Functional Identification of Proteus mirabilis eptC Gene Encoding a Core Lipopolysaccharide Phosphoethanolamine Transferase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification of Putative LPS PEtN Transferases
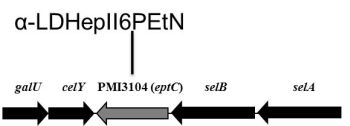
2.2. Identification of a Core LPS PEtN Transferase

2.3. eptC Gene Distribution
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, and Growth Conditions
3.2. General DNA Methods
3.3. DNA Sequencing and Computer Analysis of Sequence Data
3.4. Plasmid Constructions and Mutant Complementation Studies
3.5. LPS Isolation and SDS-PAGE
3.6. Large-Scale Isolation and Mild-Acid Degradation of LPS
3.7. Mass Spectrometry and NMR Studies
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| OS | oligosaccharide |
| O-PS | O-polysaccharide or O-antigen |
| PEtN | phosphoethanolamine |
| l,d-Hep | l-glycero-d-manno-heptose |
| Kdo | 3-deoxy-d-manno-oct-2-ulosonic acid or 3-deoxyoctulosonic acid |
| l-Ara4N | 4-amino-4-deoxy-l-arabinose |
- Author ContributionsAll the authors contributed to experimental data, their analysis, and the writing of the paper.
References
- O’Hara, C.M.; Brenner, F.W.; Miller, J.M. Classification, identification, and clinical significance of Proteus, Providencia, andMoganella. Clin. Microbiol. Rev 2000, 13, 534–546. [Google Scholar]
- Rozalski, A.; Sidorczyk, Z.; Kotelko, K. Potential virulence factors of Proteus bacilli. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev 1997, 61, 65–89. [Google Scholar]
- Belas, R. Proteus Mirabilis swarmer cell differentiation and urinary tract infection. In Tract Infections: Molecular Pathogenesis and Clinical Management; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; pp. 271–298. [Google Scholar]
- Himpsl, S.D.; Lockatell, C.V.; Hebel, J.R.; Jhonson, D.E.; Mobley, H.L.T. Identification of virulence determinants in uropathogenic Proteus mirabilis using signature-tagged mutagenesis. J. Med. Microbiol 2008, 57, 1068–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Torzewska, A.; Ruan, X.; Wang, X.; Rozalski, A.; Shao, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhou, H.; Feng, L.; Wang, L. Molecular and genetic analyses of the putative Proteus O antigen gene locus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2010, 76, 5471–5478. [Google Scholar]
- Knirel, Y.A.; Perepelov, A.V.; Kondakova, A.N.; Senchenkova, S.N.; Sydorczyk, Z.; Rozalsky, A.; Kaca, W. Structure and serology of O-antigens as the basis for classification of Proteus strains. Innate Immun 2011, 17, 70–96. [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradov, V. Structure of the core part of the lipopolysaccharide from Proteus mirabilis HI4320. Biochemistry 2010, 76, 803–887. [Google Scholar]
- Coderch, N.; Piqué, N.; Lindner, B.; Abitiu, N.; Merino, S.; Izquierdo, L.; Jimenez, N.; Tomás, J.M.; Holst, O.; Regué, M. Genetic and structural characterization of the core region of the lipopolysaccharide from Serratia marcescens N28b (serovar O4). J. Bacteriol 2004, 186, 978–988. [Google Scholar]
- Regué, M.; Izquierdo, L.; Fresno, S.; Piqué, N.; Corsaro, M.M.; Naldi, T.; de Castro, C.; Waidelich, D.; Merino, S.; Tomás, J.M. A second outer-core region in Klebsiella pneumoniae lipopolysaccharide. J. Bacteriol 2005, 187, 4198–4206. [Google Scholar]
- Aquilini, E.; Azevedo, J.; Jimenez, N.; Bouamama, L.; Tomás, J.M.; Regué, M. Functional identification of the Proteus mirabilis core lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis genes. J. Bacteriol 2010, 192, 4413–4424. [Google Scholar]
- Aquilini, E.; Azevedo, J.; Merino, S.; Jimenez, N.; Tomás, J.M.; Regué, M. Three enzymatic steps required for the galactosamine incorporation into core lipopolysaccharide. J. Biol. Chem 2010, 285, 39739–39749. [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel, C.Q.; Michael, F.S.; Stupak, J.; Li, J.; Cox, A.D.; Richards, J.C. Functional characterization of Lpt3 and Lpt6, the inner-core lipooligosaccharide phosphoethanolamine transferases fromNeisseria meningitidis. J. Bacteriol 2010, 192, 208–216. [Google Scholar]
- Tamayo, R.; Choudhury, B.; Septer, A.; Merighi, M.; Carlson, R.; Gunn, J.S. Identification of cptA, a PmrA-regulated locus required for phosphoethanolamine modification of the Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium lipopolysaccharide core. J. Bacteriol 2005, 187, 3391–3399. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, C.M.; Kalb, S.R.; Cotter, R.J.; Raetz, C.R.H. A phosphoethanolamine transferase specific for outer 3-deoxy-d-manno-octulosonic acid residue of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. J. Biol. Chem 2005, 280, 21202–21211. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Hsu, F.F.; Turk, J.; Groisman, E.A. The PmrA-regulated pmrC mediates phosphoethanolamine modifications of lipid A and polymyxin resistance inSalmonella enterica. J. Bacteriol 2004, 146, 4124–4133. [Google Scholar]
