation of three-phase scaffolds for bone regeneration made of PCL, Zein, and HA. J. Cell. Plast. 2011, 47, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Reddy, N.; Yang, Y. Cytocompatible cross-linking of electrospun zein fibers for the development of water-stable tissue engineering scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 4042–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, S.; Miyoshi, S.; Kaneko, T.; Tanaka, H. Angiotensin-i-converting enzyme inhibitory activities of synthetic peptides related to the tandem repeated sequence of a maize endosperm protein. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1989, 53, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, S.; Kaneko, T.; Yoshizawa, Y.; Fukui, F.; Tanaka, H.; Maruyama, S. Hypotensive activity of enzymatic alpha-zein hydrolysate. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1991, 55, 1407–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.C.; Puchalska, P.; Esteve, C.; Marina, M.L. Vegetable foods: A cheap source of proteins and peptides with antihypertensive, antioxidant, and other less occurrence bioactivities. Talanta 2013, 106, 328–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parris, N.; Moreau, R.A.; Johnston, D.B.; Dickey, L.C.; Aluko, R.E. Angiotensin I converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides from commercial wet- and dry-milled corn germ. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 2620–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, N.; Ejiri, M.; Mizuno, S. Biogenic peptides and their potential use. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2003, 9, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Ma, H.; Mao, S.; Zhou, H. Effects of sweeping frequency ultrasound treatment on enzymatic preparations of ACE-inhibitory peptides from zein. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 238, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joye, I.J.; Davidov-Pardo, G.; McClements, D.J. Nanotechnology for increased micronutrient bioavailability. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, A.R.; Bouwens, E.C.M.; Velikov, K.P. Sodium caseinate stabilized zein colloidal particles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 12497–12503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.; Hu, Y.; Tiwari, J.K.; Velikov, K.P. Synthesis and characterisation of zein-curcumin colloidal particles. Soft Matter. 2010, 6, 6192–6199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Heussen, P.C.M.; Hazekamp, J.; Drost, E.; Velikov, K.P. Quercetin loaded biopolymeric colloidal particles prepared by simultaneous precipitation of quercetin with hydrophobic protein in aqueous medium. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Heussen, P.C.M.; Dorst, E.; Hazekamp, J.; Velikov, K.P. Colloidal approach to prepare colour blends from colourants with different solubility profiles. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1466–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.R.; Velikov, K.P. Zein as a source of functional colloidal nano- and microstructures. Curr. Opin. Coll. Interface Sci. 2014, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Haworth, I.S.; Zuo, Z.; Chow, M.S.S.; Chow, A.H.L. Physicochemical and structural characterization of quercetin-beta-cyclodextrin complexes. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luecha, J.; Hsiao, A.; Brodsky, S.; Liu, G.L.; Kokini, J.L. Green microfluidic devices made of corn proteins. Lab. Chip 2011, 11, 3419–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Huang, W.; Xing, Y.; Li, R.; Dai, J. Preparation of durable superhydrophobic surface by sol-gel method with water glass and citric acid. J. Sol.-Gel Sci. Technol. 2011, 58, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Padua, G.W.; Wang, Y. Controlled formation of hydrophobic surfaces by self-assembly of an amphiphilic natural protein from aqueous solutions. Soft Matter. 2013, 9, 5933–5941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corradini, E.; Curti, P.S.; Meniqueti, A.B.; Martins, A.F.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Recent Advances in Food-Packing, Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications of Zein and Zein-Based Materials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 22438-22470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151222438
Corradini E, Curti PS, Meniqueti AB, Martins AF, Rubira AF, Muniz EC. Recent Advances in Food-Packing, Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications of Zein and Zein-Based Materials. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(12):22438-22470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151222438
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorradini, Elisângela, Priscila S. Curti, Adriano B. Meniqueti, Alessandro F. Martins, Adley F. Rubira, and Edvani Curti Muniz. 2014. "Recent Advances in Food-Packing, Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications of Zein and Zein-Based Materials" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 12: 22438-22470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151222438
APA StyleCorradini, E., Curti, P. S., Meniqueti, A. B., Martins, A. F., Rubira, A. F., & Muniz, E. C. (2014). Recent Advances in Food-Packing, Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications of Zein and Zein-Based Materials. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(12), 22438-22470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151222438