Doublecortin May Play a Role in Defining Chondrocyte Phenotype
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
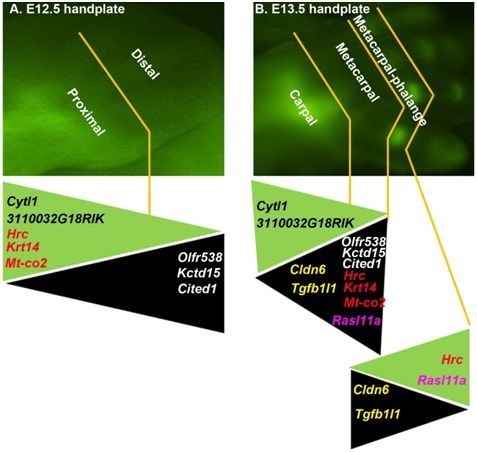
2.1. The DCX-Positive Proximal and DCX-Negative Distal Regions of E12.5 Mouse Handplate Express Different Genes
2.2. The DCX-Positive and DCX-Negative Regions of E13.5 Mouse Handplate Express Different Genes
2.3. Dynamic Gene Expression Profiles between the DCX-Positive Proximal Region of E12.5 Mouse Handplate and the DCX-Positive Carpal or Metacarpal-Phalange Region of E13.5 Mouse Handplate
2.4. DCX Affects Expression of Genes Associated with Chondrocyte Phenotype
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Animals
3.2. RNA Extraction and Microarray
3.3. Microarray Data Analysis
3.4. Cultures of Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells
3.5. Transduction of Human ASCs
3.6. Pellet Culture
3.7. Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcriptase PCR (qRT-PCR)
3.8. Western Blot Analysis
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Information
ijms-15-06941-s001.pdfAcknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
- Author ContributionsD.G. did the pellet culture and isolated RNA from mouse embryos; Q.-S.Z participated in study design, animal husbandry, and manuscript preparation; J.Z. did Illumina microarray analysis; Q.Z. participated in animal husbandry and taking photos of mouse embryos; S.L. did Western blot analysis; B.R. annotated the microarray data; B.A.B. provided human ASCs and participated in study design; S.E.B. constructed the lentiviral vectors; M.J.O. and F.H.S. participated in study design; Z.Y. participated in study design, data analysis, and manuscript preparation. All authors contributed to manuscript preparation, agreed to be listed, and approved the submitted version of the manuscript.
References
- Singh, G.; Miller, J.D.; Lee, F.H.; Pettitt, D.; Russell, M.W. Prevalence of cardiovascular disease risk factors among US adults with self-reported osteoarthritis: Data from the third national health and nutrition examination survey. Am. J. Manag. Care 2002, 8, S383–S391. [Google Scholar]
- Tuan, R.S. Stemming cartilage degeneration: Adult mesenchymal stem cells as a cell source for articular cartilage tissue engineering. Arthritis Rheumatol 2006, 54, 3075–3078. [Google Scholar]
- Yamane, S.; Cheng, E.; You, Z.; Reddi, A.H. Gene expression profiling of mouse articular and growth plate cartilage. Tissue Eng 2007, 13, 2163–2173. [Google Scholar]
- Muneoka, K.; Bryant, S.V. Evidence that patterning mechanisms in developing and regenerating limbs are the same. Nature 1982, 298, 369–371. [Google Scholar]
- Reddi, A.H. Cartilage-derived morphogenetic proteins and cartilage morphogenesis. Microsc. Res. Tech 1998, 43, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, P. Tissue patterning in the developing mouse limb. Int. J. Dev. Biol 1990, 34, 323–336. [Google Scholar]
- Mitrovic, D. Development of the diarthrodial joints in the rat embryo. Am. J. Anat 1978, 151, 475–485. [Google Scholar]
