Use of Atomic Force Microscopy to Study the Multi-Modular Interaction of Bacterial Adhesins to Mucins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
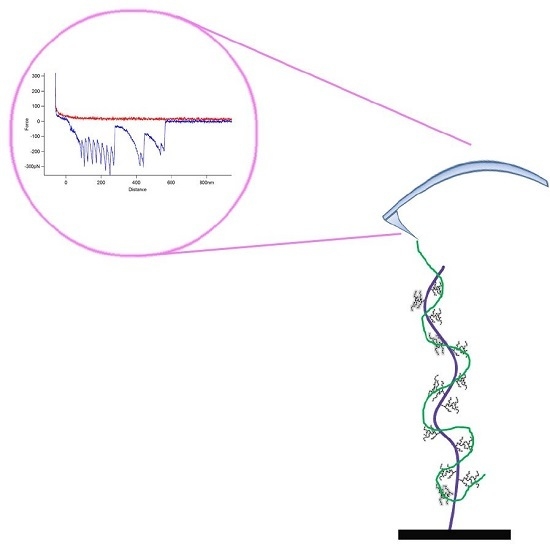
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Full-Length MUB Purification
4.3. Gal-3 Heterologous Expression and Purification
4.4. Atomic Force Microscopy
4.5. Force Spectroscopy
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bäckhed, F.; Ley, R.E.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Peterson, D.A.; Gordon, J.I. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 2005, 307, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Lin, H. Dysbiosis in gastrointestinal disorders. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 30, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.E.; Ambort, D.; Pelaseyed, T.; Schütte, A.; Gustafsson, J.K.; Ermund, A.; Subramani, D.B.; Holmén-Larsson, J.M.; Thomsson, K.A.; Bergström, J.H.; et al. Composition and functional role of the mucus layers in the intestine. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 3635–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockhausen, I.; Schachter, H.; Stanley, P. O-GalNAc glycans. Essentials of Glycobiology; Varki, A., Cummings, R.D., Esko, J.D., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 115–128. [Google Scholar]
- Juge, N. Microbial adhesins to gastrointestinal mucus. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tailford, L.E.; Crost, E.H.; Kavanaugh, D.; Juge, N. Mucin glycan foraging in the human gut microbiome. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerbino, E.; Carasi, P.; Mobili, P.; Serradell, M.A.; Gómez-Zavaglia, A. Role of S-layer proteins in bacteria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 31, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hymes, J.P.; Johnson, B.R.; Barrangou, R.; Klaenhammer, T.R. Functional analysis of an S-Layer-associated fibronectin-binding protein in Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 2676–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granato, D.; Perotti, F.; Masserey, I.; Rouvet, M.; Golliard, M.; Servin, A.; Brassart, D. Cell Surface-Associated Lipoteichoic Acid Acts as an Adhesion Factor for Attachment of Lactobacillus johnsonii La1 to Human Enterocyte-Like Caco-2 Cells. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walter, J.; Loach, D.M.; Alqumber, M.; Rockel, C.; Hermann, C.; Pfitzenmaier, M.; Tannock, G.W. d-alanyl ester depletion of teichoic acids in Lactobacillus reuteri 100–23 results in impaired colonization of the mouse gastrointestinal tract. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1750–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankainen, M.; Paulin, L.; Tynkkynen, S.; von Ossowski, I.; Reunanen, J.; Partanen, P.; Satokari, R.; Vesterlund, S.; Hendrickx, A.P.; Lebeer, S.; et al. Comparative genomic analysis of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG reveals pili containing a human-mucus binding protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17193–17198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Ossowski, I.; Reunanen, J.; Satokari, R.; Vesterlund, S.; Kankainen, M.; Huhtinen, H.; Tynkkynen, S.; Salminen, S.; de Vos, W.M.; Palva, A. Mucosal adhesion properties of the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG SpaCBA and SpaFED pilin subunits. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2049–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelain, M.; Duviau, M.P.; Oxaran, V.; Schmitz, P.; Cocaign-Bousquet, M.; Loubière, P.; Piard, J.C.; Mercier-Bonin, M. Oligomerized backbone pilin helps piliated Lactococcus lactis to withstand shear flow. Biofouling 2016, 32, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, K.; Ueno, S.; Sugiyama, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Mukai, T. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG SpaC pilin subunit binds to the carbohydrate moieties of intestinal glycoconjugates. Anim. Sci. J. 2016, 87, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Nishiyama, K.; Miyajima, H.; Osawa, R.; Yamamoto, Y.; Mukai, T. Adhesion properties of a putative polymorphic fimbrial subunit protein from Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2016, 35, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granato, D.; Bergonzelli, G.E.; Pridmore, R.D.; Marvin, L.; Rouvet, M.; Corthésy-Theulaz, I.E. Cell surface-associated elongation factor Tu mediates the attachment of Lactobacillus johnsonii NCC533 (La1) to human intestinal cells and mucins. