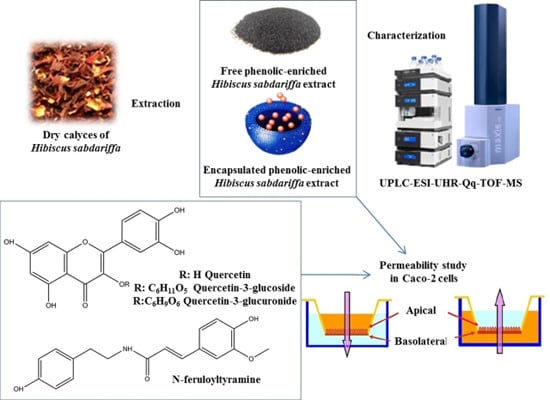
Permeability Study of Polyphenols Derived from a Phenolic-Enriched Hibiscus sabdariffa Extract by UHPLC-ESI-UHR-Qq-TOF-MS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of the Phenolic-Enriched Hibiscus sabdariffa (PEHS) Extract

| Peak Number | Retention Time (min) | m/z Experimental | m/z Calculated | Error (ppm) | Molecular Formula | Proposed Compound |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.4 | 207.0146 | 207.0146 | −0.0 | C6H8O8 | Hydroxycitric acid |
| 2 | 3.6 | 189.0041 | 189.0041 | −0.1 | C6H6O7 | Hibiscus acid |
| 3 | 4.3 | 235.0458 | 235.0459 | 0.4 | C8H12O8 | Hibiscus acid hydroxyethylesther |
| 4 | 4.5 | 595.1303 | 595.1305 | 0.3 | C26H28O16 | Delphinidin-3-sambubioside |
| 5 | 4.8 | 315.0720 | 315.0722 | 0.4 | C13H16O9 | Chlorogenic acid quinone |
| 6 | 5.3 | 353.0874 | 353.0878 | 1.0 | C16H18O9 | Neochlorogenic acid |
| 7 | 5.5 | 579.1350 | 579.1355 | 0.9 | C26H28O15 | Cyanidin-3-sambubioside |
| 8 | 6.0 | 217.0352 | 217.0354 | 1.0 | C8H10O7 | Hibiscus acid dimethylesther |
| 9 | 6.3 | 353.0877 | 353.0878 | 0.3 | C16H18O9 | Chlorogenic acid |
| 10 | 6.7 | 353.0877 | 353.0878 | 0.3 | C16H18O9 | Cryptochlorogenic acid |
| 11 | 7.1 | 335.0408 | 335.0409 | 0.1 | C15H12O9 | Methyl digallate |
| 12 | 7.9 | 369.0460 | 369.0463 | 0.8 | C15H14O11 | 2-O-trans-caffeoyl-hydroxicitric acid |
| 13 | 8.2 | 353.0874 | 353.0878 | 1.0 | C16H18O9 | 1-O-caffeoylquinic acid |
| 14 | 8.5 | 611.1246 | 611.1254 | 1.3 | C26H28O17 | Myricetin-3-arabinogalactoside |
| 15 | 9.0 | 337.0925 | 337.0929 | 1.3 | C16H18O8 | Coumaroylquinic acid |
| 16 | 9.2 | 236.0563 | 236.0564 | 0.6 | C11H11NO5 | UK |
| 17 | 9.7 | 263.0772 | 263.0772 | 0.0 | C10H16O8 | Hibiscus acid hydroxyethyldimethylesther |
| 18 | 10.7 | 595.1305 | 595.1305 | −0.0 | C26H28O16 | Quercetin-3-sambubioside |
| 19 | 11.3 | 335.0771 | 335.0772 | 0.4 | C16H16O8 | 5-O-caffeoylshikimic acid |
| 20 | 12.0 | 263.0773 | 263.0772 | −0.3 | C10H16O8 | 2-O-trans-feruloyl-hydroxicitric acid |
| 21 | 12.3 | 609.1458 | 609.1461 | 0.5 | C27H30O16 | Quercetin-3-rutinoside |
| 22 | 13.1 | 385.1139 | 385.1140 | 0.3 | C17H22O10 | UK |
| 23 | 13.6 | 579.1356 | 579.1355 | −0.2 | C26H28O15 | Kaempferol-3-O-sambubioside |
| 24 | 14.0 | 463.0882 | 463.0882 | 0.0 | C21H20O12 | Quercetin-3-glucoside |
| 25 | 15.3 | 593.1512 | 593.1512 | −0.0 | C27H30O15 | Kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside |
| 26 | 15.5 | 381.1190 | 381.1191 | 0.1 | C18H22O9 | Ethylchlorogenate |
| 27 | 17.1 | 319.0826 | 319.0823 | −0.8 | C16H16O7 | Methylepigallocatechin |
| 28 | 17.7 | 457.1716 | 457.1715 | −0.1 | C21H30O11 | UK |
| 29 | 20.3 | 317.0309 | 317.0303 | −1.8 | C15H10O8 | Myricetin |
| 30 | 24.5 | 312.1245 | 312.1241 | −1.2 | C18H19NO4 | N-feruloyltyramine |
| 31 | 26.4 | 301.0358 | 301.0354 | −1.4 | C15H10O7 | Quercetin |
| 32 | 29.1 | 285.0415 | 285.0404 | −3.6 | C15H10O6 | Kaempferol |
2.2. Permeability of Free and Encapsulated PEHS Extracts
| Extract | Free PEHS | Encapsulated PEHS | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | Transport Medium | Cytoplasm | Membrane | Transport Medium | Cytoplasm | Membrane | ||||||
Ap-Bas  | Bas-Ap  | Ap-Bas  | Bas-Ap  | Ap-Bas  | Bas-Ap  | Ap-Bas  | Bas-Ap  | Ap-Bas  | Bas-Ap  | Ap-Bas  | Bas-Ap  | |
| Hibiscus acid | + | |||||||||||
| Neochlorogenic acid | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| Hibiscus acid dimethylesther | + | + | + | |||||||||
| Chlorogenic acid | + | + | + | + | ||||||||
| Cryptochlorogenic acid | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| Methyldigallate | + | + | + | |||||||||
| Coumaroylquinic acid | + | + | ||||||||||
| 5-O-caffeoylshikimic acid | + | + | + | |||||||||
| Methylepigallocatechin | + | |||||||||||
| N-feruloyltyramine | + | + | + | + | ||||||||
| Quercetin | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||
2.3. Permeation of Pure Compounds Related to PEHS Composition
| Analyte | LOD (μg/mL) | LOQ (μg/mL) | Calibration Range (μg/mL) | Calibration Equations | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin | 0.05 | 0.17 | 0.17–20 | y = 13.372 x − 0.0038 | 0.998 |
| Quercetin-3-glucoside | 0.07 | 0.23 | 0.23–55 | y = 2.5235 x + 0.0113 | 0.988 |