- Koyama, E.; Shibukawa, Y.; Nagayama, M.; Sugito, H.; Young, B.; Yuasa, T.; Okabe, T.; Ochiai, T.; Kamiya, N.; Rountree, R.B.; et al. A distinct cohort of progenitor cells participates in synovial joint and articular cartilage formation during mouse limb skeletogenesis. Dev. Biol 2008, 316, 62–73. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Cigan, A.D.; Marrero, L.; Lopreore, C.; Liu, S.; Ge, D.; Savoie, F.H.; You, Z. Expression of doublecortin reveals articular chondrocyte lineage in mouse embryonic limbs. Genesis 2011, 49, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Ramos, R.L.; Ackman, J.B.; Thomas, A.M.; Lee, R.V.; LoTurco, J.J. RNAi reveals doublecortin is required for radial migration in rat neocortex. Nat. Neurosci 2003, 6, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson, J.G.; Allen, K.M.; Fox, J.W.; Lamperti, E.D.; Berkovic, S.; Scheffer, I.; Cooper, E.C.; Dobyns, W.B.; Minnerath, S.R.; Ross, M.E.; et al. Doublecortin, a brain-specific gene mutated in human X-linked lissencephaly and double cortex syndrome, encodes a putative signaling protein. Cell 1998, 92, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Des Portes, V.; Francis, F.; Pinard, J.M.; Desguerre, I.; Moutard, M.L.; Snoeck, I.; Meiners, L.C.; Capron, F.; Cusmai, R.; Ricci, S.; et al. Doublecortin is the major gene causing X-linked subcortical laminar heterotopia (SCLH). Hum. Mol. Genet 1998, 7, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Ryan, J.A.; di Cesare, P.E.; Liu, J.; Walsh, C.A.; You, Z. Doublecortin is expressed in articular chondrocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2007, 363, 694–700. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Qanie, D.; Jafari, A.; Taipaleenmaki, H.; Jensen, C.H.; Saamanen, A.M.; Sanz, M.L.; Laborda, J.; Abdallah, B.M.; Kassem, M. Delta-like 1/fetal antigen-1 (Dlk1/FA1) is a novel regulator of chondrogenic cell differentiation via inhibition of the Akt kinase-dependent pathway. J. Biol. Chem 2011, 286, 32140–32149. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.S.; Ryoo, Z.Y.; Chun, J.S. Cytokine-like 1 (Cytl1) regulates the chondrogenesis of mesenchymal cells. J. Biol. Chem 2007, 282, 29359–29367. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, J.; Oh, H.; Lee, G.; Ryu, J.H.; Rhee, J.; Kim, J.H.; Chung, K.H.; Song, W.K.; Chun, C.H.; Chun, J.S. Cytokine-like 1 knock-out mice (Cytl1−/−) show normal cartilage and bone development but exhibit augmented osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. J. Biol. Chem 2011, 286, 27206–27213. [Google Scholar]
- Leussink, B.; Brouwer, A.; el Khattabi, M.; Poelmann, R.E.; Gittenberger-de Groot, A.C.; Meijlink, F. Expression patterns of the paired-related homeobox genes MHox/Prx1 and S8/Prx2 suggest roles in development of the heart and the forebrain. Mech. Dev 1995, 52, 51–64. [Google Scholar]
- Minogue, B.M.; Richardson, S.M.; Zeef, L.A.; Freemont, A.J.; Hoyland, J.A. Characterization of the human nucleus pulposus cell phenotype and evaluation of novel marker gene expression to define adult stem cell differentiation. Arthritis Rheumatol 2010, 62, 3695–3705. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, E.; Yang, M.; Lu, L. Overexpression of Wnt11 promotes chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in synergism with TGF-β. Mol. Cell. Biochem 2014, 390, 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Zanotti, S.; Canalis, E. Notch suppresses nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) transactivation and Nfatc1 expression in chondrocytes. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 762–772. [Google Scholar]
- Yamagami, T.; Molotkov, A.; Zhou, C.J. Canonical Wnt signaling activity during synovial joint development. J. Mol. Histol 2009, 40, 311–316. [Google Scholar]
- Pitsillides, A.A.; Beier, F. Cartilage biology in osteoarthritis—Lessons from developmental biology. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol 2011, 7, 654–663. [Google Scholar]