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 2160–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergonzelli, G.E.; Granato, D.; Pridmore, R.D.; Marvin-Guy, L.F.; Donnicola, D.; Corthésy-Theulaz, I.E. GroEL of Lactobacillus johnsonii La1 (NCC 533) is cell surface associated: potential role in interactions with the host and the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, H.; Uchida, H.; Kawai, Y.; Kawasaki, T.; Wakahara, N.; Matsuo, H.; Watanabe, M.; Kitazawa, H.; Ohnuma, S.; Miura, K.; et al. Cell surface Lactobacillus plantarum LA 318 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) adheres to human colonic mucin. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, K.; Ochiai, A.; Tsubokawa, D.; Ishihara, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Mukai, T. Identification and characterization of sulfated carbohydrate-binding protein from Lactobacillus reuteri. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.K.; Shah, K.R.; Pappachan, A.; Gupta, S.; Singh, D.D. Cloning, expression and characterization of a mucin-binding GAPDH from Lactobacillus acidophilus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrova, M.I.; Imholz, N.C.; Verhoeven, T.L.; Balzarini, J.; van Damme, E.J.; Schols, D.; Vanderleyden, J.; Lebeer, S. Lectin-Like molecules of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG inhibit pathogenic Escherichia coli and Salmonella biofilm formation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valeriano, V.D.; Bagon, B.B.; Balolong, M.P.; Kang, D.K. Carbohydrate-binding specificities of potential probiotic Lactobacillus strains in porcine jejunal (IPEC-J2) cells and porcine mucin. J. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etzold, S.; Juge, N. Structural insights into bacterial recognition of intestinal mucins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2014, 28, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, S.; Jonsson, H. A high-molecular-mass cell-surface protein from Lactobacillus reuteri 1063 adheres to mucus components. Microbiology 2002, 148, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKenzie, D.A.; Jeffers, F.; Parker, M.L.; Vibert-Vallet, A.; Bongaerts, R.J.; Roos, S.; Walter, J.; Juge, N. Strain-specific diversity of mucus-binding proteins in the adhesion and aggregation properties of Lactobacillus reuteri. Microbiology 2010, 156, 3368–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etzold, S.; Kober, O.I.; MacKenzie, D.A.; Tailford, L.E.; Gunning, P.; Walshaw, J.; Hemmings, A.M.; Juge, N. Structural basis for adaptation of lactobacilli to gastrointestinal mucus. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 888–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukić, J.; Strahinić, I.; Jovčić, B.; Filipić, B.; Topisirović, L.; Kojić, M.; Begović, J. Different roles for lactococcal aggregation factor and mucin binding protein in adhesion to gastrointestinal mucosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7993–8000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, H.; Uchida, H.; Kawai, Y.; Kitazawa, H.; Miura, K.; Shiiba, K.; Horii, A.; Saito, T. Quantitative evaluation of adhesion of lactobacilli isolated from human intestinal tissues to human colonic mucin using surface plasmon resonance (BIACORE assay). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, I.N.; Okawara, T.; Watanabe, M.; Kawai, Y.; Kitazawa, H.; Ohnuma, S.; Shibata, C.; Horii, A.; Kimura, K.; Taketomo, N.; et al. New screening methods for probiotics with adhesion properties to sialic acid and sulphate residues in human colonic mucin using the Biacore assay. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, K.; Kawanabe, A.; Miyauchi, H.; Abe, F.; Tsubokawa, D.; Ishihara, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Mukai, T. Evaluation of bifidobacterial adhesion to acidic sugar chains of porcine colonic mucins. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 1444–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, K.; Nakamata, K.; Ueno, S.; Terao, A.; Aryantini, N.P.; Sujaya, I.N.; Fukuda, K.; Urashima, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Mukai, T. Adhesion properties of Lactobacillus rhamnosus mucus-binding factor to mucin and extracellular matrix proteins. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2015, 79, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naughton, J.; Duggan, G.; Bourke, B.; Clyne, M. Interaction of microbes with mucus and mucins: Recent developments. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffers, F.; Fuell, C.; Tailford, L.E.; MacKenzie, D.A.; Bongaerts, R.J.; Juge, N. Mucin-lectin interactions assessed by flow cytometry. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 1486–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naughton, J.A.; Mariño, K.; Dolan, B.; Reid, C.; Gough, R.; Gallagher, M.E.; Kilcoyne, M.; Gerlach, J.Q.; Joshi, L.; Rudd, P.; et al. Divergent mechanisms of interaction of Helicobacter pylori and Campylobacter jejuni with mucus and mucins. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 2838–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukic, J.; Strahinic, I.; Milenkovi, M.; Nikolic, M.; Tolinacki, M.; Kojic, M.; Begovic, J. Aggregation factor as an inhibitor of bacterial binding to gut mucosa. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 68, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altamimi, M.; Abdelhay, O.; Rastall, R.A. Effect of oligosaccharides on the adhesion of gut bacteria to human HT-29 cells. Anaerobe 2016, 39, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaussart, A.; El-Kirat-Chatel, S.; Sullan, R.M.; Alsteens, D.; Herman, P.; Derclaye, S.; Dufrêne, Y.F. Quantifying the forces guiding microbial cell adhesion using single-cell force spectroscopy. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinterdorfer, P.; Gruber, H.J.; Kienberger, F.; Kada, G.; Riener, C.; Broken, C.; Schindler, H. Surface attachment of ligands and receptors for molecular recognition force microscopy. Colloids Surf. 2002, 23, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dague, E.; Le, D.T.; Zanna, S.; Marcus, P.; Loubière, P.; Mercier-Bonin, M. Probing in vitro interactions between Lactococcus lactis and mucins using AFM. Langmuir 2010, 26, 11010–11017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, D.T.; Tran, T.L.; Duviau, M.P.; Meyrand, M.; Guérardel, Y.; Castelain, M.; Loubière, P.; Chapot-Chartier, M.P.; Dague, E.; Mercier-Bonin, M. Unraveling the role of surface mucus-binding protein and pili in muco-adhesion of Lactococcus lactis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, P.; Beaussart, A.; Alsteens, D.; Dupres, V.; Claes, I.; von Ossowski, I.; de Vos, W.M.; Palva, A.; Lebeer, S.; Vanderleyden, J.; et al. Adhesion and nanomechanics of pili from the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3685–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunning, A.P.; Kirby, A.R.; Fuell, C.; Pin, C.; Tailford, L.E.; Juge, N. Mining the “glycocode”—Exploring the spatial distribution of glycans in gastrointestinal mucin using force spectroscopy. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 2342–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, S.K.; Shriver-Lake, L.C.; Prior, K.J.; Georger, J.H.; Calvert, J.M.; Bredehorst, R.; Ligler, F.S. Use of thiol terminated silanes and heterobifunctional crosslinkers for immobilisation of antibodies on silica surfaces. Anal. Biochem. 1989, 178, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratky, O.; Porod, G. Röntgenuntersuchung gelöster Fadenmoleküle. Recl. Trav. Chim. 1949, 68, 1106–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flory, P.J.; Volkenstein, M. Statistical mechanics of chain molecules. Biopolymers 1969, 8, 699–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuche, F. Physical Properties of Polymers; Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1962; p. 354. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, S.B.; Cui, Y.; Bustamante, C. Overstretching B-DNA: The elastic response of individual double-stranded and single-stranded DNA molecules. Science 1996, 271, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rounsevell, R.; Forman, J.R.; Clarke, J. Atomic Force Microscopy: Mechanical unfolding of proteins. Methods 2004, 34, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, V.J.; Kirby, A.R.; Gunning, A.P. Atomic Force Microscopy for Biologists, 2nd ed.; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2009; pp. 384–387. [Google Scholar]
- Gunning, A.P.; Pin, C.; Morris, V.J. Galectin 3-β-galactobiose interactions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bresalier, R.S.; Byrd, J.C.; Wang, L.; Raz, A. Colon cancer mucin: A new ligand for the β-galactoside-binding protein galectin-3. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 4354–4357. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shan, M.; Gentile, M.; Yeiser, J.R.; Walland, A.C.; Bornstein, V.U.; Chen, K.; He, B.; Cassis, L.; Bigas, A.; Cols, M.; et al. Mucus enhances gut homeostasis and oral tolerance by delivering immunoregulatory signals. Science 2013, 342, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumic, J.; Dabelic, S.; Flögel, M. Galectin-3: An open-ended story. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1760, 616–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boekhorst, J.; Helmer, Q.; Kleerebezem, M.; Siezen, R.J. Comparative analysis of proteins with a mucus-binding domain found exclusively in lactic acid bacteria. Microbiology 2006, 152, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gruszka, D.T.; Whelan, F.; Farrance, O.E.; Fung, H.K.H.; Paci, E.; Jeffries, C.M.; Svergun, D.I.; Baldock, C.; Baumann, C.G.; Brockwell, D.J.; et al. Cooperative folding of intrinsically disordered domains drives assembly of a strong elongated protein. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKenzie, D.A.; Tailford, L.E.; Hemmings, A.M.; Juge, N. Crystal structure of a mucus-binding protein repeat reveals an unexpected functional immunoglobulin binding activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 32444–32453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullan, R.M.; Beaussart, A.; Tripathi, P.; Derclaye, S.; El-Kirat-Chatel, S.; Li, J.K.; Schneider, Y.J.; Vanderleyden, J.; Lebeer, S.; Dufrêne, Y.F. Single-cell force spectroscopy of pili-mediated adhesion. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 1134–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strunz, T.; Oroszlan, K.; Schumakovitch, I.; Güntherodt, H.J.; Hegner, M. Model energy landscapes and the force-induced dissociation of ligand-receptor bonds. Biophys. J. 2000, 79, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kirat-Chatel, S.; Beaussart, A.; Boyd, C.D.; O'Toole, G.A.; Dufrêne, Y.F. Single-cell and single-molecule analysis deciphers the localization, adhesion, and mechanics of the biofilm adhesin LapA. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touhami, A.; Hoffmann, B.; Vasella, A.; Denis, F.; Dufrene, Y.F. Probing specific lectin-carbohydrate interactions using atomic force microscopy imaging and force measurements. Langmuir 2003, 19, 1745–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Limenitakis, J.P.; Fuhrer, T.; Geuking, M.B.; Lawson, M.A.; Wyss, M.; Brugiroux, S.; Keller, I.; Macpherson, J.A.; Rupp, S.; et al. The outer mucus layer hosts a distinct intestinal microbial niche. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johansson, M.E.; Phillipson, M.; Petersson, J.; Velcich, A.; Holm, L.; Hansson, G.C. The inner of the two Muc2 mucin-dependent mucus layers in colon is devoid of bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15064–15069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, J.M.; Karlsson, H.; Sjövall, H.; Hansson, G.C. A complex, but uniform O-glycosylation of the human MUC2 mucin from colonic biopsies analyzed by nanoLC/MSn. Glycobiology 2009, 19, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crost, E.H.; Tailford, L.E.; Le Gall, G.; Fons, M.; Henrissat, B.; Juge, N. Utilisation of mucin glycans by the human gut symbiont Ruminococcus gnavus is strain-dependent. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutter, J.L.; Bechhoefer, J. Calibration of atomic force microscope tips. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1993, 64, 1868–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunning, A.P.; Chambers, S.; Pin, C.; Man, A.L.; Morris, V.J.; Nicoletti, C. Mapping specific adhesive interactions on living human intestinal epithelial cells with atomic force microscopy. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 2331–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gunning, A.P.; Kavanaugh, D.; Thursby, E.; Etzold, S.; MacKenzie, D.A.; Juge, N. Use of Atomic Force Microscopy to Study the Multi-Modular Interaction of Bacterial Adhesins to Mucins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111854
Gunning AP, Kavanaugh D, Thursby E, Etzold S, MacKenzie DA, Juge N. Use of Atomic Force Microscopy to Study the Multi-Modular Interaction of Bacterial Adhesins to Mucins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(11):1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111854
Chicago/Turabian StyleGunning, A. Patrick, Devon Kavanaugh, Elizabeth Thursby, Sabrina Etzold, Donald A. MacKenzie, and Nathalie Juge. 2016. "Use of Atomic Force Microscopy to Study the Multi-Modular Interaction of Bacterial Adhesins to Mucins" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 11: 1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111854
APA StyleGunning, A. P., Kavanaugh, D., Thursby, E., Etzold, S., MacKenzie, D. A., & Juge, N. (2016). Use of Atomic Force Microscopy to Study the Multi-Modular Interaction of Bacterial Adhesins to Mucins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(11), 1854. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111854