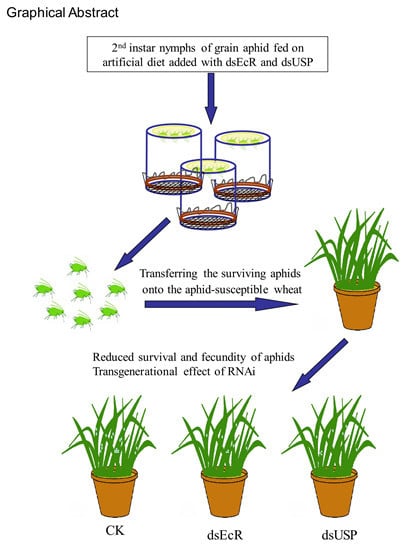
RNA Interference of the Ecdysone Receptor Genes EcR and USP in Grain Aphid (Sitobion avenae F.) Affects Its Survival and Fecundity upon Feeding on Wheat Plants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Characterization of EcR and USP Genes from Grain Aphid
2.2. The Effects of dsRNAs of SaEcR and SaUSP on Aphid Development and Mortality
2.3. Persistent Silencing and Transgenerational Effects of RNAi in Grain Aphid after Switching onto Aphid-Susceptible Wheat Plants
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant and Insects
4.2. Isolation and Characterization of SaEcR and SaUSP Genes from Grain Aphid
4.3. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR Analyses
4.4. dsRNA Design and Synthesis
4.5. Artificial Diet Bioassay
4.6. Evaluation of the Persistence and Transgenerational Effects of RNAi after Switching onto Aphid-Susceptible Wheat Plants
4.7. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Aphid Genomics Consortium. Genome sequence of the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000313. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, L.Q.; Ma, Y.Z.; He, Y.; Jones, H.D. GM wheat development in China: Current status and challenges to commercialization. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 1785–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackman, R.L.; Eastop, V.F. Aphids on the World’s Crops: An Identification and Information Guide; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1984; p. 476. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, W.P.; Peairs, F.B. Response model concept and economic impact. In Response Model for an Introduced Pest—The Russian Wheat Aphid; Lanham: Annapolis, MD, USA, 1998; pp. 65–99. [Google Scholar]
- Oerke, E.C. Estimated crop losses in wheat. In Crop Production and Crop Protection: Estimated Losses in Major Food and Cash Crops.; Oerke, E.C., Dehne, H.W., Schönbeck, F., Weber, A, Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 179–296. [Google Scholar]
- Stoger, E.; Williams, S.; Christou, P.; Down, R.E.; Gatehouse, J.A. Expression of the insecticidal lectin from snowdrop (Galanthus nivalis agglutinin; GNA) in transgenic wheat plants: Effects on predation by the grain aphid Sitobion avenae. Mol. Breed. 1999, 5, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagu, D.; Klingler, J.P.; Moya, A.; Simon, J.C. Early progress in aphid genomics and consequences for plant-aphid interactions studies. Mol. Plant Microb. Interact. 2008, 21, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.D.; Wang, G.P.; Huang, S.L.; Ma, Y.Z.; Xia, L.Q. Engineering plants for aphid resistance: Current status and future perspectives. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 2065–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y.W.; Wang, H.; Jones, H.; Gao, Q.; Wang, D.; Ma, Y.Z.; Xia, L.Q. Identifying potential RNAi targets in grain aphid (Sitobion avenae F.) based on transcriptome profiling of its alimentary canal after feeding on wheat plants. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.D.; Liu, Z.C.; Huang, S.L.; Chen, Z.Q.; Sun, Y.W.; Duan, P.F.; Ma, Y.Z.; Xia, L.Q. RNAi-mediated plant protection against aphids. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, D.R.; Gatehouse, J.A. RNAi-mediated crop protection against insects. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huvenne, H.; Smagghe, G. Mechanisms of dsRNA uptake in insects and potential of RNAi for pest control: A review. J. Insect Physiol. 2010, 56, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terenius, O.; Papanicolaou, A.; Garbutt, J.S.; Eleftherianos, I.; Huvenne, H.; Kanginakudru, S.; Albrechtsen, M.; An, C.; Aymeric, J.L.; Barthel, A. RNA interference in Lepidoptera: An overview of successful and unsuccessful studies and implications for experimental design. J. Insect Physiol. 2011, 57, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baum, J.A.; Bogaert, T.; Clinton, W.; Heck, G.R.; Feldmann, P.; Ilagan, O.; Johnson, S.; Plaetinck, G.; Munyikwa, T.; Pleau, M. Control of coleopteran insect pests through RNA interference. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.H.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.W.; Wang, H.; Xia, L.Q. Double-stranded RNA in the biological control of grain aphid (Sitobion avenae F.). Funct. Integr. Genom. 2015, 15, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiaens, O.; Iga, M.; Velarde, R.A.; Rouge, P.; Smagghe, G. Halloween genes and nuclear receptors in ecdysteroid biosynthesis and signalling in the pea aphid. Insect Mol. Biol. 2010, 19, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King-Jones, K.; Thummel, C.S. Nuclear receptors—A perspective from Drosophila. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Henrich, V.C. Arthropod nuclear receptors and their role in molting. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 6128–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieprzyk, J.; Zbela, A.; Jakob, M.; Ozyhar, A.; Orlowski, M. Homodimerization propensity of the intrinsically disordered N-terminal domain of Ultraspiracle from Aedes aegypti. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1844, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riddiford, L.M.; Hiruma, K.; Zhou, X.; Nelson, C.A. Insights into the molecular basis of the hormonal control of molting and metamorphosis from Manduca sexta and Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 33, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escriva, H.; Delaunay, F.; Laudet, V. Ligand binding and nuclear receptor evolution. BioEssays 2000, 22, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, A.; Dura, J.M. Nuclear receptors and Drosophila neuronal remodeling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1849, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, T.P.; Forman, B.M.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Cheabas, L.; Chen, J.D.; McKeown, M.; Cherbas, P.; Evans, R.M. Functional ecdysone receptor is the product of EcR and Ultraspiracle genes. Nature 1993, 366, 476–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrich, V.C.; Siiter, T.J.; Lubahn, D.B.; Maclntyre, A.; Gilbert, L.I. A steroid/thyroid hormone receptor superfamily member in Drosophila melanogaster that shares extensive sequence similarity with a mammalian homologue. Nucl. Acids Res. 1990, 18, 4143–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelle, M.R.; Talbot, W.S.; Segraves, W.A.; Bender, M.T.; Cherbas, P.; Hogness, D.S. The Drosophila EcR gene encodes an ecdysone receptor, a new member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Cell 1991, 67, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palli, S.R.; Retnakaran, A. Ecdysteroid and juvenile hormone receptors: Properties and importance in developing novel insecticides. In Biochemical Sites of Insecticide Action and Resistance; Ishaaya, I., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 107–132. [Google Scholar]
- Minakuchi, C.; Nakagawa, Y.; Kiuchi, M.; Tomita, S.; Kamimura, M. Molecular cloning, expression analysis and functional confirmation of two ecdysone receptor isoforms from the rice stem borer Chilo suppressalis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 32, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, D.C.; Dhadialla, T.S.; Zhou, S.; Kuiper, M.J.; Ball, E.E.; Wyatt, G.R.; Walker, V.K. Ligand specificity and developmental expression of RXR and ecdysone receptor in the migratory locust. J. Insect Physiol. 2003, 49, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siaussat, D.; Bozzolan, F.; Queguiner, I.; Porcheron, P.; Debernard, S. Effects of juvenile hormone on 20-hydroxyecdysone-inducible EcR, HR3, E75 gene expression in imaginal wing cells of Plodia interpunctella lepidoptera. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 3017–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmichael, J.A.; Lawrence, M.C.; Graham, L.D.; Pilling, P.A.; Epa, V.C.; Noyce, L.; Lovrecz, G.; Winkler, D.A.; Pawlak-Skrzecz, A.; Eaton, R.E.; et al. The X-ray structure of a hemipteran ecdysone receptor ligand-binding domain: Comparison with a lepidopteran ecdysone receptor ligand-binding domain and implications for insecticide design. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 22258–22269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.; Palli, S.R. Identification and characterization of nuclear receptors from the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, G.; Thummel, C.S. Inducible expression of double-stranded RNA directs specific genetic interference in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Q.; Liu, S.M.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.Q.; Qi, H.S.; Wei, Z.J.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, W.Q.; Li, S. Improvement of pest resistance in transgenic tobacco plants expressing dsRNA of an insect-associated gene EcR. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutti, N.S.; Park, Y.; Reese, J.C.; Reeck, G.R. RNAi knockdown of a salivary transcript leading to lethality in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. J. Insect Sci. 2006, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitino, M.; Coleman, A.D.; Maffei, M.E.; Ridout, C.J.; Hogenhout, S.A. Silencing of aphid genes by dsRNA feeding from plants. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiaens, O.; Smagghe, G. The challenge of RNAi-mediated control of hemipterans. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2014, 6, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiaens, O.; Swevers, L.; Smagghe, G. DsRNA degradation in the pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum) associated with lack of response in RNAi feeding and injection assay. Peptides 2014, 53, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, A.D.; Wouters, R.H.M.; Mugford, S.T.; Hogenhout, S.A. Persistence and transgenerational effect of plant-mediated RNAi in aphids. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucher, G.; Scholten, J.; Klingler, M. Parental RNAi in Tribolium (Coleoptera). Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, R85–R86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatef, E.; Will, T.; Koch, A.; Imani, J.; Vilcinskas, A.; Kogel, K.H. Silencing the expression of the salivary sheath protein causes transgenerational feeding suppression in the aphid Sitobion avenae. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutti, N.S.; Louis, J.; Pappan, L.K.; Pappan, K.; Begum, K.; Chen, M.S.; Park, Y.; Dittmer, N.; Marshall, J.; Reese, J.C.; Reeck, G.R. A protein from the salivary glands of the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum, is essential in feeding on a host plant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9965–9969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, N.; Christiaens, O.; Liu, J.; Niu, J.; Cappelle, K.; Caccia, S.; Huvenne, H.; Smagghe, G. Delivery of dsRNA for RNAi in insects: An overview and future directions. J. Insect Sci. 2013, 20, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachman, P.M.; Bolognesi, R.; Moar, W.J.; Mueller, G.M.; Paradise, M.S.; Ramaseshadri, P.; Tan, J.; Uffman, J.P.; Warren, J.; Wiggins, B.E.; et al. Characterization of the spectrum of insecticidal activity of a double-stranded RNA with targeted activity against Western Corn Rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte). Transgenic Res. 2013, 22, 1207–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, B.S.; Gascuel, O. Fast and accurate method to estimate large phylogenies by maximum-likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2010, 52, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyard, S.; Singh, A.D.; Wong, S. Ingested double-stranded RNAs can act as species-specific insecticides. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Treatments | Adult Longevity (Day) | Fecundity Period (Day) | Daily Fecundity | Total Production |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 10.30 ± 0.23 | 8.43 ± 0.15 | 1.50 ± 0.04 | 12.63 ± 0.53 |
| dsGFP | 10.00 ± 0.21 | 8.30 ± 0.23 | 1.41 ± 0.03 | 11.62 ± 0.16 |
| dsSaEcR | 4.73 ± 0.15 ** | 3.10 ± 0.23 ** | 0.33 ± 0.05 ** | 1.97 ± 0.19 ** |
| dsSaUSP | 3.83 ± 0.17 ** | 2.63 ± 0.05 ** | 0.34 ± 0.05 ** | 2.17 ± 0.09 ** |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, T.; Chen, H.; Sun, Y.; Yu, X.; Xia, L. RNA Interference of the Ecdysone Receptor Genes EcR and USP in Grain Aphid (Sitobion avenae F.) Affects Its Survival and Fecundity upon Feeding on Wheat Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2098. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122098
Yan T, Chen H, Sun Y, Yu X, Xia L. RNA Interference of the Ecdysone Receptor Genes EcR and USP in Grain Aphid (Sitobion avenae F.) Affects Its Survival and Fecundity upon Feeding on Wheat Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(12):2098. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122098
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Ting, Hongmei Chen, Yongwei Sun, Xiudao Yu, and Lanqin Xia. 2016. "RNA Interference of the Ecdysone Receptor Genes EcR and USP in Grain Aphid (Sitobion avenae F.) Affects Its Survival and Fecundity upon Feeding on Wheat Plants" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 12: 2098. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122098
APA StyleYan, T., Chen, H., Sun, Y., Yu, X., & Xia, L. (2016). RNA Interference of the Ecdysone Receptor Genes EcR and USP in Grain Aphid (Sitobion avenae F.) Affects Its Survival and Fecundity upon Feeding on Wheat Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(12), 2098. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122098