- James, C.G.; Appleton, C.T.; Ulici, V.; Underhill, T.M.; Beier, F. Microarray analyses of gene expression during chondrocyte differentiation identifies novel regulators of hypertrophy. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 5316–5333. [Google Scholar]
- Klatt, A.R.; Paulsson, M.; Wagener, R. Expression of matrilins during maturation of mouse skeletal tissues. Matrix Biol 2002, 21, 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Segat, D.; Frie, C.; Nitsche, P.D.; Klatt, A.R.; Piecha, D.; Korpos, E.; Deak, F.; Wagener, R.; Paulsson, M.; Smyth, N. Expression of matrilin-1, -2 and -3 in developing mouse limbs and heart. Matrix Biol 2000, 19, 649–655. [Google Scholar]
- Craft, A.M.; Ahmed, N.; Rockel, J.S.; Baht, G.S.; Alman, B.A.; Kandel, R.A.; Grigoriadis, A.E.; Keller, G.M. Specification of chondrocytes and cartilage tissues from embryonic stem cells. Development 2013, 140, 2597–2610. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H.; Sierra, R.A.; McGee, D.J.; Zabaleta, J. Transcriptional profiling of gastric epithelial cells infected with wild type or arginase-deficient Helicobacter pylori. BMC Microbiol 2012, 12, 175. [Google Scholar]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Gene Database. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 16 April 2014).
- UniProt Protein Knowledgebase Database. Available online: http://www.uniprot.org/ (accessed on 16 April 2014).
- Yu, G.; Wu, X.; Dietrich, M.A.; Polk, P.; Scott, L.K.; Ptitsyn, A.A.; Gimble, J.M. Yield and characterization of subcutaneous human adipose-derived stem cells by flow cytometric and adipogenic mRNA analyzes. Cytotherapy 2010, 12, 538–546. [Google Scholar]
- Strong, A.L.; Strong, T.A.; Rhodes, L.V.; Semon, J.A.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, S.; Gimble, J.M.; Burow, M.E.; Bunnell, B.A. Obesity associated alterations in the biology of adipose stem cells mediate enhanced tumorigenesis by estrogen dependent pathways. Breast Cancer Res 2013, 15, R102. [Google Scholar]
- Naldini, L.; Blomer, U.; Gallay, P.; Ory, D.; Mulligan, R.; Gage, F.H.; Verma, I.M.; Trono, D. In vivo gene delivery and stable transduction of nondividing cells by a lentiviral vector. Science 1996, 272, 263–267. [Google Scholar]
- Szymczak, A.L.; Workman, C.J.; Wang, Y.; Vignali, K.M.; Dilioglou, S.; Vanin, E.F.; Vignali, D.A. Correction of multi-gene deficiency in vivo using a single ‘self-cleaving’ 2A peptide-based retroviral vector. Nat. Biotechnol 2004, 22, 589–594. [Google Scholar]
- Mostoslavsky, G.; Kotton, D.N.; Fabian, A.J.; Gray, J.T.; Lee, J.S.; Mulligan, R.C. Efficiency of transduction of highly purified murine hematopoietic stem cells by lentiviral and oncoretroviral vectors under conditions of minimal in vitro manipulation. Mol. Ther 2005, 11, 932–940. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, D.; Dauchy, R.T.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Mao, L.; Dauchy, E.M.; Blask, D.E.; Hill, S.M.; Rowan, B.G.; Brainard, G.C.; et al. Insulin and IGF1 enhance IL-17-induced chemokine expression through a GSK3B-dependent mechanism: a new target for melatonin’s anti-inflammatory action. J. Pineal Res 2013, 55, 377–387. [Google Scholar]
- Corbo, J.C.; Deuel, T.A.; Long, J.M.; LaPorte, P.; Tsai, E.; Wynshaw-Boris, A.; Walsh, C.A. Doublecortin is required in mice for lamination of the hippocampus but not the neocortex. J. Neurosci 2002, 22, 7548–7557. [Google Scholar]