- Izquierdo, L.; Coderch, N.; Piqué, N.; Bedini, E.; Corsaro, M.M.; Merino, S.; Fresno, S.; Tomás, J.M.; Regué, M. The Klebsiella. pneumoniae wabG gene: Its role in the biosynthesis of the core lipopolysaccharide and virulence. J. Bacteriol 2003, 185, 7213–7221. [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradov, E.; Sidorczyk, Z.; Knirel, Y.A. Structure of the lipopolysaccharide core region of the bacteria of the genus. Proteus. Aust. J. Chem 2002, 55, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Kondakova, A.N.; Vinogradov, E.; Lindner, B.; Kocharova, N.A.; Rozalski, A.; Knirel, Y.A. Elucidation of the lipopolysaccharide core structures of bacteria of the genus. Providencia. J. Carbohydr. Chem 2006, 25, 499–520. [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan, D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J. Mol. Biol 1983, 166, 557–580. [Google Scholar]
- Guzman, L.M.; Belin, D.; Carson, M.J.; Beckwith, J. Tight regulation, modulation, and high-level expression by vectors containing the arabinose PBAD promoter. J. Bacteriol 1995, 177, 4121–4130. [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Sanger, F.; Nicklen, S.; Coulson, A.R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 5463–5467. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock, P.J.; Brown, T.M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J. Bacteriol 1983, 154, 269–277. [Google Scholar]
- Westphal, O.; Jann, K. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide extraction with phenol–water and further application of the procedure. Methods Carbohydr. Chem 1965, 5, 83–89. [Google Scholar]







| Sugar residue | C-1; H-1 | C-2; H-2 | C-3; H-3 (H-3a,3e) | C-4; H-4 | C-5; H-5 | C-6; H-6 (H-6a,6b) | C-7; H-7 (H-7a,7b) | C-8; H-8 (H-8a,8b) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-Glcp-(1→ | 103.7; 4.55 | 74.9; 3.32 | 76.7; 3.52 | 71.2; 3.37 | 77.5; 3.47 | 62.7; 3.97, 3.74 | ||
| α-ldHepp6P-(1→ | 102.5; 5.34 | 70.9; 4.15 | 71.5; 3.91 | 67.2; 3.91 | 72.4; 3.79 | 74.6; 4.57 | 62.5; 3.76, 3.85 | |
| →3,4)-α-ldHepp-(1→ | 102.2; 5.08 | 71.4; 4.17 | 74.8; 4.15 | 74.9; 4.26 | 72.5; 4.15 | 69.5; 4.13 | 64.4; 3.72, 3.74 | |
| →5)-α-Kdop | n.f. | 97.0 | 35.4; 2.11, 1.94 | 67.0; 4.12 | 75.9; 4.12 | 72.3; 3.88 | 70.3; 3.70 | 64.4; 3.81, 3.65 |
| NH2CH2CH2O- | 63.3; 4.17 | 41.2; 3.31 |
| Strain or plasmid | Relevant characteristics | Reference or source |
|---|---|---|
| P. mirabilis | ||
| HI4320 | Wild type | H.L.T. Mobley a |
| S1959 | Wild type, serovar O3 | Z. Sydorckzyk |
| R110 | Rough mutant of strain S 1959 | Z. Sydorckzyk b |
| 51/57 | Serovar O28 | Z. Sydorckzyk b |
| 50/57 | Serovar O27 | Z. Sydorckzyk b |
| 14/57 | Serovar O6 | Z. Sydorckzyk b |
| TG83 | Serovar O57 | Z. Sydorckzyk b |
| K. pneumoniae | ||
| 52145ΔwabH | Non-polar wabH mutant | [9] |
| 52145ΔwabG | Non-polar wabG mutant | [16] |
| E. coli | ||
| DH5α | F− endA hsdR17 (rk− mk−) supE44 thi-1 recA1 gyr-A96 φ80lacZ | [19] |
| Plasmid | ||
| pGEMT easy | PCR generated DNA fragment cloning vector AmpR | Promega c |
| pGEMT-eptC | pGEMT with eptC from strain HI4320, ApR | This study |
| pBAD18-Cm | Arabinose-inducible expression vector, CmR | [20] |
| pBAD18-Cm-eptC | Arabinose-inducible eptC, CmR | This study |
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Aquilini, E.; Merino, S.; Knirel, Y.A.; Regué, M.; Tomás, J.M. Functional Identification of Proteus mirabilis eptC Gene Encoding a Core Lipopolysaccharide Phosphoethanolamine Transferase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6689-6702. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15046689
Aquilini E, Merino S, Knirel YA, Regué M, Tomás JM. Functional Identification of Proteus mirabilis eptC Gene Encoding a Core Lipopolysaccharide Phosphoethanolamine Transferase. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(4):6689-6702. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15046689
Chicago/Turabian StyleAquilini, Eleonora, Susana Merino, Yuriy A. Knirel, Miguel Regué, and Juan M. Tomás. 2014. "Functional Identification of Proteus mirabilis eptC Gene Encoding a Core Lipopolysaccharide Phosphoethanolamine Transferase" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 4: 6689-6702. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15046689
APA StyleAquilini, E., Merino, S., Knirel, Y. A., Regué, M., & Tomás, J. M. (2014). Functional Identification of Proteus mirabilis eptC Gene Encoding a Core Lipopolysaccharide Phosphoethanolamine Transferase. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(4), 6689-6702. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15046689