| Quercetin-3-glucuronide | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.2–45 | y = 11.545 x + 0.0087 | 0.992 |
| N-feruloyltyramine | 0.014 | 0.048 | 0.2–40 | y = 14.995 x + 0.1088 | 0.990 |
| Apical-Basolateral Flux | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (min) | 30 | 60 | 90 | 120 |
| Quercetin | 0.28 ± 0.02 | 0.49 ± 0.03 | 1.33 ± 0.02 | 1.32 ± 0.01 |
| Quercetin-3-glucoside | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0.47 ± 0.03 |
| Quercetin-3-glucuronide | ND | ND | ND | <LOQ |
| N-feruloyltyramine | 0.69 ± 0.02 | 2.3 ± 0.2 | 4.2 ± 0.5 | 6.6 ± 0.8 |
| Basolateral-Apical Flux | ||||
| Time (min) | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Quercetin | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 1.1 ± 0.4 |
| Quercetin-3-glucoside | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| Quercetin-3-glucuronide | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| N-feruloyltyramine | 1.35 ± 0.04 | 1.35 ± 0.04 | 1.35 ± 0.04 | 1.35 ± 0.04 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Preparation of PEHS
3.3. Cell Culture and Permeability Studies
3.4. Sample Treatments
3.5. Analytical Methodology
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, B.H.; Al Wabel, N.; Blunden, G. Phytochemical, pharmacological and toxicological aspects of Hibiscus sabdariffa L.: A review. Phytother. Res. 2005, 19, 369–375. [Google Scholar]
- McKay, D.L.; Chen, C.O.; Saltzman, E.; Blumberg, J.B. Hibiscus sabdariffa L. tea (tisane) lowers blood pressure in prehypertensive and mildly hypertensive adults. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ajay, M.; Chai, H.J.; Mustafa, A.M.; Gilani, A.H.; Mustafa, M.R. Mechanisms of the anti-hypertensive effect of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. calyces. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 109, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari-Khosravi, H.; Jalali-Khanabadi, B.; Afkhami-Ardekani, M.; Fatehi, F. Effects of sour tea (Hibiscus sabdariffa) on lipid profile and lipoproteins in patients with type II diabetes. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2009, 15, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oboh, G.; Rocha, J.B.T. Antioxidant and neuroprotective properties of sour tea (Hibiscus sabdariffa, calyx) and green tea (Camellia sinensis) on some pro-oxidant-induced lipid peroxidation in brain in vitro. Food Biophys. 2008, 3, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farombi, E.O.; Fakoya, A. Free radical scavenging and antigenotoxic activities of natural phenolic compounds in dried flowers of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2005, 49, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaroni, D.; Ravishankar, S. Bactericidal effects of roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa) against foodborne pathogens in vitro and on romaine lettuce and alfalfa sprouts. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Foods 2012, 4, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, P.; Seok, J.; Kim, Y.; Eun, J.; Oh, S. Antimicrobial and antioxidative effects of roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) flower extract and its fractions on skin microorganisms and oxidation. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2007, 16, 409–414. [Google Scholar]
- Mounnissamy, V.M.; Gopal, V.; Gunasegaran, R.; Saraswathy, A. Antiinflammatory activity of gossypetin isolated from Hibiscus sabdariffa. Indian J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2002, 12, 85–86. [Google Scholar]
- Fakeye, T.O.; Pal, A.; Bawankule, D.U.; Khanuja, S.P.S. Immunomodulatory effect of extracts of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. (Family Malvaceae) in a mouse model. Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herranz-López, M.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Pérez-Sanchez, A.; Barrajón-Catalán, E.; Beltrán-Debón, R.; Menéndez, J.A.; Alonso-Villaverde, C.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Joven, J.; Micol, V. Synergism of plant-derived polyphenols in adipogenesis: Perspectives and implications. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Wang, W.; Hsu, J.; Yang, M.; Wang, C. The protective effects of Hibiscus sabdariffa extract on CCl 4-induced liver fibrosis in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, G.; Cao, L.; Xu, P.; Jeney, G.; Nakao, M. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of Hibiscus sabdariffa extract against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatocyte damage in Cyprinus carpio. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2011, 47, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Huang, H.; Huang, C.; Chen, J.; Wang, C. Hibiscus polyphenol-rich extract induces apoptosis in human gastric carcinoma cells via p53 phosphorylation and p38 MAPK/FasL cascade pathway. Mol. Carcinog. 2005, 43, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Chen, J.; Kuo, W.; Wang, C. Chemopreventive properties of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. on human gastric carcinoma cells through apoptosis induction and JNK/p38 MAPK signaling activation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2007, 165, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvajal-Zarrabal, O.; Hayward-Jones, P.M.; Orta-Flores, Z.; Nolasco-Hipólito, C.; Barradas-Dermitz, D.M.; Aguilar-Uscanga, M.G.; Pedroza-Hernández, M.F. Effect of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. dried calyx ethanol extract on fat absorption-excretion, and body weight implication in rats. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2009, 2009, 394592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Herranz-López, M.; Beltrán-Debón, R.; Borrás-Linares, I.; Barrajón-Catalán, E.; Joven, J.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Micol, V. Bioavailability study of a polyphenol-enriched extract from Hibiscus Sabdariffa in rats and associated antioxidant status. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 1590–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, A.L.; Lamm, M.G.; Funk, J.L.; Ritenbaugh, C. Hibiscus sabdariffa L. in the treatment of hypertension and hyperlipidemia: A comprehensive review of animal and human studies. Fitoterapia 2013, 85, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcón-Alonso, J.; Zamilpa, A.; Aguilar, F.A.; Herrera-Ruiz, M.; Tortoriello, J.; Jimenez-Ferrer, E. Pharmacological characterization of the diuretic effect of Hibiscus sabdariffa Linn (Malvaceae) extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.L.; Morris, B.; Tonnis, B.; Davis, J.; Pederson, G.A. Assessment of oil content and fatty acid composition variability in two economically important hibiscus species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 6620–6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Medina, I.C.; Beltrán-Debón, R.; Molina, V.M.; Alonso-Villaverde, C.; Joven, J.; Menéndez, J.A.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A. Direct characterization of aqueous extract of Hibiscus sabdariffa using HPLC with diode array detection coupled to ESI and ion trap MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 3441–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Rodríguez-Medina, I.C.; Beltrán-Debón, R.; Pasini, F.; Joven, J.; Micol, V.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A. Quantification of the polyphenolic fraction and in vitro antioxidant and in vivo anti-hyperlipemic activities of Hibiscus sabdariffa aqueous extract. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-Debón, R.; Alonso-Villaverde, C.; Aragonès, G.; Rodríguez-Medina, I.; Rull, A.; Micol, V.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A.; Camps, J.; Joven, J. The aqueous extract of Hibiscus sabdariffa calices modulates the production of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in humans. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joven, J.; Espinel, E.; Rull, A.; Aragonès, G.; Rodríguez-Gallego, E.; Camps, J.; Micol, V.; Herranz-López, M.; Menéndez, J.A.; Borrás, I.; et al. Plant-derived polyphenols regulate expression of miRNA paralogs miR-103/107 and miR-122 and prevent diet-induced fatty liver disease in hyperlipidemic mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2012, 1820, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joven, J.; Rull, A.; Rodriguez-Gallego, E.; Camps, J.; Riera-Borrull, M.; Hernández-Aguilera, A.; Martin-Paredero, V.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Micol, V.; Alonso-Villaverde, C.; et al. Multifunctional targets of dietary polyphenols in disease: A case for the chemokine network and energy metabolism. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 51, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joven, J.; March, I.; Espinel, E.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Rodríguez-Gallego, E.; Aragonès, G.; Beltrán-Debón, R.; Alonso-Villaverde, C.; Rios, L.; Martin-Paredero, V.; et al. Hibiscus sabdariffa extract lowers blood pressure and improves endothelial function. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1374–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Li, Y.; Feng, Z.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, P. Hepatoprotective constituents from the roots and stems of Erycibe hainanesis. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.C.; Bi, P.X.; Huang, R.C.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, S.F. Determination of the antiviral caffeoyl quinic acids isolated from L. japonica thunb. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2005, 25, 751–755. [Google Scholar]
- Amaki, K.; Saito, E.; Taniguchi, K.; Joshita, K.; Murata, M. Role of chlorogenic acid quinone and interaction of chlorogenic acid quinone and catechins in the enzymatic browning of apple. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Sugiura, M.; Sonokawa, Y.; Shimamura, T.; Homma, S. Properties of chlorogenic acid quinone: Relationship between browning and the formation of hydrogen peroxide from a quinone solution. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 2525–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Simon, J.E.; Aviles, I.F.; He, K.; Zheng, Q.; Tadmor, Y. Analysis of antioxidative phenolic compounds in artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakya, R.; Navarre, D.A. Rapid screening of ascorbic acid, glycoalkaloids, and phenolics in potato using high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 5253–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Romero, M.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A. Metabolite profiling and quantification of phenolic compounds in methanol extracts of tomato fruit. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 1848–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, T.; Nishikiori, T.; Takino, Y. Three new substituted cinnamoyl hydroxycitric acids from corn plant. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1977, 41, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obouayeba, A.P.; Djyh, N.B.; Diabate, S.; Djaman, A.J.; N’Guessan, J.D.; Kone, M.; Kouakou, T.H. Phytochemical and antioxidant activity of roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) petal extracts. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 1453–1465. [Google Scholar]
- Artursson, P.; Karlsson, J. Correlation between oral drug absorption in humans and apparent drug permeability coefficients in human intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 175, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artursson, P.; Palm, K.; Luthman, K. Caco-2 monolayers in experimental and theoretical predictions of drug transport. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funes, L.; Laporta, O.; Cerdán-Calero, M.; Micol, V. Effects of verbascoside, a phenylpropanoid glycoside from Lemon verbena, on phospholipid model membranes. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2010, 163, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caturla, N.; Vera-Samper, E.; Villalaín, J.; Mateo, C.R.; Micol, V. The relationship between the antioxidant and the antibacterial properties of galloylated catechins and the structure of phospholipid model membranes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 648–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laporta, O.; Pérez-Fons, L.; Mallavia, R.; Caturla, N.; Micol, V. Isolation, characterization and antioxidant capacity assessment of the bioactive compounds derived from Hypoxis rooperi corm extract (African potato). Food Chem. 2007, 101, 1425–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joven, J.; Micol, V.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Alonso-Villaverde, C.; Menéndez, J.A.; Aragonès, G.; Barrajón-Catalán, E.; Beltrán-Debón, R.; Camps, J.; Cufí, S.; et al. Polyphenols and the modulation of gene expression pathways: Can we eat our way out of the danger of chronic disease? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 985–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, T.L.; Gomez-Juaristi, M.; Poquet, L.; Redeuil, K.; Nagy, K.; Renouf, M.; Williamson, G. Absorption of dimethoxycinnamic acid derivatives in vitro and pharmacokinetic profile in human plasma following coffee consumption. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, I.; Nave, F.; Gonçalves, R.; de Freitas, V.; Mateus, N. On the Bioavailability of flavanols and anthocyanins: Flavanol-anthocyanin dimers. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, Y.; Shimizu, M. Transepithelial transport of ferulic acid by monocarboxylic acid transporter in Caco-2 cell monolayers. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2003, 67, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Shimizu, M. Transepithelial transport of p-coumaric acid and gallic acid in Caco-2 cell monolayers. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2003, 67, 2317–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konishi, Y.; Kobayashi, S. Transepithelial transport of chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, and their colonic metabolites in intestinal Caco-2 cell monolayers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2518–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morand, C.; Manach, C.; Crespy, V.; Remesy, C. Quercetin 3-O-β-glucoside is better absorbed than other quercetin forms and is not present in rat plasma. Free Radic. Res. 2000, 33, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morand, C.; Manach, C.; Crespy, V.; Remesy, C. Respective bioavailability of quercetin aglycone and its glycosides in a rat model. Biofactors 2000, 12, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walgren, R.A.; Walle, U.K.; Walle, T. Transport of quercetin and its glucosides across human intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998, 55, 1721–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manach, C.; Morand, C.; Crespy, V.; Demigné, C.; Texier, O.; Régérat, F.; Rémésy, C. Quercetin is recovered in human plasma as conjugated derivatives which retain antioxidant properties. FEBS Lett. 1998, 426, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabane, M.N.; Al Ahmad, A.; Peluso, J.; Muller, C.D.; Ubeaud, G. Quercetin and naringenin transport across human intestinal Caco-2 cells. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borrás-Linares, I.; Herranz-López, M.; Barrajón-Catalán, E.; Arráez-Román, D.; Gonzálezlvarez, I.; Bermejo, M.; Gutiérrez, A.F.; Micol, V.; Segura-Carretero, A. Permeability Study of Polyphenols Derived from a Phenolic-Enriched Hibiscus sabdariffa Extract by UHPLC-ESI-UHR-Qq-TOF-MS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 18396-18411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818396
Borrás-Linares I, Herranz-López M, Barrajón-Catalán E, Arráez-Román D, Gonzálezlvarez I, Bermejo M, Gutiérrez AF, Micol V, Segura-Carretero A. Permeability Study of Polyphenols Derived from a Phenolic-Enriched Hibiscus sabdariffa Extract by UHPLC-ESI-UHR-Qq-TOF-MS. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(8):18396-18411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818396
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorrás-Linares, Isabel, María Herranz-López, Enrique Barrajón-Catalán, David Arráez-Román, Isabel Gonzálezlvarez, Marival Bermejo, Alberto Fernández Gutiérrez, Vicente Micol, and Antonio Segura-Carretero. 2015. "Permeability Study of Polyphenols Derived from a Phenolic-Enriched Hibiscus sabdariffa Extract by UHPLC-ESI-UHR-Qq-TOF-MS" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 8: 18396-18411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818396
APA StyleBorrás-Linares, I., Herranz-López, M., Barrajón-Catalán, E., Arráez-Román, D., Gonzálezlvarez, I., Bermejo, M., Gutiérrez, A. F., Micol, V., & Segura-Carretero, A. (2015). Permeability Study of Polyphenols Derived from a Phenolic-Enriched Hibiscus sabdariffa Extract by UHPLC-ESI-UHR-Qq-TOF-MS. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(8), 18396-18411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818396