| No. | Gene ID | Gene Symbol | Proximal/Distal Ratio of Expression | Gene Name | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13386 | Dlk1 | 14.40 | Delta-like 1 homolog (Drosophila) | Inhibitory non-canonical protein ligand for the NOTCH1 receptor |
| 2 | 15464 | Hrc | 4.84 | Histidine rich calcium binding protein | Interactions with SERCA2 and triadin |
| 3 | 231162 | Cytl1 | 4.53 | Cytokine-like 1 | Cytl1-null mice show normal cartilage and bone development but exhibit augmented osteoarthritic cartilage destruction |
| 4 | 53412 | Ppp1r3c | 3.19 | Protein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 3C | Activates glycogen synthase, reduces glycogen phosphorylase activity and limits glycogen breakdown |
| 5 | 16664 | Krt14 | 3.15 | Keratin 14 | Enhances the mechanical properties involved in resilience of keratin intermediate filaments |
| 6 | 74194 | Rnd3 | 2.90 | Rho family GTPase 3 | Binds GTP but lacks intrinsic GTPase activity |
| 7 | 12306 | Anxa2 | 2.39 | Annexin A2 | Calcium-regulated membrane-binding protein |
| 8 | 14314 | Fstl | 2.34 | Follistatin-like 1 | May modulate the action of some growth factors on cell proliferation and differentiation |
| 9 | 21847 | Klf10 | 2.32 | Kruppel-like factor 10 | Inhibits cell growth |
| 10 | 16002 | Igf2 | 2.31 | Insulin-like growth factor 2 | Growth-promoting activity |
| 11 | 17709 | Mt-co2 | 2.18 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit II | Component of the respiratory chain |
| 12 | 73121 | 3110032G18RIK | 2.05 | Family with sequence similarity 101, member A | Unknown |
| 13 | 15401 | Hoxa4 | 0.49 | Homeobox A4 | Sequence-specific transcription factor |
| 14 | 15117 | Has2 | 0.48 | Hyaluronan synthase 2 | Hyaluronan/hyaluronic acid (HA) synthesis |
| 15 | 77087 | 3010027A04RIK | 0.44 | Ankyrin repeat domain 11 | Bone development |
| 16 | 258201 | Olfr538 | 0.43 | Olfactory receptor 538 | Interact with odorant molecules in the nose |
| 17 | 233107 | Kctd15 | 0.39 | Potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 15 | Unknown |
| 18 | 12705 | Cited1 | 0.36 | Cbp/p300-interacting transactivator with Glu/Asp-rich carboxy-terminal domain 1 | Transcriptional coactivator of the p300/CBP-mediated trancription complex |
| 19 | 20204 | Prrx2 | 0.29 | Paired related homeobox 2 | A developmental protein |
| No. | Gene ID | Gene Name | Carpal/Metacarpal Ratio of Expression | Gene Name | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 73121 | 3110032G18rik | 4.55 | Family with sequence similarity 101, member A | A novel gene uniquely expressed in developing forebrain and midbrain, but its null mutant exhibits no obvious phenotype |
| 2 | 231162 | Cytl1 | 3.54 | Cytokine-like 1 | Cytl1-null mice show normal cartilage and bone development but exhibit augmented osteoarthritic cartilage destruction |
| 3 | 50781 | Dkk3 | 3.26 | Dickkopf homolog 3 (Xenopus laevis) | Antagonizes canonical Wnt signaling |
| 4 | 77853 | Msl2 | 2.17 | Male-specific lethal 2 homolog (Drosophila) | Promotes Mdm2-independent cytoplasmic localization of p53 |
| 5 | 17709 | Mt-co2 | 0.46 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit II | Component of the respiratory chain |
| 6 | 21804 | Tgfb1I1 | 0.46 | Transforming growth factor beta 1 induced transcript 1 | A molecular adapter coordinating multiple protein-protein interactions |
| 7 | 233107 | Kctd15 | 0.46 | Potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 15 | Unknown |
| 8 | 93897 | Fzd10 | 0.45 | Frizzled homolog 10 (Drosophila) | Receptor for Wnt proteins |
| 9 | 258201 | Olfr538 | 0.45 | Olfactory receptor 538 | Interact with odorant molecules in the nose |
| 10 | 106565 | Dlk2 | 0.42 | Delta-like 2 homolog (Drosophila) | Acts as inhibitory non-canonical protein ligands for the NOTCH1 receptor |
| 11 | 12705 | Cited1 | 0.41 | Cbp/p300-interacting transactivator with Glu/Asp-rich carboxy-terminal domain 1 | Transcriptional coactivator of the p300/CBP-mediated trancription complex |
| 12 | 15464 | Hrc | 0.32 | Histidine rich calcium binding protein | May play a key role in the regulation of SR Ca cycling through its direct interactions with SERCA2 and triadin |
| 13 | 54419 | Cldn6 | 0.29 | Claudin 6 | Plays a major role in tight junction-specific obliteration of the intercellular space, through calcium-independent cell-adhesion |
| 14 | 16664 | Krt14 | 0.15 | keratin 14 | The nonhelical tail domain is involved in promoting KRT5-KRT14 filaments to self-organize into large bundles |
| No. | Gene ID | Gene Symbol | Metacarpal/Metacarpal-Phalange Ratio of Expression | Gene Name | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13386 | Dlk1 | 2.64 | Delta-like 1 homolog (Drosophila) | Acts as inhibitory non-canonical protein ligand for the NOTCH1 receptor |
| 2 | 71706 | Slc46a3 | 2.35 | Solute carrier family 46, member 3 | Unknown |
| 3 | 11806 | Apoa1 | 2.25 | Apolipoprotein A-I | Reverse transport of cholesterol from tissues to the liver for excretion |
| 4 | 54419 | Cldn6 | 2.15 | Claudin 6 | Role in tight junction-specific obliteration of the intercellular space, through calcium-independent cell-adhesion activity |
| 5 | 21804 | Tgfb1I1 | 2.12 | Transforming growth factor beta 1 induced transcript 1 | Functions as a molecular adapter coordinating multiple protein-protein interactions at the focal adhesion complex in nucleus |
| 6 | 12709 | Ckb | 2.06 | Creatine kinase, brain | Phospholipid biosynthesis |
| 7 | 11472 | Actn2 | 0.48 | Actinin alpha 2 | F-actin cross-linking protein which is thought to anchor actin to a variety of intracellular structures |
| 8 | 15464 | Hrc | 0.48 | Histidine rich calcium binding protein | Regulation of SR Ca cycling through its direct interactions with SERCA2 and triadin |
| 9 | 16876 | Lhx9 | 0.46 | LIM homeobox protein 9 | Gonadal development |
| 10 | 56360 | Acot9 | 0.46 | Acyl-CoA thioesterase 9 | Catalyze the hydrolysis of acyl-CoAs to the free fatty acid and coenzyme A |
| 11 | 72739 | Zkscan3 | 0.46 | Zinc finger with KRAB and SCAN domains 3 | Acts as a transcriptional regulator |
| 12 | 16704 | Krtap8-2 | 0.45 | Keratin associated protein 8-2 | Essential for the formation of a rigid and resistant hair shaft through their extensive disulfide bond cross-linking |
| 13 | 68895 | Rasl11a | 0.44 | RAS-like, family 11, member A | Regulator of rDNA transcription. Acts in cooperation UBF/UBTF and positively regulates RNA polymerase I transcription |
| 14 | 17883 | Myh3 | 0.39 | Myosin, heavy polypeptide 3, skeletal muscle, embryonic | Mutations in this gene have been associated Freeman-Sheldon syndrome and Sheldon-Hall syndrome |
| 15 | 17885 | Myh8 | 0.38 | Myosin, heavy polypeptide 8, skeletal muscle, perinatal | Motor protein of muscle thick filaments |
| 16 | 19791 | Rn18s | 0.28 | 18S Ribosomal RNA | A 45S rRNA, which serves as the precursor for the 18S, 5.8S and 28S rRNA, is transcribed from rDNA unit by RNA polymerase I |
| 17 | 226856 | Lpgat1 | 0.26 | Lysophosphatidylglycerol acyltransferase 1 | Recognizes various acyl-CoAs and LPGs as substrates but demonstrates a clear preference |
| No. | Gene ID | Gene Symbol | E12.5 Proximal/E13.5 Carpal Ratio of Expression | Gene Name | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 231162 | Cytl1 | 18.15 | Cytokine-like 1 | Cytl1-null mice show normal cartilage and bone development but exhibit augmented osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. |
| 2 | 73121 | 3110032G18rik | 7.09 | Family with sequence similarity 101, member A | A novel gene uniquely expressed in developing forebrain and midbrain |
| 3 | 50781 | Dkk3 | 6.15 | Dickkopf homolog 3 (Xenopus laevis) | Antagonizes canonical Wnt signaling |
| 4 | 19791 | Rn18s | 6.07 | 18S ribosomal RNA | Encodes a 18S rRNA |
| 5 | 319480 | Itga11 | 3.89 | Integrin alpha 11 | Regulating Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-2 and transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1 |
| 6 | 13386 | Dlk1 | 2.93 | Delta-like 1 homolog (Drosophila) | Acts as inhibitory non-canonical protein ligand for the NOTCH1 receptor |
| 7 | 15401 | Hoxa4 | 2.70 | Homeobox A4 | Sequence-specific transcription factor |
| 8 | 20680 | Sox7 | 2.29 | SRY-box containing gene 7 | A member of the SOX (SRY-related HMG-box) family of transcription factors involved in regulation |
| 9 | 67586 | D4bwg1540e | 2.29 | UBX domain protein 11 | May be involved in the reorganization of actin cytoskeleton mediated by RND1, RND2, and RND3 |
| 10 | 26433 | Plod3 | 2.11 | Procollagen-lysine, 2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 3 | Forms hydroxylysine residues in -Xaa-Lys-Gly- sequences in collagens |
| 11 | 100034361 | Mfap1b | 0.48 | Microfibrillarassociated protein 1B | Component of the elastin-associated microfibrils By similarity |
| 12 | 21371 | Tbca | 0.47 | Tubulin cofactor A | Tubulin-folding protein; involved in the early step of the tubulin folding pathway |
| 13 | 26941 | Slc9a3r1 | 0.41 | Solute carrier family 9 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger), member 3 regulator 1 | Scaffold protein that connects plasma membrane proteins with members of the ezrin/moesin/radixin |
| 14 | 12301 | Cacybp | 0.29 | Calcyclin binding protein | CacyBP/SIP interacts with tubulin in neuroblastoma NB2a cells and induces formation of globular tubulin assemblies. |
| 15 | 93897 | Fzd10 | 0.25 | Frizzled homolog 10 (Drosophila) | Receptor for Wnt proteins. Most of frizzled receptors are coupled to the beta-catenin canonical signaling pathway |
| 16 | 18590 | Pdgfa | 0.24 | Platelet derived growth factor, alpha | Growth factor that plays an essential role in the regulation of embryonic development |
| 17 | 66643 | Lix1 | 0.24 | Limb expression 1 homolog (chicken) | Unknown |
| 18 | 16664 | Krt14 | 0.15 | Keratin 14 | Involved in resilience of keratin intermediate filaments |
| No. | Gene ID | Gene Symbol | E12.5 Proximal/E13.5 Metacarpal-Phalange Ratio of Expression | Gene Name | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 19791 | Rn18s | 6.66 | Rn18s 18S ribosomal RNA | Encodes a 18S rRNA |
| 2 | 319480 | Itga11 | 4.54 | Integrin alpha 11 | Regulating Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-2 and transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1 |
| 3 | 231162 | Cytl1 | 4.09 | Cytokine-like 1 | Cytl1-null mice show normal cartilage and bone development but exhibit augmented osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. |
| 4 | 72053 | 2010008E23Rik | 3.93 | Transmembrane and ubiquitin-like domain containing 2 | Unknown |
| 5 | 21804 | Tgfb1i1 | 3.16 | Transforming growth factor beta 1 induced transcript 1 | A molecular adapter coordinating multiple protein-protein interactions at the focal adhesion complex and in the nucleus |
| 6 | 108903 | Tbcd | 2.79 | Tubulin-specific chaperone d | Tubulin-folding protein |
| 7 | 67586 | Ubxn11 | 2.3 | UBX domain protein 11 | Reorganization of actin cytoskeleton |
| 8 | 20680 | Sox7 | 2.24 | SRY-box containing gene 7 | member of the SOX (SRY-related HMG-box) family of transcription factors |
| 9 | 50781 | Dkk3 | 2.16 | Dickkopf homolog 3 (Xenopus laevis) | Inhibit Wnt regulated processes |
| 10 | 258201 | Olfr538 | 2.06 | Olfactory receptor 538 | Olfactory receptors interact with odorant molecules in the nose |
| 11 | 100034361 | Mfap1b | 0.45 | Microfibrillar-associated protein 1B | Component of the elastin-associated microfibrils by similarity |
| 12 | 66643 | Lix1 | 0.15 | Limb expression 1 homolog (chicken) | Little is known about LIX1, except that it is evolutionarily conserved and highly expressed in spinal cord motor neurons |
| Gene | Primer | Nucleotide Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Collagen I | sense | CACCAATCACCTGCGTACAGAA |
| antisense | ACAGATCACGTCATCGCACAAC | |
| Collagen II | sense | GGCAATAGCAGGTTCACGTACA |
| antisense | CGATAACAGTCTTGCCCCACTT | |
| Aggrecan (core protein) | sense | AAGTATCATCAGTCCCAGAATCTAGCA |
| antisense | CGTGGAATGCAGAGGTGGTT | |
| SZP | sense | TTGCGCAATGGGACATTAGTT |
| antisense | AGCTGGAGATGGTGGACTGAA | |
| Matrilin 1 | sense | AGGGACTGCGTTTGCATTTTT |
| antisense | TCAGTAAAGAAATTCACAGCACTCAGA | |
| Matrilin 2 | sense | GACGGACGGGCTCAGGAT |
| antisense | GATACCATTGGCCTTGGCTTTA | |
| GDF5 | sense | ATTTGTGCCTGGTGACTTCC |
| antisense | AGCCCTCTCCTCTTCTCTCC | |
| GAPDH | sense | TAAAAGCAGCCCTGGTGACC |
| antisense | CCACATCGCTCAGACACCAT | |
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, D.; Zhang, Q.-S.; Zabaleta, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, S.; Reiser, B.; Bunnell, B.A.; Braun, S.E.; O'Brien, M.J.; Savoie, F.H.; et al. Doublecortin May Play a Role in Defining Chondrocyte Phenotype. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6941-6960. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15046941
Ge D, Zhang Q-S, Zabaleta J, Zhang Q, Liu S, Reiser B, Bunnell BA, Braun SE, O'Brien MJ, Savoie FH, et al. Doublecortin May Play a Role in Defining Chondrocyte Phenotype. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(4):6941-6960. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15046941
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Dongxia, Qing-Song Zhang, Jovanny Zabaleta, Qiuyang Zhang, Sen Liu, Brendan Reiser, Bruce A. Bunnell, Stephen E. Braun, Michael J. O'Brien, Felix H. Savoie, and et al. 2014. "Doublecortin May Play a Role in Defining Chondrocyte Phenotype" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 4: 6941-6960. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15046941
APA StyleGe, D., Zhang, Q. -S., Zabaleta, J., Zhang, Q., Liu, S., Reiser, B., Bunnell, B. A., Braun, S. E., O'Brien, M. J., Savoie, F. H., & You, Z. (2014). Doublecortin May Play a Role in Defining Chondrocyte Phenotype. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(4), 6941-6960. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15046941